在《Spring AOP初级——入门及简单应用》中对AOP作了简要的介绍,以及一些专业术语的解释,同时写了一个简单的Spring AOPdemo。本文将继续探讨Spring AOP在实际场景中的应用。
对用户操作日志的记录是很常见的一个应用场景,本文选取“用户管理”作为本文Spring AOP的示例。当然,该示例只是对真实场景的模拟,实际的环境一定比该示例更复杂。
该示例的完整代码路径在https://github.com/yu-linfeng/BlogRepositories/tree/master/repositories/Spring%20AOP%E4%B8%AD%E7%BA%A7%E2%80%94%E2%80%94%E5%BA%94%E7%94%A8%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF。本文仅对Spring AOP相关的代码进行讲解。
在这个示例中首次采用RESTful架构风格,对于以下RESTful API的设计可能并不完美,如果有熟悉、精通RESTful架构风格的朋友希望能够指出我的错误。

使用RESTful的前后端分离架构风格后,我感受到了前所未有的畅快,所以此次示例并没有前端页面的展示,完全使用JUnit进行单元测试包括对HTTP请求的Mock模拟,这部分代码不会进行详细讲解,之后会继续深入JUnit单元测试的一些学习研究。
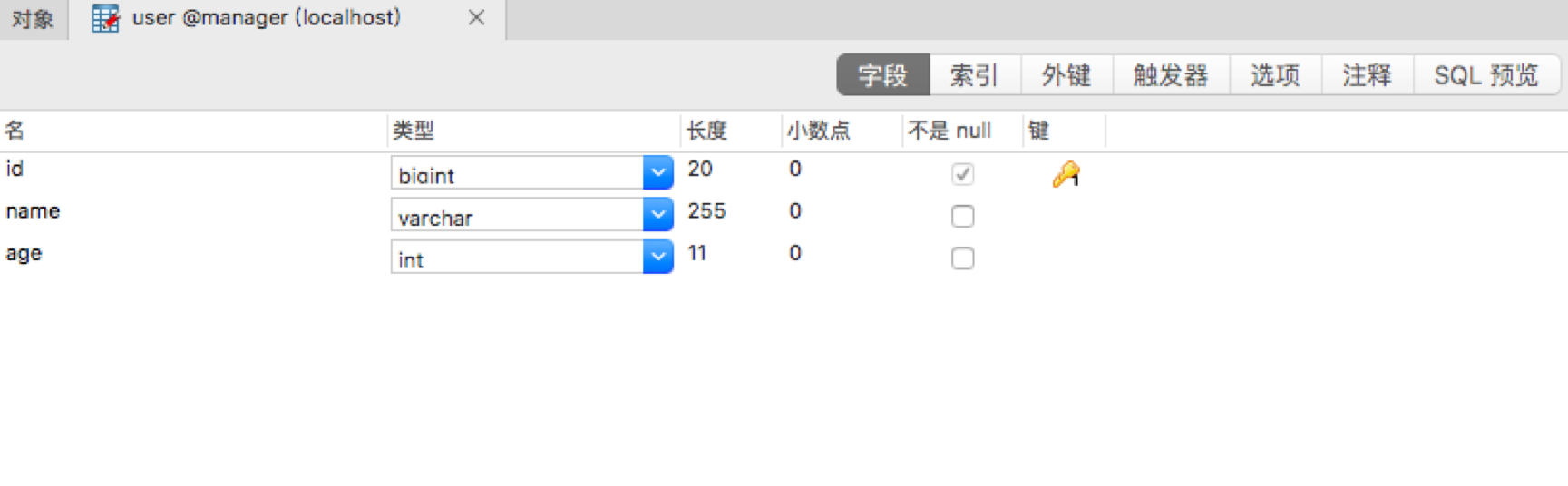
数据库只有一张表:
回到正题,我们回顾下切面由哪两个部分组成: 通知 切点 首先明确我们需要在何时记录日志:
通知
切点
首先明确我们需要在何时记录日志:
1. 查询所有用户时,并没有参数(此示例没有作分页),只有在返回时才会有数据的返回,所以对查询所有用户的方法采用返回通知(AfterReturning)。
2. 新增用户时,会带有新增的参数,此时可采用前置通知(Before)。
3. 修改用户时,也会带有新增的参数,此时同样采用前置通知(Before)。
4. 删除用户时,通常会带有唯一标识符ID,此时采用前置通知(Before)记录待删除的用户ID。
在明确了通知类型后,此时我们需要明确切点,也就是在哪个地方记录日志。当然上面实际已经明确了日志记录的位置,但主要是切面表达式的书写。 在有了《Spring AOP初级——入门及简单应用》的基础,相信对日志切面类已经比较熟悉了:
1 package com.manager.aspect; 2 3 import org.apache.log4j.Logger; 4 import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; 5 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*; 6 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; 7 8 import java.util.Arrays; 9 10 /** 11 * 日志切面 12 * Created by Kevin on 2017/10/29. 13 */ 14 @Aspect 15 @Component 16 public class LogAspect { 17 /** 18 * 操作日志文件名 19 */ 20 private static final String OPERATION_LOG_NAME = "operationLog"; 21 private static final String LOG_FORMATTER = "%s.%s - %s"; 22 Logger log = Logger.getLogger(OPERATION_LOG_NAME); 23 /** 24 * 对查询方法记录日志的切点 25 */ 26 @Pointcut("execution(* com.manager..*.*Controller.query*(..))") 27 public void query(){} 28 29 /** 30 * 对新增方法记录日志的切点 31 */ 32 @Pointcut("execution(* com.manager..*.*Controller.add*(..))") 33 public void add(){} 34 35 /** 36 * 对修改方法记录日志的切点 37 */ 38 @Pointcut("execution(* com.manager..*.*Controller.update*(..))") 39 public void update(){} 40 41 /** 42 * 对删除方法记录日志的切点 43 */ 44 @Pointcut("execution(* com.manager..*.*Controller.delete*(..))") 45 public void delete(){} 46 47 @AfterReturning(value = "query()", returning = "rvt") 48 public void queryLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object rvt) { 49 String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName(); 50 String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); 51 String returnResult = rvt.toString(); 52 log.info(String.format(LOG_FORMATTER, className, methodName, returnResult)); 53 } 54 55 @Before("add()") 56 public void addLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) { 57 String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName(); 58 String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); 59 Object[] params = joinPoint.getArgs(); 60 log.info(String.format(LOG_FORMATTER, className, methodName, Arrays.toString(params))); 61 } 62 63 @Before("update()") 64 public void updateLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) { 65 String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName(); 66 String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); 67 Object[] params = joinPoint.getArgs(); 68 log.info(String.format(LOG_FORMATTER, className, methodName, Arrays.toString(params))); 69 } 70 71 @Before("delete()") 72 public void deleteLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) { 73 String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName(); 74 String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); 75 Object[] params = joinPoint.getArgs(); 76 log.info(String.format(LOG_FORMATTER, className, methodName, Arrays.toString(params))); 77 } 78 }
上面的日志切面类中出现了JointPoint类作为参数的情况,这个参数能够传递被通知方法的相信,例如被通知方法所处的类以及方法名等。在第47行中的Object rvt参数就是获取被通知方法的返回值。 上面的切面并没有关注被通知方法的参数,如果要使得切面和被通知方法参数参数关联可以使用以下的方式:
@Pointcut("execution(* com.xxx.demo.Demo.method(int)) && args(arg)")
public void aspectMethod(int arg){}
@Before(“aspectMedhot(arg)”)
public void method(int arg) {
//此时arg参数就是被通知方法的参数
}
本例中最主要的切面部分就完成了。注意在结合Spring时需要在applicationContext.xml中加入以下语句:
<!--启用AspectJ自动代理,其中proxy-target-class为true表示使用CGLib的代理方式,false表示JDK的代理方式,默认false--> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
示例中关于log4j、pom.xml依赖、JUnit如何结合Spring进行单元测试等等均可可以参考完整代码。特别是JUnit是很值得学习研究的一部分,这部分在将来慢慢我也会不断学习推出新的博客,在这里就只贴出JUnit的代码,感兴趣的可以浏览一下:
1 package com.manager.user.controller; 2 3 import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; 4 import com.manager.user.pojo.User; 5 import org.junit.Before; 6 import org.junit.Test; 7 import org.junit.runner.RunWith; 8 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 9 import org.springframework.http.MediaType; 10 import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; 11 import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; 12 import org.springframework.test.context.web.WebAppConfiguration; 13 import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc; 14 import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders; 15 import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers; 16 import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders; 17 import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext; 18 19 import static org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull; 20 21 /** 22 * UserController单元测试 23 * Created by Kevin on 2017/10/26. 24 */ 25 @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) 26 @ContextConfiguration({"classpath*:applicationContext.xml", "classpath*:spring-servlet.xml"}) 27 @WebAppConfiguration 28 public class UserControllerTest { 29 @Autowired 30 private WebApplicationContext wac; 31 private MockMvc mvc; 32 33 @Before 34 public void initMockHttp() { 35 this.mvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(wac).build(); 36 } 37 38 @Test 39 public void testQueryUsers() throws Exception { 40 mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/users")) 41 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()); 42 } 43 44 @Test 45 public void testAddUser() throws Exception { 46 User user = new User(); 47 user.setName("kevin"); 48 user.setAge(23); 49 mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/users") 50 .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8) 51 .content(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(user))) 52 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()) 53 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.name").value("kevin")) 54 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.age").value(23)); 55 } 56 57 @Test 58 public void testQueryUserById() throws Exception { 59 User user = new User(); 60 user.setId(8); 61 mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/users/" + user.getId())) 62 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()) 63 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.name").value("kevin")) 64 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.age").value(23)); 65 66 } 67 68 @Test 69 public void testUpdateUserById() throws Exception { 70 User user = new User(); 71 user.setId(9); 72 user.setName("tony"); 73 user.setAge(99); 74 mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.put("/users/" + user.getId()) 75 .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8) 76 .content(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(user))) 77 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()); 78 } 79 80 @Test 81 public void testDeleteUserById() throws Exception { 82 long id = 10; 83 mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.delete("/users/" + id)) 84 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()); 85 } 86 }
有了初级和中级,接下来必然就是Spring AOP高级——源码实现。
这是一个能给程序员加buff的公众号
