1、使用
- 排序
2、原理
-
事实上Collections.sort方法底层就是调用的array.sort方法,而且不论是Collections.sort或者是Arrays.sort方法,
-
跟踪下源代码吧,首先我们写个demo
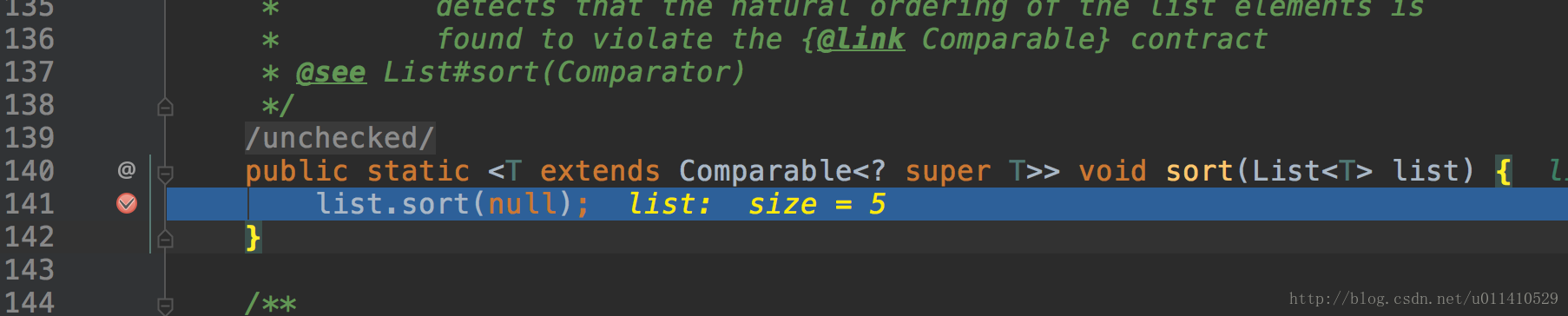
public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("6", "1", "3", "1","2"); Collections.sort(strings);//sort方法在这里 for (String string : strings) { System.out.println(string); } }
简单得不能再简单的方法了,让我们一步步跟踪
- OK,往下面看,发现collections.sort方法调用的list.sort
- 然后跟踪一下,list里面有个sort方法,但是list是一个接口,肯定是调用子类里面的实现,这里我们demo使用的是一个Arrays.asList方法,所以事实上我们的子类就是arraylist了。OK,看arraylist里面sort实现,选择第一个,为什么不选择第二个呢?(可以看二楼评论,解答得很正确,简单说就是用Arrays.sort创建的ArrayList对象)
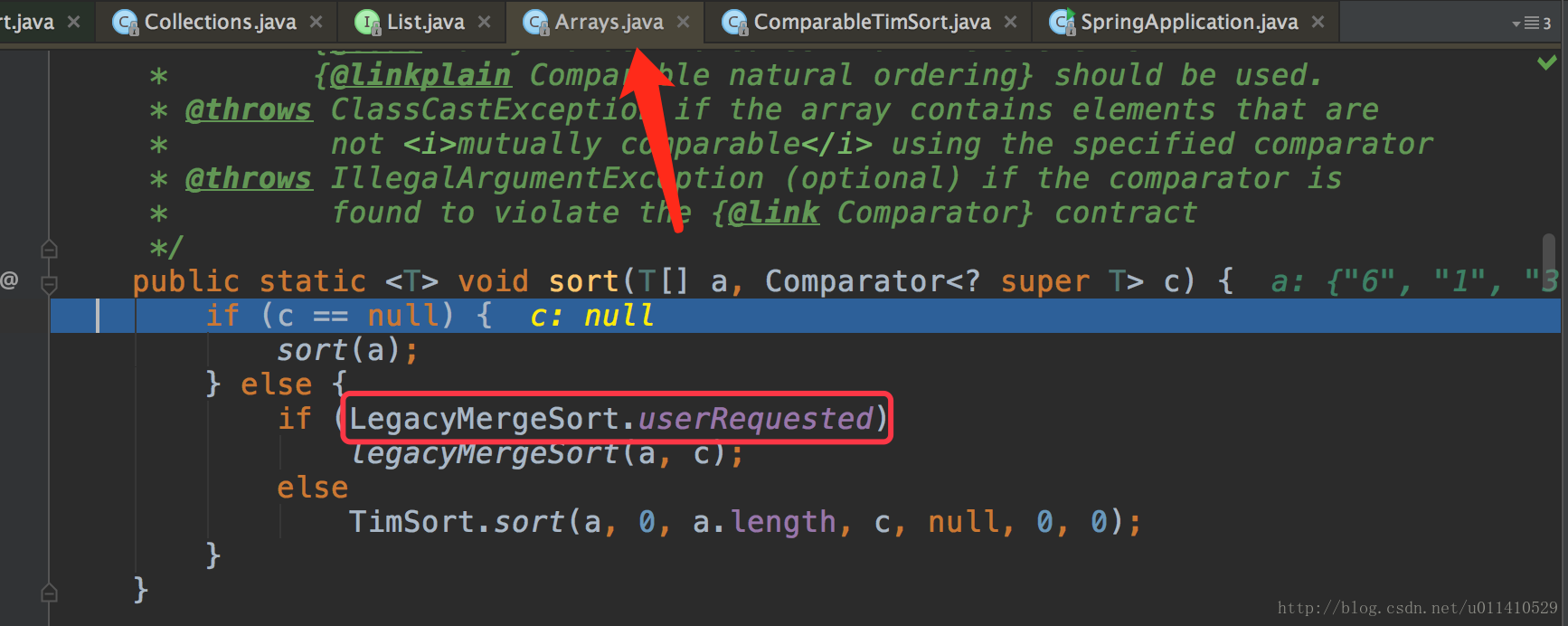
- OK,发现里面调用的Arrays.sort(a, c); a是list,c是一个比较器,我们来看一下这个方法
我们没有写比较器,所以用的第二项,LegacyMergeSort.userRequested这个bool值是什么呢?
跟踪这个值,我们发现有这样的一段定义:
> Old merge sort implementation can be selected (for > compatibility with broken comparators) using a system property. > Cannot be a static boolean in the enclosing class due to > circular dependencies. To be removed in a future release. 反正是一种老的归并排序,不用管了现在默认是关的
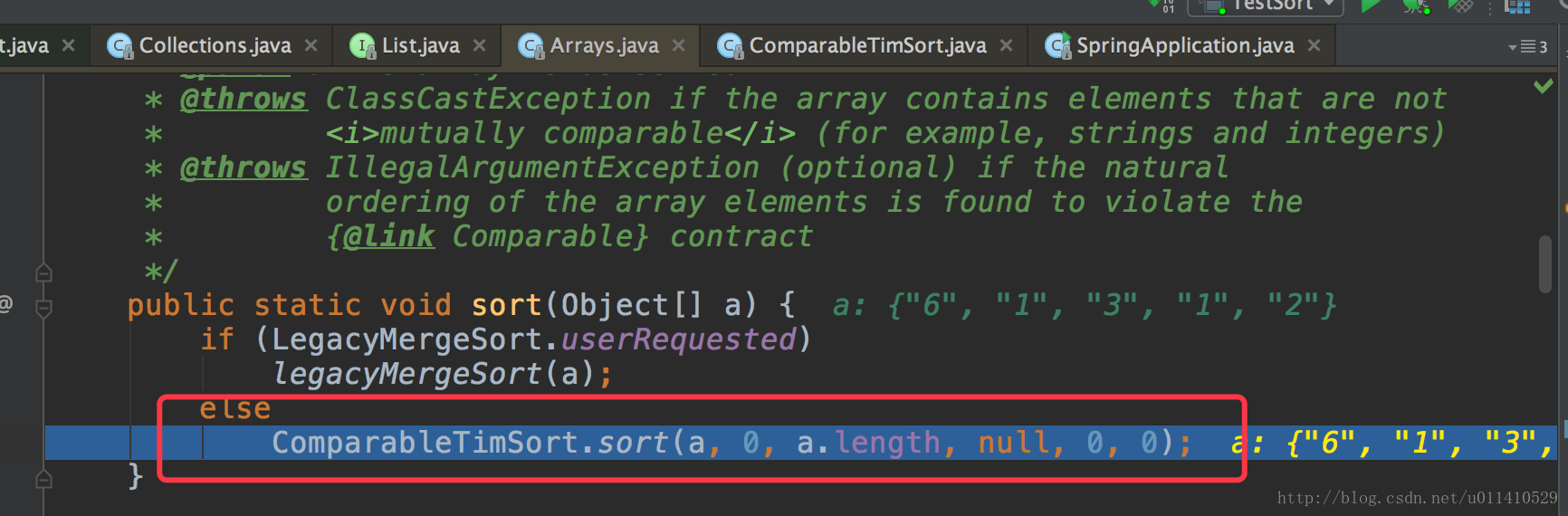
- OK,我们走的是sort(a)这个方法,接着进入这个
- 接着看我们重要的sort方法
static void sort(Object[] a, int lo, int hi, Object[] work, int workBase, int workLen) { assert a != null && lo >= 0 && lo <= hi && hi <= a.length; int nRemaining = hi - lo; if (nRemaining < 2) return; // array的大小为0或者1就不用排了 // 当数组大小小于MIN_MERGE(32)的时候,就用一个"mini-TimSort"的方法排序,jdk1.7新加 if (nRemaining < MIN_MERGE) { //这个方法比较有意思,其实就是将我们最长的递减序列,找出来,然后倒过来 int initRunLen = countRunAndMakeAscending(a, lo, hi); //长度小于32的时候,是使用binarySort的 binarySort(a, lo, hi, lo + initRunLen); return; } //先扫描一次array,找到已经排好的序列,然后再用刚才的mini-TimSort,然后合并,这就是TimSort的核心思想 ComparableTimSort ts = new ComparableTimSort(a, work, workBase, workLen); int minRun = minRunLength(nRemaining); do { // Identify next run int runLen = countRunAndMakeAscending(a, lo, hi); // If run is short, extend to min(minRun, nRemaining) if (runLen < minRun) { int force = nRemaining <= minRun ? nRemaining : minRun; binarySort(a, lo, lo + force, lo + runLen); runLen = force; } // Push run onto pending-run stack, and maybe merge ts.pushRun(lo, runLen); ts.mergeCollapse(); // Advance to find next run lo += runLen; nRemaining -= runLen; } while (nRemaining != 0); // Merge all remaining runs to complete sort assert lo == hi; ts.mergeForceCollapse(); assert ts.stackSize == 1; }
- 回到5,我们可以看到当我们写了比较器的时候就调用了
TimSort.sort方法,源码如下
static <T> void sort(T[] a, int lo, int hi, Comparator<? super T> c, T[] work, int workBase, int workLen) { assert c != null && a != null && lo >= 0 && lo <= hi && hi <= a.length; int nRemaining = hi - lo; if (nRemaining < 2) return; // Arrays of size 0 and 1 are always sorted // If array is small, do a "mini-TimSort" with no merges if (nRemaining < MIN_MERGE) { int initRunLen = countRunAndMakeAscending(a, lo, hi, c); binarySort(a, lo, hi, lo + initRunLen, c); return; } /** * March over the array once, left to right, finding natural runs, * extending short natural runs to minRun elements, and merging runs * to maintain stack invariant. */ TimSort<T> ts = new TimSort<>(a, c, work, workBase, workLen); int minRun = minRunLength(nRemaining); do { // Identify next run int runLen = countRunAndMakeAscending(a, lo, hi, c); // If run is short, extend to min(minRun, nRemaining) if (runLen < minRun) { int force = nRemaining <= minRun ? nRemaining : minRun; binarySort(a, lo, lo + force, lo + runLen, c); runLen = force; } // Push run onto pending-run stack, and maybe merge ts.pushRun(lo, runLen); ts.mergeCollapse(); // Advance to find next run lo += runLen; nRemaining -= runLen; } while (nRemaining != 0); // Merge all remaining runs to complete sort assert lo == hi; ts.mergeForceCollapse(); assert ts.stackSize == 1; }
和上面的sort方法是一样的,其实也就是TimSort的源代码
3、总结
不论是Collections.sort方法或者是Arrays.sort方法,底层实现都是TimSort实现的,这是jdk1.7新增的,以前是归并排序。TimSort算法就是找到已经排好序数据的子序列,然后对剩余部分排序,然后合并起来