from multiprocessing import Process import time class MyProcess(Process): def __init__(self): super(MyProcess, self).__init__() #self.name = name def run(self): time.sleep(1) print ('hello', self.name,time.ctime()) if __name__ == '__main__': p_list=[] for i in range(3): p = MyProcess() p.start() p_list.append(p) for p in p_list: p.join() print('end')
一、类式调用
二、线程锁
2.1 全局解释器锁
一次只允许一个线程进入
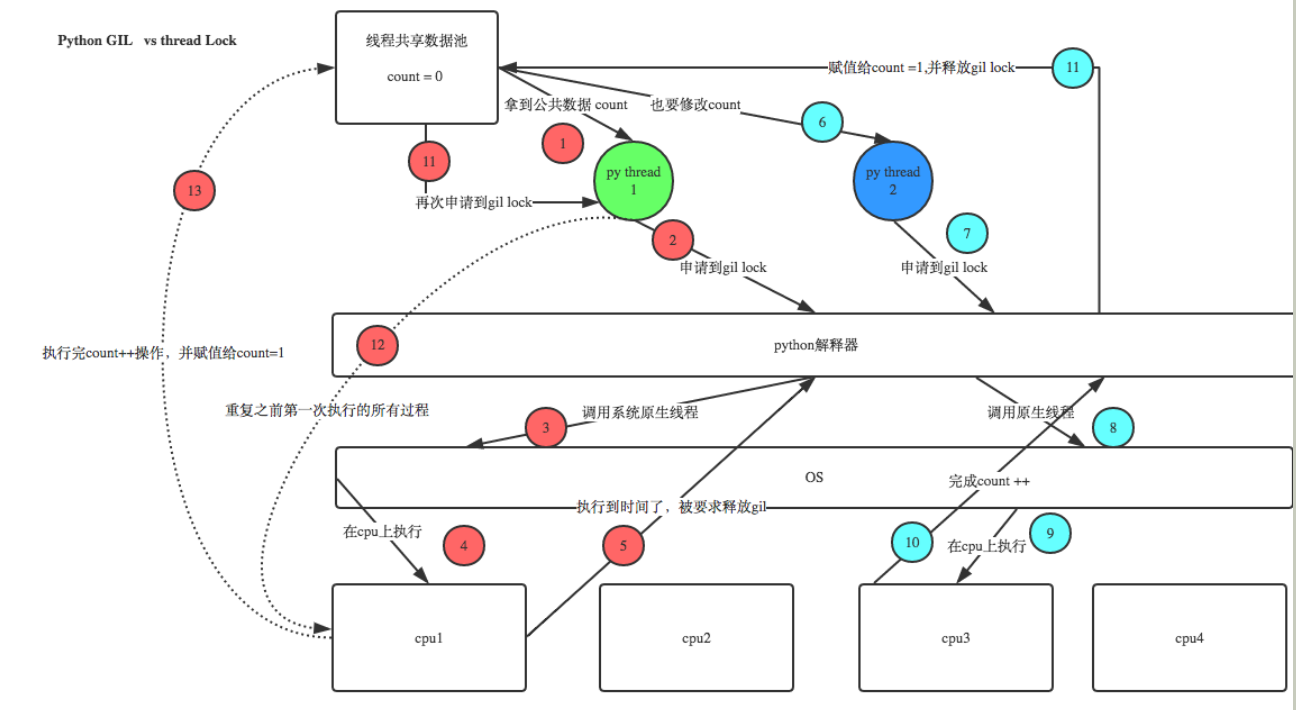
在Cpython解释器中,同一个进程下开启的多线程,同一时刻只能有一个线程执行,无法利用多核优势
2.2 互斥锁
def sub(): global count lock.acquire() #上锁,第一个线程如果申请到锁,会在执行公共数据的过程中持续阻塞后续线程 #即后续第二个或其他线程依次来了发现已经被上锁,只能等待第一个线程释放锁 #当第一个线程将锁释放,后续的线程会进行争抢 '''线程的公共数据 下''' temp=count time.sleep(0.001) count=temp+1 '''线程的公共数据 上''' lock.release() #释放锁 time.sleep(2) count=0 l=[] lock=threading.Lock() #将锁内的代码串行化 for i in range(100): t=threading.Thread(target=sub,args=()) t.start() l.append(t) for t in l: t.join() print(count)
2.3 递归锁
import threading import time def foo(): rlock.acquire() print('func foo ClockA lock') rlock.acquire() print('func foo ClockB lock') rlock.release() rlock.release() def bar(): rlock.acquire() print('func bar ClockB lock') time.sleep(2) rlock.acquire() print('func bar ClockA lock') rlock.release() rlock.release() def run(): foo() bar() rlock=threading.RLock() #RLock本身有一个计数器,如果碰到acquire,那么计数器+1 #如果计数器大于0,那么其他线程无法查收,如果碰到release,计数器-1 for i in range(10): t=threading.Thread(target=run,args=()) t.start()
2.4 信号量
# 互斥锁同时只允许一个线程更改数据,而Semaphore是同时允许一定数量的线程更改数据,比如 # 一个厕所有3个坑,那么最多只允许3个人上厕所,后面的人只能等里面有人出来了才能再进去 import threading import time def run(n): semaphore.acquire() time.sleep(1) print("run the thread: %s" %n) semaphore.release() if __name__ == '__main__': num = 0 semaphore = threading.BoundedSemaphore(3) #最多允许3个线程同时运行 for i in range(20): t = threading.Thread(target=run,args=[i,]) t.start() while threading.active_count() != 1: print(threading.active_count()) pass else: print("----all threads done----------") print(num)
2.5 条件变量
# *-* coding=gb2312 *-* ''' 信号量semaphore 是一个变量,控制着对公共资源或者临界区的访问。信号量维护着一个计数器,指定可同时访问资源或者进入临界区的线程数。 每次有一个线程获得信号量时,计数器-1。若计数器为0,其他线程就停止访问信号量,直到另一个线程释放信号量。 ''' import threading import random import time class MyThread(threading.Thread): availableTables=['A','B','C','D','E'] def __init__(self,threadName,semaphore): self.interval =random.randrange(1,6) self.semaphore =semaphore threading.Thread.__init__(self,name=threadName) def run(self): self.semaphore.acquire() #acquire a semaphore table = MyThread.availableTables.pop() print "%s entered;seated at table %s." %(self.getName(),table) time.sleep(self.interval) #free a table print "%s exiting,freeing table %s." %(self.getName(),table) MyThread.availableTables.append(table) self.semaphore.release() mySemaphore = threading.Semaphore(len(MyThread.availableTables)) def Test(): threads=[] for i in range(1,10): threads.append(MyThread("thread"+str(i),mySemaphore)) for i in range(len(threads)): threads[i].start() if __name__ == '__main__': Test()
2.6 同步变量
ecent的4个方法:
event.isSet():返回event的状态值
event.set():将event的状态值设置为True
event.wait():等待,直到event的值变为True,否则,一直阻塞住
event.clear():将event的值设置为False
例子:
import threading import time event = threading.Event()#创建了一个event class boss(threading.Thread): def run(self): print("开始工作了") event.isSet() or event.set()#将event的状态置为ture,让worker开始干活 time.sleep(4)#在这个时间段,工人们开始干活 print('可以下班了') event.isSet() or event.set()#将event的状态置为ture,工人们下班 class worker(threading.Thread): def run(self): # r.acquire() event.wait()#等待boss发指令 print("不要阿") time.sleep(1)#开始干活 # r.release() event.clear()#将event的状态置为false event.wait()#等待boss的进一步指令 print("好也,回家吃莽莽") if __name__ == '__main__': p = [] for i in range(3): p.append(worker()) p.append(boss()) for i in p: i.start() # for i in p: # i.join()