面向对象(OOD)(OOP):在研究复杂问题时,需要使类和类之间产生关系。分别为Inheritance(继承),Composition(复合),Delegation(委托)。
复合(composition):即一个类的中包含另一个类的成员。表示为has-a的关系
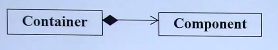
例如:
文件名:
composition.h
1 #ifndef __COMPOSITION__
2 #define __COMPOSITION__
3 #include <iostream>
4 #include <deque>
5 #include <vector>
6 using namespace std;
7
8 template <class T,class Sequence=deque<T>>
9 class queue
10 {
11 private:
12 Sequence c;
13 public:
14 bool empty() const{return c.empty();}
15 vector<int>::size_type size() const {return c.size();}
16 //reference front(){return c.front();}
17 //reference back(){return c.back();}
18 void push(const vector<int>::value_type& x){c.push_back(x);}
19 void pop(){c.pop_front();}
20 };
21 #endif // __COMPOSITION_
在类里面定义一个已经定义好的类的成员,这里deque<T>已经定义好了。这样在queue类里面可以通过c随意使用deque<T>的成员函数。
在设计模式里,Adapter就是通过复合形成的,方法就是将已经设计好的类改造一下,例如将deque类的成员函数换一个名字。这样可以借助已经设计出来的类和接口,可以选择变量或者方法进行改装,封装成自己想到的类。上面这个例子就是Adapter的典型。
复合函数的调用顺序:
例子:
文件名:composition.h
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class B 4 { 5 public: 6 B():b(){cout<<"construct a object B!!!"<<endl;} 7 ~B(){cout<<"destruct a object B!!!"<<endl;} 8 private: 9 int b; 10 }; 11 12 13 class A 14 { 15 public: 16 A(){cout<<"construct a object A!!!"<<endl;} 17 ~A(){cout<<"destruct a object A!!!"<<endl;} 18 private: 19 B c; 20 int a; 21 };
调用:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "composition.h" 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 A a; 7 return 0; 8 }
此时结果为:

可见:构造函数调用顺序先里后外,析构函数的调用顺序是先外后里。
委托:composition by referrence Handle/Body 在设计模式中的应用为pImpl
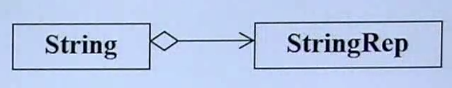
一个类的成员变量里面有另外一个类的指针,它的优点是可以跟别人共享一份资源。
并且调用和实现不在一起。叫做编译防火墙。
一个不好的例子:
文件名:delegation.h
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class stringRep 5 { 6 friend class sstring; 7 public: 8 stringRep():count_n(0){cout<<"construct a objectStringRep"<<endl;} 9 ~stringRep(){cout<<"destruct a objectStringRep"<<endl;} 10 stringRep(char* chr):count_n(0){this->chr=chr;cout<<"construct a objectStringRep"<<endl;} 11 char* getchr() const {return chr;} 12 int get_n() const {return count_n;} 13 private: 14 int count_n; 15 char* chr; 16 }; 17 18 19 class sstring 20 { 21 public: 22 sstring(){cout<<"construct a objectSTRING"<<endl;} 23 sstring(stringRep& sr):rep(&sr){sr.count_n++;cout<<"construct a objectSTRING"<<endl;} 24 ~sstring(){(rep->count_n)--;cout<<"construct a objectString"<<endl;} 25 private: 26 stringRep* rep; 27 };
调用:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "delegation.h" 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 stringRep sr("乌兹 never give up!!!"); 8 sstring str1(sr); 9 sstring str2(sr); 10 sstring str3(sr); 11 cout<<endl<<"count_n="<<sr.get_n()<<endl<<endl; 12 cout<<sr.getchr()<<endl<<endl; 13 return 0; 14 }
运行结果:

注意:之所以说这个例子不好,因为虽然这里包含了类的指针,也即是委托。但是它并不是纯粹的pImpl模式,因为在sstring类里面还是包含了stringRep的成员,做这个例子只是为了实现count_n的功能而已,即表示多少sstring对象指向一个stringRep对象。
继承: 父类的数据完全地被继承下来。表示is-a(是一种)的关系
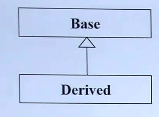
例如:
文件名:inheritance.h
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class A 4 { 5 public: 6 A(){cout<<"construct a objectA"<<endl;} 7 ~A(){cout<<"destruct a objectA"<<endl;} 8 }; 9 10 11 class B:public A 12 { 13 public: 14 B(){cout<<"construct a objectB"<<endl;} 15 ~B(){cout<<"destruct a objectB"<<endl;} 16 };
调用:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "inheritance.h" 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 B b; 8 return 0; 9 }
运行结果:
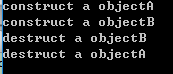
表示构造函数调用的顺序是先父后子,析构的顺序是先子后父。
虚函数和非虚函数和纯虚函数:
非虚函数:不希望子类重写(override)的父类函数。但是若子类强行要重写,那也不会报错。
例如:
int getvalue() const {return value;}
虚函数:希望子类进行重写的父类成员函数。在父类中有实现。
例如:
virtual int getvalue() const {return value;}
纯虚函数:要求子类必须重写,否则报错。
例如:
virtual int getvalue() const =0;