表操作使用django集成的方法,
比如有一张User表:User.objects.all() 返回一个Queryset对象(数据类型list),里面是User表的所有行封装成的User对象。
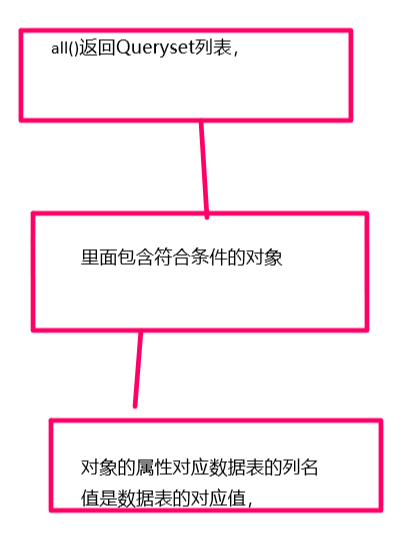
User.objects是一个QuerySet实例。django查找一个对象显然是先查看是否内存中已经有了此对象,如果没有再去数据库查看。
增删改查的方法:
增:objects.create()方法,此方法直接修改数据库
- 实例化一个子类对象,再用save()方法
- 如果子类对象里面有多对多关系,
那么需要给多对多关系字段添加数据,有1个方法
例子:
title=request.POST.get("title") price=request.POST.get("price") date=request.POST.get("date") publish_id=request.POST.get("publish_id") author_pk_list=request.POST.getlist("author_pk_list") # [1,2]
book_obj=Book.objects.create(title=title,price=price,date=date,publish_id=publish_id),
上面这一步是在数据库生成这条数据,然后添加多对多关系:添加pk值可以,添加对象也可,多个添加用列表形式如下 book_obj.authors.add(*author_pk_list)
- 多条记录一次增加:使用save()方法,因为只要向数据库发起一次请求
改:updata()方法,updata_or_create()方法,select_for_update()
updata()
"""
更新当前QuerySet中的所有元素,将所有给定字段设置为适当的值
"""
select_for_update()
"""
返回一个新的QueReSET实例,该实例将选择更新锁定的对象。
"""
updata_or_create()
"""
Look up an object with the given kwargs, updating one with defaults
if it exists, otherwise create a new one.
Return a tuple (object, created), where created is a boolean
specifying whether an object was created.
"""
删: