中国MOOC《Pyhton计算计算三维可视化》总结
课程url:here ,教师:黄天宇,嵩天
下文的图片和问题,答案都是从eclipse和上完课后总结的,转载请声明。
Python数据三维可视化
1Introduction
1.1可视化计算工具
1.1.1TVTK 科学计算三维可视化基础
Mayavi 三维网格面绘制,三维标量场和矢量场绘制
TraitsUI 交互式三维可视化
SciPy 拟合,线性差值,统计,插值
数据过滤器
需要安装的软件:VTK, Mayavi, numpy, PyQt4, Traits, TraitsUI
1.2内容组织
流体数据的标量可视化、矢量可视化实例
三维扫描数据(模型/地形)
三维地球场景可视化实例
曲线UI交互控制可视化
2基础运用
2.1TVTK入门
科学计算可视化主要方法
- 二维标量数据场:颜色映射法,等值线法,立体图/层次分割法
- 三维标量数据场:面绘制法,体绘制法
- 矢量数据场:直接法,流线法
下载python开源库网站:https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/ 这里基本上集成了python需要用到的各个库的资源。
VTK库安装方法是将文件放在<C:WINDOWSsystem32>下面,这样系统可以自动检测到并安装,安装在使用如下操作,在开始菜单栏,输入cmd,用管理员身份启动cmd,输入pip install xxx(VTK版本号),有时候安装不行是因为pip需要更新,或者VTK文件放的位置不对,只要根据系统提示正确操作就行。
2.2创建一个基本三维对象
tvtk.CubeSource()的使用代码为s = tvtk.CubeSource(traits)
tvtk中CubeSource()的调用方式:
s = tvtk.CubeSource(x_length=1.0,y_length=2.0,z_length=3.0)
- x_length:立方体在X轴的长度
- y_length:立方体在Y轴的长度
- z_length:立方体在Z轴的长度
以下是s的输出结果:
Debug: Off
Modified Time: 1903583
Reference Count: 2
Registered Events:
Registered Observers:
vtkObserver (000001813DFDB520)
Event: 33
EventName: ModifiedEvent
Command: 000001813DBFDF80
Priority: 0
Tag: 1
Executive: 000001813D838460
ErrorCode: No error
Information: 000001813D864210
AbortExecute: Off
Progress: 0
Progress Text: (None)
X Length: 1
Y Length: 2
Z Length: 3
Center: (0, 0, 0)
Output Points Precision: 0
- 可以用s.x_length/s.y_length/s.z_length获取长方体在三个方向上的长度。
- CubeSource对象的方法
|
方法 |
说明 |
|
Set/get_x_length() |
设置/获取长方体对象在X轴方向的长度 |
|
Set/get_y_length() |
设置/获取长方体对象在Y轴方向的长度 |
|
Set/get_z_length() |
设置/获取长方体对象在Z轴方向的长度 |
|
Set/get_center() |
设置/获取长方体对象所在坐标系的原点 |
|
Set/get_bounds() |
设置/获取长方体对象的包围盒 |
TVTK库的基本三维对象
|
三维对象 |
说明 |
|
CubeSource |
立方体三维对象数据源 |
|
ConeSource |
圆锥三维对象数据源 |
|
CylinderSource |
圆柱三维对象数据源 |
|
ArcSource |
圆弧三维对象数据源 |
|
ArrowSource |
箭头三维对象数据源 |
比如建立圆锥model,输入
from tvtk.api import tvtk
s = tvtk.ConeSource(height=3.0,radius=1.0,resolution=36)
可以用s.height/s.radius/s.resolution(分辨率)查到高度,半径和分辨率的数据,如果要详细指导所有数据,可以用print(s)命令。
vtkConeSource (000001813DE1E0E0)
Debug: Off
Modified Time: 1903620
Reference Count: 2
Registered Events:
Registered Observers:
vtkObserver (000001813DFDC000)
Event: 33
EventName: ModifiedEvent
Command: 000001813DBFDD40
Priority: 0
Tag: 1
Executive: 000001813D839090
ErrorCode: No error
Information: 000001813D864120
AbortExecute: Off
Progress: 0
Progress Text: (None)
Resolution: 36
Height: 3
Radius: 1
Capping: On
Center: (0, 0, 0)
Direction: (1, 0, 0)
Output Points Precision: 0
2.3显示一个基本三维对象
2.3.1如何利用tvtk绘制三维图形
tvtk使用管线(pipeline)绘制三维图形,其中一下函数
CubeSource(xxx)
PolyDataMapper(xxx)
Actor(xxx)
Renderer(xxx)
RenderWindow(xxx)
RenderWindowInteracotor(xxx)
协作完成管线任务
2.3.2实现一个三维长方体代码
代码例1
from tvtk.api import tvtk
s = tvtk.CubeSource(x_length=1.0,y_length=2.0,z_length=3.0)
m = tvtk.PolyDataMapper(input_connection = s.output_port)
a = tvtk.Actor(mapper=m)
r = tvtk.Renderer(background=(0,0,0))
r.add_actor(a)
w = tvtk.RenderWindow(size=(300,300))
w.add_renderer(r)
i = tvtk.RenderWindowInteractor(render_window = w)
i.initialize()
i.start()
2.4TVTK管线与数据加载
- TVTK管线分两部分:数据预处理和图形可视化
- 数据预处理以s.output_port和m.input_connection形式输出
- 管线的两种类型:可视化管线(将原始数据加工成图形数据),图形管线(图形数据加工成图像)
- 可视化管线分两个对象:PolyData(计算输出一组长方形数据)和PolyDataMapper(通过映射器映射为图形数据)
|
TVTK对象 |
说明 |
|
Actor |
场景中一个实体,描述实体位置,方向,大小的属性 |
|
Renderer |
渲染作用,包括多个Actor |
|
RenderWindow |
渲染用的图形窗口,包括一个或多个Render |
|
RenderWindowInteractor |
交互功能,评议,旋转,放大缩小,不改变Actor或数据属性,只调整场景中照相机位置 |
- 管线的数据可以表示如下:

- 总结下TVTK管线就分为以下几个部分:数据预处理,数据映射,图形绘制,图形显示与交互
- 建立长方形模型:
2.4.1IVTK观察管线
代码例2
from tvtk.api import tvtk from tvtk.tools import ivtk from pyface.api import GUI s = tvtk.CubeSource(x_length=1.0,y_length=2.0,z_length=3.0) m = tvtk.Actor(mapper=m) gui = GUI() win = ivtk.IVTKWithCrustAndBrowser() win.open() True win.scene.add_actor(a) gui.start_event_loop()
显示结果:
有会出现bug,在主窗口缩放时左侧串口处于游离状态。
Debug程序:
from tvtk.api import tvtk from tvtk.tools import ivtk from pyface.api import GUI s = tvtk.CubeSource(x_length=1.0,y_length=2.0,z_length=3.0) m = tvtk.PolyDataMapper(input_connection=s.output_port) a = tvtk.Actor(mapper=m) gui = GUI() win = ivtk.IVTKWithCrustAndBrowser() win.open() win.scene.add_actor(a) dialog = win.control.centralWidget().widget(0).widget(0) from pyface.qt import QtCore dialog.setWindowFlags(QtCore.Qt.WindowFlags(0x00000000)) dialog.show() gui.start_event_loop()
Debug后第窗口界面,注意左侧的菜单栏,有分级
Model 建立后,可以在命令框输入代码,获取数据,比如:
输入print(scene.renderer.actors[0].mapper.input.points.to_array),可以得到长方体各个顶点的坐标。
如果要集成开发,可以将函数单独封装,放到python.exe目录下,比如上一个生成长方体的代码可以封装成以下两部分:
主函数
from tvtk.api import tvtk from tvtkfunc import ivtk_scene,event_loop s = tvtk.CubeSource(x_length=1.0,y_length=2.0,z_length=3.0) m = tvtk.PolyDataMapper(input_connection=s.output_port) a = tvtk.Actor(mapper=m) win = ivtk_scene(a) win.scene.isometric_view() event_loop()
调用函数
def ivtk_scene(actors): from tvtk.tools import ivtk # 创建一个带Crust(Python Shell)的窗口 win = ivtk.IVTKWithCrustAndBrowser() win.open() win.scene.add_actor(actors) # 修正窗口错误 dialog = win.control.centralWidget().widget(0).widget(0) from pyface.qt import QtCore dialog.setWindowFlags(QtCore.Qt.WindowFlags(0x00000000)) dialog.show() return win def event_loop(): from pyface.api import GUI gui = GUI() gui.start_event_loop()
2.4.1Tvtk数据集(TVTK数据加载例1)
Tvtk中有5中数据集:
- ImageData表示二维/三维图像的数据结构,有三个参数,spacing,origin,dimensions
from tvtk.api import tvtk img = tvtk.ImageData(spacing=(1,1,1),origin=(1,2,3),dimensions=(3,4,5)) img.get_point(0) #attain the data of first point (1.0, 2.0, 3.0) for n in range(6): ... print("%1.f,%1.f,%1.f"%img.get_point(n))
最后得到结果
1,2,3
2,2,3
3,2,3
1,3,3
2,3,3
3,3,3
- RectilinearGrid 表示创建间距不均匀的网格,所有点都在正交的网格上通过如下代码构建数据集:
r.y_coordinates = y r.z_coordinates = z r.dimensions = len(x),len(y),len(z) r.x_coordinates = x r.y_coordinates = y r.z_coordinates = z r.dimensions = len(x),len(y),len(z) for n in range(6): ... print(r.get_point(n))
得到数据结果,在轴上数据递增:
(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
(3.0, 0.0, 0.0)
(9.0, 0.0, 0.0)
(15.0, 0.0, 0.0)
(0.0, 1.0, 0.0)
(3.0, 1.0, 0.0)
- StructuredGrid 表示创建任意形状网格,需要指定点的坐标
- PolyData 表示由一系列的点、点之间的联系以及由点构成的多边形组成
- UnstructuredGrid 无组织网格
|
TVTK数据集 |
特点 |
|
Imagedata |
正交等间距 |
|
RectilinearGrid |
正交不等间距 |
|
StructuredGrid |
任意形状网格 |
|
PolyData |
点和点之间的联系 |
|
UnstructuredGrid |
无组织点 |
2.4.3Tvtk读取stl文件
STL文件调用形式:
S = tvtk.STLReader(file_name = “stl文件名”)
文件调用形式
vtkOBJReader()
ply文件调用形式
vtkPLYReader()
调用外部数据
VtkMultiBlockPLOT3DReander()
from tvtk.api import tvtk from tvtkfunc import ivtk_scene,event_loop s = tvtk.STLReader(file_name = 'python.stl') m = tvtk.PolyDataMapper(input_connection = s.output_port) a = tvtk.Actor(mapper=m) win = ivtk_scene(a) win.scene.isometric_view() event_loop()

Stl格式数据,可以在python三维可视化中打开,也就是说solidworks中创建的stl文件也可以在python三维可视化中打开。
2.4.4Tvtk读取MultiBlock3D数据文件
3D文件读取用MultiBlock数据读取。
网格(XYZ文件),空气动力学结果(Q文件),通用结果文件
源码:但是执行失败,错误类型是tvtk没有定义,或者plot3d没有定义
1. from tvtk.api import tvtk 2. 3. def read_data():# 读入数据 4. plot3d = tvtk.MultiBlockPLOT3DReader( 5. xyz_file_name="combxyz.bin",#网格文件 6. q_file_name="combq.bin",#空气动力学结果文件 7. scalar_function_number=100,#设置标量数据数量 8. vector_function_number=200#设置矢量数据数量 9. ) 10. plot3d.update() 11. return plot3d 12. 13. plot3d = read_data() 14. grid = plot3d.output.get_block(0)
3VTK可视化基础实战
介绍三类可视化方法:标量可视化,矢量可视化,轮廓化可视化
3.1可视化实例
3.1.1标量可视化
等值面:标量值相等的面
Generate_value() 设定N条等值线的值,一般用于重新绘制等值线
Set_value() 设定一条等值线的值,一般用于覆盖某条等值线或者新增加一条等值线
代码例2:绘制流体数据模型的标量场
from tvtk.api import tvtk from tvtkfunc import ivtk_scene,event_loop plot3d = tvtk.MultiBlockPLOT3DReader( ... xyz_file_name="combxyz.bin", ... q_file_name="combq.bin", ... scalar_function_number=100,vector_function_number=200) plot3d.update() grid=plot3d.output.get_block(0) con = tvtk.ContourFilter() con.set_input_data(grid) con.generate_values(20,grid.point_data.scalars.range) m = tvtk.PolyDataMapper(scalar_range=grid.point_data.scalars.range,input_connection=con.output_port) a = tvtk.Actor(mapper=m) a.property.opacity=0.5 win = ivtk_scene(a) #以下3行为交互代码 win.scene.isometric_view() event_loop()
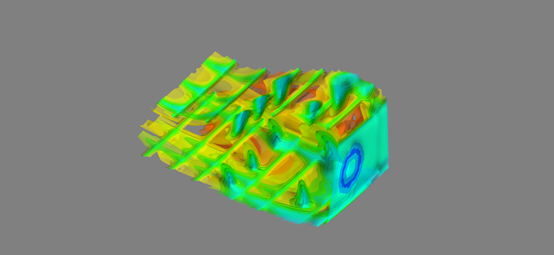
Generate_values(x,y)两个参数意义:x代表指定轮廓数,y代表数据范围
同样set_values(x,y)中也有同样的两个参数,含义相同,改变这两个参数会改变轮廓数和数据范围
3.1.2矢量可视化
Tvtk.Glyph3D() 符号化技术,可以解决矢量数据可视化问题。
Tvtk.MaskPoints() 降采样
箭头表示标量大小,箭头方向表示矢量方向。
代码例3 矢量化向量
from tvtk.api import tvtk from tvtkfunc import ivtk_scene,event_loop plot3d = tvtk.MultiBlockPLOT3DReader( ... xyz_file_name = "combxyz.bin", ... q_file_name = "combq.bin", ... scalar_function_number = 100,vector_function_number = 200) plot3d.update() grid = plot3d.output.get_block(0) mask = tvtk.MaskPoints(random_mode=True,on_ratio=50) mask.set_input_data(grid) glyph_source = tvtk.ConeSource() glyph = tvtk.Glyph3D(input_connection=mask.output_port,scale_factor=4) glyph.set_source_connection(glyph_source.output_port) m = vtk.PolyDataMapper(scalar_range=grid.point_data.scalars.range,input_connection=glyph.output_port) a = tvtk.Actor(mapper = m) win = ivtk_scene(a) win.scene.isometric_view() event_loop()
得到结果:
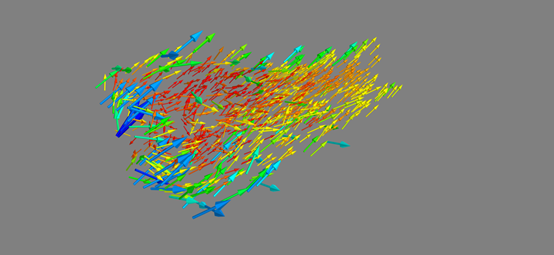
- vtk.Glyph3D() 符号化技术
为了表示矢量数据,TVTK库中运用tvtk.Glyph3D()方法,同时运用MaskPoints()方法进行降维采样。
3.1.3空间轮廓线可视化
需要用到tvtk.StructuredGridOutlineFilter()
Python清空命令行代码函数:
Import os def clear(): os.system(‘cls’) clear()
代码例4
from tvtk.api import tvtk from tvtk.common import configure_input from tvtkfunc import ivtk_scene, event_loop plot3d = tvtk.MultiBlockPLOT3DReader( xyz_file_name="combxyz.bin", q_file_name="combq.bin", scalar_function_number=100, vector_function_number=200 )#读入Plot3D数据 plot3d.update()#让plot3D计算其输出数据 grid = plot3d.output.get_block(0)#获取读入的数据集对象 outline = tvtk.StructuredGridOutlineFilter()#计算表示外边框的PolyData对象 configure_input(outline, grid)#调用tvtk.common.configure_input() m = tvtk.PolyDataMapper(input_connection=outline.output_port) a = tvtk.Actor(mapper=m) a.property.color = 0.3, 0.3, 0.3 #窗口绘制 win = ivtk_scene(a) win.scene.isometric_view() event_loop()
显示结果
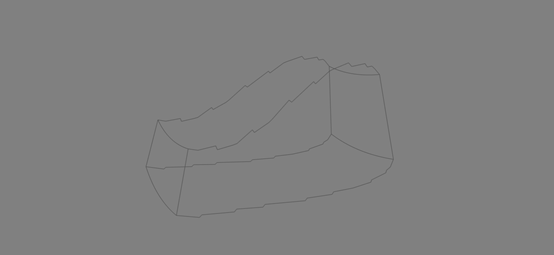
- PolyData对象的外边框处理使用了什么方法?
PolyData对象外边框使用了StructuredGridOutlineFilter()的方法。
3.1.4结合矢量可视化和空间轮廓线可视化
对标量/轮廓属性进行赋值,不会处理。
from tvtk.api import tvtk from tvtk.common import configure_input from tvtkfunc import ivtk_scene, event_loop plot3d = tvtk.MultiBlockPLOT3DReader( ... xyz_file_name = "combxyz.bin", ... q_file_name = "combq.bin", ... scalar_function_number = 100,vector_function_number = 200) plot3d.update() grid = plot3d.output.get_block(0) con = tvtk.ContourFilter() con.set_input_data(grid) con.generate_values(20,grid.point_data.scalars.range) #20代表等值面 outline = tvtk.StructuredGridOutlineFilter()#计算表示外边框的PolyData对象 configure_input(outline, grid)#调用tvtk.common.configure_input() m = tvtk.PolyDataMapper(scalar_range=grid.point_data.scalars.range,input_connection=con.output_port) m = tvtk.PolyDataMapper(input_connection=outline.output_port) a = tvtk.Actor(mapper=m) a.property.color = 0.3, 0.3, 0.3 a.property.opacity=0.5 win = ivtk_scene(a) #以下3行为交互代码 win.scene.isometric_view() event_loop()
3.2TVTK库实战练习
- 练习1:用tvtk绘制一个圆锥,圆锥的数据源对象为ConeSource(),圆锥高度为6.0,圆锥半径为2.0,背景色为红色。
代码例5
from tvtk.api import tvtk from tvtk.tools import ivtk from pyface.api import GUI s = tvtk.ConeSource(height=6.0,radius=1.0,resolution=36) m = tvtk.PolyDataMapper(input_connection=s.output_port) a = tvtk.Actor(mapper=m) gui = GUI() win = ivtk.IVTKWithCrustAndBrowser() win.open() win.scene.add_actor(a) dialog=win.control.centralWidget().widget(0).widget(0) from pyface.qt import QtCore dialog.setWindowFlags(QtCore.Qt.WindowFlags(0x00000000)) dialog.show() gui.start_event_loop()

代码例6
from tvtk.api import tvtk s = tvtk.ConeSource(height=6.0,radius=2.0,resolution=36) m = tvtk.PolyDataMapper(input_connection=s.output_port) a = tvtk.Actor(mapper=m) r = tvtk.Renderer(background=(1,0,0)) r.add_actor(a) w = tvtk.RenderWindow(size=(300,300)) w.add_renderer(r) i = tvtk.RenderWindowInteractor(render_window=w) i.initialize() i.start()

- 练习2:使用tvtk库读取obj,并显示出来。
from tvtk.api import tvtk from tvtkfunc import ivtk_scene,event_loop s = tvtk.OBJReader(file_name = 'python.obj') m = tvtk.PolyDataMapper(input_connection = s.output_port) a = tvtk.Actor(mapper=m) win = ivtk_scene(a) win.scene.isometric_view() event_loop()
- x.obj文件应该放在anaconda(python)安装目录下。
- Stl和obj模型包括哪些信息?
Stl全称是stereolithograph,模型包括三角面片数,每个三角面片的几何信息(法矢,三个顶点的坐标),三角面片属性。
Obj是3D模型文件模式,模型包括顶点数据,自由形态曲线/表面属性,元素,自由形态曲线/表面主题陈述,自由形态表面之间的连接,成组,显示/渲染属性。
- 练习3:通过get_value()和set_value()设定第一个等值面的值为原来的2倍
3.3Mayavi库入门
|
类别 |
说明 |
|
绘图函数 |
Barchar, contour3d, contour_surf, flow, imshow, mesh, plot3d, points3d, quiver3d, surf, triangular, mesh |
|
图形控制函数 |
Clf, close, draw, figure, fcf, savefig, screenshot, sync_camera |
|
图形修饰函数 |
Colorbar, scalarbar, xlabel, ylabel, zlabel |
|
相机控制函数 |
Move, pitch, roll, view, set_engine |
|
其他函数 |
Animate, axes, get_engine, show, set_engine |
|
Mlat管线控制 |
Open, set_tvk_src,adddataset, scalar_cut_plane |
Mayavi API
|
类别 |
说明 |
|
管线基础对象 |
Scene, source, filter, modulemanager, module, pipelinebase, engine |
|
主视窗和UI对象 |
DecoratedScene, mayaviscene, sceneeditor, mlabscenemodel, engineview, enginerichview |
3.3.1快速绘图实例
代码例7
#定义10个点的三维坐标,建立简单立方体
x = [[-1,1,1,-1,-1],[-1,1,1,-1,-1]] y = [[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1],[1,1,1,1,1]] z = [[1,1,-1,-1,1],[1,1,-1,-1,1]] from mayavi import mlab s = mlab.mesh(x,y,z)
代码例8
#建立复杂几何体
From numpy import pi,sin,cos,mgrid from mayavi import mlab dphi,dtheta = pi/250.0, pi/250.0 [phi,theta] = mgrid[0:pi+dphi*1.5:dphi,0:2*pi+dtheta*1.5:dtheta] m0 = 4; m1 =3; m2 =2; m3 = 3; m4 = 6; m5= 2; m6 = 6; m7 = 4 r = sin(m0*phi)**m1 + cos(m2*phi)**m3 + sin(m4*theta)**m5 + cos(m6*theta)**m7 x = r*sin(phi)*cos(theta) y = r*cos(phi) z = r*sin(phi)*sin(theta) s = mlab.mesh(x,y,z) mlab.show()
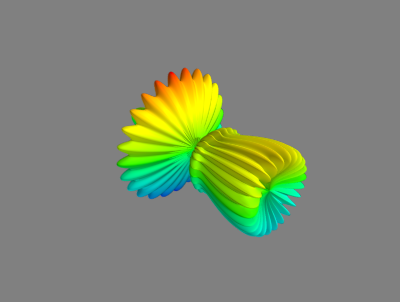
Mesh函数是三个二维的参数,点之间的连接关系,尤其由x,y,z之间的位置关系所决定。
上面这个例子如果改变代码行为mlab.mesh(x,y,z,representation="wireframe",line_width=1.0)
则结果为

3.3.2Mayavi管线(分析mayavi如何控制画面)
Mayavi管线的层级
- Engine:建立和销毁Scenes
- Scenes:多个数据集合Sources
- Filters:对数据进行变换
- Modules Manager:控制颜色,Colors and Legends
- Modules:最终数据的表示,如线条、平面等
程序配置属性的步骤:
- 获得场景对象,mlab.gcf()
- 通过children属性,在管线中找到需要修改的对象
配置窗口有多个选项卡,属性需要一级一级获得
s = mlab.gcf #获得s对象当前场景 print(s) #输出当前对象状态 print(s.scene.background) #输出当前设置的场景的背景色 source = s.children[0] #获取对象 print(repr(source)) #输出mlab儿子数组对象的第一个值地址 print(source.name) #返回该节点名称 print(repr(source.data.points)) #输出该节点坐标 print(repr(source.data.point_data.scalars)) manager = source.children[0] #数据源法向量 print(manager) #通过程序更改物体颜色和对应颜色值 colors = manager.children[0] colors.scalar_lut_manager.show_legend = True surface = colors.children[0] #获取颜色的第一个子节点。Surface可以设置图形的显示方式 surface.actor.property.representation = “wireframe” surface.actor.property.opacity = 0.6 #透明度设置为0.6
mayavi与tvtk处理三维可视化的异同点:tvtk处理三维可视化要通过映射,预处理步骤,而mayavi在获取数据,可以通过mlab.mesh(x,y,z)生成三维可视化图形。
3.4Mayavi库入门
3.4.1基于numpy数组的绘图函数
- Mlab对numpy建立可视化过程:
- 建立数据源
- 使用filter(可选)
- 添加可视化模块
3D绘图函数-Points3d()
- 函数形式:
Points3d(x,y,z,…) points3d(x,y,z,s,...) points3d(x,y,z,f,…)
X,y,z便是numpy数组、列表或者其他形式的点三维坐标
s表示在该坐标点处的标量值
F表示通过函数f(x,y,z)返回的标量值
代码例9
t = np.linspace(0, 4 * np.pi, 20) x = np.sin(2 * t) y = np.cos(t) z = np.cos(2 * t) s = 2 + np.sin(t) points = mlab.points3d(x,y,z,s,colormap='Reds',scale_factor=.25)

|
参数 |
说明 |
|
Color |
VTK对象的颜色,定义为(0,1)的三元组 |
|
Colormap |
Colormap的类型,例如Reds、Blues、Copper等 |
|
Extent |
x,y,z数组范围[xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax,zmin,zmax] |
|
Figure |
画图 |
|
Line_width |
线的宽度,该值为float,默认为0.2 |
|
Mask_points |
减小/降低大规模点数据集的数量 |
|
Mode |
符号的模式,例如2darrow、2dcircle、arrow、cone等 |
|
Name |
VTK对象名字 |
|
Opcity |
VTK对象的整体透明度,改值为float型,默认为1.0 |
|
Reset_zoom |
对新加入场景数据的缩放进行重置。默认为True |
|
Resolution |
符号的分辨率,如球体的细分数,该值为整型,默认为8 |
|
Scale_factor |
符号放缩的比例 |
|
Scale_mode |
符号的放缩模式,如vector、scalar、none |
|
Transparent |
根据标量值确定actor的透明度 |
|
Vmax |
对colormap放缩的最大值 |
|
Vmin |
对colormap放缩的最小值 |
- 3D绘图函数-Plot3d()
函数形式:
Plot3d(x,y,z…) plot3d(x,y,z,s,…)
X,y,z表示numpy数组,或列表。给出了线上连续的点的位置。S表示在该坐标点处的标量值
|
参数 |
说明 |
|
Tube_radius |
线管的半径,用于描述线的粗细 |
|
Tube_sides |
表示线的分段数,该值为整数,默认为6 |
X,y,z表示numpy数组,给出了线上连续的点的位置。
Np.sin(mu)表示在该坐标点处的标量值
Tube_radius绘制线的半径为0.025
Colormap采用Spectral颜色模式
代码例10
import numpy as np from mayavi import mlab n_mer, n_long = 6,11 dphi = np.pi / 1000.0 phi = np.arange(0.0, 2 * np.pi + 0.5 * dphi, dphi) mu = phi * n_mer x = np.cos(mu) * (1 + np.cos(n_long * mu / n_mer) * 0.5) y = np.sin(mu) * (1 + np.cos(n_long * mu / n_mer) * 0.5) z = np.sin(n_long * mu /n_mer) * 0.5 l = mlab.plot3d(x,y,z,np.sin(mu),tube_radius=0.025,colormap="Spectral")
X,y,z便是numpy数组,给出了线上连续的点的位置。
Np.sin(mu)表示在该坐标点处的标量值
Tube_radius绘制线的半径为0.025
Colormap采用Spectral颜色模式
- 3D绘图函数-2D数据
Imshow()-3D绘图函数
Interpolate 图像中的像素是否被插值,该值为布尔型,默认为True
代码例11
import numpy from mayavi import mlab s = numpy.random.random((10,10)) img = mlab.imshow(s,colormap='gist_earth') mlb.show()
3D绘图函数 - surf()
函数形式:
Surf(s,...)
Surf(x,y,s…)
Surf(x,y,f,..)
S是一个高程矩阵,用二维数组表示
代码例12
import numpy as np from mayavi improt mlab from mayavi import mlab def f(x,y): return np.sin(x - y) + np.cos(x + y) x, y = np.mgrid[-7.:7.05:0.1,-5.:5.05:0.05] s = mlab.surf(x,y,f) mlab.show()
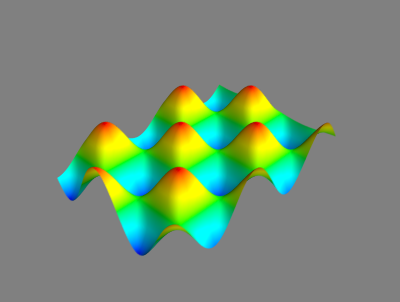
3D绘制函数 - contour_surf(),与surf()类似求解曲面,contour_surf求解等值线
代码例13
import numpy as np from mayavi import mlab def f(x,y): return np.sin(x - y) + np.cos(x + y) x,y = np.mgrid[-7.:7.05:0.1,-5.:5.05:0.05] con_s = mlab.contour_surf(x,y,f)
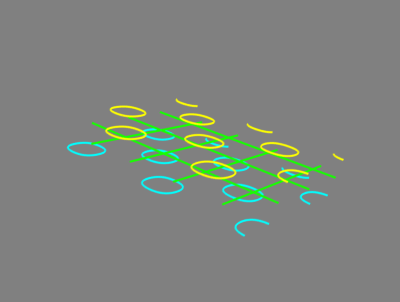
3D绘图函数 - contour3d()
函数形式:
Contour3D(scalars…)
Contour3d(x,y,z,scalar,..)
Scalars 网络上的数据,用三维numpy数组shuming,x,y,z代表三维空间坐标
|
参数 |
说明 |
|
Contours |
定义等值面的数量 |
代码例14
import numpy from mayavi import mlab x,y,z = numpy.ogrid[-5:5:64j,-5:5:64j,-5:5:64j] scalars = x * x + y * y + z * z obj = mlab.contour3d(scalars, contours=8,transparent=True)
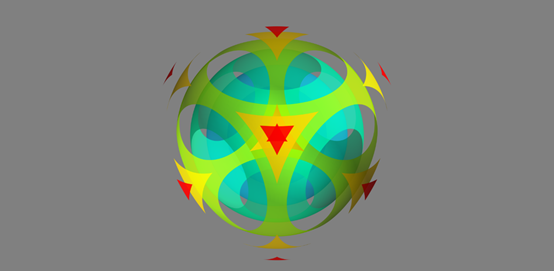
3D绘图函数 – quiver3d()
函数形式:
quiver3d(u,v,w…)
quiver3d(x,y,z,u,v,w…)
quiver3d(x,y,z,f,…)
u,v,w用numpy数组表示的向量
x,y,z表示箭头的位置,u,v,w矢量元素
f需要返回咋给定位置(x,y,z)的(u,v,w)矢量
代码例15
r = np.sqrt(x ** 2 + y ** 2 + z ** 4) u = y * np.sin(r) / (r + 0.001) v = -x * np.sin(r)/ (r + 0.001) w = np.zeros_like(z) obj = mlab.quiver3d(x,y,z,u,v,w,line_width=3,scale_factor=1)
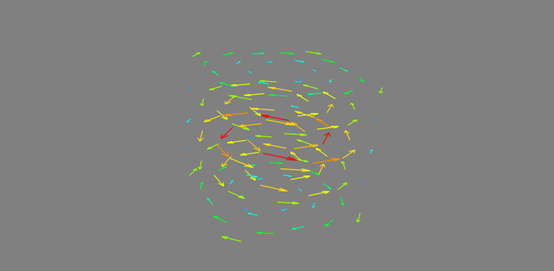
Questions:
- points3D和Plot3D两个函数之间的区别于联系是什么?
- Imshow()方法是如何确定二维数组可视化图像颜色的?
- Surf()方法实例中通过什么方法获取x,y二维数组的?
- Mlab中可以进行矢量数据可视化的方法有哪些?
Corresponding answers:
- Points3D是基于Numpy数组x,y,z提供的数据点坐标,绘制图形;Plot3D是基于1维numpy数组x,y,z供的三维坐标数据绘制图形;
- Imshow()通过colormap关键字确定颜色,比如colormap='gist_earth',确定颜色为“类似地球表面颜色”;
- Surf()方法是通过np.mgrid(xxx,xxx)获取x,y二维数组;
- mlab.Flow()和mlab.quiver3d()
3.4.2改变物体的外观
- 改变颜色
代码例16
Colormap定义的颜色,也叫LUT即look up table.
import numpy as np from mayavi import mlab x,y = np.mgrid[-10:10:200j,-10:10:200j] z = 100 * np.sin(x * y) / (x * y) mlab.figure(bgcolor=(1,1,1)) <mayavi.core.scene.Scene object at 0x00000214003D6678> surf = mlab.surf(z,colormap='cool') mlab.show()

代码例17
当代码例16增加以下代码到代码例17时,图像的颜色变淡,透明度增加。
import numpy as np from mayavi import mlab #建立数据 x,y = np.mgrid[-10:10:200j,-10:10:200j] z = 100 * np.sin(x * y) / (x * y) #对数据进行可视化 mlab.figure(bgcolor=(1,1,1)) <mayavi.core.scene.Scene object at 0x00000214003D6678> surf = mlab.surf(z,colormap='cool') mlab.show() #访问surf对象的LUT #LUT是一个255x4的数组,列向量表示RGBA,每个值的范围从0-255 lut = surf.module_manager.scalar_lut_manager.lut.table.to_array() #增加透明度,修改alpha通道 lut[:,-1] = np.linspace(0,255,256) surf.module_manager.scalar_lut_manager.lut.table = lut #更新视图,并显示图像 mlab.show()
3.4.3Mlab控制函数
图像控制函数:
|
函数图像 |
说明 |
|
Clf |
清空当前图像mlab.clf(figure=None) |
|
close |
关闭图形窗口 mlab.close(scene=None, all=False) |
|
Draw |
重新绘制当前图像mlab.close(figure=None) |
|
Figure |
建立一个新的scene或者访问一个存在的scene mlab.figure(figure=None,bgcolor=None,fgcolor=None,engine=None,size=(400,350)) |
|
Gcf |
返回当前图像的handle mlab.gcf(figure=None) |
|
Savefig |
存储当前的前景,输出为一个文件,如png,jpg,bmp,tiff,pdf,obj,vrml等 |
图像装饰函数
|
函数图像 |
说明 |
|
Cololorbar |
为对象的颜色映射增加颜色条 |
|
Scalarbar |
为对象的标量颜色映射增加颜色条 |
|
Vectorbar |
为对象的矢量颜色映射增加颜色条 |
|
xlabel |
建立坐标轴,并添加x轴的标签mlab.xlabel(text,object=None) |
|
Ylabel |
建立坐标轴,并添加y轴的标签 |
|
zlabel |
建立坐标轴,并添加z轴的标签 |
相机控制函数
|
函数图像 |
说明 |
|
Move |
移动相机和焦点 Mlab.move(forward=None,right=None,up=None) |
|
Pitch |
沿着“向右”轴旋转角度mlab.pitch(degrees) |
|
View |
设置/获取当前视图中相机的视点 Mlab.view(azimuth=None,elevation=None,distance=None,focalpoint=None,roll=None Reset_roll=True,figure=None |
|
Yaw |
沿着“向上”轴旋转一定角度,mlab.yaw(degrees) |
其他控制函数
|
函数图像 |
说明 |
|
animate |
动画控制函数mlab.animate(func=None,delay=500,ui=True) |
|
Axes |
为当前物体设置坐标轴mlab.axes(*args,**kwargs) |
|
Outline |
为当前物体建立外轮廓mlab.outline(*args,**kwargs) |
|
Show |
与当前图像开始交互mlab.show(func=None,stop=False) |
|
Show_pipeline |
显示mayavi的管线对话框,可以进行场景属性的设置和编辑 |
|
Text |
为图像添加文本mlab.text(*args,**kwargs) |
|
Title |
为绘制图像建立标题mlab.title(*args,**kwargs) |
3.4.4鼠标选取交互操作
On_mouse_pick(callback,type=”point”,Button=”left”,Remove=False)提供鼠标响应操作
Type:”point”,”cell” or “world”
Button:”Left”,”Middle” or “Right”
Remove:如果值为True,则callback函数不起作用
返回:一个vtk picker对象
代码例18
程序框架:
#场景初始化 figure = mlab.gcf() #用mlab.points3d建立红色和白色小球的集合 # … … #处理选取事件 def picker_callback(picker) #建立响应机制 Picker = figure.on_mouse_pick(picker_callback) mlab.show() import numpy as np from mayavi import mlab figure = mlab.gcf() x1, y1, z1 = np.random.random((3, 10)) red_glyphs = mlab.points3d(x1, y1, z1, color=(1, 0, 0), resolution=10) x2, y2, z2 = np.random.random((3, 10)) white_glyphs = mlab.points3d(x2, y2, z2, color=(0.9, 0.9, 0.9), resolution=10) outline = mlab.outline(line_width=3) outline.outline_mode = 'cornered' outline.bounds = (x1[0] - 0.1, x1[0] + 0.1, y1[0] - 0.1, y1[0] + 0.1, z1[0] - 0.1, z1[0] + 0.1) glyph_points = red_glyphs.glyph.glyph_source.glyph_source.output.points.to_array() def picker_callback(picker): if picker.actor in red_glyphs.actor.actors: point_id = int(picker.point_id / glyph_points.shape[0]) if point_id != -1: x, y, z = x1[point_id], y1[point_id], z1[point_id] outline.bounds = (x - 0.1, x + 0.1, y - 0.1, y + 0.1, z - 0.1, z + 0.1) picker = figure.on_mouse_pick(picker_callback) mlab.title('Click on red balls') mlab.show()
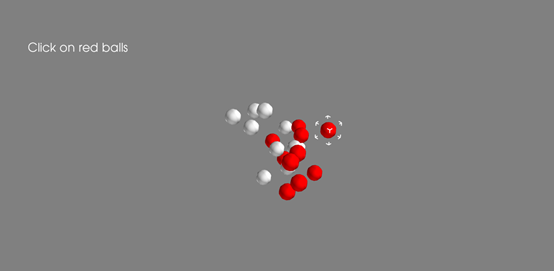
简述选取红色小球问题分析实例程序的基本框架和搭建流程。
1.绘制初始状态选取框时,为什么数组下标为0?
2.实例中是如何计算被获取的红色小球的位置坐标的?
3.实例程序优化中是如何解决小球初始化速度太慢的问题的
Answers:
基本框架:初始化场景-建立小球模型-处理响应事件(建立立方体套框模型)-建立响应机制(把框套到球上)
1. 绘制初始状态选取框时,希望放在第一个球上
2. 同过一下代码:
glyph_points = red_glyphs.glyph.glyph_source.glyph_source.output.points.to_array()
3. Before drawing the object add the code of figure.scene.disable_render = True, and after drawing the object add the code of figure.scene.disable_render = False
In the phase of creating response mechanism, add the code of Picker.tolerance = 0.01 after picker = xxx
3.4.5Mlab控制函数(23 module函数)
Mlab管线控制函数的调用
Sources: 数据源
Filters: 用来数据变换
Modules: 用来实现可视化
mlab.pipeline.function()
Sources
|
Grid_source |
建立而为网络数据 |
|
Line_source |
建立线数据 |
|
Open |
打开一个数据文件 |
|
scalar_field |
建立标量场数据 |
|
Vector_field |
建立矢量场数据 |
|
Volume_field |
建立提数据 |
Filters
|
Filters |
说明 |
|
Contour |
对输入数据集计算等值面 |
|
Cut_plane |
对数据进行切面计算,可以交互的更改和移动切面 |
|
delaunay2D |
执行二维delaunay三角化 |
|
Delaunay3D |
执行三维delaunay三角化 |
|
Extract_grid |
允许用户选择structured grid的一部分数据 |
|
Extract_vector_norm |
计算数据矢量的法向量,特别用于计算矢量数据的梯度时 |
|
Mask_points |
对输入数据进行采样 |
|
Threshold |
去一定阈值范围内的数据 |
|
Transform_data |
对输入数据执行线性变换 |
|
Tube |
将线转成管线 |
Modules
|
Axes |
绘制坐轴 |
|
Glyph |
对输入点绘制不同类型的符号,符号的颜色和方向有该点的标量和向量数据决定 |
|
Glyph |
对输入点绘制不同类型的符号,符号的类型和方向由该点的标量和矢量数据决定 |
|
iso_surface |
对输入数据绘制等值面 |
|
Outline |
对输入数据绘制外轮廓 |
|
Scalar_cut_plane |
对输入的标量数据绘制特定位置的切平面 |
|
Streamline |
对输入矢量数据绘制流线 |
|
Surface |
对数据(KTV dataset, mayavi sources)建立外表面 |
|
Text |
绘制一段文本 |
|
Vector_cut_plane |
对输入的矢量数据绘制特定位置的切平面 |
|
Volume |
表示对标量场数据进行体绘制 |
Question: 如果需要对静电场中的等势面进行可视化,需要使用什么控制函数对输入数据进行计算?
Answer: Modules.streamline()
3.4.6标量数据可视化
生成标量数据
import numpy as np x,y,z = np.ogrid[-10:10:20j, -10:10:20j, -10:10:20j] s = np.sin(x*y*z)/(x*y*z) from mayavi import mlab mlab.contour3d(s)
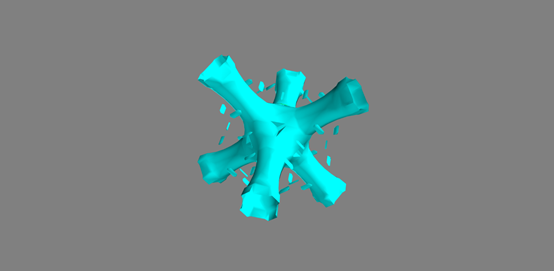
切平面
mlab.pipeline.scalar_field(s) #设定标量数据场
plane_orientation = “x_axes” #设定切平面的方向
index.slice(10) #每10个点用1个点显示
from mayavi import mlab from mayavi.tools import pipeline mlab.pipeline.image_plane_widget(mlab.pipeline.scalar_field(s), plane_orientation = "x_axes", slice_index = 10 ) mlab.pipeline.image_plane_widget(mlab.pipeline.scalar_field(s), plane_orientation="y_axes", slice_index = 10, ) mlab.outline()
对物体设置透明度,再做切割
from mayavi import mlab from mayavi.tools import pipeline src = mlab.pipeline.scalar_field(s) mlab.pipeline.iso_surface(src,contours=[s.min()+0.1*s.ptp(),],opacity=0.1) mlab.pipeline.iso_surface(src,contours=[s.max()-0.1*s.ptp(),]) mlab.pipeline.image_plane_widget(src, plane_orientation="z_axes", slice_index=10, ) mlab.show()

Disagreemet:
Question:
1. 1.Mlab中什么控制函数进行切平面绘制?有什么特点?
2. 2.实例中,可视化使用了什么方法绘制特定平面的特平面?
Answers:
1. 1.使用mlab.pipeline.image_plane_widget对切平面绘制,特点是切平面可以任意移动和旋转
2. 2.使用mlab.pipeline.scalar_cut_plane绘制特定平面的切平面
3.4.7矢量数据可视化
import numpy as np #构建3维坐标 x,y,z = np.mgrid[0:1:20j,0:1:20j,0:1:20j] #定义三维点分布函数 u = np.sin(np.pi*x) * np.cos(np.pi*z) v = -2*np.sin(np.pi*y) * np.cos(2*np.pi*z) w = np.cos(np.pi*x)*np.sin(np.pi*z) + np.cos(np.pi*y)*np.sin(2*np.pi*z) #显示函数 from mayavi import mlab mlab.quiver3d(u,v,w) #框架 mlab.outline() mlab.show()
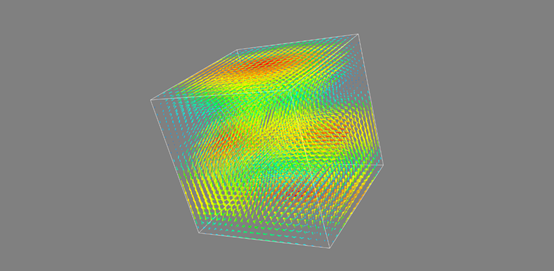
降采样
由于函数立方体分布过于密集,用Masking Vector采样中的mlab.pipeline.vectors(x,x,x)进行降采样
import numpy as np from mayavi.filters import mask_points x,y,z = np.mgrid[0:1:20j,0:1:20j,0:1:20j] u = np.sin(np.pi*x) * np.cos(np.pi*z) v = -2*np.sin(np.pi*y) * np.cos(2*np.pi*z) w = np.cos(np.pi*x)*np.sin(np.pi*z) + np.cos(np.pi*y)*np.sin(2*np.pi*z) from mayavi import mlab # mlab.quiver3d(u,v,w) # mlab.outline() # mlab.show() src = mlab.pipeline.vector_field(u,v,w) mlab.pipeline.vectors(src, mask_points=10, scale_factor=2.0) #放缩比例为2.0 mlab.show()

采用切面的方式:mlab.pipeline.vector_cut_plane(u,v,w)
级数的等值面
import numpy as np from mayavi.filters import mask_points x,y,z = np.mgrid[0:1:20j,0:1:20j,0:1:20j] u = np.sin(np.pi*x) * np.cos(np.pi*z) v = -2*np.sin(np.pi*y) * np.cos(2*np.pi*z) w = np.cos(np.pi*x)*np.sin(np.pi*z) + np.cos(np.pi*y)*np.sin(2*np.pi*z) from mayavi import mlab src = mlab.pipeline.vector_field(u,v,w) # mlab.pipeline.vector_cut_plane(src, mask_points=10, scale_factor=2.0) magnitude = mlab.pipeline.extract_vector_norm(src) mlab.pipeline.iso_surface(magnitude, contours=[2.0,0.5]) mlab.outline() mlab.show()
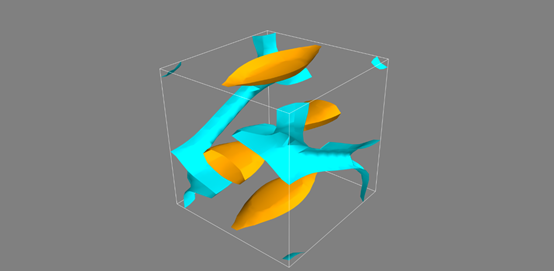
流线可视化
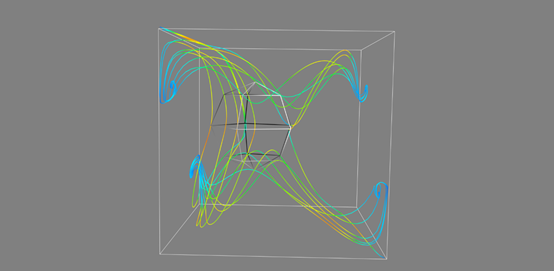
import numpy as np from mayavi.filters import mask_points x,y,z = np.mgrid[0:1:20j,0:1:20j,0:1:20j] u = np.sin(np.pi*x) * np.cos(np.pi*z) v = -2*np.sin(np.pi*y) * np.cos(2*np.pi*z) w = np.cos(np.pi*x)*np.sin(np.pi*z) + np.cos(np.pi*y)*np.sin(2*np.pi*z) from mayavi import mlab # mlab.quiver3d(u,v,w) # mlab.outline() # mlab.show() src = mlab.pipeline.vector_field(u,v,w) # mlab.pipeline.vector_cut_plane(src, mask_points=10, scale_factor=2.0) flow = mlab.flow(u,v,w,seed_scale=1, seed_resolution=5, integration_direction="both")
mlab.outline() mlab.show()
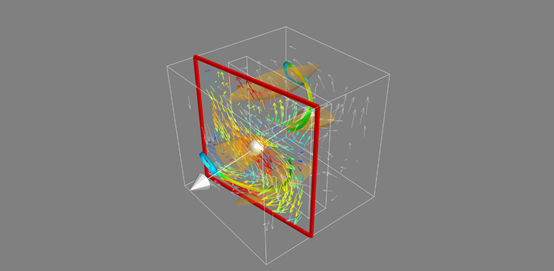
矢量场复合观测
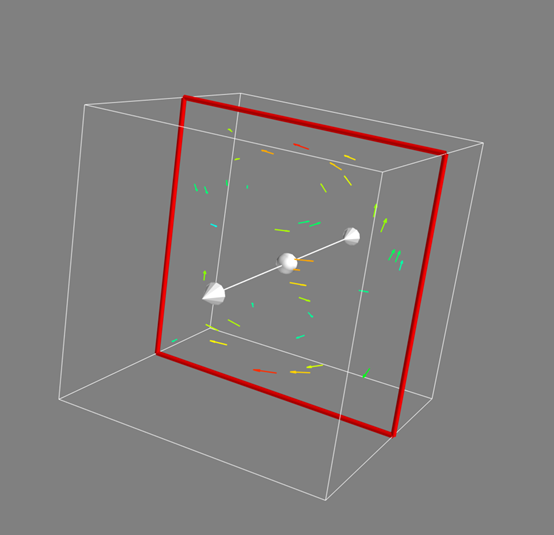
import numpy as np from mayavi.filters import mask_points from matplotlib.scale import scale_factory x,y,z = np.mgrid[0:1:20j,0:1:20j,0:1:20j] u = np.sin(np.pi*x) * np.cos(np.pi*z) v = -2*np.sin(np.pi*y) * np.cos(2*np.pi*z) w = np.cos(np.pi*x)*np.sin(np.pi*z) + np.cos(np.pi*y)*np.sin(2*np.pi*z) from mayavi import mlab # mlab.quiver3d(u,v,w) # mlab.outline() # mlab.show() src = mlab.pipeline.vector_field(u,v,w) magnitude = mlab.pipeline.extract_vector_norm(src) iso = mlab.pipeline.iso_surface(magnitude,contours=[2.0,],opacity=0.3) vec = mlab.pipeline.vectors(magnitude,mask_points=40, line_width=1, color=(0.8,0.8,0.8), scale_factor=4.) # mlab.pipeline.vector_cut_plane(src, mask_points=10, scale_factor=2.0) flow = mlab.pipeline.streamline( magnitude, seedtype="plane", seed_visible=False, seed_scale=0.5, seed_resolution=1, linetype="ribbon") vcp = mlab.pipeline.vector_cut_plane(magnitude, mask_points=2, scale_factor=4, colormap="jet", plane_orientation="x_axes") mlab.outline() mlab.show()
Ques:
1.标量数据和矢量数据分别使用什么方法进行绘制?
2. 2.矢量数据可视化实例中是如何对数据进行降采样的?
Answer:
1. 1.mlab.contour3d(x,y,z) and mlab.quiver3d(x,y,z)进行绘制
2. 2.Masking vector采样中的mlab.pipeline.vectors(src,mask_points=10,scale_factor=2.0)
4Mayavi三维可视化
4.1绘制数据dragon
程序框架:
- 打开文件
- 使用modules绘制数据的surface
- 显示可交互的结果
渲染dragon ply文件:
from mayavi import mlab import shutill #shutil可以中间删除显现的文件 mlab.pipeline.surface(mlab.pipeline.open(dragon_ply_file)) mlab.show()
代码例19

#coding=gbk from os.path import join from mayavi import mlab import tarfile #读取压缩文件内容 dragon_tar_file = tarfile.open("dragon.tar.gz") try: os.mkdir("dragon_data") except: pass #将所有读取到的数据放入同一个文件夹中 dragon_tar_file.extractall("dragon_data") dragon_tar_file.close() #加入数据到dragon_ply_file中 dragon_ply_file = join("dragon_data","dragon_recon","dragon_vri.ply") #渲染dragon.ply文件 mlab.pipeline.surface(mlab.pipeline.open(dragon_ply_file)) mlab.show() #删除中间过程文件夹 import shutil shutil.rmtree("dragon_data")

4.2绘制数据canyon
代码例20

#1_import packages import zipfile import numpy as np from mayavi import mlab # from pygame.examples.textinput import BGCOLOR # from mayavi.tools.filters import warp_scalar #2_hgt(Height File Format) hgt = zipfile.ZipFile("N36W113.hgt.zip").read("N36W113.hgt") # to certify a data type of integer,2X8=16 bit data data = np.fromstring(hgt,">i2") # to certify the type of data data.shape = (3601,3601) # to transform the type of data to 32bit data = data.astype(np.float32) # to increase the efficiency of showing, only choose sort of data data = data[500:1000,500:1000] #if there is any clearance in the source of data, set those to the minimum data[data == -32768] = data[data > 0].min() #3_use mlab.figure() to refresh the shape of the data and surf() to figure out the surface of the data #the size of window with (400,320), background, color of shining upon, enlargement and contraction scale, mlab.figure(size = (400,320),bgcolor=(0.16,0.28,0.46)) mlab.surf(data, colormap="gist_earth",warp_scale=0.2,vmin=1200,vmax=1610) #4_clear the RAM for decomposition del data #5_create a window of Visualization, angle of position, height, distance mlab.view(-5.9,83,570,[5.3,20,238]) mlab.show()
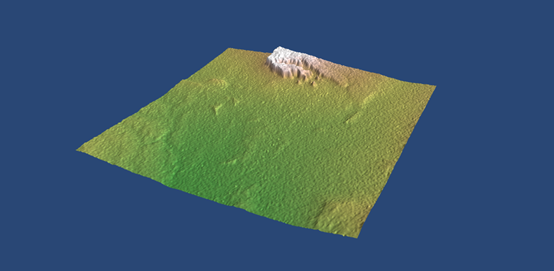
4.3绘制数据canyon
二维坐标如何转换成三维坐标?
x = R*cos(lat)*cos(lng); y = R*cos(lat)*sin(lng); z = R*sin(lat); 如果R = 1, 则 x = cos(lat)*cos(lng); y = cos(lat)*sin(lng); z = sin(lat); lng表示经度,lat表示维度
代码例21

#get data of several cities and get their longitude as well as latitude) from clyent import color cities_data = """ Bei Jing, 116.23,39.54 Shang Hai, 121.52, 30.91 Hong Kong,114.19,22.38 Delhi,77.21,28.67 Johannesburg,28.04,-26.19 Doha,51.53,25.29 Sao Paulo,-46.63,-23.53 Toronto,-79.38,43.65 New York,-73.94,40.67 San Francisco,-122.45,37.77 Dubai,55.33,25.27 Sydney,151.21,-33.87 """ # part2_create a list consisting of cities' indexes about their longtitudes and latitudes import csv #create a dict and a list cities = dict() coords = list() # print(cities,coords) # read data for line in list(csv.reader(cities_data.split(" ")))[1:-1]: name, long_, lat = line cities[name] = len(coords) coords.append((float(long_),float(lat))) # data transformation import numpy as np # from [1 line n row] to [n line, 1 list] coords = np.array(coords) # transform the angle to the arc lat, long = coords.T * np.pi / 180 # transform 2D data to 3D data # lat = ori_long # long = ori_lat x = np.cos(long) * np.cos(lat) y = np.cos(long) * np.sin(lat) z = np.sin(long) #create a window from mayavi import mlab mlab.figure(bgcolor=(0.48,0.48,0.48), size=(400,400)) # to define a sphere # set the opacity of the surface of earth to 0.7 sphere = mlab.points3d(0, 0, 0, scale_factor=2, color = (0.67, 0.77, 0.93), resolution = 50, opacity = 0.7, name = "Earth") # to adjust the parameter of mirror reflection sphere.actor.property.specular = 0.45 sphere.actor.property.specular_power = 5 # delete the opposite side to better show the effect of opacity sphere.actor.property.backface_culling = True # use points to describe sites of cities points = mlab.points3d(x, y, z, scale_mode = "none", scale_factor = 0.03, color = (0, 0, 1)) #create names of cities # for cities.items output the names of cities and the series of cities for city, index in cities.items(): #x,y,z mean x,y,z coordinates; color means text's color; width means text's width; name means text's object label = mlab.text(x[index], y[index], city, z=z[index], color=(0,0,1), width=0.016 * len(city), name=city) #create continents from mayavi.sources.builtin_surface import BuiltinSurface continents_src = BuiltinSurface(source="earth", name="Continents") #set the LDD to 2 continents_src.data_source.on_ratio = 2 continents = mlab.pipeline.surface(continents_src, color=(0,0,0)) #create the equitor # distribute every 360 to 100 theta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 50) x = np.cos(theta) y = np.sin(theta) z = np.zeros_like(theta) mlab.plot3d(x,y,z,color=(1,1,1),opacity=0.2,tube_radius=None) #show the window for interation mlab.view(100,60,4,[-0.05,0,0]) mlab.show()
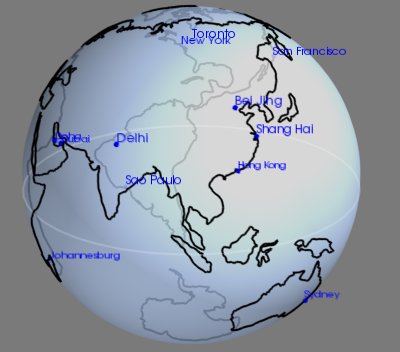
5Mayavi三维可视化
5.1三维可视之基础应用homework1
pass见下文url
5.2三维可视之基础应用homework2
pass见下文url
5.3三维可视之基础应用homework3
pass见下文url
5.4三维可视之基础应用homework4
pass见下文url
5.5三维可视之进阶实战homework5
构造一个旋转抛物面,并使用mlab.mesh绘制出来。首先在(r, theta)中创建一个20*20的二维网格:
r, theta = mgrid[0:1:10j, 0:2*pi:10j]
并将圆柱坐标系,转换为直角坐标系,其中:
z = r*r x = r*cos(theta) y = r*sin(theta)
(数学函数等值可从numpy中导出。)
代码例22
from mayavi import mlab import numpy as np pi = np.pi cos = np.cos sin = np.sin mgrid = np.mgrid r,theta = pi/250,pi/250 [r,theta] = np.mgrid[0:1:10j,0:2*pi:10j] x = r * cos(theta) y = r * sin(theta) z = r * r s = mlab.mesh(x,y,z) mlab.show()
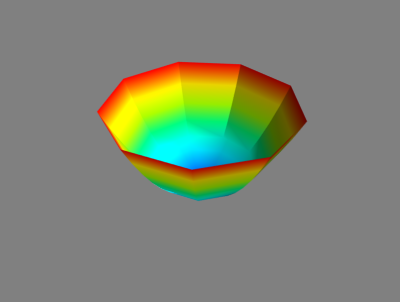
5.6三维可视之进阶实战homework6
对“编程练习8.1”中旋转抛物面方程进一步绘制,计算一个二维数组 s,并且把它传递给mesh()的scalars 参数。观察一下绘制结果的变化。其中 s = x*y*z. 同时,请绘制该旋转抛物面的轮廓线。
空间轮廓线可视化代码:

#coding=gbk from mayavi import mlab import numpy as np from tvtk.api import tvtk from tvtk.common import configure_input from tvtkfunc import ivtk_scene, event_loop pi = np.pi cos = np.cos sin = np.sin mgrid = np.mgrid r,theta = pi/250,pi/250 [r,theta] = np.mgrid[0:1:10j,0:2*pi:10j] x = r * cos(theta) y = r * sin(theta) z = r * r s = x * y * z s = scalars s = mlab.mesh(scalars,x,y,z) plot3d = tvtk.MultiBlockPLOT3DReader( xyz_file_name="s", q_file_name="s", scalar_function_number=100, vector_function_number=200 )#读入Plot3D数据 plot3d.update()#让plot3D计算其输出数据 grid = plot3d.output.get_block(0)#获取读入的数据集对象 outline = tvtk.StructuredGridOutlineFilter()#计算表示外边框的PolyData对象 configure_input(outline, grid)#调用tvtk.common.configure_input() m = tvtk.PolyDataMapper(input_connection=outline.output_port) a = tvtk.Actor(mapper=m) a.property.color = 0.3, 0.3, 0.3 #窗口绘制 win = ivtk_scene(a) win.scene.isometric_view() event_loop() mlab.show()
5.7三维可视之进阶实战homework7
可视化模型数据文件(附件),能发现了什么?
能发现一只白色雕塑的兔子
对于tar.gz类型压缩包的处理,可以参考dragon模型,可以参考以下代码:

#coding=gbk from mayavi import mlab from os.path import join import tarfile dragon_tar_file = tarfile.open("dragon.tar.gz") try: os.mkdir("dragon_data") except: pass dragon_tar_file.extractall("dragon_data") dragon_tar_file.close() dragon_ply_file = join("dragon_data","dragon_recon","dragon_vrip.ply") #渲染dragon ply文件 mlab.pipeline.surface(mlab.pipeline.open(dragon_ply_file)) mlab.show() import shutil shutil.rmtree("dragon_data")
大致逻辑如下:
选中并打开bunny.tar.gz---新建文件夹bunny_data---解压bunny.tar.gz到bunny_data文件夹---关闭bunny.tar.gz---串联路径从bun.zipper.ply(一般ply文件是最终目录下的扫描文件)到上一级再到上一级到最终建立的文件夹bunny_data---打开上面构建好的路径下的ply文件,用mlab.pipeline.surface()构建表面---用shutil.rmtree删除用于放置压缩文件的文件夹。
代码:

# 3D scanning files from mayavi import mlab from os.path import join import tarfile bunny_tar_file = tarfile.open("bunny.tar.gz") try: os.mkdir("bunny_data") except: pass bunny_tar_file.extractall("bunny_data") bunny_tar_file.close() # combine the path of bun_vrip and its packages' name, such as dragon_data/dragon_recon/dragon_vrip.ply bunny_ply_file = join("bunny_data","bunny","reconstruction","bun_zipper.ply") mlab.pipeline.surface(mlab.pipeline.open(bunny_ply_file)) mlab.show() import shutil shutil.rmtree("bunny_data")
补充:mlab绘图函数的x、y、z、s、w、u、v到底是什么含义?假设这些参数描述了一个磁场,它们可能分别代表什么含义?加入这些参数描述了一个流体,它们可能分别代表什么含义?
X,y,z表示点三维坐标;
S表示该坐标点处的标量值;
U,v,w表示矢量元素
如果应用到磁场中,x,y,z表示磁场位置,s表示该位置处磁场大小,u,v,w表示该处磁场方向。
如果应用到流体,x,y,z表示流体位置,s表示该处流量大小,u,v,w表示该处流量方向。
LOD:level of details
5.8三维可视之进阶实战homework8
1.为mayavi可视化提供数据的mayavi管线层级是Filters,这句话对吗?为什么?
不对,因为为mayavi可视化提供数据的是scence场景,scence每个场景下有多个数据集合sources,为mayavi可视化提供数据,Filter是应用于source上对数据进行变换。
2.基于1维Numpy数组x、y、z提供的三维坐标数据,绘制线图形的函数是Point3D()。这句话正确吗?为什么?
不对,因为基于1维Numpy数组x,y,z提供的三维坐标数据,绘制线图形的函数是plot3D(), point3d()是基于数组x,y,z提供的三维点坐标,绘制点图形。
3.mayavi管线中处于最顶层表示场景的对象是什么?获取当前场景的方法是什么?
Mayavi中处于最顶层的对象是mayavi Engine,表示建立和销毁场景Scene。
获取当前场景的方法是s.scene.background()
4.3D绘图函数Point3D()中,根据标量值确定actor透明度的参数是opcity。这句话正确吗?为什么?
不对,根据标量值确定actor透明度的参数是transparent,opcity用于VTK对象的整体透明度,该值为float型,默认为1.0
5.3D绘图函数中,绘制由三个二维数组x、y、z描述坐标点的网格平面的方法是imshow()。这句话正确吗?为什么?
不对,imshow()是用于绘制二维数组的,但是没有z轴,只有x和y两个轴,x作为第一轴的下标,y轴作为第二轴的下标
比如:s = numpy.random.random((10,10)),img = mlab.imshow(s,colormap='gist_earth')
6.3D绘图函数中,三维矢量数据的可视化的方法是contour3d()。这句话正确吗?为什么?
Contour3d是用来绘制标量数据3d视图的,三维矢量数据可视化的方法是mlab.quiver3d()。
7.在鼠标选取操作中,on_mouse_pick()方法返回值是什么?
On_mouse_pick()返回一个vtk对象。
8.mlab管线中,用来进行数据变换的层级是什么?用来实现数据可视化的层级是什么?
用filter对数据进行交换,用modules来对最终的数据进行可视化。
9.在mlab管线的modules层级中,用来对VTK dataset和mayavi sources建立外表面的方法是surface()。这句话正确吗?为什么?
正确,但是要却别与iso_surface(),iso_surface()是用于对输入的体数据绘制其等值面。
10.在mayavi可视化实例三中,绘制大洲边界时大洲边界粗糙的解决办法是什么?
调整LOD,比如调整continents_src.data_source.on_ratio = 2
6三维可视化之交互界面
6.1三维可视之进阶实战homework8
• Traits背景:
Python动编程态语言,变量没有类型,比如:颜色属性
“Red”字符创
0xff0000整数
(255,0,0)元组
• Traits库可以为python添加类型定义
• Traits属于解决color类型的问题
o 接受能表示颜色的各种类型值
o 赋值为非法的颜色值时,能够捕捉到错误,并给提供错误报告。
o 提供一个内部的标注你颜色
• c.color可以支持颜色命令,如c.color = “red”,但不支持c.color = “abc”的字符串
• c.configure_traits()可以设置颜色,c.color.getRgb()可以获取设置颜色后的三原色的值
比如设置c.configure_traits()为红色,即在桌面弹出的窗口中设置Red,那么回击c.color.getRgb可以得到(255,0,0,255)这样的feedback。
6.2attributes of traits
traits的五个功能:initialization, verification, procuration, monitoring, visualization
代码23 traits
from traits.api import Delegate, HasTraits, Instance, Int, Str class Parent(HasTraits): # 初始化 last_name = Str('Zhang') class Child(HasTraits): age = Int # 验证 father = Instance(Parent) # 代理 last_name = Delegate('father') # 监听 def _age_changed(self, old, new): print('Age change from %s to %s' % (old, new))
练习过程如下:

>>> P = Parent() >>> c = Child() >>> c.father = P >>> c.last_name 'Zhang' >>> P.last_name 'Zhang' >>> c.age = 4 Age changed from 0 to 4 >>> >>> c.configure_traits() Age changed from 4 to 3 Age changed from 3 to 4 True >>> c.print_traits() age: 4 father: <__main__.Parent object at 0x0000022BA2A2F8E0> last_name: 'Zhang' >>> c.get() {'age': 4, 'father': <__main__.Parent object at 0x0000022BA2A2F8E0>, 'last_name': 'Zhang'} >>> c.set(age = 8) Age changed from 4 to 8 <__main__.Child object at 0x0000022BA2A2F990>
在traits属性功能的实例中,能否直接修改Child的last_name属性?
不能,因为Child对象的last_name是直接继承自Parent类的,要通过父类改变
如果定义P = Parent(), c = Child();
直接输出c.last_name 没有结果
所以输出c.father = P, 再输入c.last_name就有子类名字
或者也可以直接输入P.last_name也可以得到子类名字
6.3traits属性监听
Trait属性监听:静态监听,动态监听
Trait监听属性顺序:name, age, doing---静态监听函数---动态监听1---动态监听2
静态监听函数的几种形式:属性名+changed+发生变化前的名+发生变化后的名字
_age_changed(self)
_age_changed(self,new)
_age_changed(self, old, new)
_age_changed(self, name, old, new)
动态监听:
@on_trait_change(names)
Def any_method_name(self, ..)

问:为什么对Infoupdated任意赋值都会触发监听事件?
因为Infoupdated直接由Event赋值,无论如何都会调用_Infoupdated_fired()函数,所以会触发self.reprint()函数输出self.name和self.age内容。
6.5Traits_property
用traits_property.py遍好程序后,得到area被监听的结果;如果命令行输入w/h发生变化,print输出的就是变化后的值。
调用r.edit_traits()直接触发_get_area()函数,同时在界面中显示area结果。
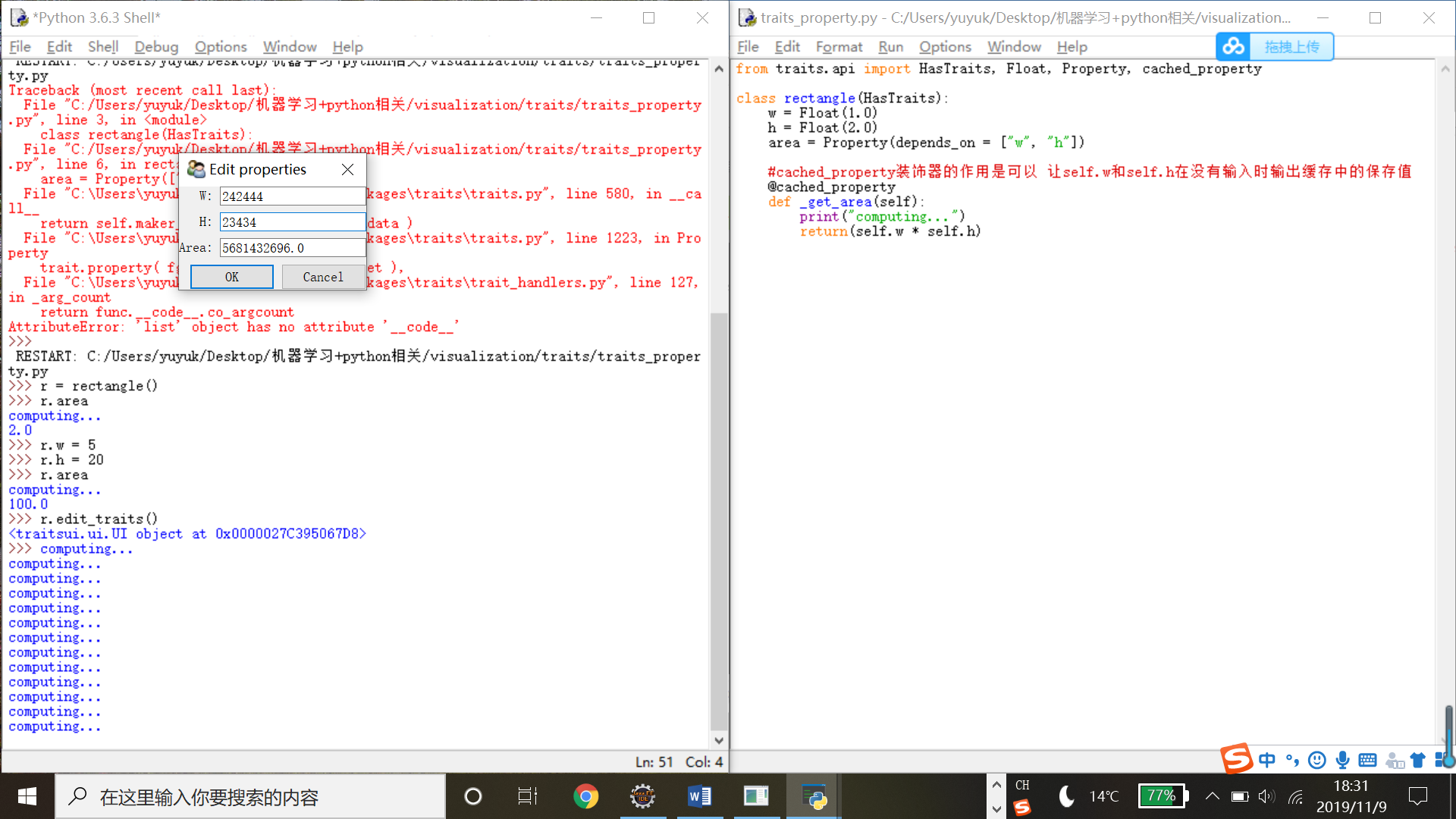
6.6TraitsUI
Tkinter, wxPython, pyQt4, TraitsUI(based on MVC:Model-View-Controller)
MVC是traitsUI所使用的架构模型
6.6.1Traits_UI交互
from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Int model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits()

6.6.2View定义界面
TraitsUI自定义界面支持的后台库界面有:qt4(-toolkit qt4)和wx(-toolkit wx)
|
MVC类别 |
MVC说明 |
|
Model |
HasTraits的派生类用Trait保存数据,相当于模型 |
|
View |
没有指定界面显示方式时,Traits自动建立默认界面 |
|
Controller |
起到视图和模型之间的组织作用,控制程序的流程 |
•Item对象属性
Item(id,name,label)
|
属性 |
说明 |
|
id |
Item的唯一ID |
|
name |
Trait属性的名称 |
|
Label |
静态文本,用于显示编辑器的标签 |
|
Tooltip |
编辑器的提示文本 |
•View对象属性
|
属性 |
说明 |
|
Title |
窗口标题栏 |
|
Width |
窗口高度 |
|
Height |
串口高度 |
|
Resizable |
串口大小可变,默认为True |
代码和界面如下:
问:如果想要编辑器窗口大小不能改变,应如何修改view中的哪个属性?
答:修改title中的resizable = False可以是标签大小不可变
6.6.3Group组织对象
Group对象
from traitsui.api import Group
Group(…)属性有:
|
属性 |
说明 |
|
Orientation |
编辑器的排列方向 |
|
Layout |
布局方式normal,flow,split,tabbed |
|
Show_labels |
是否显示编辑器的标签 |
|
Columns |
布局的列数,范围为(1,50) |
· Group类继承的HSplit类
Hsplit定义: Class HSplit(Group): #... #... Layout = “split” Orientation = “horizontal”
代码等价于:
Group(…, layout = “split”, orientation = “horizontal”)
•Group的各种派生类
|
属性 |
说明 |
|
HGroup |
内容水平排列 Group(orientation = “horizontal”) |
|
HFlow |
内容水平排列,超过水平宽度,自动换行,隐藏标签文字。Group(orientation = “horizontal”, layout=”flow”, show_labels = False) |
|
HSplit |
内容水平分隔,中间插入分隔条 |
|
Tabbed |
内容分标签页显示 Group(orientation=”horizontal”,layout=”tabber”) |
|
Vgroup |
内容垂直排列 Group(orientation=”vertical”) |
|
Vflow |
内容垂直排列,超过垂直高度时,自动换列,隐藏标签文字Group(orientation=”vertical”,layout=”flow”,show_labels=False) |
|
Vfold |
内容垂直排列,可折叠 Group(orientation=”vertical”,layout=”fold”,show_labels=False) |
|
Vgrid |
按照多列网格进行垂直排列,columns属性决定网格的列数 Group(orientation=”vertical”,columns=2) |
|
Vsplit |
内容垂直排列,中间插入分隔条 Gorup(orientation=”vertical”,layout=”split”) |
代码24 多视图界面代码

from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int from traitsui.api import View, Item,Group from traitsui.menu import ModalButtons class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Str vertices = Int view1 = View( Group( Item("model_name",label=u"模型名称"), Item("model_name",label=u"文件名"), Item("category",label=u"模型类型"), label = u"模型信息", show_border = True), Group( Item("model_number",label=u"模型数量"), Item("vertices",label=u"顶点数量"), label = u"统计数据", show_border = True), kind = "modal", buttons = ModalButtons ) model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits(view=view1)

•垂直排列多视图

from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int from traitsui.api import View, Item, Group from traitsui.menu import ModalButtons class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Int vertices = Int view1 = View( Group( Group( Item('model_name', label=u"模型名称"), Item('model_file', label=u"文件名"), Item('category', label=u"模型类型"), label = u'模型信息', show_border = True), Group( Item('model_number',label=u"模型数量"), Item('vertices',label=u"顶点数量"), label = u'统计数据', show_border = True) ) ) model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits(view=view1)
•水平排列多视图

from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int from traitsui.api import View, Item, Group from traitsui.menu import ModalButtons class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Int vertices = Int view1 = View( Group( Group( Item('model_name', label=u"模型名称"), Item('model_file', label=u"文件名"), Item('category', label=u"模型类型"), label = u'模型信息', show_border = True), Group( Item('model_number',label=u"模型数量"), Item('vertices',label=u"顶点数量"), label = u'统计数据', show_border = True), orientation = "horizontal" ) ) model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits(view=view1)
•Hsplit和VGroup定义水平/垂直并排视图
同样也可以用HSplit和VGroup去生成水平/垂直排列

from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int from traitsui.api import View, Item, VGroup, HSplit from traitsui.menu import ModalButtons class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Int vertices = Int view1 = View( #HSplit表示外层垂直排列 HSplit( VGroup( Item('model_name', label=u"模型名称"), Item('model_file', label=u"文件名"), Item('category', label=u"模型类型"), label = u'模型信息'), VGroup( Item('model_number',label=u"模型数量"), Item('vertices',label=u"顶点数量"), label = u'统计数据') ) ) model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits(view=view1)

- 外层垂直排列

from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int from traitsui.api import View, Item, HGroup, VSplit from traitsui.menu import ModalButtons class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Int vertices = Int view1 = View( #HSplit表示外层垂直排列 VSplit( HGroup( Item('model_name', label=u"模型名称"), Item('model_file', label=u"文件名"), Item('category', label=u"模型类型"), label = u'模型信息'), HGroup( Item('model_number',label=u"模型数量"), Item('vertices',label=u"顶点数量"), label = u'统计数据') ) ) model = ModelManager() model.configure_traits(view=view1)
- 内外部视图显示
-
代码25

from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Int from traitsui.api import View, Item,Group from traitsui.menu import ModalButtons g1 = [Item("model_name", label=u"模型名称"), Item("category", label=u"模型类型")] g2 = [Item("model_number", label=u"模型数量"), Item("vertices", label=u"顶点数量")] class ModelManager(HasTraits): model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Str vertices = Int traits_view = View( Group(*g1, label = u"模型信息", show_border = True), Group(*g2, label = u"统计数据", show_border = True), title = u"内部视图") global_view = View( Group(*g1, label = u"模型信息", show_border = True), Group(*g2, label = u"统计数据", show_border = True), title = u"外部视图") model = ModelManager()
- 在命令行输入不同代码出现不同界面:
>>> model.configure_traits(view = global_view)
>>> model.configure_traits()
>>> model.configure_traits(view = "traits_view")
如果想要在编辑器中水平并列显示三组group对象
Q1.如果想要在编辑器中水平并列显示三组group对象,应该如何修改group对象的属性?
A1.把原来的Group()改成HGroup()或者在列完3个内层Group同级上写orientation = “horizontal”
Q2.如果想要在编辑器中垂直分标签页显示若干组group对象,可以使用哪些方法?
同理把原来的Group()改成VGroup()或者在列完若干个内层Group()同级上写orientation = “vertical”
6.6.4视图配置
通过kind属性设置view显示类型
|
| 显示类型(采用窗口显示内容) |
| Modal |
| Live |
| Livemodal |
| nonmodal |
模态窗口:在窗口关闭之前,其他窗口不能激活;
无模态窗口:在窗口关闭之前,其他窗口能激活;
即时更新:修改空间内容,立即反映到模型数据上;
非即时更新:只有当用户点ok,apply等命令时,效果才会反应在模型上;
Wizard:向导窗口,模态窗口,即时更新;
Panel:向导窗口,模态窗口,即时更新
subpanel :嵌入窗口中的面板
视图配置的实例:view = view(… kind = ‘modal=’)
模态与非模态的小例子
| Configure_traits | Edit_traits() |
| 界面显示后,进入消息循环 | 界面显示后,不进入消息循环 |
| 主界面窗口或模态对话框 | 无模态窗口或对话框 |
Traits UI按钮配置
|
标准命令按钮 |
|
UndoButton |
|
Applybutton |
|
ReverButton |
|
OKbutton |
|
CancelButton |
|
HelpButton |
Traitsui.menu预定义了命令按钮: OKcancelButtons = [OKButton,CancelButton] ModelButtons = [ApplyButton,RevertButton,OKButton,CancelButton,HelpButton] LiveButtons = [UndoButton,ReverButton,OKButton,Cancel]
6.6.5TraitsUI控件
文本编译器:Str, Int
文本编译器与密码窗口:

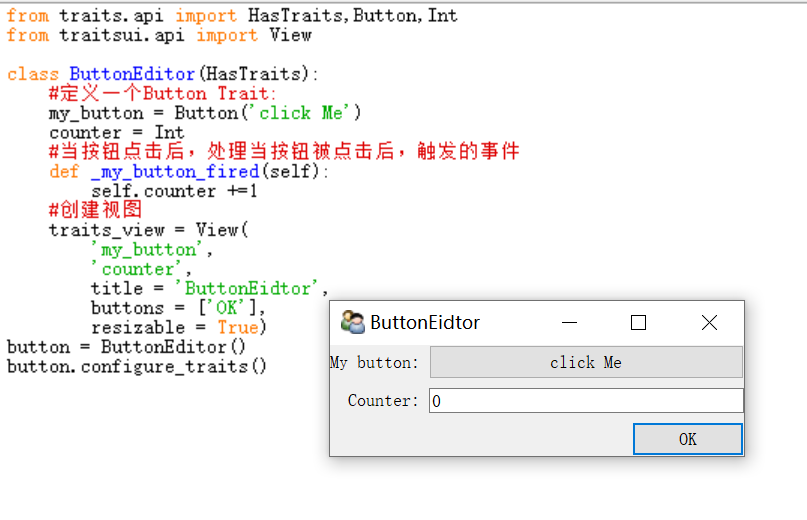
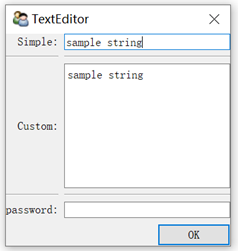
from traits.api import HasTraits, Str, Password from traitsui.api import Item, Group, View class TextEditor(HasTraits): #定义文本编辑器变量 string_trait = Str('sample string') password = Password #定义布局 text_str_group = Group( Item('string_trait',style = 'simple',label = 'Simple'), Item("_"), Item('string_trait',style = 'custom',label = 'Custom'), Item("_"), Item('password',style = 'simple',label = 'password'), ) #定义视图 traits_view = View( text_str_group, title = 'TextEditor', buttons = ['OK'] ) 代码25 按键触发计数器 from traits.api import HasTraits,Button,Int from traitsui.api import View class ButtonEditor(HasTraits): #定义一个Button Trait: my_button = Button('click Me') counter = Int #当按钮点击后,处理当按钮被点击后,触发的事件 def _my_button_fired(self): self.counter +=1 #创建视图 traits_view = View( 'my_button', 'counter', title = 'ButtonEidtor', buttons = ['OK'], resizable = True) button = ButtonEditor() button.configure_traits()
代码26 滑动条

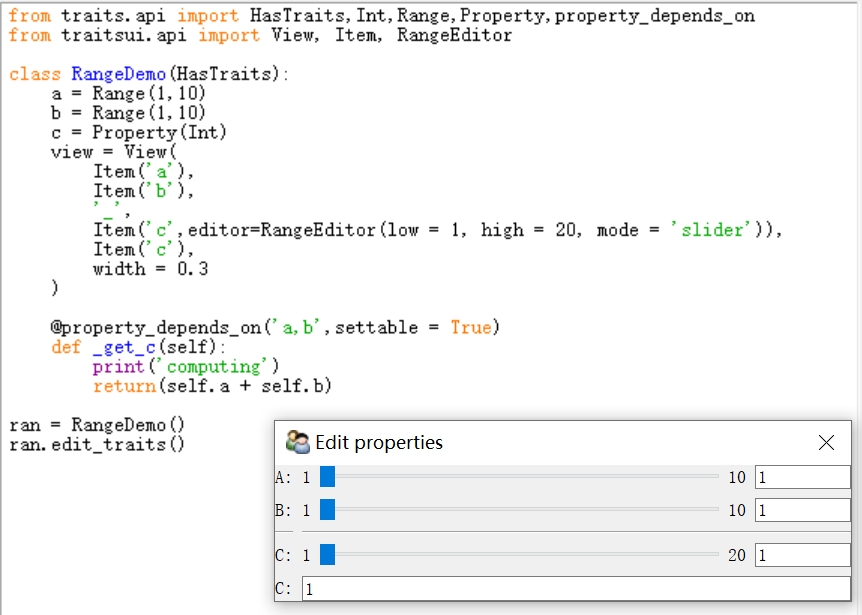
from traits.api import HasTraits,Int,Range,Property,property_depends_on from traitsui.api import View, Item, RangeEditor class RangeDemo(HasTraits): a = Range(1,10) b = Range(1,10) c = Property(Int) view = View( Item('a'), Item('b'), '_', Item('c',editor=RangeEditor(low = 1, high = 20, mode = 'slider')), Item('c'), width = 0.3 ) @property_depends_on('a,b',settable = True) def _get_c(self): print('computing') return(self.a + self.b) ran = RangeDemo() ran.edit_traits()
text = TextEditor()
text.configure_traits()
按钮Button Editor
监听方法: _TraitName_fired()
TraitName是Button Trait 的名字,即my_button
Def _my_button_fired(self):
Self.counter += 1
程序框架:
from traits.api import Button #导入控件模块 class ButtonEditor(HasTraits): TraitName = Button() #定义按钮变量名 def _TraitName_fired(self) #定义监听函数 … … view = View() button = Button() button.configure_traits()
菜单、工具栏
From traitsui.menu import Action…
|
对象 |
说明 |
|
Action |
在Menu对象中,通过Action对象定义菜单中的每个选项 |
|
ActionGroup |
在菜单中的选项中进行分组 |
|
Menu |
定义菜单栏中的一个菜单 |
|
MenuBar |
菜单栏对象,由多个Menu对象组成 |
|
ToolBar |
工具栏对象,它由多个Action对象组成,每个Aciton对应工具挑中的一个按钮 |
fdf控件列表
|
对象 |
说明 |
|
Array |
数组空间 |
|
Bool |
单选框、复选框 |
|
Button |
按钮 |
|
Code |
代码编辑器 |
|
Color |
颜色对话框 |
|
Directory |
目录控件 |
|
Enum |
枚举控件 |
|
File |
文件控件 |
|
Font |
字体选择控件 |
|
Html |
Html网页控件 |
|
List |
列表框 |
|
Str |
文本框 |
|
Password |
密码控件 |
|
Tuple |
元组控件 |
7三维可视化之界面实战
7.1TraitsUI与mayavi实战
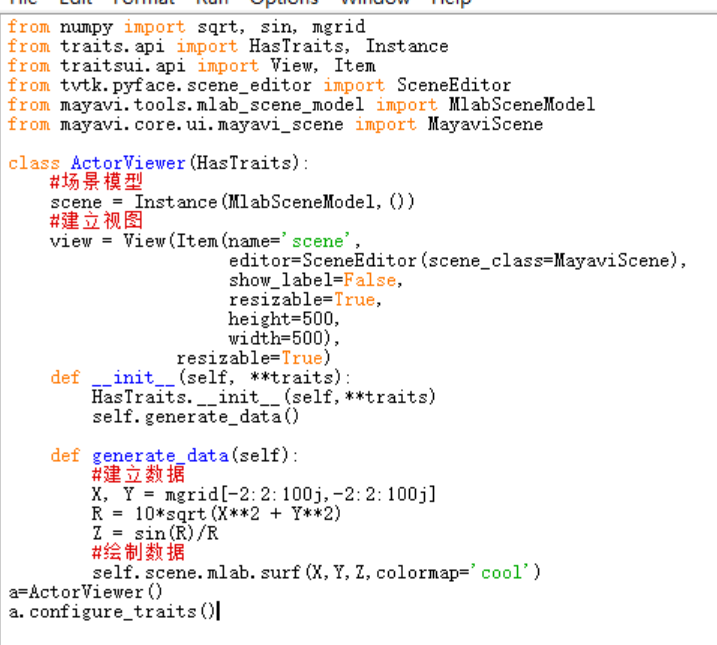
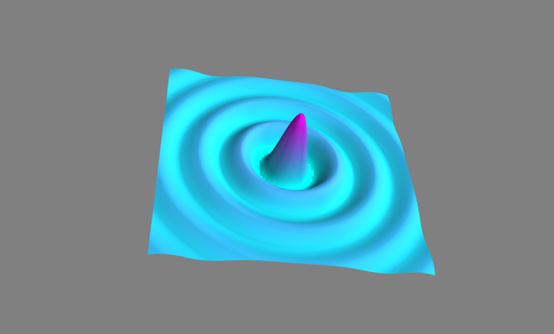
7.1.1Mayavi可视化实例
建立mayavi窗口步骤:
1. 建立从HasTraits继承的类
a. 建立MlabSceneMode场景实例scene
b. 建立view视图
c. 定义_init_函数,生成数据
2. 建立类的实例,调用configure_traits()方法
Numpy 用于建立数据
Traits.api,traitsui.api 用于建立场景模型
Tvtk.pyface.scene_editor 用于建立视图
Tools.mlab_scene_model 用于绘制数据
Core.ui.mayavi_scene 用于绘制数据
7.1.2TraitsUI可视化实例
程序框架
#1.定义HasTraits继承类
Class MyModel(HasTraits): #1.1定义窗口的变量 n_meridional n_longitudinal scene #1.2更新视图绘制 @on_trait_change() Def update_plot(self): … … #1.3建立视图布局 View = View()
#2.显示窗口
model = MyModel()
Model.configure_traits()

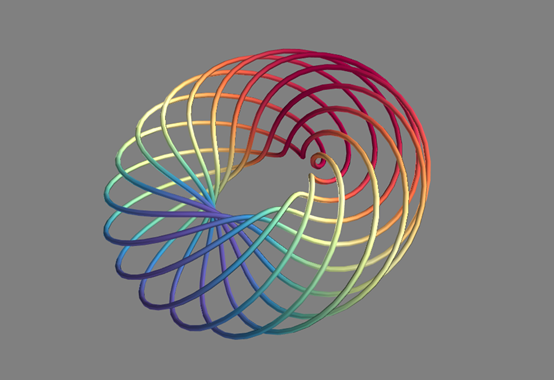
7.1.3三维可视之交互界面homework6
pass见下文url
8三维可视化之总结
8.1客观题练习homework7
pass见下文url
8.2主观题练习
8.2.1练习1
请参考SV11V02“TraitsUI可视化实例”,将本课程所学的TVTK或者Mayavi可视化例子,补充TraitsUI的交互控制,即通过TraitsUI的交互控制能够实现可视化视图中参数的相应改变,交互控件的种类不少于2种(如滑动条、文本框)、交互控件数量不少于3个(如2个滑动条、1个文本框)。要求代码规范,有注释。
SV11V02 TraitsUI可视化实例参考代码
一个简单的例子,在原有基础上,融合了文本框和[‘OK’]按钮

from traits.api import HasTraits, Range, Instance, on_trait_change from traitsui.api import View, Item, Group from mayavi.core.api import PipelineBase from mayavi.core.ui.api import MayaviScene, SceneEditor, MlabSceneModel from numpy import arange, pi, cos, sin dphi = pi/300. phi = arange(0.0, 2*pi + 0.5*dphi, dphi, 'd') def curve(n_mer, n_long): mu = phi*n_mer x = cos(mu) * (1 + cos(n_long * mu/n_mer)*0.5) y = sin(mu) * (1 + cos(n_long * mu/n_mer)*0.5) z = 0.5 * sin(n_long*mu/n_mer) t = sin(mu) return x, y, z, t class MyModel(HasTraits): n_meridional = Range(0, 30, 6) n_longitudinal = Range(0, 30, 11) # 场景模型实例 scene = Instance(MlabSceneModel, ()) # 管线实例 plot = Instance(PipelineBase) #当场景被激活,或者参数发生改变,更新图形 @on_trait_change('n_meridional,n_longitudinal,scene.activated') def update_plot(self): x, y, z, t = curve(self.n_meridional, self.n_longitudinal) if self.plot is None:#如果plot未绘制则生成plot3d self.plot = self.scene.mlab.plot3d(x, y, z, t, tube_radius=0.025, colormap='Spectral') else:#如果数据有变化,将数据更新即重新赋值 self.plot.mlab_source.set(x=x, y=y, z=z, scalars=t) # 建立视图布局 view = View(Item('scene', editor=SceneEditor(scene_class=MayaviScene), height=250, width=300, show_label=False), Group('_', 'n_meridional', 'n_longitudinal'), resizable=True) model = MyModel() model.configure_traits()
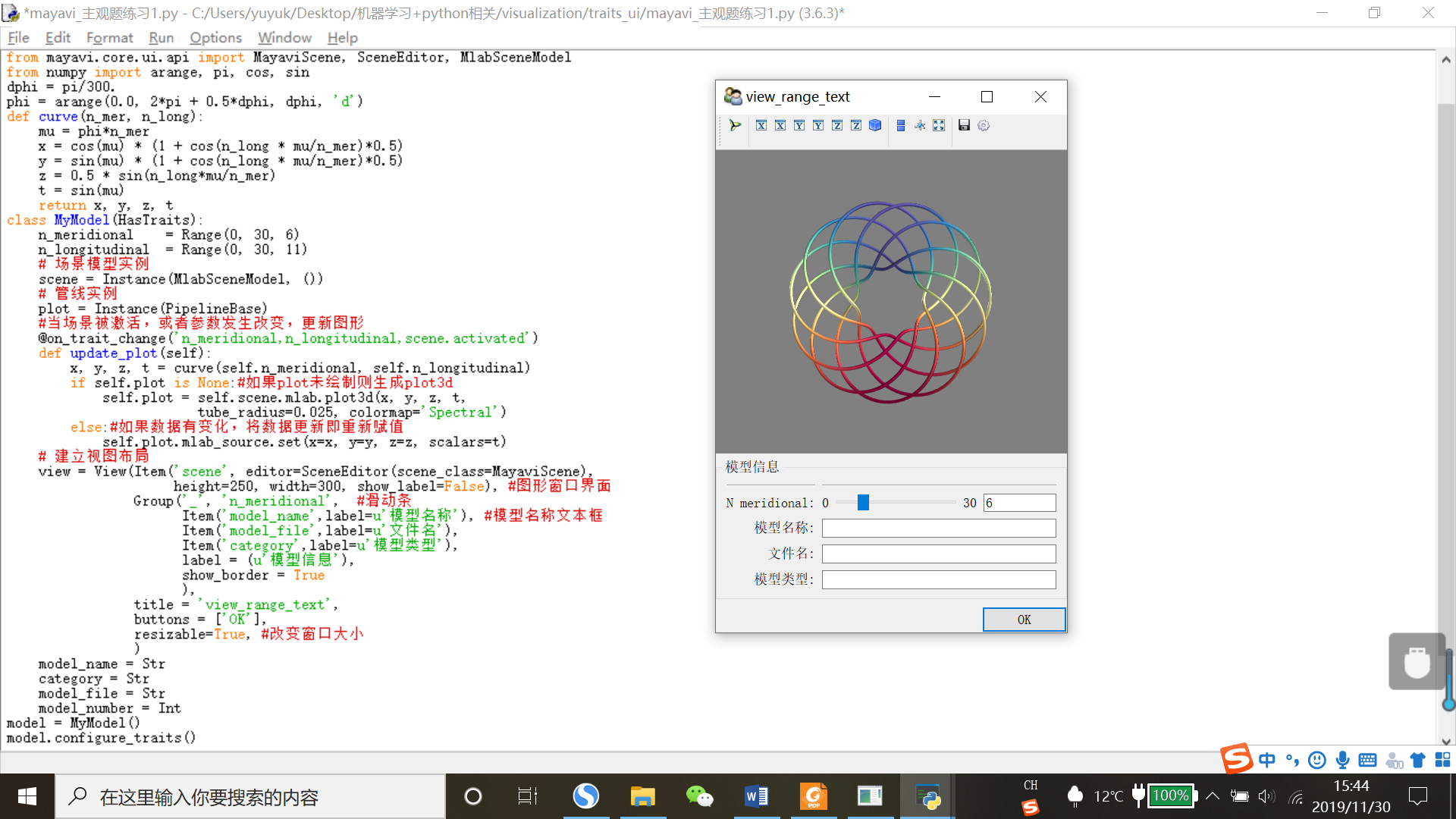
代码27 view_range_text

from traits.api import HasTraits, Range, Instance, on_trait_change, Str, Int, Button from traitsui.api import View, Item, Group from mayavi.core.api import PipelineBase from mayavi.core.ui.api import MayaviScene, SceneEditor, MlabSceneModel from numpy import arange, pi, cos, sin dphi = pi/300. phi = arange(0.0, 2*pi + 0.5*dphi, dphi, 'd') def curve(n_mer, n_long): mu = phi*n_mer x = cos(mu) * (1 + cos(n_long * mu/n_mer)*0.5) y = sin(mu) * (1 + cos(n_long * mu/n_mer)*0.5) z = 0.5 * sin(n_long*mu/n_mer) t = sin(mu) return x, y, z, t class MyModel(HasTraits): n_meridional = Range(0, 30, 6) n_longitudinal = Range(0, 30, 11) # 场景模型实例 scene = Instance(MlabSceneModel, ()) # 管线实例 plot = Instance(PipelineBase) #当场景被激活,或者参数发生改变,更新图形 @on_trait_change('n_meridional,n_longitudinal,scene.activated') def update_plot(self): x, y, z, t = curve(self.n_meridional, self.n_longitudinal) if self.plot is None:#如果plot未绘制则生成plot3d self.plot = self.scene.mlab.plot3d(x, y, z, t, tube_radius=0.025, colormap='Spectral') else:#如果数据有变化,将数据更新即重新赋值 self.plot.mlab_source.set(x=x, y=y, z=z, scalars=t) # 建立视图布局 view = View(Item('scene', editor=SceneEditor(scene_class=MayaviScene), height=250, width=300, show_label=False), #图形窗口界面 Group('_', 'n_meridional', #滑动条 Item('model_name',label=u'模型名称'), #模型名称文本框 Item('model_file',label=u'文件名'), Item('category',label=u'模型类型'), label = (u'模型信息'), show_border = True ), title = 'view_range_text', buttons = ['OK'], resizable=True, #改变窗口大小 ) model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str model_number = Int model = MyModel() model.configure_traits()
参考SV09V02“TraitsUI可视化实例”,将本课程所学的TVTK或者Mayavi可视化例子,补充TraitsUI的交互控制,即通过TraitsUI的交互控制能够实现可视化视图中参数的相应改变,交互控件的种类不少于3种(如滑动条、文本框、颜色对话框)、交互控件数量不少于3个(如1个滑动条、1个文本框、1个颜色对话框)。要求代码规范,有注释。
8.2.2练习2
SV09V02“TraitsUI可视化实例”参考代码:
from traits.api import Delegate, HasTraits, Instance, Int, Str class Parent(HasTraits): # 初始化 last_name = Str('Zhang') class Child(HasTraits): age = Int # 验证 father = Instance(Parent) # 代理 last_name = Delegate('father') # 监听 def _age_changed(self, old, new): print('Age change from %s to %s' % (old, new))
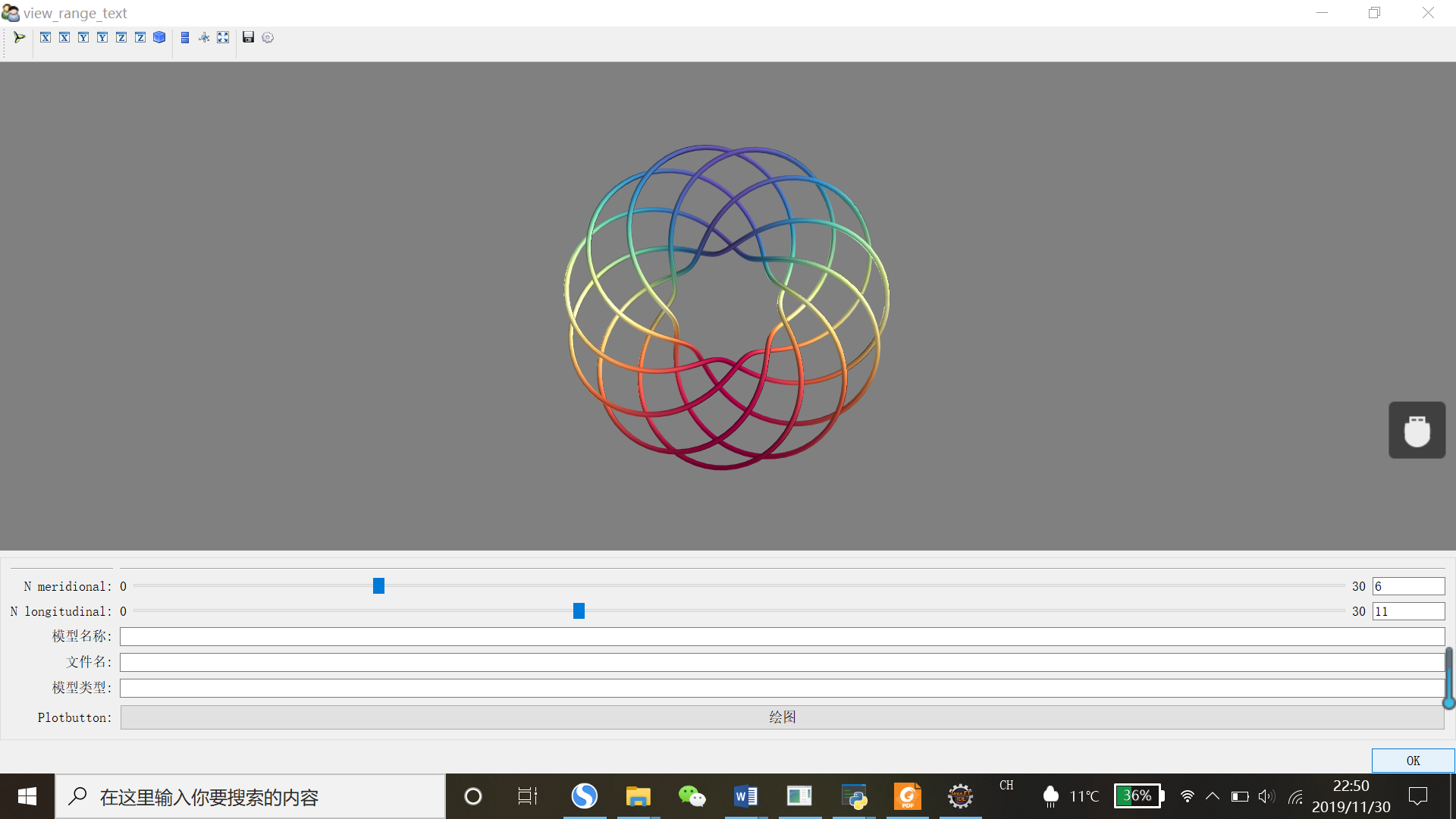
代码28 在TraitsUI中嵌入mayavi
颜色对话框没有找到,不会实现这个功能,不过添加了一个点击绘图的命令,代码稍微修改了下,添加了_plotbutton_fired(self)和plot(self)函数,同时在绘图之前要给图形一个初始化,在出现图形界面后,再动态监听图形参数的变化

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from traits.api import * from traits.api import HasTraits, Range, Instance, on_trait_change, Str, Int, Button from traitsui.api import View, Item, VGroup,Group from mayavi.core.api import PipelineBase from mayavi.core.ui.api import MayaviScene, SceneEditor, MlabSceneModel from numpy import arange, pi, cos, sin dphi = pi/300. phi = arange(0.0, 2*pi + 0.5*dphi, dphi, 'd') def curve(n_mer, n_long): mu = phi*n_mer x = cos(mu) * (1 + cos(n_long * mu/n_mer)*0.5) y = sin(mu) * (1 + cos(n_long * mu/n_mer)*0.5) z = 0.5 * sin(n_long*mu/n_mer) t = sin(mu) return x, y, z, t class DemoApp(HasTraits): n_meridional = Range(0, 30, 6) n_longitudinal = Range(0, 30, 11) plotbutton = Button(u"绘图") # 场景模型实例 scene = Instance(MlabSceneModel,()) #当场景被激活,或者参数发生改变,更新图形 @on_trait_change('n_meridional,n_longitudinal,scene.activated') def update_plot(self): x, y, z, t = curve(self.n_meridional, self.n_longitudinal) if self.plot is None:#如果plot未绘制则生成plot3d self.plot = self.scene.mlab.plot3d(x, y, z, t, tube_radius=0.025, colormap='Spectral') else:#如果数据有变化,将数据更新即重新赋值 self.plot.mlab_source.set(x=x, y=y, z=z, scalars=t) #建立视图 view = View( Item('scene', editor=SceneEditor(scene_class=MayaviScene),height=250, width=300,show_label=False), #图形窗口界面 Group('_','n_meridional','n_longitudinal', Item('model_name',label=u'模型名称'), Item('model_file',label=u'文件名'), Item('category',label=u'模型类型'), 'plotbutton', show_border = True ), title = 'view_range_text', buttons = ['OK'], resizable=True, #可变窗口大小 ) def _plotbutton_fired(self): self.plot() def plot(self): # 管线实例,初始化函数 plot = Instance(PipelineBase) x, y, z, t = curve(self.n_meridional, self.n_longitudinal) self.plot = self.scene.mlab.plot3d(x, y, z, t,tube_radius=0.025, colormap='Spectral') model_name = Str category = Str model_file = Str app = DemoApp() app.configure_traits()
本博客中能提供到的
1.pdfhomework文本和答案;
2.部分数据集代码,如果选哟全部数据集,最好还是取中国MOOC顶部的url课程链接中下载,资料全;
3.关于这个课程,我做过编程训练的代码
4.pdf课程笔记。
github地址:here,上面对应的资料都在里面,不专业,不过代码都走了一遍,有些问题也想了下,供参考。
关于如何git上传,转一下这个大佬帖子,here
简单老说就是以下几个步骤:
1).在github中创建好新的repository,如下图,其次就是命名,其他默认即可。

2).把要上传的文件装在一个文件夹下;
3).右击这个文件夹,会出现git Bash和git GUI这个命令,点击git Bash(前提是已经装好了git);
4).进入git Bash后,是这个界面
5).刚才创建好的repository里,复制链接

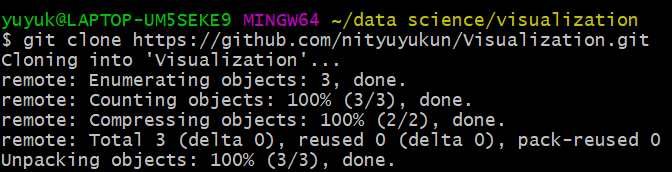
6).截下来在git Bash中输入下面命令
a)git clone xxxx(刚才复制的地址),此时在本地要上传的文件夹里会多出一个文件夹(同文件名github中,创建的repository),比如我是Visualization;
e.g. git clone https://github.com/nityuyukun/Visualization.git
b).切换到本地仓库的文件夹,比如Visualiazation

c)git add . //注意add后有一个空格,再加点,加点表示上传所有文件到本地仓库;
d)git commit -m "xxx" //"xxx"中的xxx可以任意替换,表示想要备注的名字,比如我下面是second commit,这一步表示确认上传所有文件到本地仓库,并备份;
这两步完后,出现下图

e)git push -u origin master 这一步表示把本地仓库里的东西推到github上。
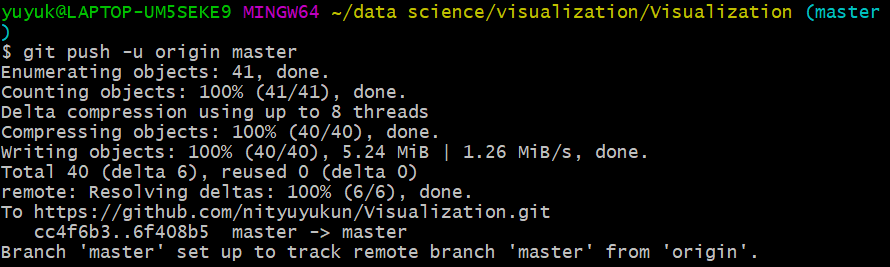
finished.
