由于web接口自动化测试需要用到python的第三方库--requests库,运用requests库可以模拟发送http请求,再结合unittest测试框架,就能完成web接口自动化测试。
所以笔者今天先来总结一下requests库的用法。希望对大家(尤其是新手)有帮助哦!大家可要仔细阅读,加油!
前提:
requests库是python的第三方库,需要提前安装哦,可以直接用pip命令:python –m pip install requests
按照惯例,先将requests库的属性打印出来,看看哪些属性。
>>> import requests
>>> dir(requests) #查看requests库的属性
['ConnectionError', 'HTTPError', 'NullHandler', 'PreparedRequest', 'Request', 'RequestException', 'Response', 'Session', 'Timeout', 'TooManyRedirects', 'URLRequired', '__author__', '__build__', '__builtins__', '__copyright__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__license__', '__name__', '__package__', '__path__', '__title__', '__version__', 'adapters', 'api', 'auth', 'certs', 'codes', 'compat', 'cookies', 'delete', 'exceptions', 'get', 'head', 'hooks', 'logging', 'models', 'options', 'packages', 'patch', 'post', 'put', 'request', 'session', 'sessions', 'status_codes', 'structures', 'utils']
所以可以看到requests的属性有get,post,delete,put,对应http请求的method方法。
常用的是get和post请求。get请求一般是查询获取资源信息。post一般是更新资源信息。
>>> help(requests.get) #查看requests库的属性get请求函数的使用
Help on function get in module requests.api:
get(url, params=None, **kwargs)
Sends a GET request.
:param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param params: (optional) Dictionary or bytes to be sent in the query string for the :class:`Request`.
:param **kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes.
:return: :class:`Response <Response>` object
:rtype: requests.Response
url:调用接口的URL地址。
params:为可选参数,该参数是一个字典类型。数据会以键/值对的形式置于 URL 中,跟在一个问号的后面。举例说明,若r=requests.get("http://httpbin.org/get",params={'key1':'value1','key2':'value2'}) 那么,最终请求的目标URL为http://bin.org/get?key1=val1& key2=val2。
**kwargs:其他可选参数,例如headers,files,cookies,auth,timeout,json等。
例如:auth=(‘username',’password’):接口安全测试中用到的用户认证。
例如:headers = {'user-agent': 'my-app/0.0.1'}:可定制发送请求头。
返回的是response类对象(requests.models.Response)。来自requests模块 models.py里的Response类
>>> r=requests.get('http://httpbin.org/get') #查看response的属性
>>> dir(r)
['__attrs__', '__bool__', '__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__doc__', '__format__', '__getattribute__', '__getstate__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__module__', '__new__', '__nonzero__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__setstate__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', '_content', '_content_consumed', 'apparent_encoding', 'close', 'connection', 'content', 'cookies', 'elapsed', 'encoding', 'headers', 'history', 'is_permanent_redirect', 'is_redirect', 'iter_content', 'iter_lines', 'json', 'links', 'ok', 'raise_for_status', 'raw', 'reason', 'request', 'status_code', 'text','url']
对于返回对象常用的属性如下:
json():生成json数据对象的方法。如果 JSON 解码失败, r.json 就会抛出一个异常。例如,响应内容是 401 (Unauthorized),尝试访问 r.json 将会抛出 ValueError: No JSON object could be decoded 异常。
status_code:响应状态码。
encoding:编码,如utf-8。
url:目标url。
headers:响应头。类型为字典类型,若键不存在则返回None。
text:响应内容。字符串方式,会自动根据响应头部的字符编码进行解码。如果你改变了编码r.encoding,每当你访问 r.text ,Request 都将会使用 r.encoding 的新值。
content:二进制响应内容。字节方式,会自动为你解码gzip和deflate压缩。
raw:原始响应内容,也就是 urllib 的 response 对象,请求中要加stream=True,再使用 r.raw.read() 读取。
r.raise_for_status:失败请求(非200响应)抛出异常。
>>> payload={'key1':'value1','key2':'value2'}
>>> r=requests.get("http://httpbin.org/get",params=payload)
>>> r.status_code
200
>>> r.json()
{u'origin': u'113.98.252.236', u'headers': {u'Host': u'httpbin.org', u'Accept-Encoding': u'gzip, deflate', u'Accept': u'*/*', u'User-Agent': u'python-requests/2.7.0 CPython/2.7.11 Windows/7'}, u'args': {u'key2': u'value2', u'key1': u'value1'}, u'url': u'http://httpbin.org/get?key2=value2&key1=value1'}
>>> r.url #url:params数据会以键/值对的形式置于 URL 中,跟在一个问号的后面。
u'http://httpbin.org/get?key2=value2&key1=value1'
>>> r.headers
{'content-length': '334', 'server': 'nginx', 'connection': 'keep-alive', 'access-control-allow-credentials': 'true', 'date': 'Fri, 09 Dec 2016 09:04:40 GMT', 'access-control-allow-origin': '*', 'content-type': 'application/json'}
>>> r.headers['content-type']
'application/json'
>>> r.raw
<requests.packages.urllib3.response.HTTPResponse object at 0x0000000002E64E10>
>>> r.cookies
<RequestsCookieJar[]>
>>> r.text
u'{ "args": { "key1": "value1", "key2": "value2" }, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.7.0 CPython/2.7.11 Windows/7" }, "origin": "113.98.252.236", "url": "http://httpbin.org/get?key2=value2&key1=value1" } '
>>> r.content
'{ "args": { "key1": "value1", "key2": "value2" }, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.7.0 CPython/2.7.11 Windows/7" }, "origin": "113.98.252.236", "url": "http://httpbin.org/get?key2=value2&key1=value1" } '
>>> payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
>>> r = requests.get("http://httpbin.org/get", params=payload,stream=True)
>>> r.raw
<requests.packages.urllib3.response.HTTPResponse object at 0x0000000003105940>
>>> r.raw.read()
'{ "args": { "key1": "value1", "key2": "value2" }, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.7.0 CPython/2.7.11 Windows/7" }, "origin": "113.98.252.236", "url": "http://httpbin.org/get?key2=value2&key1=value1" } '
r.json():json数据,可以看出与1.4中的r.json()值一致。
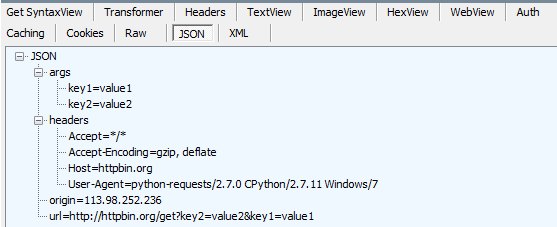
r.headers:响应头数据,可以看出与1.4中r.headers值一致。

r.raw:响应原始数据
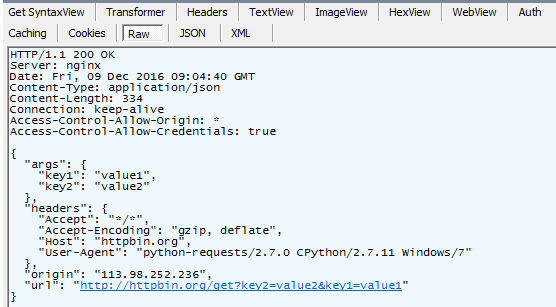
综上所述,通过requests.get("某url",params={字典类型参数键值对})模拟浏览器发送一个http的请求(其中请求的方法是get,请求的url地址如下形式
http://httpbin.org/get?key2=value2&key1=value1),服务器处理数据后,会返回一个response对象,通过读取response对象的属性值,如json数据,可以做一系列的断言,从而验证该接口返回的数据是否正确。
>>> help(requests.post) #查看requests库的属性post请求函数的使用
post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs)
Sends a POST request.
:param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param data: (optional) Dictionary, bytes, or file-like object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param json: (optional) json data to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param **kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes.
:return: :class:`Response <Response>` object
:rtype: requests.Response
url:调用接口的URL地址。
data:为可选参数,该参数是一个字典类型。
json:为可选参数,该参数是一个json类型。
**kwargs:其他可选参数,例如headers等。
同1.3
json():生成json数据对象的方法。如果 JSON 解码失败, r.json 就会抛出一个异常。例如,响应内容是 401 (Unauthorized),尝试访问 r.json 将会抛出 ValueError: No JSON object could be decoded 异常。
status_code:响应状态码。
encoding:编码,如utf-8。
url:目标url。
headers:响应头。类型为字典类型,若键不存在则返回None。
text:响应内容。字符串方式,会自动根据响应头部的字符编码进行解码。如果你改变了编码r.encoding,每当你访问 r.text ,Request 都将会使用 r.encoding 的新值。
content:二进制响应内容。字节方式,会自动为你解码gzip和deflate压缩。
raw:原始响应内容,也就是 urllib 的 response 对象,请求中要加stream=True,再使用 r.raw.read() 读取。
r.raise_for_status:失败请求(非200响应)抛出异常。
>>> payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
>>> r = requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post", data=payload)
>>> r.status_code
200
>>> r.json()
{u'files': {}, u'origin': u'113.98.252.236', u'form': {u'key2': u'value2', u'key1': u'value1'}, u'url': u'http://httpbin.org/post', u'args': {}, u'headers': {u'Content-Length': u'23', u'Accept-Encoding': u'gzip,deflate', u'Accept': u'*/*', u'User-Agent': u'python-requests/2.7.0 CPython/2.7.11 Windows/7', u'Host': u'httpbin.org', u'Content-Type': u'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}, u'json': None, u'data': u''}
>>> r.url
u'http://httpbin.org/post'
>>> r.headers
{'content-length': '461', 'server': 'nginx', 'connection': 'keep-alive', 'access-control-allow-credentials': 'true', 'date': 'Mon, 12 Dec 2016 02:46:14 GMT', 'access-control-allow-origin': '*', 'content-type': 'application/json'}
>>> r.headers['content-type']
'application/json'
>>> r.raw
<requests.packages.urllib3.response.HTTPResponse object at 0x0000000002EE4A58>
>>> r.text
u'{ "args": {}, "data": "", "files": {}, "form": { "key1": "value1", "key2": "value2" }, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Content-Length": "23", "Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.7.0 CPython/2.7.11 Windows/7" }, "json": null, "origin": "113.98.252.236", "url": "http://httpbin.org/post" } '
>>> r.content
'{ "args": {}, "data": "", "files": {}, "form": { "key1": "value1", "key2": "value2" }, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Content-Length": "23", "Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.7.0 CPython/2.7.11 Windows/7" }, "json": null, "origin": "113.98.252.236", "url": "http://httpbin.org/post" } '
>>> payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
#获取原始响应内容
>>> r = requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post", data=payload,stream=True)
>>> r.raw
<requests.packages.urllib3.response.HTTPResponse object at 0x0000000003105208>
>>> r.raw.read()
'{ "args": {}, "data": "", "files": {}, "form": { "key1": "value1", "key2": "value2" }, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Content-Length": "23", "Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.7.0 CPython/2.7.11 Windows/7" }, "json": null, "origin": "113.98.252.236", "url": "http://httpbin.org/post" } '
#使用 json 参数直接传递
>>> payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
>>> r = requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post", json=payload)
>>> r.text
u'{ "args": {}, "data": "{\"key2\": \"value2\", \"key1\": \"value1\"}", "files": {}, "form": {}, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Content-Length": "36", "Content-Type": "application/json", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.7.0 CPython/2.7.11 Windows/7" }, "json": { "key1": "value1", "key2": "value2" }, "origin": "113.98.252.236", "url": "http://httpbin.org/post" } '
r.json():json数据,可以看出与2.4中的r.json()值一致。

注:通过json进行传参的json数据
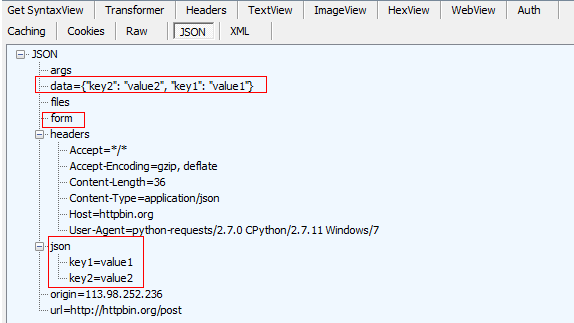
r.headers:响应头数据,可以看出与2.4中r.headers值一致。

r.raw:响应原始数据
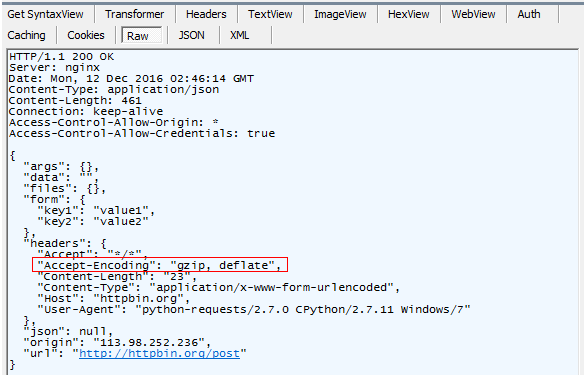
综上所述,通过requests.post("某url",data={字典类型参数键值对})模拟浏览器发送一个http的请求(其中请求的方法是post,请求的url地址如下形式
http://httpbin.org/get),服务器处理数据后,会返回一个response对象,通过读取response对象的属性值,如json数据,可以做一系列的断言,从而验证该接口返回的数据是否正确。
>>> payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
>>> headers = {'user-agent': 'my-app/0.0.1'}
>>> r = requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post", data=payload,headers=headers)
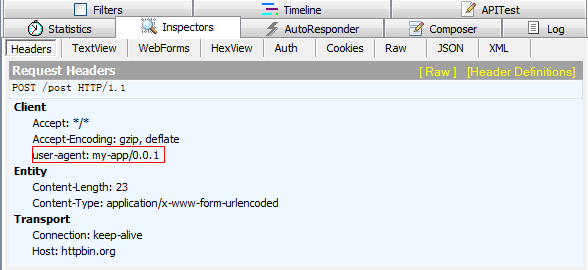
用fiddler抓包,可以看到,发送请求的请求头中的user-agent的值为设置的值。
注意: 所有的 header 值必须是 string、bytestring 或者 unicode。
>>> import os
>>> os.getcwd()
'D:\pythontest'
>>> f=open('1.txt','w+')
>>> f.write('test')
>>> os.listdir('D:\pythontest')
['1.txt',]
>>> import requests
>>> url = 'http://httpbin.org/post'
>>> files = {'file': open('1.txt', 'rb')}
>>> r = requests.post(url, files=files)
>>> r.text
u'{ "args": {}, "data": "", "files": { "file": "" }, "form": {}, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Content-Length": "141", "Content-Type": "multipart/form-data; boundary=37de3eb22a754f34849771891b77bd23", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.7.0 CPython/2.7.11 Windows/7" }, "json": null, "origin": "113.98.252.236", "url": "http://httpbin.org/post" } '
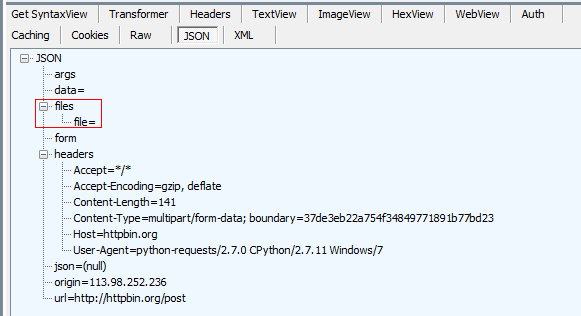
用fiddler抓包,可以看到,响应的JSON数据中有file。
>>> url = 'http://httpbin.org/cookies'
>>> cookies = dict(cookies_are='working')
>>> r = requests.get(url, cookies=cookies)
>>> r.text
u'{
"cookies": {
"cookies_are": "working"
}
}
'
通过上面抓包可以看出:
GET请求的数据会附在URL之后(就是 把数据放置在HTTP协议头中),以?分割URL和传输数据,参数之间以&相连,如:login.action?name=hyddd& password=idontknow&verify=%E4%BD%A0%E5%A5%BD。如果数据是英文字母/数字,原样发送,如果是空格,转换为+,如果是中文/其他字符,则直接把字符串用BASE64加密,得出如:%E4%BD%A0%E5%A5%BD,其中%XX中的XX为该符号以 16进制表示的ASCII。
POST把提交的数据则放置在是HTTP包的包体中。
4.2关于请求的Headers的Accept-Encoding说明
请求的headers中的client项中的Accept-Encoding的,例如Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate。浏览器申明自己接收的编码方法,通常指定压缩方法,是否支持压缩,支持什么压缩方法(gzip,deflate)(注意:这不是只字符编码)。
4.3关于响应的Headers的Content-Type说明
Content-Type是返回消息中非常重要的内容,表示后面的文档属于什么MIME类型。
Content-Type: [type]/[subtype]; parameter。例如最常见的就是text/html,它的意思是说返回的内容是文本类型,这个文本又是HTML格式的。原则上浏览器会根据 Content-Type来决定如何显示返回的消息体内容。
type有下面的形式:
Text:用于标准化地表示的文本信息,文本消息可以是多种字符集和或者多种格式的;
Multipart:用于连接消息体的多个部分构成一个消息,这些部分可以是不同类型的数据;
Application:用于传输应用程序数据或者二进制数据;
Message:用于包装一个E-mail消息;
Image:用于传输静态图片数据;
Audio:用于传输音频或者音声数据;
Video:用于传输动态影像数据,可以是与音频编辑在一起的视频数据格式。
subtype用于指定type的详细形式。
parameter可以用来指定附加的信息,更多情况下是用于指定text/plain和text/htm等的文字编码方式的charset参数。
注:如果想要做好web自动化接口测试,必须要了解HTTP协议,想要了解更多HTTP协议,可查看HTTP协议详解 转自小坦克
文档地址:http://docs.python-requests.org/en/master/
中文文档地址:http://cn.python-requests.org/zh_CN/latest/
Python下载地址:https://pypi.python.org/pypi/requests
Github资源:https://github.com/kennethreitz/requests
requests作者:https://www.kennethreitz.org/
测试接口服务端:http://httpbin.org/
(尊重笔者的劳动哦,转载请说明出处哦。)