一、静态变量初始化顺序
大家先看两个例子:
(1)

1 public class SingleTon { 2 public static int count1; 3 public static int count2 = 1; 4 private static SingleTon singleTon = new SingleTon(); 5 6 private SingleTon() { 7 count1++; 8 count2++; 9 } 10 11 public static SingleTon getInstance() { 12 return singleTon; 13 } 14 } 15 16 class Test { 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 SingleTon singleTon = SingleTon.getInstance(); 19 System.out.println("count1=" + singleTon.count1); 20 System.out.println("count2=" + singleTon.count2); 21 } 22 }
输出
count1=1
count2=2
(2)

1 public class SingleTon { 2 3 private static SingleTon singleTon = new SingleTon(); //(1)这一步初始化后,count1=1,count2=1 4 public static int count1; //(2)这一步只是定义了count1变量,并未进行count1初始化,因此count1 =1 count2=1 5 public static int count2 = 3;//(3)这一步 进行count2初始化,因此将原来的值覆盖,因此count2=3,count1 =1 6 7 private SingleTon() { 8 count1++; // 此时,count1还未被初始化,因此初始值为0,++后值为1 9 count2++; // 此时,count2还未被初始化,因此初始值为0,++后值为1 10 } 11 12 public static SingleTon getInstance() { 13 return singleTon; 14 } 15 } 16 17 class Test { 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 SingleTon singleTon = SingleTon.getInstance(); 20 System.out.println("count1=" + singleTon.count1); 21 System.out.println("count2=" + singleTon.count2); 22 } 23 }
count1=1
count2=3
在调用类静态成员(不管是方法还是变量)的时候,按顺序初始化静态属性和代码块,之后才会调用静态方法,非静态成员变量因为没有初始化类,故不会初始化。
二、继承中的初始化
看两个例子:
(1)

1 class Meal { 2 Meal() { 3 System.out.println("Meal()"); 4 } 5 } 6 7 class Bread { 8 Bread() { 9 System.out.println("Bread()"); 10 } 11 } 12 13 class Cheese { 14 Cheese() { 15 System.out.println("Cheese()"); 16 } 17 } 18 19 class Lettuce { 20 Lettuce() { 21 System.out.println("Letuce()"); 22 } 23 } 24 25 class Lunch extends Meal { 26 Lunch() { 27 System.out.println("Lunch()"); 28 } 29 } 30 31 class PortabLunch extends Lunch { 32 PortabLunch() { 33 System.out.println("PortabLunch"); 34 } 35 } 36 37 public class Main extends PortabLunch{ 38 Bread bread = new Bread(); 39 Cheese cheese = new Cheese(); 40 Lettuce lettuce = new Lettuce(); 41 42 Main() { 43 System.out.println("Main"); 44 } 45 46 public static void main(String[] args) { 47 new Main(); 48 } 49 }
输出:
Meal() Lunch() PortabLunch Bread() Cheese() Letuce() Main
说明:子类初始化前要(0)在其他任何事情发生之前,将分配给对象的存储空间初始化为二进制零(1)寻找父类构造器,并且步骤会不断递归,直到找到根类为止。然后自顶向下,逐层调用构造函数,直到最底层的父类构造器。(2)然后按照代码编译顺序依次初始化各成员变量 (3)最后调用本类的构造函数进行初始化。
(2)

1 public class Glyph { 2 void draw() { 3 System.out.println("Glphy draw()"); 4 } 5 6 Glyph() { 7 System.out.println("Glphy() before draw"); 8 draw();//当子类调用父类构造器的时候,父类其实尚未初始化,因此调用的是子类的draw方法 9 System.out.println("Glphy() after draw"); 10 } 11 } 12 13 class RoundGlyph extends Glyph { 14 private int radius = 1; 15 16 RoundGlyph(int r) { 17 radius = r; 18 System.out.println("RoundGlyph.RoundGlyph(),radius:" + radius); 19 } 20 21 void draw() { 22 System.out.println("RoundGlyph.draw(),radius:" + radius); 23 } 24 } 25 26 class PolyConstruct { 27 public static void main(String[] args) { 28 new RoundGlyph(5); 29 } 30 }
输出
Glphy() before draw RoundGlyph.draw(),radius:0 Glphy() after draw RoundGlyph.RoundGlyph(),radius
说明:在调用父类构造器时,因为draw方法被子类RoundGlyph覆写,因此在Glyph中调用的是子类的draw方法,并且此时由于radius还未进行初始化,因此其值是默认的初始值0.
(3)

1 public class Glyph { 2 void draw() { 3 System.out.println("Glphy draw()"); 4 } 5 6 Glyph() { 7 System.out.println("Glphy() before draw"); 8 draw();//当子类调用父类构造器的时候,父类其实尚未初始化,因此调用的是子类的draw方法 9 System.out.println("Glphy() after draw"); 10 } 11 } 12 13 class RoundGlyph extends Glyph { 14 private int radius = 1; 15 16 RoundGlyph(int r) { 17 radius = r; 18 System.out.println("RoundGlyph.RoundGlyph(),radius:" + radius); 19 } 20 21 // void draw() { 22 // System.out.println("RoundGlyph.draw(),radius:" + radius); 23 // } 24 } 25 26 class PolyConstruct { 27 public static void main(String[] args) { 28 new RoundGlyph(5); 29 } 30 }
输出:
Glphy() before draw Glphy draw() Glphy() after draw RoundGlyph.RoundGlyph(),radius:5
说明:本例子中,子类RoundGlyph中不包含draw方法,因此也就不存在覆写的问题。所以父类初始化时调用的是本类中的draw方法。
通过例子(2)(3)说明,在编写构造器时需要遵循一条准则:"用尽可能简单的方法使得对象进入正常状态;如果可以的话,尽量避免调用其他的方法"。在构造器内能够被唯一安全调用的方法是基类中的final方法(或者是private方法,因为它自动属于final方法),这些方法不能被覆盖,因此也不会 出项一些奇怪的问题。
下面附一张,JAVA成员变量初始化思维导图,对于理解这一块的知识很有帮助
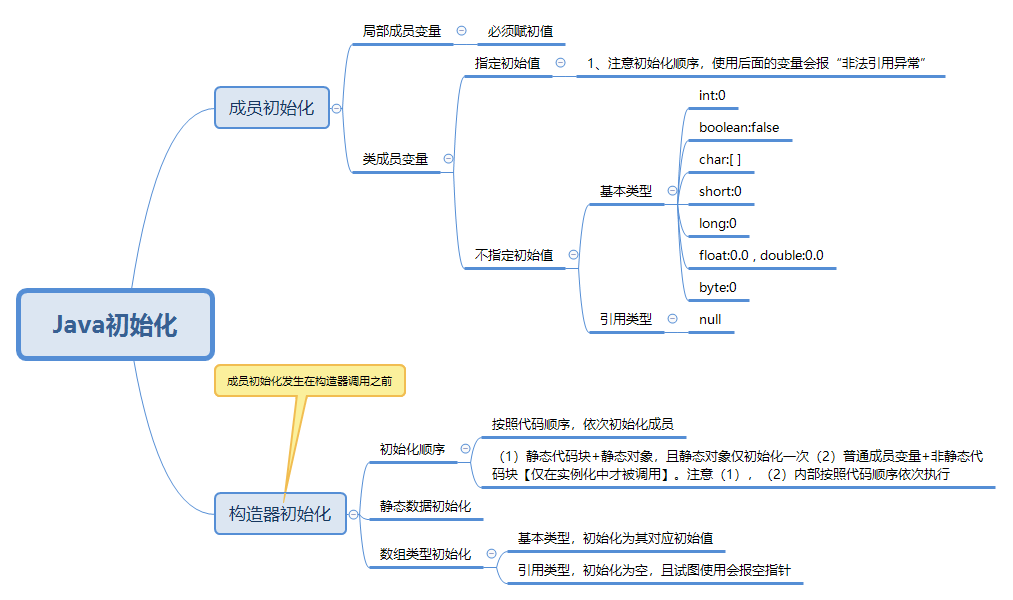
详细可参考这一文章:https://blog.csdn.net/fly_grass_fish/article/details/81116348 java静态变量static初始化顺序
