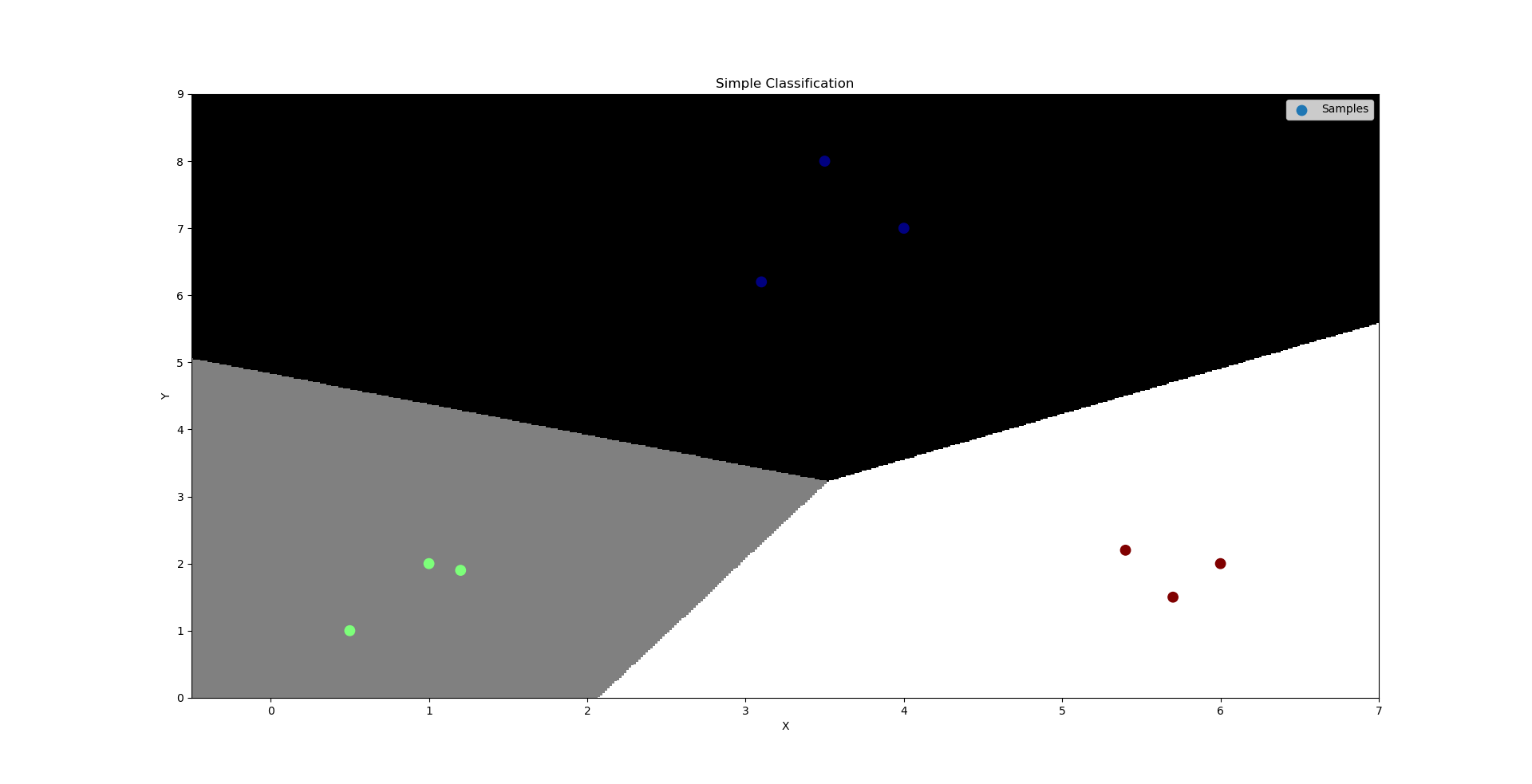
''' 逻辑分类:----底层为线性回归问题 通过输入的样本数据,基于多元线型回归模型求出线性预测方程。 y = w0+w1x1+w2x2 但通过线型回归方程返回的是连续值,不可以直接用于分类业务模型,所以急需一种方式使得把连续的预测值->离散的预测值。 [-oo, +oo]->{0, 1} 逻辑函数(sigmoid):y = 1 / (1+e^(-x)), 该逻辑函数当x>0,y>0.5;当x<0, y<0.5; 可以把样本数据经过线性预测模型求得的值带入逻辑函数的x,即将预测函数的输出看做输入被划分为1类的概率, 择概率大的类别作为预测结果,可以根据函数值确定两个分类。这是连续函数离散化的一种方式。 逻辑回归相关API: import sklearn.linear_model as lm # 构建逻辑回归器 # solver:逻辑函数中指数的函数关系(liblinear为线型函数关系) # C:参数代表正则强度,为了防止过拟合。正则越大拟合效果越小。 model = lm.LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear', C=正则强度) model.fit(训练输入集,训练输出集) result = model.predict(带预测输入集) 案例:基于逻辑回归器绘制网格化坐标颜色矩阵。 ''' import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as mp import sklearn.linear_model as lm x = np.array([[3, 1], [2, 5], [1, 8], [6, 4], [5, 2], [3, 5], [4, 7], [4, -1]]) y = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0]) # 根据找到的某些规律,绘制分类边界线 l, r = x[:, 0].min() - 1, x[:, 0].max() + 1 b, t = x[:, 1].min() - 1, x[:, 1].max() + 1 n = 500 grid_x, grid_y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(l, r, n), np.linspace(b, t, n)) # 构建逻辑回归模型,并训练模型 model = lm.LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear', C=1) model.fit(x, y) # 把网格坐标矩阵中500*500做类别预测 test_x = np.column_stack((grid_x.ravel(), grid_y.ravel())) # grid_x,grid_y撑平后合并为两列 test_y = model.predict(test_x) grid_z = test_y.reshape(grid_x.shape) # 绘制样本数据 mp.figure('Simple Classification', facecolor='lightgray') mp.title('Simple Classification') mp.xlabel('X') mp.ylabel('Y') # 绘制分类边界线(填充网格化矩阵) mp.pcolormesh(grid_x, grid_y, grid_z, cmap='gray') mp.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], s=80, c=y, cmap='jet', label='Samples') mp.legend() mp.show()
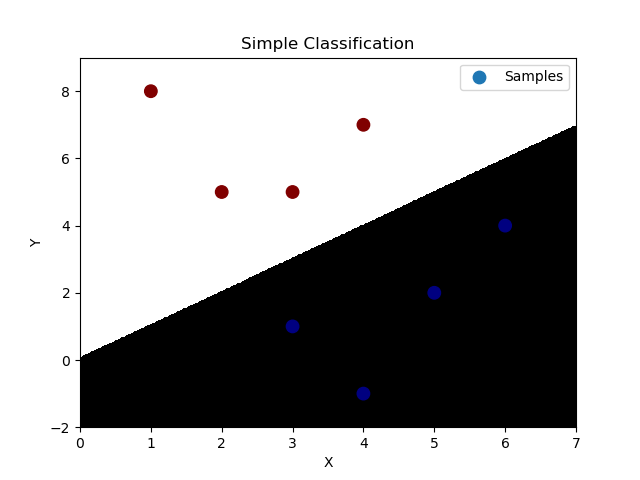
''' 多元逻辑分类:----底层为线性回归问题 通过多个二元分类器解决多元分类问题。 特征1 特征2 ==> 所属类别 4 7 ==> A 3.5 8 ==> A 1.2 1.9 ==> B 5.4 2.2 ==> C 若拿到一组新的样本,可以基于二元逻辑分类训练出一个模型判断属于A类别的概率。 再使用同样的方法训练出两个模型分别判断属于B、C类型的概率,最终选择概率最高的类别作为新样本的分类结果。 逻辑回归相关API: import sklearn.linear_model as lm # 构建逻辑回归器 # solver:逻辑函数中指数的函数关系(liblinear为线型函数关系) # C:参数代表正则强度,为了防止过拟合。正则越大拟合效果越小。 model = lm.LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear', C=正则强度) model.fit(训练输入集,训练输出集) result = model.predict(带预测输入集) 案例:基于逻辑分类模型的多元分类。 ''' import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as mp import sklearn.linear_model as lm x = np.array([[4, 7], [3.5, 8], [3.1, 6.2], [0.5, 1], [1, 2], [1.2, 1.9], [6, 2], [5.7, 1.5], [5.4, 2.2]]) y = np.array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2]) # 根据找到的某些规律,绘制分类边界线 l, r = x[:, 0].min() - 1, x[:, 0].max() + 1 b, t = x[:, 1].min() - 1, x[:, 1].max() + 1 n = 500 grid_x, grid_y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(l, r, n), np.linspace(b, t, n)) # 构建逻辑回归模型,并训练模型 model = lm.LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear', C=200) model.fit(x, y) # 把网格坐标矩阵中500*500做类别预测 test_x = np.column_stack((grid_x.ravel(), grid_y.ravel())) # grid_x,grid_y撑平后合并为两列 test_y = model.predict(test_x) grid_z = test_y.reshape(grid_x.shape) # 绘制样本数据 mp.figure('Simple Classification', facecolor='lightgray') mp.title('Simple Classification') mp.xlabel('X') mp.ylabel('Y') # 绘制分类边界线(填充网格化矩阵) mp.pcolormesh(grid_x, grid_y, grid_z, cmap='gray') mp.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], s=80, c=y, cmap='jet', label='Samples') mp.legend() mp.show()