为什么要使用广播(broadcast)变量?
Spark中因为算子中的真正逻辑是发送到Executor中去运行的,所以当Executor中需要引用外部变量时,需要使用广播变量。
进一步解释:
- 如果executor端用到了Driver的变量,如果不使用广播变量在Executor有多少task就有多少Driver端的变量副本。
- 如果Executor端用到了Driver的变量,如果使用广播变量在每个Executor中只有一份Driver端的变量副本。
Spark中Broadcast定义
官网定义:
A broadcast variable. Broadcast variables allow the programmer to keep a read-only variable cached on each machine rather than shipping a copy of it with tasks. They can be used, for example, to give every node a copy of a large input dataset in an efficient manner. Spark also attempts to distribute broadcast variables using efficient broadcast algorithms to reduce communication cost.
Broadcast variables are created from a variable v by calling SparkContext.broadcast(T, scala.reflect.ClassTag<T>). The broadcast variable is a wrapper around v, and its value can be accessed by calling the value method. The interpreter session below shows this:
[翻译]它是一个广播变量。广播变量允许程序员在每台计算机上缓存只读变量,而不是将其副本与任务一起发送。例如,它们可以有效地为每个节点提供一个大型输入数据集的副本。Spark还尝试使用有效的广播算法来分配广播变量,以降低通信成本。
广播变量是通过调用sparkcontext.broadcast(t,scala.reflect.classtag<t>)从变量v创建的。广播变量是围绕v的包装器,它的值可以通过调用value方法来访问。下面的口译员会话显示了这一点:
scala> val broadcastVar = sc.broadcast(Array(1, 2, 3)) broadcastVar: org.apache.spark.broadcast.Broadcast[Array[Int} = Broadcast(0) scala> broadcastVar.value res0: Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3)
After the broadcast variable is created, it should be used instead of the value v in any functions run on the cluster so that v is not shipped to the nodes more than once. In addition, the object v should not be modified after it is broadcast in order to ensure that all nodes get the same value of the broadcast variable (e.g. if the variable is shipped to a new node later).
[翻译]创建广播变量后,应在集群上运行的任何函数中使用它,而不是使用值v,这样V就不会多次发送到节点。此外,对象v在广播后不应进行修改,以确保所有节点都获得广播变量的相同值(例如,如果变量稍后被发送到新节点)。
Broadcast.scala类定义:
package org.apache.spark.broadcast import java.io.Serializable import scala.reflect.ClassTag import org.apache.spark.SparkException import org.apache.spark.internal.Logging import org.apache.spark.util.Utils /** * A broadcast variable. * 。。。。。。 * @param id A unique identifier for the broadcast variable. * @tparam T Type of the data contained in the broadcast variable. */ abstract class Broadcast[T: ClassTag](val id: Long) extends Serializable with Logging { /** * Flag signifying whether the broadcast variable is valid(that is, not already destroyed) or not. * 指示广播变量是否有效的标志(即,尚未销毁)或未销毁。 */ @volatile private var _isValid = true private var _destroySite = "" /** Get the broadcasted value. */ def value: T = { assertValid() getValue() } /** * Asynchronously delete cached copies of this broadcast on the executors. If the broadcast is used after this is called, it will need to be re-sent to each executor. * 异步删除执行器上此广播的缓存副本。如果在调用后使用广播,则需要将其重新发送给每个执行者。 */ def unpersist() { unpersist(blocking = false) } /** * Delete cached copies of this broadcast on the executors. If the broadcast is used after this is called, it will need to be re-sent to each executor. * 删除执行器上此广播的缓存副本。如果在调用后使用广播,则需要将其重新发送给每个执行者。 * @param blocking Whether to block until unpersisting has completed 是否阻止直到unpersist完成 */ def unpersist(blocking: Boolean) { assertValid() doUnpersist(blocking) } /** * Destroy all data and metadata related to this broadcast variable. Use this with caution; once a broadcast variable has been destroyed, it cannot be used again. This method blocks until destroy has completed * 销毁与此广播变量相关的所有数据和元数据。小心使用;广播变量一旦被销毁,就不能再使用。此方法在销毁完成之前阻止 */ def destroy() { destroy(blocking = true) } /** * Destroy all data and metadata related to this broadcast variable. Use this with caution; once a broadcast variable has been destroyed, it cannot be used again. * 销毁与此广播变量相关的所有数据和元数据。小心使用;广播变量一旦被销毁,就不能再使用。 * @param blocking Whether to block until destroy has completed 是否阻止直到销毁完成 */ private[spark] def destroy(blocking: Boolean) { assertValid() _isValid = false _destroySite = Utils.getCallSite().shortForm logInfo("Destroying %s (from %s)".format(toString, _destroySite)) doDestroy(blocking) } /** * Whether this Broadcast is actually usable. This should be false once persisted state is removed from the driver. * 广播变量是否实际可用。一旦持久化状态从driver中被移除将会返回false. */ private[spark] def isValid: Boolean = { _isValid } /** * Actually get the broadcasted value. Concrete implementations of Broadcast class must define their own way to get the value. * 实际获取广播值。广播类的具体实现必须定义自己的方法来获取值。 */ protected def getValue(): T /** * Actually unpersist the broadcasted value on the executors. Concrete implementations of Broadcast class must define their own logic to unpersist their own data. */ protected def doUnpersist(blocking: Boolean) /** * Actually destroy all data and metadata related to this broadcast variable. Implementation of Broadcast class must define their own logic to destroy their own state. */ protected def doDestroy(blocking: Boolean) /** Check if this broadcast is valid. If not valid, exception is thrown. */ protected def assertValid() { if (!_isValid) { throw new SparkException("Attempted to use %s after it was destroyed (%s) ".format(toString, _destroySite)) } } override def toString: String = "Broadcast(" + id + ")" }
其中隐含的概念:
1)broadcast的定义必须在Driver端,不能再executor端定义;
2)调用unpersist(),unpersist(boolean blocking),destroy(),distroy(boolean blocking)方法这些方法必须在driver端调用。
3)在Driver端可以修改广播变量的值,在Executor端无法修改广播变量的值。具体操作步骤:
a.在driver端调用unpersist(true)方法;
b.对该broadcast实例对象进行重新赋值。
参考《Spark2.2(三十三):Spark Streaming和Spark Structured Streaming更新broadcast总结(一)》、《Spark2.3(四十二):Spark Streaming和Spark Structured Streaming更新broadcast总结(二)》
Broadcast工作流程
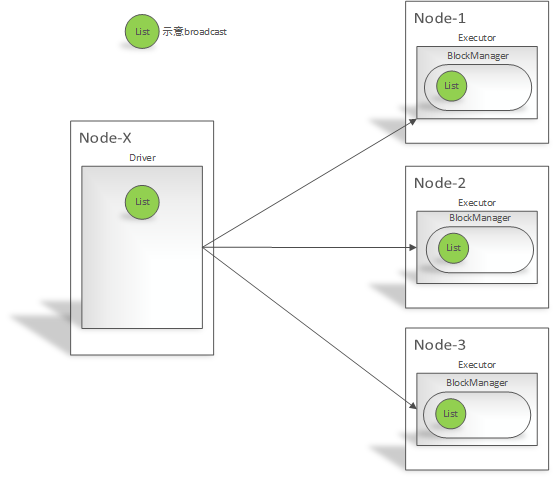
Broadcast使用时注意事项
注意事项
1、能不能将一个RDD使用广播变量广播出去?
不能,因为RDD是不存储数据的。可以将RDD的结果广播出去。
2、广播变量只能在Driver端定义,不能在Executor端定义。
3、在Driver端可以修改广播变量的值,在Executor端无法修改广播变量的值。
4、如果executor端用到了Driver的变量,如果不使用广播变量在Executor有多少task就有多少Driver端的变量副本。
5、如果Executor端用到了Driver的变量,如果使用广播变量在每个Executor中只有一份Driver端的变量副本。