from numpy import * import operator from os import listdir def classify0(inX, dataSet, labels, k): dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0] diffMat = tile(inX, (dataSetSize,1)) - dataSet sqDiffMat = diffMat**2 sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1) distances = sqDistances**0.5 sortedDistIndicies = distances.argsort() classCount={} for i in range(k): voteIlabel = labels[sortedDistIndicies[i]] classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel,0) + 1 sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.iteritems(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True) return sortedClassCount[0][0] def createDataSet(): group = array([[1.0,1.1],[1.0,1.0],[0,0],[0,0.1]]) labels = ['A','A','B','B'] return group, labels
用到的函数。
数组的行数。
shape函数是numpy.core.fromnumeric中的函数,它的功能是查看矩阵或者数组的维数。
>>> e = eye(3)
>>> e
array([[ 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1.]])
>>> e.shape
(3, 3)
>>> c = array([[1,1],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4]])
>>> c.shape
(4, 2)
>>> c.shape[0]
4
>>> c.shape[1]
2
一个单独的数值,返回值为空
>>> shape(3)
()
-------------------------------------------------
tile函数位于python模块 numpy.lib.shape_base中,
他的功能是重复某个数组。比如tile(A,n),功能是将数组A重复n次,
构成一个新的数组,我们还是使用具体的例子来说明问题:
>>> tile(1,2)
array([1, 1])
>>> tile((1,2,3),3)
array([1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3])
>>> b=[1,3,5]
>>> tile(b,[2,3])
array([[1, 3, 5, 1, 3, 5, 1, 3, 5],
[1, 3, 5, 1, 3, 5, 1, 3, 5]])
----------------------------------------
python中的几个括号
python中的小括号( ):代表tuple元组数据类型,元组是一种不可变序列
>>> tup = (1,2,3)
>>> tup
(1, 2, 3)
>>>
>>> ()#空元组
()
>>>
>>> 55,#一个值的元组
(55,)
python中的中括号[ ]:代表list列表数据类型,列表是一种可变的序列。其创建方法即简单又特别,像下面一样:
>>> list('python')
['p', 'y', 't', 'h', 'o', 'n']
python大括号{ }花括号:代表dict字典数据类型,字典是由键对值组组成。冒号':'分开键和值,逗号','隔开组。用大括号创建的方法如下:
>>> dic={'jon':'boy','lili':'girl'}
>>> dic
{'lili': 'girl', 'jon': 'boy'}
>>>
------------------------------------------
python 自己的sum()
>>>sum([0,1,2])
3
>>> sum((2, 3, 4), 1) # 元组计算总和后再加 1
10
>>> sum([0,1,2,3,4], 2) # 列表计算总和后再加 2
12
python的 numpy当中sum()
现在对于数据的处理更多的还是numpy。
没有axis参数表示全部相加,axis=0表示按列相加,axis=1表示按照行的方向相加
>>> import numpy as np
>>> a=np.sum([[0,1,2],[2,1,3]])
>>> a
9
>>> a.shape
()
>>> a=np.sum([[0,1,2],[2,1,3]],axis=0)
>>> a
array([2, 2, 5])
>>> a.shape
(3,)
>>> a=np.sum([[0,1,2],[2,1,3]],axis=1)
>>> a
array([3, 6])
>>> a.shape
(2,)
---------------------------------------
浅述python中argsort()函数的用法 # arguments 参数
import numpy as np
x=np.array([1,4,3,-1,6,9])
x.argsort()
输出定义为y=array([3,0,2,1,4,5])。
------------------------------------
range () 函数的使用是这样的:
range(start, stop[, step]),分别是起始、终止和步长
range(3)即:从0到3,不包含3,即0,1,2
>>> for i in range(3):
print(i)
0
1
2
range(1,3) 即:从1到3,不包含3,即1,2
for i in range(1,3):
print(i)
1
2
range(1,3,2)即:从1到3,每次增加2,因为1+2=3,所以输出只有1
第三个数字2是代表步长。如果不设置,就是默认步长为1
>>> for i in range(1,3,2):
print(i)
1
如果改成range(1,5,2),就会输出1和3
>>> for i in range(1,5,2):
print(i)
1
3
-----------------------------------------
Python 字典(Dictionary) get() 函数返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回默认值。
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 27}
print "Value : %s" % dict.get('Age')
print "Value : %s" % dict.get('Sex', "Never")
以上实例输出结果为:
Value : 27
Value : Never
----------------------------------------
Python内置的sorted()函数就可以对list进行排序:
>>> sorted([36, 5, -12, 9, -21])
[-21, -12, 5, 9, 36]
此外,sorted()函数也是一个高阶函数,它还可以接收一个key函数来实现自定义的排序,例如按绝对值大小排序:
>>> sorted([36, 5, -12, 9, -21], key=abs)
[5, 9, -12, -21, 36]
>>> sorted(['bob', 'about', 'Zoo', 'Credit'])
['Credit', 'Zoo', 'about', 'bob']
默认情况下,对字符串排序,是按照ASCII的大小比较的,由于'Z' < 'a',结果,大写字母Z会排在小写字母a的前面。
我们给sorted传入key函数,即可实现忽略大小写的排序:
>>> sorted(['bob', 'about', 'Zoo', 'Credit'], key=str.lower)
['about', 'bob', 'Credit', 'Zoo']
要进行反向排序,不必改动key函数,可以传入第三个参数reverse=True:
>>> sorted(['bob', 'about', 'Zoo', 'Credit'], key=str.lower, reverse=True)
['Zoo', 'Credit', 'bob', 'about']
operator.itemgetter函数
operator模块提供的itemgetter函数用于获取对象的哪些维的数据,参数为一些序号(即需要获取的数据在对象中的序号),下面看例子。
a = [1,2,3]
>>> b=operator.itemgetter(1) //定义函数b,获取对象的第1个域的值
>>> b(a)
2
>>> b=operator.itemgetter(1,0) //定义函数b,获取对象的第1个域和第0个的值
>>> b(a)
(2, 1)
要注意,operator.itemgetter函数获取的不是值,而是定义了一个函数,通过该函数作用到对象上才能获取值。
op={'1':(1,0,6),'3':(0,45,8),'2':(2,34,10)}
lp3=sorted(op.items(),key=operator.itemgetter(0),reverse=True)
print(lp3)
输出:[('3', (0, 45, 8)), ('2', (2, 34, 10)), ('1', (1, 0, 6))]
lp3=sorted(op.items(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=False)
输出:[('3', (0, 45, 8)), ('1', (1, 0, 6)), ('2', (2, 34, 10))]
------------------------------------------------------
语句classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]作用为:
将dataSet中的数据先按行依次放入example中,然后取得example中的example[-1]元素,放入列表classList中
linux下代码
KNN.py

#! /usr/bin/python #coding:utf-8 print 'hello' from numpy import * import operator #创建一个数据集,包含2个类别共4个样本 def createDataSet(): # 生成一个矩阵,每行表示一个样本 group = array([[1.0,0.9],[1.0,1.0],[0.1,0.2],[0.0,0.1]]) # 4个样本分别所属的类别 labels = ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B'] return group, labels # KNN分类算法函数定义 def KNNClassify(newInput, dataSet, labels, k): numSamples = dataSet.shape[0] #shape[0]表示行数 ## step1:计算距离 # tile(A, reps):构造一个矩阵,通过A重复reps次得到 # the following copy numSamples rows for dataSet diff = tile(newInput, (numSamples, 1)) -dataSet #按元素求差值 squareDiff = diff ** 2 #将差值平方 squareDist = sum(squareDiff, axis = 1) # 按行累加 ##step2:对距离排序 # argsort() 返回排序后的索引值 sortedDistIndices = argsort(squareDist) classCount = {} # define a dictionary (can be append element) for i in xrange(k): ##step 3: 选择k个最近邻 voteLabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]] ## step 4:计算k个最近邻中各类别出现的次数 # when the key voteLabel is not in dictionary classCount,get() # will return 0 classCount[voteLabel] = classCount.get(voteLabel, 0) + 1 ##step 5:返回出现次数最多的类别标签 maxCount = 0 for key, value in classCount.items(): if value > maxCount: maxCount = value maxIndex = key return maxIndex
测试代码
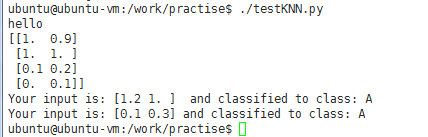
testKNN.py

#! /usr/bin/python #coding:utf-8 import KNN from numpy import * #生成数据集和类别标签 dataSet,labels = KNN.createDataSet() #定义一个未知类别的数据 testX = array([1.2, 1.0]) k=3 print dataSet #调用分类函数对未知数据分类 outputLabel = KNN.KNNClassify(testX, dataSet, labels, 3) print "Your input is:", testX, " and classified to class:", outputLabel testX = array([0.1, 0.3]) outputLabel = KNN.KNNClassify(testX,dataSet, labels, 3) print "Your input is:", testX, "and classified to class:", outputLabel