一、前言
本篇文章介绍两个重点
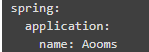
(1) 工程核心配置文件application.yml
(2) 如何在一个标准的的SpringCloud工程上构建起一个基本的web结构
二、配置文件application.yml
下面贴一个简单的application.yml配置文件,以此展开说明
(1)默认情况下,application.yml放在src / main / resources 根目录下,如果想更改配置文件路径或自定义配置文件名称,需要启动时指定如下,一般不建议修改:
(2)你也可以使用application.properties,只需要将yml文件的属性层级结构在properties文件中改为一行即可,使用的时候与yml一致,如下图
 --->
---> ![]()
(3)配置属性 spring.profiles.active,此属性可指定在不同环境下使用对应环境的配置文件,如下

定义了application-dev.yml 与 application-prod.yml 文件 ,分别代表 开发环境 下的配置与 生成环境 下的配置,通过spring.profiles.active = dev 指定使用哪个配置文件,dev则代表使用application-dev.yml。
另外,如果你不想定义很多配置文件,还可以通过 “---”方式在同一个文件中进行不同环境下属性的定义,如下
---注 开始---
关于“---”:“---”在yml文件中的作用用来区分多个文件,写了几个“---”等同于写了几个配置文件,最终的效果是一样的,关于yml文件的介绍与基本使用,大家自行查阅,此处不做过多介绍,这里给大家推荐一篇:http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/07/yaml.html?f=tt
---注 结束---
当然spring.profiles.active属性的应用不止于此,你可以根据实际情况灵活运用
三、application.yml配置文件读取
application.yml配置文件读取有3中方式,分别如下:
(1)使用@Value注解
![]()
如上图所示,可以直接在属性上定义@Value注解,可以使用SpEL表达式,${} 中的属性对应配置文件的属性名称
(2)使用@ConfigurationProperties注解,配合Pojo类实现
配置定义类如下,使用@ConfigurationProperties,同时使用@Component 声明为Spring组件,在任意使用的地方进行注入
具体使用
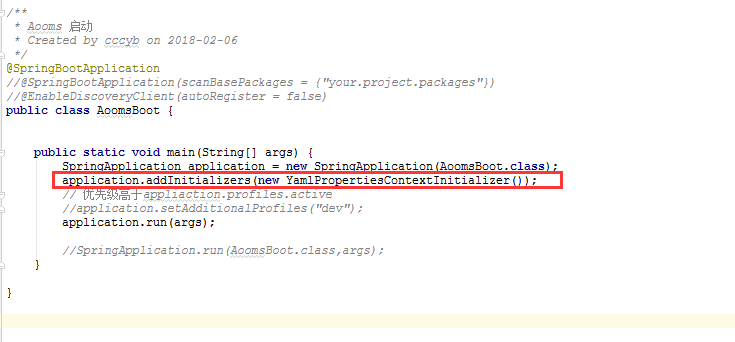
(3)自定义ApplicationContextInitializer,配合Environment类实现
自定义ApplicationContextInitializer类
添加到启动
具体使用
四、自定义配置文件的读取
自定义yml配置文件的读取,可使用如下两种方式
(1)可以通过上面的第三中自定义ApplicationContextInitializer实现,关于自定义及使用参考上面
(2)properties文件可以直接使用@PropertySource配合pojo实现,yml文件无法使用@PropertySource注解,可以使用@PropertySource结合@ConfigurationProperties的方式
配置定义类如下,使用@ConfigurationProperties,同时使用@Component 声明为Spring组件,在任意使用的地方进行注入
具体使用
四、日志框架logback配置
Aooms目前使用的SpringBoot版本是2.0.0.M7,默认内置日志框架为logback,集成了logback的默认配置文件,可在spring-boot.jar包org.springframework.boot.logging.logback中找到,配置在application.yml中可进行定义,如下:
五、简单的控制器Demo
一个简单的控制器,为了方面后面框架的测试、调试,此demo会随着框架不断更新,最终会是一个完整的包含SpringMVC各种情况的使用
六、页面、静态资源的集成
SpringBoot默认加载的静态资源路径为/static /public /resources /META-INF/resources,默认的搜索路径为/**,也就是会在上面的所有路径中进行资源搜索加载,可以通过spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/resources/** 进行路径自定义
SpringBoot默认使用的模版引擎为thymeleaf,首先需要添加maven依赖
然后thymeleaf 在application.yml中的配置如下
Aooms框架中,将静态资源全部放在/META-INF/resources目录下,Servlet3.0规范也是定义了资源文件在/META-INF/resources目录下,为了提高框架的兼容性,统一结构,因此将资源文件放置在此目录下。
七、调试、访问
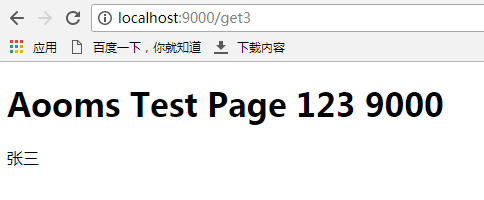
/META-INF/resources目录下有 test.html 与 jquery.min.js 文件
TestController控制器 get3 方法渲染了test.html模版
启动应用后,访问http://localhost:9000/get3,出现如下内容,说明一个基本的web工程构建及配置文件定义完成