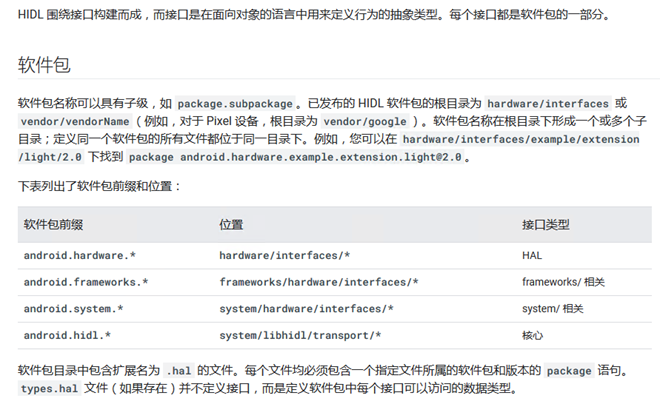
https://source.android.com/devices/architecture/hidl/interfaces
https://www.jianshu.com/p/fd73ab98e423
https://www.jianshu.com/p/ca6823b897b5
mkdir -p hardware/interfaces/naruto/1.0/default
创建接口文件。
vim hardware/interfaces/naruto/1.0/INaruto.hal
package android.hardware.naruto@1.0; interface INaruto { helloWorld(string name) generates (string result); };
项目目录下生成hidl-gen后
# PACKAGE=android.hardware.naruto@1.0 # LOC=hardware/interfaces/naruto/1.0/default/ # make hidl-gen -j64 # hidl-gen -o $LOC -Lc++-impl -randroid.hardware:hardware/interfaces -randroid.hidl:system/libhidl/transport $PACKAGE # hidl-gen -o $LOC -Landroidbp-impl -randroid.hardware:hardware/interfaces -randroid.hidl:system/libhidl/transport $PACKAGE
自动生成 Android,mk, Android.bp
default 目录会生成.cpp和.h 文件
制作service
touch hardware/interfaces/naruto/1.0/default/service/android.hardware.naruto@1.0-service.rc touch hardware/interfaces/naruto/1.0/default/service/service.cpp
./hardware/interfaces/update-makefiles.sh
mmm hardware/interfaces/naruto/1.0/default/ 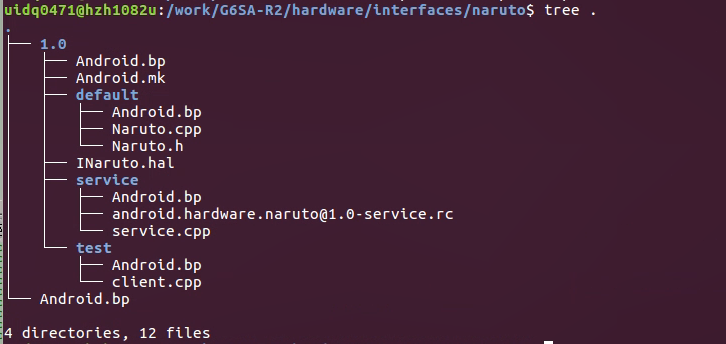
会生成一个android.hardware.naruto@1.0-impl.so, 生成在/vendor/lib64/hw/
会生成一个android.hardware.naruto@1.0.so, 生成在/system/lib64/
实现service
我们知道,HIDL的实现有两种方式,一种是Binderized模式,另一种是Passthrough模式,我们看到上面有两行注释掉的代码,看来这个代码是关键,来选择实现方式是Binderized还是Passthrough。
我们这里使用Passthrough模式来演示,其实大家后面尝试这两种方式后会发现其实这两种本质是一样的,目前大部分厂商使用的都是Passthrough来延续以前的很多代码,但是慢慢的都会被改掉的,所以我们来打开这个注释。
实现接口
Naruto.h
# ifndef ANDROID_HARDWARE_NARUTO_V1_0_NARUTO_H # define ANDROID_HARDWARE_NARUTO_V1_0_NARUTO_H # include <android/hardware/naruto/1.0/INaruto.h> # include <hidl/MQDescriptor.h> # include <hidl/Status.h> namespace android { namespace hardware { namespace naruto { namespace V1_0 { namespace implementation { using ::android::hardware::hidl_array; using ::android::hardware::hidl_memory; using ::android::hardware::hidl_string; using ::android::hardware::hidl_vec; using ::android::hardware::Return; using ::android::hardware::Void; using ::android::sp; struct Naruto : public INaruto { // Methods from INaruto follow. Return<void> helloWorld(const hidl_string& name, helloWorld_cb _hidl_cb) override; // Methods from ::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase follow. }; // FIXME: most likely delete, this is only for passthrough implementations extern "C" INaruto* HIDL_FETCH_INaruto(const char* name); } // namespace implementation } // namespace V1_0 } // namespace naruto } // namespace hardware } // namespace android # endif // ANDROID_HARDWARE_NARUTO_V1_0_NARUTO_H
Naruto.cpp
# include "Naruto.h" namespace android { namespace hardware { namespace naruto { namespace V1_0 { namespace implementation { // Methods from INaruto follow. Return<void> Naruto::helloWorld(const hidl_string& name, helloWorld_cb _hidl_cb) { // TODO implement char buf[100]; ::memset(buf, 0x00, 100); ::snprintf(buf, 100, "Hello World, %s", name.c_str()); hidl_string result(buf); _hidl_cb(result); return Void(); } // Methods from ::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase follow. INaruto* HIDL_FETCH_INaruto(const char* /* name */) { return new Naruto(); } } // namespace implementation } // namespace V1_0 } // namespace naruto } // namespace hardware } // namespace android
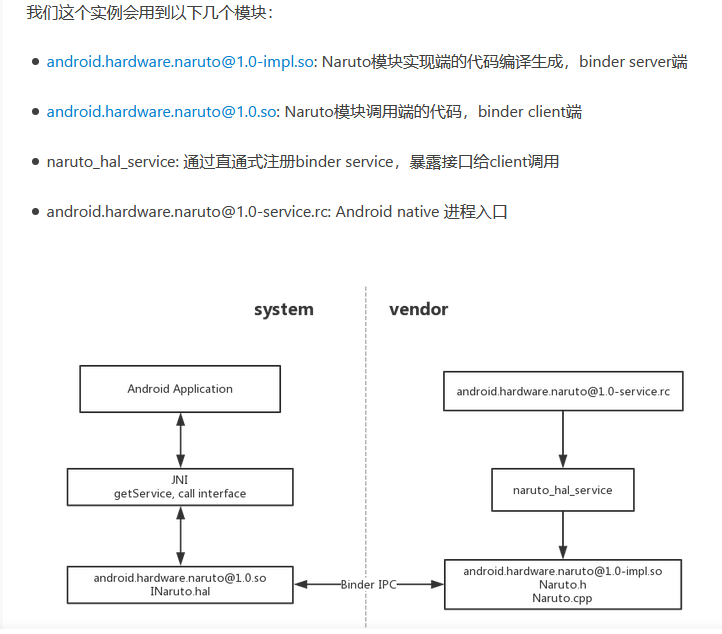
service.cpp 定义了hal服务启动时候进行的操作,两个文件具体内容如下。
rc文件
service naruto_hal_service /vendor/bin/hw/android.hardware.naruto@1.0-service class hal user system group system
service.cpp
# define LOG_TAG "android.hardware.naruto@1.0-service" # include <android/hardware/naruto/1.0/INaruto.h> # include <hidl/LegacySupport.h> using android::hardware::naruto::V1_0::INaruto; using android::hardware::defaultPassthroughServiceImplementation; int main() { return defaultPassthroughServiceImplementation<INaruto>(); }
创建test目录,添加client.cpp文件和bp文件。
cc_binary { name: "android.hardware.naruto.client", defaults: ["hidl_defaults"], proprietary: true, relative_install_path: "hw", srcs: ["client.cpp"], shared_libs: [ "libhidlbase", "libhidltransport", "libutils", "liblog", "android.hardware.naruto@1.0", ], }
client.cpp
# include <android/hardware/naruto/1.0/INaruto.h> # include <hidl/Status.h> # include <hidl/LegacySupport.h> # include <utils/misc.h> # include <hidl/HidlSupport.h> # include <stdio.h> using android::hardware::naruto::V1_0::INaruto; using android::sp; using android::hardware::hidl_string; int main() { android::sp<INaruto> service = INaruto::getService(); if(service == nullptr) { printf("Failed to get service "); return -1; } service->helloWorld("JayZhang", [&](hidl_string result) { printf("%s ", result.c_str()); }); return 0; }
执行./hardware/interfaces/update-makefiles.sh 更新编译范围,把test 和service 加到编译中。
执行mmm hardware/interfaces/naruto/1.0 编译生成客户端服务端可执行程序。
在manifest文件里添加追加
vendor接口的定义,不然在client端是没法拿到service的,在相应的manifest.xml里面加入:
<hal format="hidl"> <name>android.hardware.naruto</name> <transport>hwbinder</transport> <version>1.0</version> <interface> <name>INaruto</name> <instance>default</instance> </interface> </hal>
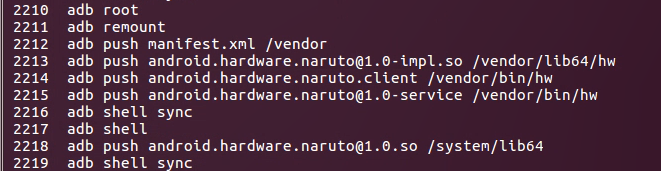
一个终端启动service,一个终端执行client。
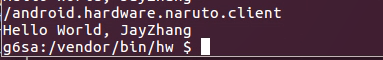
HIDL注册回调的实现。
在demo的基础上,增加一个Callback回调接口。client端 实现回调接口。
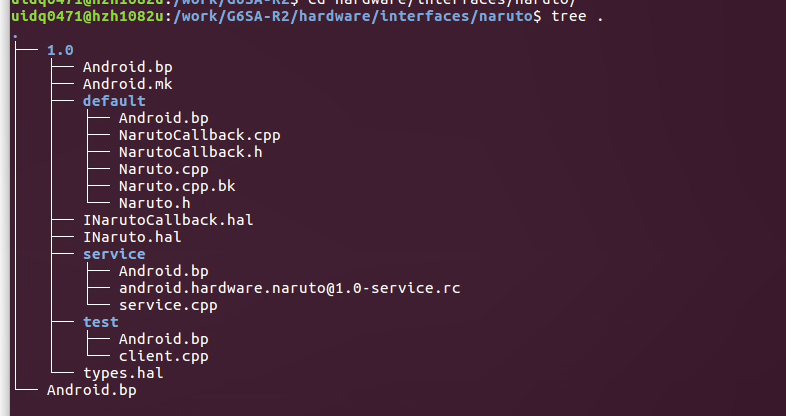
INaruto.hal
package android.hardware.naruto@1.0; import INarutoCallback; interface INaruto { helloWorld(string name) generates (string result); init() generates(); release() generates(); setCallback(INarutoCallback cb)generates(); };
INarutoCallback.hal
package android.hardware.naruto@1.0;
interface INarutoCallback {
oneway onNotify(HalEvent event);
};
types.hal
package android.hardware.naruto@1.0;
struct HalEvent{
int32_t value;
};
client.cpp
# include <android/hardware/naruto/1.0/INaruto.h> # include <android/hardware/naruto/1.0/types.h> # include <android/hardware/naruto/1.0/INarutoCallback.h> # include <hidl/Status.h> # include <hidl/LegacySupport.h> # include <utils/misc.h> # include <hidl/HidlSupport.h> # include <stdio.h> using android::hardware::naruto::V1_0::INaruto; using android::sp; using android::hardware::hidl_string; using android::hardware::naruto::V1_0::INarutoCallback; using android::hardware::naruto::V1_0::HalEvent; using android::hardware::Void; using android::hardware::Return; class myNarutoCallback:public INarutoCallback{ public: myNarutoCallback(){} ~myNarutoCallback(){} Return<void>onNotify(const HalEvent &event){ printf("onNotify,value = %d ",event.value); return Void(); } }; int main() { android::sp<INaruto> service = INaruto::getService(); if(service == nullptr) { printf("Failed to get service "); return -1; } service->helloWorld("JayZhang", [&](hidl_string result) { printf("%s ", result.c_str()); }); sp<myNarutoCallback>callback = new myNarutoCallback(); printf("Failed to callback "); service->setCallback(callback); printf(" to callback "); ::sleep(10); return 0; }
Naruto.cpp
#include "Naruto.h" namespace android { namespace hardware { namespace naruto { namespace V1_0 { namespace implementation { static sp<INarutoCallback> mCallback = nullptr; static bool mExit = false; static void threadLoop(){ static int32_t count =0; HalEvent event; while(!mExit){ ::sleep(1); event.value = count++; if(mCallback != nullptr){ mCallback->onNotify(event); } } printf("threadloop exit"); } // Methods from INaruto follow. Return<void> Naruto::helloWorld(const hidl_string& name, helloWorld_cb _hidl_cb) { // TODO implement char buf[100]; ::memset(buf, 0x00, 100); ::snprintf(buf, 100, "Hello World, %s", name.c_str()); hidl_string result(buf); _hidl_cb(result); return Void(); } Return<void> Naruto::init() { // TODO implement return Void(); } Return<void> Naruto::release() { // TODO implement return Void(); } Return<void> Naruto::setCallback(const sp<INarutoCallback>& cb) { // TODO implement printf("Naruto11111111111:: setCallback:done"); mCallback = cb; if(mCallback != nullptr) { printf("setCallback:done"); threadLoop(); } printf("Naruto222222222222:: setCallback:done"); return Void(); } // Methods from ::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase follow. INaruto* HIDL_FETCH_INaruto(const char* /* name */) { return new Naruto(); } } // namespace implementation } // namespace V1_0 } // namespace naruto } // namespace hardware } // namespace android