Altough it sounds quiet like KNN algorithm, however, KNN is a kind of classification algorithm of supervised learning while K MEANS is a kind of unsupervised learning algorithm.
K MEANS as a cluster method, can figure out k classes from the given dataset without labels, in which the class number k is given by user.
The procedure of K MEANS algorithm is:
- initial the centroids with radom points in dataset, which represent k classes
- calculate the others label based on these k classes through the minimum distence from the centroids
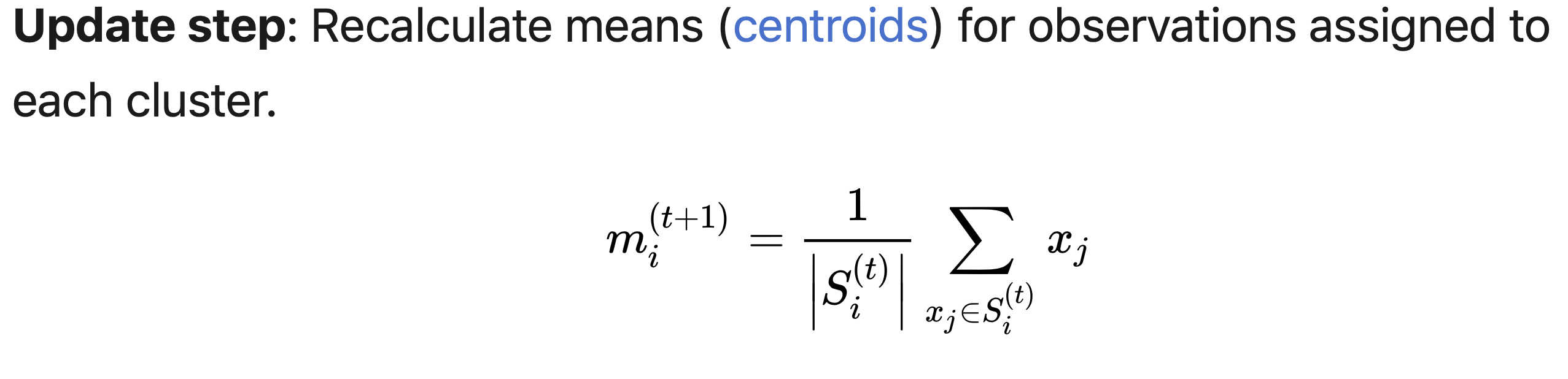
- recalcute the centroids based on the labels we calculated in the 2nd step
- repeat until the iterations ends
And here is the procedure of the naive K MEANS algorithm:


we can use K MEANS algorithm simply from sklearn:
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans Kmean = KMeans(n_clusters=2) Kmean.fit(X)
And here is a more explicit code
import numpy as np from numpy.linalg import norm class Kmeans: '''Implementing Kmeans algorithm.''' def __init__(self, n_clusters, max_iter=100, random_state=123): self.n_clusters = n_clusters self.max_iter = max_iter self.random_state = random_state def initializ_centroids(self, X): np.random.RandomState(self.random_state) random_idx = np.random.permutation(X.shape[0]) centroids = X[random_idx[:self.n_clusters]] return centroids def compute_centroids(self, X, labels): centroids = np.zeros((self.n_clusters, X.shape[1])) for k in range(self.n_clusters): centroids[k, :] = np.mean(X[labels == k, :], axis=0) return centroids def compute_distance(self, X, centroids): distance = np.zeros((X.shape[0], self.n_clusters)) for k in range(self.n_clusters): row_norm = norm(X - centroids[k, :], axis=1) distance[:, k] = np.square(row_norm) return distance def find_closest_cluster(self, distance): return np.argmin(distance, axis=1) def compute_sse(self, X, labels, centroids): distance = np.zeros(X.shape[0]) for k in range(self.n_clusters): distance[labels == k] = norm(X[labels == k] - centroids[k], axis=1) return np.sum(np.square(distance)) def fit(self, X): self.centroids = self.initializ_centroids(X) for i in range(self.max_iter): old_centroids = self.centroids distance = self.compute_distance(X, old_centroids) self.labels = self.find_closest_cluster(distance) self.centroids = self.compute_centroids(X, self.labels) if np.all(old_centroids == self.centroids): break self.error = self.compute_sse(X, self.labels, self.centroids) def predict(self, X): distance = self.compute_distance(X, old_centroids) return self.find_closest_cluster(distance)
ref:https://towardsdatascience.com/k-means-clustering-algorithm-applications-evaluation-methods-and-drawbacks-aa03e644b48a