ansible简介
Ansible是一种IT自动化工具。它可以配置系统,部署软件以及协调更高级的IT任务,例如持续部署,滚动更新。Ansible适用于管理企业IT基础设施,从具有少数主机的小规模到数千个实例的企业环境。Ansible也是一种简单的自动化语言,可以完美地描述IT应用程序基础结构。
-
简单:减少学习成本
-
强大:协调应用程序生命周期
-
ansible安装
yum -y install ansible
-
-
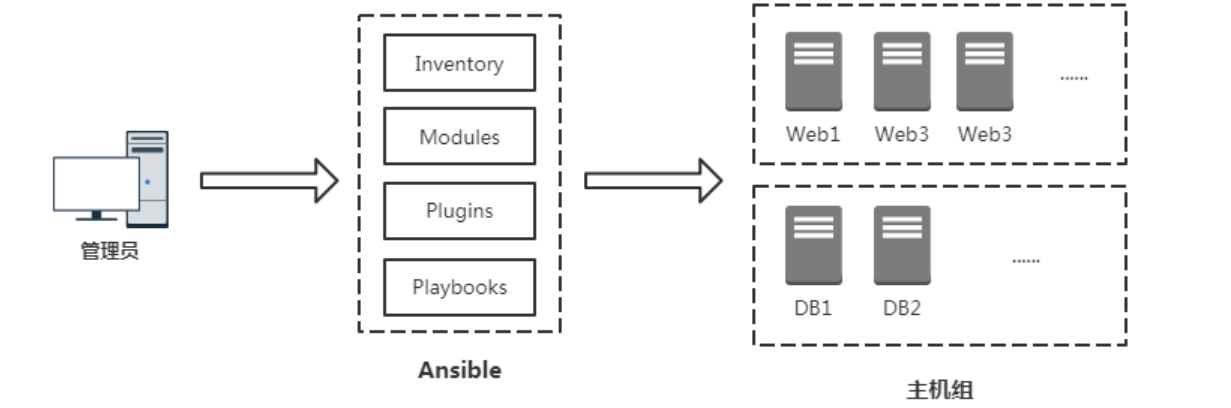
Modules:任务均有模块完成,也可以自定义模块,例如经常用的脚本。
-
Plugins:使用插件增加Ansible核心功能,自身提供了很多插件,也可以自定义插件。例如connection插件,用于连接目标主机。
-
主机清单
[webservers] alpha.example.org beta.example.org 192.168.1.100 www[001:006].example.com [dbservers] db01.intranet.mydomain.net db02.intranet.mydomain.net 10.25.1.56 10.25.1.57 db-[99:101]-node.example.com
命令行使用
ansible all -m ping ansible all -m shell -a "ls /root" -u root -k ansible webservers -m copy –a "src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/hosts"
ad-hoc命令是理解Ansible和在学习playbooks之前需要掌握的基础知识。
SSH密码认证: [webservers] 192.168.1.100:22 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=’123456’ 192.168.1.101:22 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=’123456’ SSH密钥对认证 [webservers] 10.206.240.111:22 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_key=/root/.ssh/id_rsa 10.206.240.112:22 ansible_ssh_user=root 也可以ansible.cfg在配置文件中指定: [defaults] private_key_file = /root/.ssh/id_rsa # 默认路径
常用选项:
| 描述 | |
|---|---|
| -C, --check | 运行检查,不执行任何操作 |
| -e EXTRA_VARS,--extra-vars=EXTRA_VARS | 设置附加变量 key=value |
| -u REMOTE_USER, --user=REMOTE_USER | SSH连接用户,默认None |
| -k, --ask-pass | SSH连接用户密码 |
| -b, --become | 提权,默认root |
| -K, --ask-become-pass |
常用模块
ansible-doc –s copy 查看模块文档
模块文档:https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/modules/modules_by_category.html
shell:在目标主机执行shell命令
- name: 将命令结果输出到指定文件 shell: somescript.sh >> somelog.txt - name: 切换目录执行命令 shell: cmd: ls -l | grep log chdir: somedir/ - name: 编写脚本 shell: | if [ 0 -eq 0 ]; then echo yes > /tmp/result else echo no > /tmp/result fi args: executable: /bin/bash
copy:将文件复制到远程主机
- name: 拷贝文件 copy: src: /srv/myfiles/foo.conf dest: /etc/foo.conf owner: foo group: foo mode: u=rw,g=r,o=r # mode: u+rw,g-wx,o-rwx # mode: '0644' backup: yes
file:管理文件和文件属性
- name: 创建目录 file: path: /etc/some_directory state: directory mode: '0755' - name: 删除文件 file: path: /etc/foo.txt state: absent - name: 递归删除目录 file: path: /etc/foo state: absent
yum:软件包管理
- name: 安装最新版apache yum: name: httpd state: latest - name: 安装列表中所有包 yum: name: - nginx - postgresql - postgresql-server state: present - name: 卸载apache包 yum: name: httpd state: absent - name: 更新所有包 yum: name: '*' state: latest - name: 安装nginx来自远程repo yum: name: http://nginx.org/packages/rhel/7/x86_64/RPMS/nginx-1.14.0-1.el7_4.ngx.x86_64.rpm # name: /usr/local/src/nginx-release-centos-6-0.el6.ngx.noarch.rpm state: present
service/systemd:管理服务
- name: 服务管理 service: name: etcd state: started #state: stopped #state: restarted #state: reloaded - name: 设置开机启动 service: name: httpd enabled: yes - name: 服务管理 systemd: name=etcd state=restarted enabled=yes daemon_reload=yes
unzrchive:
- name: 解压 unarchive: src=test.tar.gz dest=/tmp
debug:执行过程中打印语句
- debug: msg: System {{ inventory_hostname }} has uuid {{ ansible_product_uuid }} - name: 显示主机已知的所有变量 debug: var: hostvars[inventory_hostname] verbosity: 4
Playbook
如果Ansible模块是您工作中的工具,那么Playbook就是您的使用说明书,而您的主机资产文件就是您的原材料。
与adhoc任务执行模式相比,Playbooks使用ansible是一种完全不同的方式,并且功能特别强大。
--- - hosts: webservers vars: http_port: 80 server_name: www.xxx.com remote_user: root gather_facts: false tasks: - name: 安装nginx最新版 yum: pkg=nginx state=latest - name: 写入nginx配置文件 template: src=nginx.conf dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf notify: - restart nginx - name: 确保nginx正在运行 service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes handlers: - name: restart nginx service: name=nginx state=reloaded
......
server {
listen {{ inventory_hostename }}:{{ http_port }};
listen {{ server_name }};
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
location / {
}
}
主机和用户
- hosts: webservers
remote_user: user1
become: yes
become_user: root
定义变量
#变量是应用于多个主机的便捷方式; 实际在主机执行之前,变量会对每个主机添加,然后在执行中引用。 ###命令行传递 -e VAR=VALUE ###主机变量与组变量 #在Inventory中定义变量。 [webservers] 192.168.1.100 ansible_ssh_user=root hostname=web1 192.168.1.100 ansible_ssh_user=root hostname=web2 [webservers:vars] ansible_ssh_user=root hostname=web1 ###单文件存储 Ansible中的首选做法是不将变量存储在Inventory中。 除了将变量直接存储在Inventory文件之外,主机和组变量还可以存储在相对于Inventory文件的单个文件中。 组变量: group_vars 存放的是组变量 group_vars/all.yml 表示所有主机有效,等同于[all:vars] grous_vars/etcd.yml 表示etcd组主机有效,等同于[etcd:vars] # vi /etc/ansible/group_vars/all.yml work_dir: /data # vi /etc/ansible/host_vars/webservers.yml nginx_port: 80 ###在playbook中定义 - hosts: webservers vars: http_port: 80 server_name: www.xxx.com ###Register变量 - shell: /usr/bin/uptime register: result - debug: var: result
列表任务
#每个play包含一系列任务。这些任务按照顺序执行,在play中,所有主机都会执行相同的任务指令。play目的是将选择的主机映射到任务。 tasks: - name: 安装nginx最新版 yum: pkg=nginx state=latest
任务控制
#如果你有一个大的剧本,那么能够在不运行整个剧本的情况下运行特定部分可能会很有用。 tasks: - name: 安装nginx最新版 yum: pkg=nginx state=latest tags: install - name: 写入nginx配置文件 template: src=/srv/httpd.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf tags: config 使用: ansible-playbook example.yml --tags "install" ansible-playbook example.yml --tags "install,config" ansible-playbook example.yml --skip-tags "install"
流程控制
常用循环语句:
| 描述 | |
|---|---|
| with_items | 标准循环 |
| with_fileglob | 遍历目录文件 |
| with_dict |
#条件 tasks: - name: 只在192.168.1.100运行任务 debug: msg="{{ansible_default_ipv4.address}}" when: ansible_default_ipv4.address == '192.168.1.100' #循环 tasks: - name: 批量创建用户 user: name={{ item }} state=present groups=wheel with_items: - testuser1 - testuser2 - name: 解压 copy: src={{ item }} dest=/tmp with_fileglob: - "*.txt"
模板
vars: domain: "www.xxx.com" tasks: - name: 写入nginx配置文件 template: src=/srv/server.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/conf.d/server.conf # server.j2 {% set domain_name = domain %} server { listen 80; server_name {{ domain_name }}; location / { root /usr/share/html; } } #在jinja里使用ansible变量直接 {{ }}引用。使用ansible变量赋值jinja变量不用{{ }}引用。 定义变量: {% set local_ip = inventory_hostname %} 条件和循环: {% set list=['one', 'two', 'three'] %} {% for i in list %} {% if i == 'two' %} -> two {% elif loop.index == 3 %} -> 3 {% else %} {{i}} {% endif %} {% endfor %}
# tree .
.
├── ansible.cfg
├── docker_deploy.retry
├── docker_deploy.yaml
├── files
│ ├── daemon.json
│ ├── docker-18.09.6.tgz
│ └── docker.service
└── hosts
# cat docker_deploy.yaml
---
- hosts: docker
vars:
tmp_dir: '/tmp/docker'
remote_user: root
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: 创建临时目录
file: dest={{ tmp_dir }} state=directory
- name: 分发并解压docker二进制包
unarchive: src={{ item }} dest={{ tmp_dir }}
with_fileglob:
- "files/docker-*.tgz"
- name: 移动docker二进制文件
shell: cp -rf {{ tmp_dir }}/docker/* /usr/bin
- name: 分发service文件
copy: src=files/docker.service dest=/usr/lib/systemd/system/
- name: 创建目录
file: dest=/etc/docker state=directory
- name: 配置docker
copy: src=files/daemon.json dest=/etc/docker/daemon.json
- name: 启动docker
systemd: name=docker state=restarted enabled=yes daemon_reload=yes
- name: 查看状态
shell: docker info
register: docker
- debug: var=docker.stdout_lines
# ansible-playbook -i hosts docker_deploy.yaml -k -K
# cat generate_tls.yaml
---
- hosts: localhost
vars:
current_dir: "{{ lookup('env', 'PWD') }}"
remote_user: root
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: 创建工作目录
file: dest={{ current_dir }}/tls/cert state=directory
- name: 准备cfssl工具
unarchive: src=tls/cfssl.tar.gz dest=/usr/bin/ mode=u+x
- name: 准备etcd证书请求文件
template: src=tls/{{ item }} dest={{ current_dir }}/tls/cert/{{ item.split('.')[:-1]|join('.') }}
with_items:
- ca-config.json.j2
- ca-csr.json.j2
- server-csr.json.j2
- name: 生成etcd证书
shell: |
cd {{ current_dir }}/tls/cert
cfssl gencert -initca ca-csr.json | cfssljson -bare ca -
cfssl gencert -ca=ca.pem -ca-key=ca-key.pem -config=ca-config.json -profile=www server-csr.json | cfssljson -bare server
# cat etcd_cluster_deploy.yaml
---
- hosts: etcd
vars:
etcd_work_dir: '/opt/etcd'
tmp_dir: '/tmp/k8s'
remote_user: root
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: 创建工作目录
file: dest={{ etcd_work_dir }}/{{ item }} state=directory
with_items:
- bin
- cfg
- ssl
- name: 创建临时目录
file: dest={{ tmp_dir }} state=directory
- name: 分发并解压etcd二进制包
unarchive: src={{ item }} dest={{ tmp_dir }}
with_fileglob:
- "files/etcd-v*.tar.gz"
- name: 移动etcd二进制文件
shell: cp -rf {{ tmp_dir }}/etcd-v*/{etcd,etcdctl} {{ etcd_work_dir }}/bin
- name: 分发证书
copy: src=tls/cert/{{ item }} dest={{ etcd_work_dir }}/ssl
with_items:
- ca.pem
- server.pem
- server-key.pem
- name: 分发etcd配置文件
template: src=files/etcd.conf.j2 dest={{ etcd_work_dir }}/cfg/etcd.conf
- name: 分发service文件
template: src=files/etcd.service.j2 dest=/usr/lib/systemd/system/etcd.service
- name: 启动etcd
systemd: name=etcd state=restarted enabled=yes daemon_reload=yes
- name: 分发etcd脚本
template: src=files/etcd.sh.j2 dest={{ tmp_dir }}/etcd.sh mode=u+x
- name: 获取etcd集群状态
shell: /bin/bash {{ tmp_dir }}/etcd.sh
register: status
- debug: var=status.stdout_lines
# tree .
.
├── ansible.cfg
├── docker_deploy.yaml
├── etcd_cluster_deploy.retry
├── etcd_cluster_deploy.yaml
├── files
│ ├── etcd.conf.j2
│ ├── etcd.service.j2
│ ├── etcd.sh.j2
│ └── etcd-v3.3.10-linux-amd64.tar.gz
├── generate_tls.yaml
├── hosts
└── tls
├── ca-config.json.j2
├── ca-csr.json.j2
├── cert
├── cfssl.tar.gz
├── generate_etcd_cert.sh
└── server-csr.json.j2
# ansible-playbook -i hosts generate_tls.yaml
# ansible-playbook -i hosts etcd_cluster_deploy.yaml -k -K
site.yml webservers.yml fooservers.yml roles/ common/ tasks/ handlers/ files/ templates/ vars/ defaults/ meta/ webservers/ tasks/ defaults/ meta/
-
-
handlers-包含处理程序,此角色甚至在此角色之外的任何地方都可以使用这些处理程序。 -
defaults-角色的默认变量 -
vars-角色的其他变量 -
files-包含可以通过此角色部署的文件。 -
templates-包含可以通过此角色部署的模板。 -
meta
# roles/webservers/tasks/main.yml - name: added in 2.4, previously you used 'include' import_tasks: redhat.yml when: ansible_facts['os_family']|lower == 'redhat' - import_tasks: debian.yml when: ansible_facts['os_family']|lower == 'debian' # roles/webservers/tasks/redhat.yml - yum: name: "httpd" state: present # roles/webservers/tasks/debian.yml - apt: name: "apache2" state: present
使用角色
# site.yml - hosts: webservers roles: - common - webservers 定义多个: - name: 0 gather_facts: false hosts: all roles: - common - name: 1 gather_facts: false hosts: all roles: - webservers
角色控制
- name: 0.系统初始化 gather_facts: false hosts: all roles: - common tags: common