排序算法一般是笔试面试中经常出现的问题,最近在准备找工作,就整理了一下排序算法的有关知识。
首先附上一张图
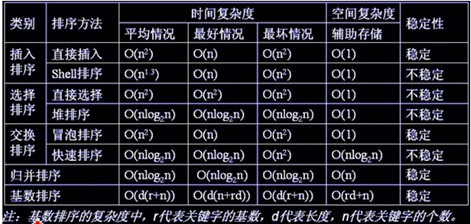
这是对各种排序算法的基本介绍。下面我们来逐一分析:
-
插入排序:
- 简单介绍:
插入排序方法分直接插入排序和折半插入排序两种,这里只介绍直接插入排序。插入排序就是每一步都将一个待排数据按其大小插入到已经排序的数据中的适当位置,直到全部插入完毕。 - 代码演示:
- 简单介绍:
1 public void sort(){ 2 int temp; 3 for(int i = 1; i<arraytoSort.length; i++){ 4 for(int j = i-1; j>=0; j--){ 5 if( arraytoSort[j+1] < arraytoSort[j] ){ 6 temp = arraytoSort[j+1]; 7 arraytoSort[j+1] = arraytoSort[j]; 8 arraytoSort[j] = temp; 9 } 10 } 11 } 12 }
-
shell排序(希尔排序):
- 简单介绍:
希尔排序的实质就是分组插入排序,是基于插入排序的一种改进。它通过加大插入排序中元素之间的间隔,并在这些有间隔的元素中进行插入排序,从而使数据项大跨度地移动,当这些数据项排过一趟序之后,希尔排序算法减小数据项的间隔再进行排序,依次进行下去。 - 代码演示:
1 public void shellSort() { 2 // 计算出最大的h值 3 int h = 1; 4 while (h <= arraytoSort.length / 3) { 5 h = h * 3 + 1; 6 } 7 while (h > 0) { 8 for (int i = h; i < arraytoSort.length; i += h) { 9 if (arraytoSort[i] < arraytoSort[i - h]) { 10 int tmp = arraytoSort[i]; 11 int j = i - h; 12 while (j >= 0 && arraytoSort[j] > tmp) { 13 arraytoSort[j + h] = arraytoSort[j]; 14 j -= h; 15 } 16 arraytoSort[j + h] = tmp; 17 } 18 } 19 // 计算出下一个h值 20 h = (h - 1) / 3; 21 } 22 }
-
选择排序:
- 简单介绍:
搜索整个值列,以找到最小值。将该值与值列中第一个位置上的值进行交换。搜索剩下的值列(第一个除外),以找到其中的最小值,然后将其与值列中第二个位置上的值进行交换。对值列中的每个位置重复该过程。在算法结束时,就完成了对值列的排序。 - 代码演示:
- 简单介绍:
1 public void sort(){ 2 for(int i = 0; i<arraytoSort.length-1; i++){ 3 int min = i; 4 int temp; 5 //find min 6 for(int j = i+1; j<arraytoSort.length ;j++){ 7 if(arraytoSort[j] <arraytoSort[min]){ 8 min = j; 9 } 10 } 11 //swap the min with the ith element 12 temp = arraytoSort[min]; 13 arraytoSort[min] = arraytoSort[i]; 14 arraytoSort[i] = temp; 15 } 16 }
-
堆排序:
-
简单介绍:
堆排序借助了堆这个数据结构,堆类似二叉树,又具有堆积的性质(子节点的关键值总小于(大于)父节点)
堆排序包括两个主要操作:- 保持堆的性质heapify(A,i) 时间复杂度O(logn)
- 建堆 buildmaxheap(A) 时间复杂度O(n)线性时间建堆
- 代码演示:
-
1 /** 2 * 最大堆的堆排序 3 * @author vonnie 4 */ 5 public class HeapSort { 6 private int[] heap; 7 private int heapsize; 8 public int times; 9 public HeapSort(int[] a) 10 { 11 heap=a; 12 heapsize=a.length; 13 times=0; 14 } 15 public void BuildMaxHeap() 16 { 17 for(int i=heapsize/2-1;i>=0;i--) 18 { 19 Maxify(i);//依次向上将当前子树最大堆化 20 } 21 } 22 public void Maxify(int i) 23 { 24 times++; 25 int l=Left(i); 26 times++; 27 int r=Right(i); 28 29 int largest; 30 times++; 31 if(l<heapsize&&heap[i]<heap[l]) 32 largest=l; 33 else 34 largest=i; 35 times++; 36 if(r<heapsize&&heap[r]>heap[largest]) 37 largest=r; 38 times++; 39 if(largest==i||largest>=heapsize) 40 return; 41 times++; 42 int temp=heap[i]; 43 times++; 44 heap[i]=heap[largest]; 45 times++; 46 heap[largest]=temp; 47 Maxify(largest); 48 } 49 50 public void MaxHeapSort() 51 { 52 for(int i=0;i<heap.length;i++) 53 { 54 //执行n次,将每个当前最大的值放到堆末尾 55 times++; 56 int tmp=heap[0]; 57 times++; 58 heap[0]=heap[heapsize-1]; 59 times++; 60 heap[heapsize-1]=tmp; 61 times++; 62 heapsize--; 63 Maxify(0); 64 } 65 } 66 67 public int[] getSortedArray() 68 { 69 this.BuildMaxHeap(); 70 this.MaxHeapSort(); 71 return heap; 72 } 73 public int Left(int i) 74 { 75 return 2*(i+1)-1; 76 } 77 public int Right(int i) 78 { 79 return 2*(i+1); 80 } 81 public int Parent(int i) 82 { 83 return (i-1)/2; 84 } 85 }
拓展:如果对100亿条数据选择Top k个数据,选择快速排序好还是堆排序好?答案是只能用堆排序。堆排序只需要维护一个k大小的空间,即在内存开辟k大小的空间。而快速排序需要开辟能存储100亿条数据的空间。
-
冒泡排序:
- 简单介绍:
冒泡排序是重复地走访过要排序的数列,一次比较两个元素,如果他们的顺序错误就把他们交换过来。走访数列的工作是重复地进行直到没有再需要交换,也就是说该数列已经排序完成。这个算法的名字由来是因为越小的元素会经由交换慢慢"浮"到数列的顶端。 - 代码演示:
- 简单介绍:
1 /** 2 * 冒泡排序: 改进了的冒泡排序,判断第一趟比较后有没有元素交换,没有就说明是排好序的数组,就直接返回 3 * @param array 4 */ 5 public static void BubbleSort(int[] array) 6 { 7 boolean isSwaped=false; 8 for(int i=0;i<array.length-1;i++) 9 { 10 for(int j=i+1;j<array.length;j++) 11 { 12 if(array[j]<array[i]) 13 { 14 isSwaped=true; 15 int a=array[i]; 16 array[i]=array[j]; 17 array[j]=a; 18 } 19 } 20 if(i==0&&!isSwaped) 21 return; 22 } 23 }
-
快速排序:
- 简单介绍:
选择一个基准元素,通常选择第一个元素或者最后一个元素,通过一趟扫描,将待排序列分成两部分,一部分比基准元素小,一部分大于等于基准元素,此时基准元素在其排好序后的正确位置,然后再用同样的方法递归地排序划分的两部分。 - 代码演示:
- 简单介绍:
1 /** 2 * 快速排序 3 * @param array 4 */ 5 public static void QuickSort(int[] array) 6 { 7 times=0; 8 qsort(array, 0, array.length-1); 9 } 10 private static void qsort(int[] arr, int low, int high){ 11 if (low < high){ 12 times++; 13 int pivot=partition(arr, low, high); //将数组分为两部分 14 qsort(arr, low, pivot-1); //递归排序左子数组 15 qsort(arr, pivot+1, high); //递归排序右子数组 16 } 17 } 18 private static int partition(int[] arr, int low, int high){ 19 int pivot = arr[low]; //枢轴记录 20 while (low<high){ 21 22 while (low<high && arr[high]>=pivot) 23 { 24 times++; 25 --high; 26 } 27 times++; 28 arr[low]=arr[high]; //交换比枢轴小的记录到左端 29 while (low<high && arr[low]<=pivot) { 30 times++; 31 ++low; 32 } 33 times++; 34 arr[high] = arr[low]; //交换比枢轴小的记录到右端 35 } 36 //扫描完成,枢轴到位 37 times++; 38 arr[low] = pivot; 39 //返回的是枢轴的位置 40 return low; 41 }
-
归并排序:
- 简单介绍:
归并排序法是将两个(或两个以上)有序表合并成一个新的有序表,即把待排序序列分为若干个子序列,每个子序列是有序的。然后再把有序子序列合并为整体有序序列。 - 代码演示:
- 简单介绍:
1 /** 2 * 归并排序 3 * @param array 4 * @param first 第一个元素的index 5 * @param last 最后一个元素的index 6 */ 7 public static int[] MergeSort(int[] array,int first,int last) 8 { 9 times=0; 10 if(first<last) 11 { 12 13 int count=(first+last)/2; 14 int[] a=Arrays.copyOfRange(array, first, count+1); 15 a=MergeSort(a,0,a.length-1); 16 int[] b=Arrays.copyOfRange(array, count+1, last+1); 17 b=MergeSort(b,0, b.length-1); 18 array=Arrays.copyOf(MergeArray(a,a.length, b,b.length), array.length); 19 } 20 return array; 21 } 22 23 /** 24 * 合并两个数组 25 * @param a 排好序的数组 26 * @param n 数组a的长度 27 * @param b 排好序的数组 28 * @param m 数组b的长度 29 * @return 30 */ 31 public static int[] MergeArray(int[] a,int n,int[] b,int m) 32 { 33 times+=3; 34 int[] array=new int[n+m]; 35 int index=0; 36 int i=0,j=0; 37 38 while(i<n&&j<m) 39 { 40 times++; 41 array[index++]=(a[i]<b[j]?a[i++]:b[j++]); 42 } 43 if(i<n) 44 { 45 for(;i<n;i++) 46 { 47 times++; 48 array[index++]=a[i]; 49 } 50 } 51 if(j<m) 52 { 53 for(;j<m;j++) 54 { times++; 55 array[index++]=b[j]; 56 } 57 } 58 return array; 59 }
-
基数排序:
- 简单介绍:
将所有待比较数值(正整数)统一为同样的数位长度,数位较短的数前面补零。然后,从最低位开始,依次进行一次排序。这样从最低位排序一直到最高位排序完成以后,数列就变成一个有序序列。 - 代码演示:
- 简单介绍:
1 public static void radixSort(int[] array){ 2 3 //首先确定排序的趟数; 4 int max=array[0]; 5 for(int i=1;i<array.length;i++){ 6 if(array[i]>max){ 7 max=array[i]; 8 } 9 } 10 11 int time=0; 12 //判断位数; 13 while(max>0){ 14 max/=10; 15 time++; 16 } 17 18 //建立10个队列; 19 LinkQueue<Integer>[] queue=new LinkQueue[10]; 20 for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ 21 queue[i]=new LinkQueue<Integer>(); 22 } 23 24 //进行time次分配和收集; 25 for(int i=0;i<time;i++){ 26 27 //分配数组元素; 28 for(int j=0;j<array.length;j++){ 29 //得到数字的第time+1位数; 30 queue[array[j]%(int)Math.pow(10, i+1)/(int)Math.pow(10, i)].enQueue(array[j]); 31 } 32 int count=0;//元素计数器; 33 //收集队列元素; 34 for(int k=0;k<10;k++){ 35 while(queue[k].size()>0){ 36 array[count]=(Integer) queue[k].deQueue().getElement(); 37 count++; 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 42 }