上一篇讲解了web.xml如何使用编码的方式替换掉,但是一直没有写web.xml是如何被加载的相关细节,觉得十分有必要写一篇文章来梳理下。
Web应用部署初始化
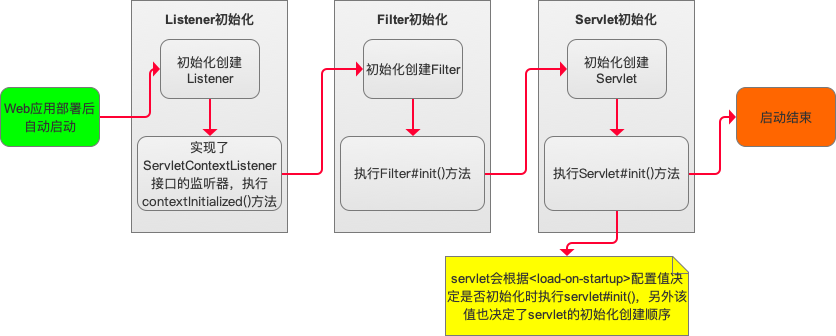
当一个web应用被部署到容器(tomcat等),tomcat系统启动过程中会执行以下处理:
1)部署描述文件(tomcat对应web.xml)中定义的(由<listener>元素标记的)事件监听器会被创建和初始化;
2)对于所有事件监听器,如果实现了ServletContextListener接口,将会执行#contextInitialized()方法;
3)部署描述文件中定义的(由<filter>元素标记的)过滤器会被创建和初始化,并调用#init()方法;
4)部署描述文件中定义的(由<servlet>元素标记的)servlet会根据<load-on-startup>的权重按顺序创建和初始化,并调用#init()方法。
备注:
1)<load-on-startup>权值如果设置为负整数,则不会在启动服务器时执行;包含>=0时,会在启动服务器时执行。
2)具体参考:《Java Servlet(十二):Servlet、Listener、Filter之间的执行流程分析》测试程序部署启动日志。
Web的初始化流程如下:
Tomcat初始化与处理Http请求
Tomcat初始化
Tomcat初始化解析Web.xml文件
要理清web.xml如何被加载、解析,需要从tomcat源码入手:
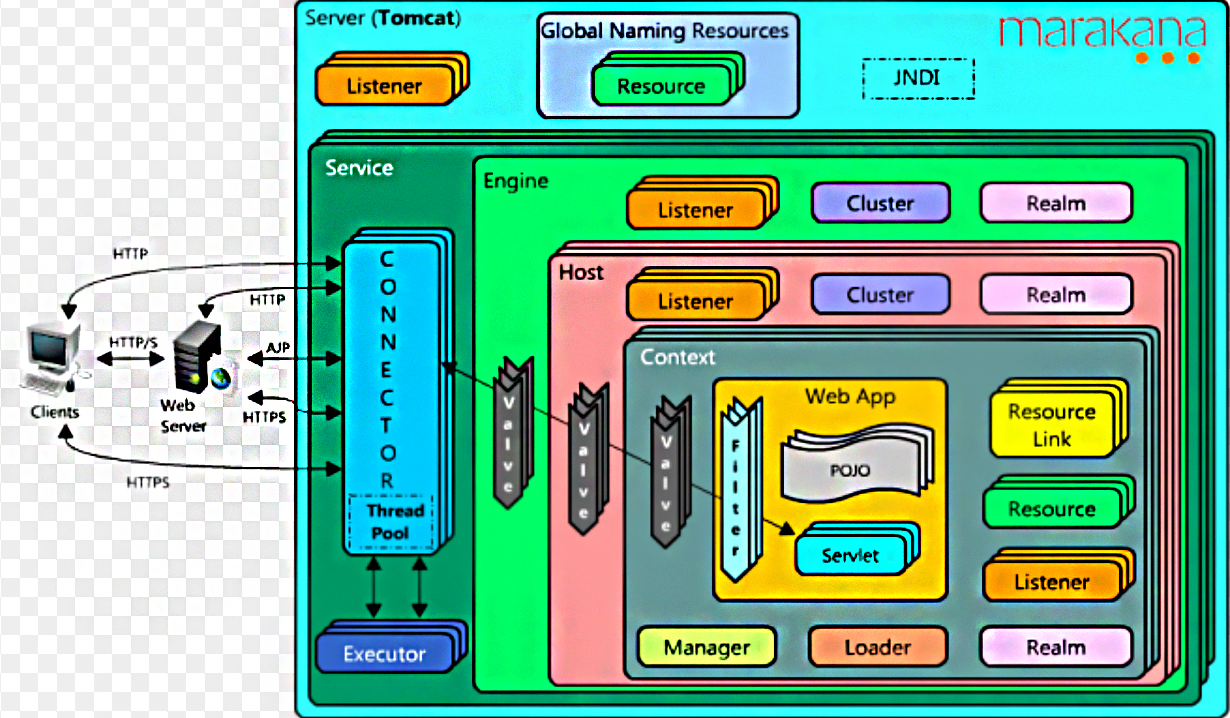
一个Tomcat中只有一个Server,一个Server可以包含多个Service,一个Service只有一个Container,但是可以有多个Connectors,这是因为一个服务可以有多个连接,如同时提供Http和Https链接,也可以提供向相同协议不同端口的连接。
在Container用于封装和管理Servlet,以及具体的处理Request请求,在Conatiner内部包含4个子容器:
1)Engine:引擎,用来管理多个站点,一个Servcie最多只能有一个Engine;
2)Host:代表一个站点,也可以叫虚拟主机,通过配置host就可以添加站点;
3)Context:代表一个应用程序,对应着平时开发的一套程序,或者一个WEB-INF目录以及下面的web.xml文件;
4)Wrapper:每一个Wrapper封装这一个Servlet。
Tomca的心脏是两个组件:Connector和Container(Engine,Host,Context,Wrapper)。一个Container可以选择多个Connecter,多个Connector和一个Container就形成了一个Service。Service可以对外提供服务,而Server服务器控制整个Tomcat的生命周期。
从上边分析可以知道Context是代表一个应程序,或者一个WEB-INF目录以及下边的web.xml文件,可以从它的作用上可以明白Context对web.xml的加载解析启动了特别重要的作用。Tomcat的启动流程:
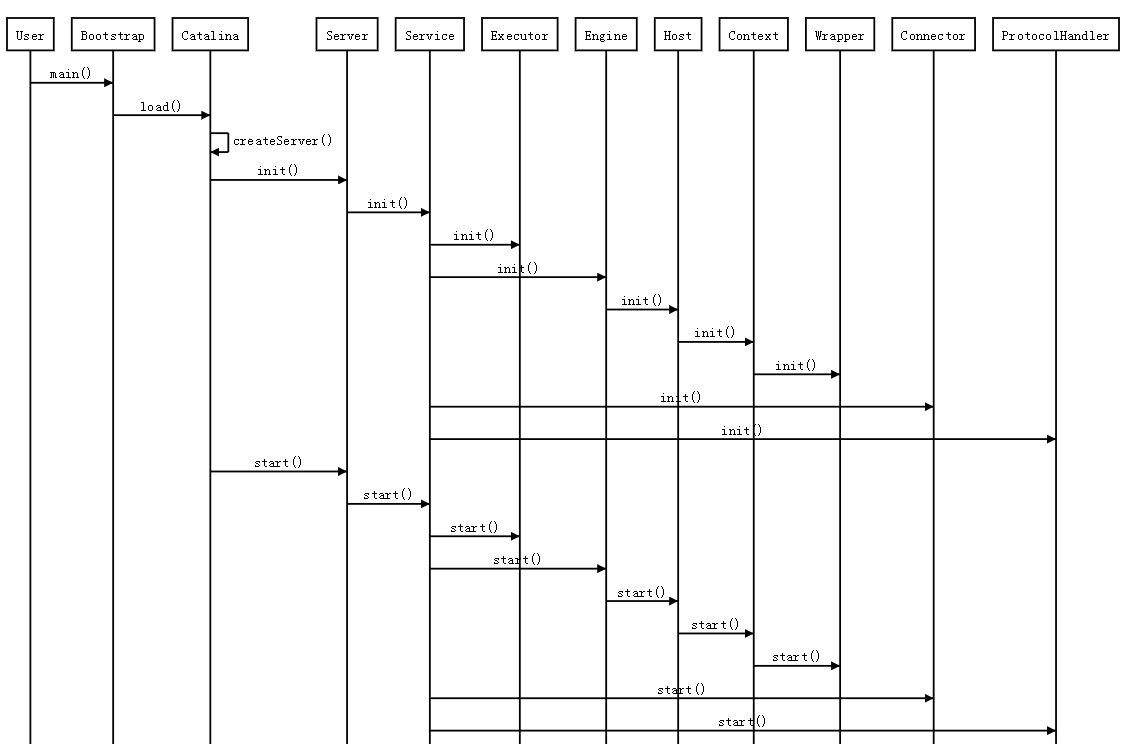
从上图可以知道Tomcat中启动过程中会调用Context的唯一实现类StandardContext的#init()和#start(),在这里Tomcat采用了模板设计模式,StandardContext中实际实现方法对应的是initInternal()和startInternal()。
StandardContext#startInternal()
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// 此处省略代码...
try {
if (ok) {
// 此处省略代码...
// 1)加载web.xml
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
fireLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
// 此处省略代码...
}
// 此处省略代码...
// 2)合并参数
// Set up the context init params
mergeParameters();
// 此处省略代码...
// 3)listener启动
// Configure and call application event listeners
if (ok) {
if (!listenerStart()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.listenerFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// 此处省略代码...
// 4)filter启动
// Configure and call application filters
if (ok) {
if (!filterStart()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.filterFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// 此处省略代码...
// 5)加载初始化servlet
// Load and initialize all "load on startup" servlets
if (ok) {
if (!loadOnStartup(findChildren())){
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.servletFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// 此处省略代码...
} finally {
// Unbinding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
}
// 此处省略代码...
}
1)调用fireLifecycleEvent()
发布一个"configure_start"
事件,在众多监听器中有一个ContextConfig监听器,在ContextConfig监听到"configure_start" 事件后,
会执行configureStart()方法;在configureStart()方法中执行webConfig()开始web.xml解析;值得一提的是webConfig中调用的两个方法:
ContextConfig#parseWebXml(contextWebXml, webXml, false)方法:
这个方法中有一个Digester工具,在Tomcat加载server.xml配置文件的时候就是使用了此工具,解析原理异曲同工。 此处使用WebRuleSet规则,将web.xml文件中的配置读取出来设置到webXml对象中去。
ContextConfig#configureContext(StandardContext context)方法:
将web.xml文件解析出来的各个组件设置到标准servlet上下文StandardContext中去。 其中就包括我们的filter ,servlet,listener。
2)mergeParameters
步骤1)中会将web.xml中的context-param元素设置到context的parameters里,此处则是把parameters设置到servletContext里。
3)启动listener
步骤1)中会将web.xml中的listener元素设置到context的applicationListeners里,此处则取出listener类名,创建实例,并将listener分为两类
eventlistener:ServletRequestAttributeListener、ServletRequestListener、HttpSessionIdListener、HttpSessionAttributeListener
lifecyclelistener:ServletContextListener、HttpSessionListener
对于ServletContextListener,会调用listener.contextInitialized(event),并触发实现了ServletContextListener接口实现类的beforeContextInitialized,afterContextInitialized方法。
4)启动filter
步骤1)中会将web.xml中的filter元素设置到filter的filterdef里,此处则会实例化filter设置到filterConfigs里。
5)启动servlet
步骤1)中会将web.xml中的servlet元素封装成wrapper并调用addChild方法设置到Context里,此处则会检查是否需要loadonstartup,如果需要则load。
更详细介绍请参考:《Tomcat(一):Tomcat启动时加载web.xml》
Tomcat处理Http请求
Tomcat处理Http请求过程流程图:
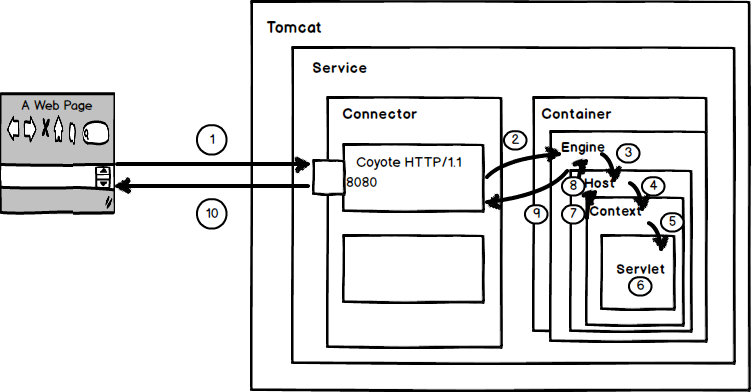
假设来自客户的请求为:http://localhost:8080/test/index.jsp 请求被发送到本机端口8080
1、用户点击网页内容,请求被发送到本机端口8080,被在那里监听的Coyote HTTP/1.1 Connector获得。
2、Connector把该请求交给它所在的Service的Engine来处理,并等待Engine的回应。
3、Engine获得请求localhost/test/index.jsp,匹配所有的虚拟主机Host。
4、Engine匹配到名为localhost的Host(即使匹配不到也把请求交给该Host处理,因为该Host被定义为该Engine的默认主机),名为localhost的Host获得请求/test/index.jsp,匹配它所拥有的所有的Context。Host匹配到路径为/test的Context(如果匹配不到就把该请求交给路径名为“
”的Context去处理)。
5、path=“/test”的Context获得请求/index.jsp,在它的mapping table中寻找出对应的Servlet。Context匹配到URL PATTERN为*.jsp的Servlet,对应于JspServlet类。
6、构造HttpServletRequest对象和HttpServletResponse对象,作为参数调用JspServlet的doGet()或doPost().执行业务逻辑、数据存储等程序。
7、Context把执行完之后的HttpServletResponse对象返回给Host。
8、Host把HttpServletResponse对象返回给Engine。
9、Engine把HttpServletResponse对象返回Connector。
10、Connector把HttpServletResponse对象返回给客户Browser。
Tomcat哪些组件参与了Http请求处理
Connector相关组件
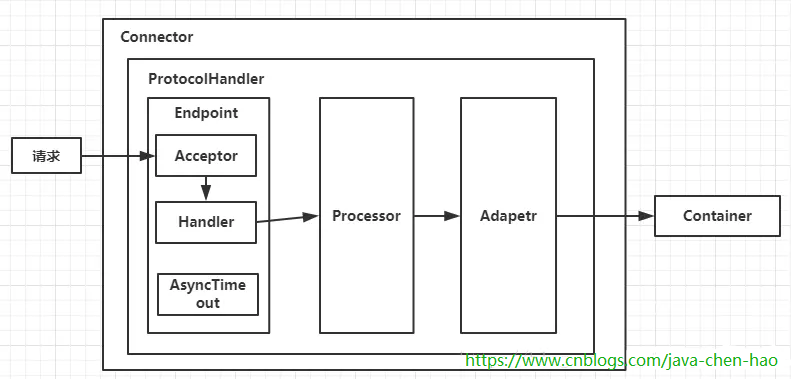
注意:不同的协议、不同的通信方式,ProtocolHandler会有不同的实现。在Tomcat8.5中,ProtocolHandler类的集成层级如下图所示:
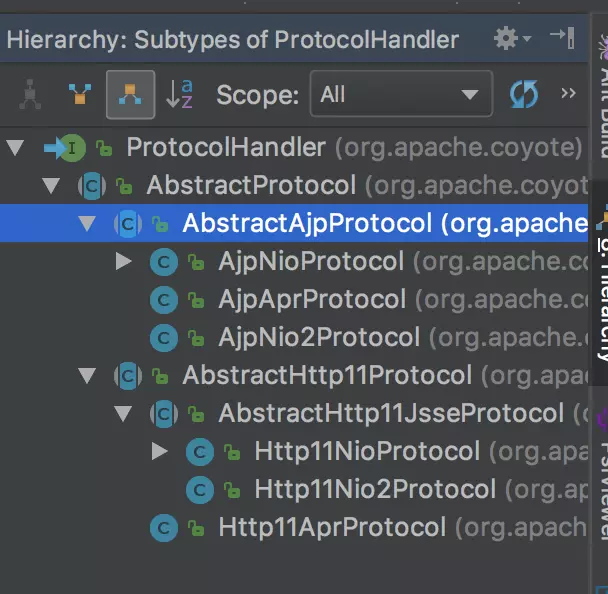
ProtocolHandler包含三个部件:Endpoint、Processor、Adapter。
1)Endpoint:用来处理底层Socket网络连接,因此Endpoint是用来实现TCP/IP协议的;Endpoint的抽象实现类AbstractEndpoint里面定义了Acceptor和AsyncTimeout两个内部类和一个Handler接口。
1.1)Acceptor:用于监听请求;
1.2)AsyncTimeout:用于检查异步Request的超时;
1.3)Handler:用于处理接收到的Socket,在内部调用Processor进行处理。

2)Processor:用来将Endpoint接收到Socket封装成Request,Precessor用来实现Http协议的;
3)Adapter:用来将Request交给Container进行具体处理,Adapter想请求适配到Servlet容器进行具体的处理。
CoyoteAdapter#service()
Adapter用于连接Connector和Container,起到承上启下的作用。Processor会调用Adapter.service()方法。
@Override public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res) throws Exception { Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); // 此处忽略代码 try { // Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific request parameters postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response); if (postParseSuccess) { //check valves if we support async request.setAsyncSupported( connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported()); // Calling the container connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke( request, response); } // 此处忽略代码 } catch (IOException e) { // Ignore } finally { // 此处忽略代码 } }
如果请求可以被传给容器的Pipeline即当postParseRequest方法返回true时,则由容器继续处理,在service方法中有connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response)这一行:
- Connector调用getService返回StandardService;
- StandardService调用getContainer返回StandardEngine;
- StandardEngine调用getPipeline返回与其关联的StandardPipeline;
接下来将会调用EnginePipeline#StandardEngineValve->HostPipeline#StandardHostValve->ContextPipeline#StandardContextValve->WrapperPipeline#StandardWrapperValve。
StandardWrapperValve#invoker(...)
/** * Invoke the servlet we are managing, respecting the rules regarding * servlet lifecycle and SingleThreadModel support. * * @param request Request to be processed * @param response Response to be produced * * @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred * @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred */ @Override public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { // 此处省略代码 StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper) getContainer(); Servlet servlet = null; Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent(); // 此处省略代码 // 分配一个servlet实例用来处理请求 // Allocate a servlet instance to process this request try { if (!unavailable) { // 调用StandardWrapper#allocate()方法,获取到servlet实例 servlet = wrapper.allocate(); } } catch (UnavailableException e) { // 此处省略代码 } catch (ServletException e) { // 此处省略代码 } catch (Throwable e) { // 此处省略代码 } // 此处省略代码 // 为当前请求创建一个过滤器链 // Create the filter chain for this request ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet); // 为当前请求调用过滤器链,注意:这也会调用servlet实例的service()方法 // Call the filter chain for this request // NOTE: This also calls the servlet's service() method try { if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) { // Swallow output if needed if (context.getSwallowOutput()) { try { SystemLogHandler.startCapture(); if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) { request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch(); } else { filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse()); } } finally { String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture(); if (log != null && log.length() > 0) { context.getLogger().info(log); } } } else { if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) { request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch(); } else { filterChain.doFilter (request.getRequest(), response.getResponse()); } } } } catch (ClientAbortException | CloseNowException e) { // 此处省略代码 } catch (IOException e) { // 此处省略代码 } catch (UnavailableException e) { // 此处省略代码 } catch (ServletException e) { // 此处省略代码 } catch (Throwable e) { // 此处省略代码 } finally { // 释放资源 // Release the filter chain (if any) for this request if (filterChain != null) { filterChain.release(); } // Deallocate the allocated servlet instance try { if (servlet != null) { wrapper.deallocate(servlet); } } catch (Throwable e) { // 此处省略代码 } // If this servlet has been marked permanently unavailable, // unload it and release this instance try { if ((servlet != null) && (wrapper.getAvailable() == Long.MAX_VALUE)) { wrapper.unload(); } } catch (Throwable e) { // 此处省略代码 } // 此处省略代码 } }
该StandardWrapperValve正是将Tomcat在处理Http请求过程中,真正调用filterChain(内部执行filter.doFilter())、调用servlet.service(...)代码的地方。
ApplicationFilterChain#doFilter(...)
/** * Invoke the next filter in this chain, passing the specified request * and response. If there are no more filters in this chain, invoke * the <code>service()</code> method of the servlet itself. * * @param request The servlet request we are processing * @param response The servlet response we are creating * * @exception IOException if an input/output error occurs * @exception ServletException if a servlet exception occurs */ @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws IOException, ServletException { if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) { final ServletRequest req = request; final ServletResponse res = response; try { java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged( new java.security.PrivilegedExceptionAction<Void>() { @Override public Void run() throws ServletException, IOException { internalDoFilter(req,res); return null; } } ); } catch( PrivilegedActionException pe) { // 此处省略代码; } } else { internalDoFilter(request,response); } } /** * 职责链模式调用filter#doFilter,并在调用最底层调用servlet.service(request,response)。 */ private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws IOException, ServletException { // Call the next filter if there is one if (pos < n) { ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = filters[pos++]; try { Filter filter = filterConfig.getFilter(); if (request.isAsyncSupported() && "false".equalsIgnoreCase( filterConfig.getFilterDef().getAsyncSupported())) { request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR, Boolean.FALSE); } if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) { final ServletRequest req = request; final ServletResponse res = response; Principal principal = ((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal(); Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res, this}; SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege ("doFilter", filter, classType, args, principal); } else { filter.doFilter(request, response, this); } } catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) { throw e; } catch (Throwable e) { // 此处省略代码 } return; } // We fell off the end of the chain -- call the servlet instance try { // 此处省略代码 // Use potentially wrapped request from this point if ((request instanceof HttpServletRequest) && (response instanceof HttpServletResponse) && Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) { final ServletRequest req = request; final ServletResponse res = response; Principal principal = ((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal(); Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res}; SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("service", servlet, classTypeUsedInService, args, principal); } else { servlet.service(request, response); } } catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) { throw e; } catch (Throwable e) { // 此处省略代码 } finally { // 此处省略代码 } }
采用职责链设计模式,在filter最深层调用servlet.service(request,response)。
在Spring+SpringMvc项目中,Tomcat处理Http请求时的流程图如下:
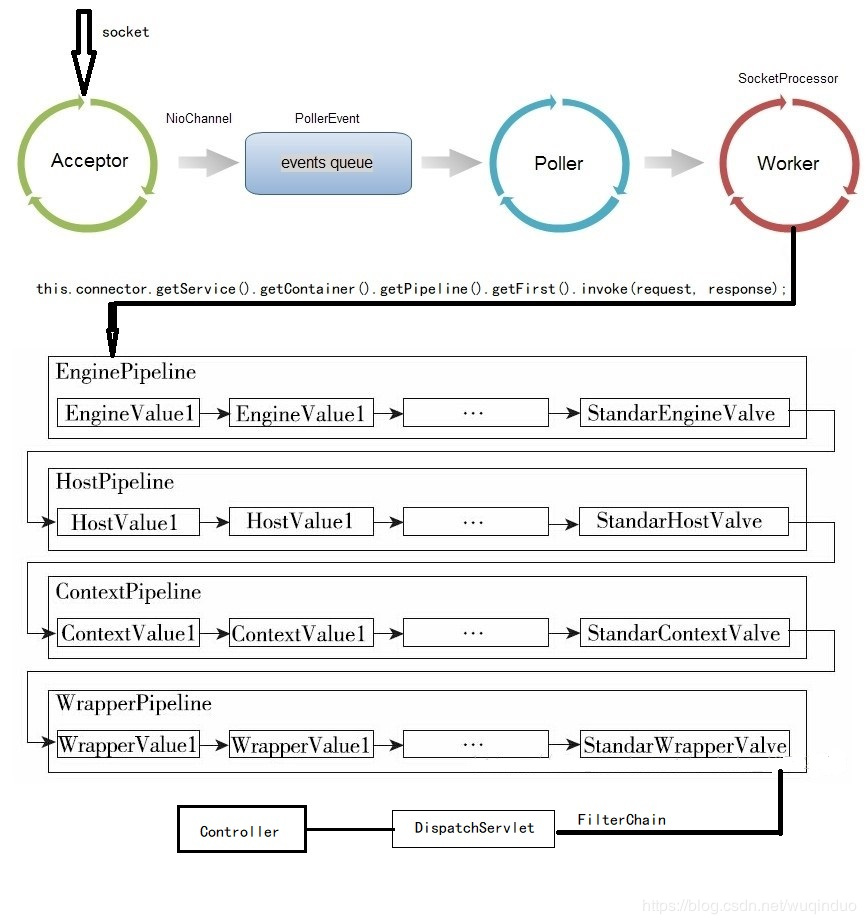
图片来自《Tomcat原理系列之二:由点到线,请求主干》
SpringMVC初始化流程
启动时需要加载部署描述文件(web.xml),我们本章的给出一个比较常见的web.xml为例,用它来分析SpringMVC的启动流程。
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" > <web-app> <display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>/index</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <!--加载dao/service/一些共享组件--> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value> classpath:applicationContext-base.xml, classpath:applicationContext-security.xml </param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.security.web.session.HttpSessionEventPublisher</listener-class> </listener> <filter> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>targetFilterLifecycle</param-name> <!-- 默认是false --> <param-value>false</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <filter> <filter-name>multipartFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.multipart.support.MultipartFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>multipartResolverBeanName</param-name> <param-value>multipartResolver</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>multipartFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <filter> <filter-name>hiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>methodParam</param-name> <param-value>_method</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>hiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <filter> <filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>forceEncoding</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <!--加载springmvc controller viewsolver 等--> <servlet> <servlet-name>spring-security-01</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring-security-01-servlet.xml</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>contextClass</param-name> <param-value>org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>spring-security-01</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
在Spring+SpringMVC项目被部署到tomcat容器,启动项目时会去加载web.xml配置文件,会根据web.xml配置内容去进行初始化。
Listener初始化
ContextLoaderListener实现了ServletContextListener,它本身就是一个listener,在Tomcat启动过程中web.xml加载后,StandardContext#startInternal()方法中调用的StandardContext#listenerStart()中执行的。
public boolean listenerStart() { ... for (int i = 0; i < instances.length; i++) { if (!(instances[i] instanceof ServletContextListener)) continue; ServletContextListener listener = (ServletContextListener) instances[i]; try { fireContainerEvent("beforeContextInitialized", listener); if (noPluggabilityListeners.contains(listener)) { listener.contextInitialized(tldEvent); } else { //执行listener的初始。传递ServletContextEvent参数 listener.contextInitialized(event);// } fireContainerEvent("afterContextInitialized", listener); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); fireContainerEvent("afterContextInitialized", listener); getLogger().error (sm.getString("standardContext.listenerStart", instances[i].getClass().getName()), t); ok = false; } } ... }
因为ContextLoaderListener实现ServletContextListener接口,因此上边调用ServletContextListener#contextInitialized(...)实现代码就是ContextLoaderListener#contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event)方法:
/** * Initialize the root web application context. 初始化web */ @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext()); }
initWebApplicationContext(...)是ContextLoader的方法(ContextLoaderListener不但实现了ServletContextListener接口,还继承了ContextLoader类),接下来查看ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext(...)源码:
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) { if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " + "check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!"); } servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext"); Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { // Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that // it is available on ServletContext shutdown. if (this.context == null) { this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext); } if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> // determine parent for root web application context, if any. ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext); cwac.setParent(parent); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext); } } servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context); ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) { currentContext = this.context; } else if (ccl != null) { currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context); } if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } return this.context; } catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) { logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex); throw ex; } }
上边代码核心方法包含两个:
1)ContextLoader#createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc):
createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc)方法用来创建WebApplicationContext实例:
/** * 返回WebApplicationContext的实现类,否则返回默认XmlWebApplicationContext或者通过开发者自定义. * 此实现要求自定义上下文实现ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口。可以在子类中重写。 * 此外,{#customizeContext}在刷新上下文之前被调用,从而允许子类对上下文执行自定义修改。 * @param sc 当前servlet上下文 * @return 根WebApplicationContext */ protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) { Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc); if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]"); } return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); }
ContextLoader#determineContextClass()方法:
/** * 返回WebApplicationContext的实现类,否则返回默认XmlWebApplicationContext或者通过开发者自定义. * @param servletContext 当前servlet上下文 * @return WebApplicationContext的实现类 */ protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) { String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);//"contextClass" if (contextClassName != null) { try { return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex); } } else { // 否则,读取ContextLoader.properties中配置的key=WebApplicationContetxt.class.getName()的value,这里返回XmlWebApplicationContext.class.getName() contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName()); try { return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex); } } }
ContextLoader#defaultStrategies属性:
/** * Name of the class path resource (relative to the ContextLoader class) * that defines ContextLoader's default strategy names. */ private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties"; private static final Properties defaultStrategies; static { // Load default strategy implementations from properties file. // This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized // by application developers. try { ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class); defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage()); } }
ContextLoader.properties是spring-web-5.2.0.RELEASE.jar中内的配置文件/org/springframework/web/context/ContextLoader.properties
# Default WebApplicationContext implementation class for ContextLoader. # Used as fallback when no explicit context implementation has been specified as context-param. # Not meant to be customized by application developers. org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
结合ContextLoader.properties中配置,可以得知ContextLoader#defaultStrategies属性值配置的值就是:{key=WebApplicationContext.class,value=XmlWebApplicationContext.class}。
2)ContextLoader#configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext):
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext)方法作用是‘配置’和‘刷新’WebApplicationContext:
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) { if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) { // The application context id is still set to its original default value // -> assign a more useful id based on available information String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM); if (idParam != null) { wac.setId(idParam); } else { // Generate default id... wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX + ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath())); } } wac.setServletContext(sc); String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM); if (configLocationParam != null) { wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam); } // The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context // is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for // use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment(); if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) { ((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null); } customizeContext(sc, wac); wac.refresh(); }
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam): CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM = "contextConfigLocation" 获取web.xml中<context-param>标签配置的全局变量,其中key为CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM,也就是我们配置的相应Bean的xml文件名,并将其放入到WebApplicationContext中
wac是一个接口类:我们知道ac的真正实现类是XmlWebApplicaitonContext,因此wac.refresh()调用就是XmlWebApplicationContext#refresh(),注意XmlWebApplcationContext的refresh()是定义在它的抽象父类接口类AbstractApplicationContext.java中。
下边看下AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()源码:
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
上边refresh()方法初始化bean,就是spring的著名的初始化方法refresh()。在Tomcat启动时,加载Spring+SpringMVC项目中web.xml定义的ContextLoaderListener,ContextLoaderListener实现ServletContextListener接口,继承ContextLoader加载器,进而把Tomcat与Spring连接到了一起。
Filter初始化
在监听器listener初始化完成后,按照文章开始的讲解,接下来会进行filter的初始化操作,filter的创建和初始化中没有涉及IoC容器的相关操作,因此不是本文讲解的重点,本文举例的filter是一个用于编码用户请求和响应的过滤器,采用utf-8编码用于适配中文。
关于Filter的在请求过程中与Servlet调用原理,请参考上边Tomcat处理Http请求过程。
Servlet(DispatcherServlet)初始化
上边在介绍Tomcat启动过程中解析web.xml时,讲到Servlet的初始化与调用核心代码,这里将主要针对启动这部分进一步介绍,关于调用部分不再阐述。
在Spring+SpringMVC项目中web.xml中servlet配置了DispatcherServlet,Tomcat在启动过程中DispatcherServlet就是一个普通的Servlet(DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet,FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean,HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet,HttpServlet extends GenericServlet,GenericServlet extends Servlet),从上边结合Tomcat加载启动web.xml过程可以知道StandardContext#startInternal()调用时,加载并初始化Servlet,调用的方法是StandardContext#loadOnStartup(...)。
/** * Load and initialize all servlets marked "load on startup" in the * web application deployment descriptor. * * @param children Array of wrappers for all currently defined * servlets (including those not declared load on startup) * @return <code>true</code> if load on startup was considered successful */ public boolean loadOnStartup(Container children[]) { // 1)收集到配置<load-on-startup>值大于等于0的servlet,后边回去初始化它们。 // Collect "load on startup" servlets that need to be initialized TreeMap<Integer, ArrayList<Wrapper>> map = new TreeMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) { Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) children[i]; int loadOnStartup = wrapper.getLoadOnStartup(); if (loadOnStartup < 0) continue; Integer key = Integer.valueOf(loadOnStartup); ArrayList<Wrapper> list = map.get(key); if (list == null) { list = new ArrayList<>(); map.put(key, list); } list.add(wrapper); } // 2)初始化<load-on-startup>值大于等于0的servlet,通过调用servlet.load()方法。 // Load the collected "load on startup" servlets for (ArrayList<Wrapper> list : map.values()) { for (Wrapper wrapper : list) { try { wrapper.load(); } catch (ServletException e) { getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardContext.loadOnStartup.loadException", getName(), wrapper.getName()), StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e)); // NOTE: load errors (including a servlet that throws // UnavailableException from the init() method) are NOT // fatal to application startup // unless failCtxIfServletStartFails="true" is specified if(getComputedFailCtxIfServletStartFails()) { return false; } } } } return true; }
Wrapper的实现类结构:
其中上边StandardContext#loadOnStartup(...)中调用的wrapper.load(),load()方法的实现就是StandardWrapper#load()。
@Override public synchronized void load() throws ServletException { instance = loadServlet(); if (!instanceInitialized) { initServlet(instance); } if (isJspServlet) { StringBuilder oname = new StringBuilder(getDomain()); oname.append(":type=JspMonitor"); oname.append(getWebModuleKeyProperties()); oname.append(",name="); oname.append(getName()); oname.append(getJ2EEKeyProperties()); try { jspMonitorON = new ObjectName(oname.toString()); Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(instance, jspMonitorON, null); } catch (Exception ex) { log.warn("Error registering JSP monitoring with jmx " + instance); } } }
主要代码:
1)loadServlet():加载Servlet类,并返回其实例对象;
2)initServlet():如果Servlet实例未初始化,则调用Servlet#init()方法初始化servlet。
public synchronized Servlet loadServlet() throws ServletException { // Nothing to do if we already have an instance or an instance pool if (!singleThreadModel && (instance != null)) return instance; PrintStream out = System.out; if (swallowOutput) { SystemLogHandler.startCapture(); } Servlet servlet; try { long t1=System.currentTimeMillis(); // Complain if no servlet class has been specified if (servletClass == null) { unavailable(null); throw new ServletException (sm.getString("standardWrapper.notClass", getName())); } InstanceManager instanceManager = ((StandardContext)getParent()).getInstanceManager(); try { servlet = (Servlet) instanceManager.newInstance(servletClass); } catch (ClassCastException e) { // 此处省略代码 } catch (Throwable e) { // 此处省略代码 } if (multipartConfigElement == null) { MultipartConfig annotation = servlet.getClass().getAnnotation(MultipartConfig.class); if (annotation != null) { multipartConfigElement = new MultipartConfigElement(annotation); } } // Special handling for ContainerServlet instances // Note: The InstanceManager checks if the application is permitted // to load ContainerServlets if (servlet instanceof ContainerServlet) { ((ContainerServlet) servlet).setWrapper(this); } classLoadTime=(int) (System.currentTimeMillis() -t1); if (servlet instanceof SingleThreadModel) { if (instancePool == null) { instancePool = new Stack<>(); } singleThreadModel = true; } initServlet(servlet); fireContainerEvent("load", this); loadTime=System.currentTimeMillis() -t1; } finally { // 此处省略代码 } return servlet; }
创建Servlet实例的方法是从Wrapper.loadServlet开始:
1)loadServlet方法要完成的就是获取servletClass,然后把它交给InstanceManager去创建一个基于servletClass.class的对象。如果这个Servlet配置了jsp-file,那么这个servletClass就是conf/web.xml中定义的JspServlet了。
2)调用initServlet(servlet),在initServlet(...)方法内部调用Servlet#init(),对servlet进行初始化。
3)触发Container load事件。
private synchronized void initServlet(Servlet servlet) throws ServletException { if (instanceInitialized && !singleThreadModel) return; // Call the initialization method of this servlet try { if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) { boolean success = false; try { Object[] args = new Object[] { facade }; SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("init", servlet, classType, args); success = true; } finally { if (!success) { // destroy() will not be called, thus clear the reference now SecurityUtil.remove(servlet); } } } else { servlet.init(facade); } instanceInitialized = true; } catch (UnavailableException f) { // 此处省略代码 } catch (ServletException f) { // 此处省略代码 } catch (Throwable f) { // 此处省略代码 } }
初始化Servlet在StandardWrapper的initServlet方法中,调用Servlet的init()方法,同时把包装了StandardWrapper对象的StandardWrapperFacade作为ServletConfig传给Servlet。
Servlet的初始化过程可以通过一张图来总结,如下所示:
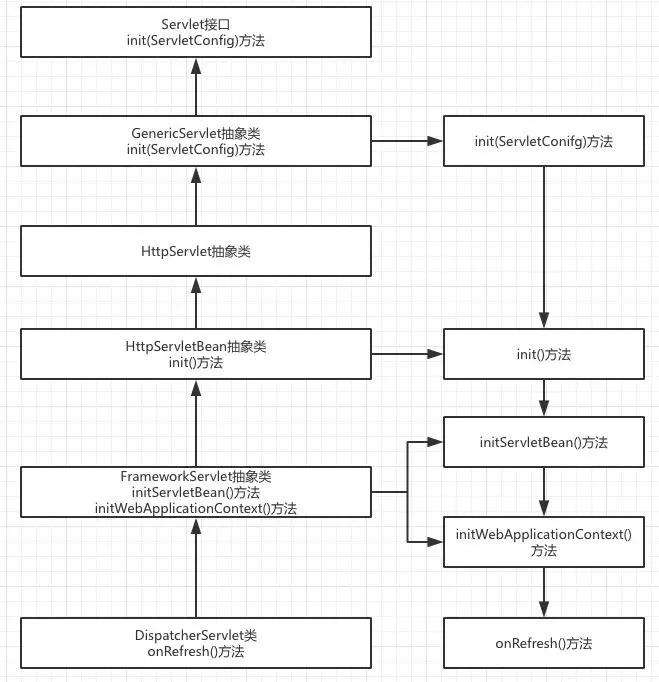
因此DispatcherServlet调用init时,实际上执行的是GenericServlet#init(ServletConfig config)
package javax.servlet; ... public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, java.io.Serializable { /** * Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet is being placed into service. See {@link Servlet#init}. * <p>This implementation stores the {@link ServletConfig} object it receives from the servlet container for later use. * When overriding this form of the method, call <code>super.init(config)</code>. * @param config the <code>ServletConfig</code> object that contains configutation information for this servlet * @exception ServletException if an exception occurs that interrupts the servlet's normal operation * @see UnavailableException */ public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { this.config = config; this.init(); } public void init() throws ServletException { } }
从GenericServlet#init(...)方法的实现上来看,它并未真正执行任何操作,因此我们继续查看GenericServlet的子类是如何实现servlet初始化操作。
package org.springframework.web.servlet; ... @SuppressWarnings("serial") public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware { /** * Map config parameters onto bean properties of this servlet, and invoke subclass initialization. * @throws ServletException if bean properties are invalid (or required properties are missing), or if subclass initialization fails. */ @Override public final void init() throws ServletException { // Set bean properties from init parameters. PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); if (!pvs.isEmpty()) { try { BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); initBeanWrapper(bw); bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) { logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex); } throw ex; } } // Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like. initServletBean(); } /** * Initialize the BeanWrapper for this HttpServletBean, possibly with custom editors. * <p>This default implementation is empty. * @param bw the BeanWrapper to initialize * @throws BeansException if thrown by BeanWrapper methods * @see org.springframework.beans.BeanWrapper#registerCustomEditor */ protected void initBeanWrapper(BeanWrapper bw) throws BeansException { } /** * Subclasses may override this to perform custom initialization. * All bean properties of this servlet will have been set before this method is invoked. * <p>This default implementation is empty. * @throws ServletException if subclass initialization fails */ protected void initServletBean() throws ServletException { } }
1)它将init-param等配置参数封装到BeanWrapper参数内,并调用HttpServletBase#initBeanWrapper(BeanWrapper bw)来进行实现Bean的包装初始化;
2)调用HttpServletBase#initServletBean()方法进进一步初始化Servlet bean。
但从initBeanWrapper(...)和initServletBean()方法定义不难发现,这里采用了模板方法设计模式,把真正的实现交给了子类去实现,那么我们不得不区分析它的子类如何去试下了。
在子类FrameworkServlet中对initServletBean()方法进行了重写,接下来我们来查看FrameworkServlet中如何重写initServletBean()方法。
package org.springframework.web.servlet; ... @SuppressWarnings("serial") public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware { /** * Overridden method of {@link HttpServletBean}, invoked after any bean properties have been set. Creates this servlet's WebApplicationContext. */ @Override protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { // 这里是重点,用于初始化子ApplicationContext对象,主要是用来加载<servlet/>对应的servletName-servlet.xml文件如:classpath:spring-security-01-servlet.xml this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); initFrameworkServlet(); } catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) { logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ? "shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" : "masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data"; logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails + "': request parameters and headers will be " + value); } if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms"); } } /** * This method will be invoked after any bean properties have been set and * the WebApplicationContext has been loaded. The default implementation is empty; * subclasses may override this method to perform any initialization they require. * @throws ServletException in case of an initialization exception */ protected void initFrameworkServlet() throws ServletException { } }
从上边代码可以发现初始化工作核心方法是 initWebApplicationContext()和initFrameworkServlet(),但是initFrameworkServlet()方法是一个空方法,因此猜测核心代码应该都在initWebApplicationContext()中实现,那么接着查看initWebApplicationContext()方法。
/** * Initialize and publish the WebApplicationContext for this servlet. * <p>Delegates to {@link #createWebApplicationContext} for actual creation of the context. Can be overridden in subclasses. * @return the WebApplicationContext instance * @see #FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext) * @see #setContextClass * @see #setContextConfigLocation */ protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { // 1)获取由ContextLoaderListener创建的根IoC容器 // 2)获取根IoC容器有两种方法,还可通过key直接获取 WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { // A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // 如果当前Servelt存在一个WebApplicationContext即子IoC容器, // 并且上文获取的根IoC容器存在,则将根IoC容器作为子IoC容器的父容器 // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set // the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null) { // 如果当前Servlet不存在一个子IoC容器则去查找一下 // No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one // has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed // that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the // user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } if (wac == null) { // 如果仍旧没有查找到子IoC容器则创建一个子IoC容器 // No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { // 调用子类DispatcherServlet覆盖的onRefresh方法完成“可变”的初始化过程 // Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh // support or the context injected at construction time had already been // refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here. synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) { onRefresh(wac); } } if (this.publishContext) { // Publish the context as a servlet context attribute. String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); } return wac; } /** * Template method which can be overridden to add servlet-specific refresh work. * Called after successful context refresh. * <p>This implementation is empty. * @param context the current WebApplicationContext * @see #refresh() */ protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { // For subclasses: do nothing by default. }
通过函数名不难发现,该方法的主要作用同样是创建一个WebApplicationContext对象,即Ioc容器每个Web应用最多只能存在一个根IoC容器,这里创建的则是特定Servlet拥有的子IoC容器。
如果当前Servlet存在一个IoC容器则为其设置根IoC容器作为其父类,并配置刷新该容器,用于构造其定义的Bean,这里的方法与前文讲述的根IoC容器类似,同样会读取用户在web.xml中配置的<servlet>中的<init-param>值,用于查找相关的xml配置文件用于构造定义的Bean,这里不再赘述了。如果当前Servlet不存在一个子IoC容器就去查找一个,如果仍然没有查找到则调用 createWebApplicationContext()方法去创建一个,查看该方法的源码如下图所示:
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) { Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass(); if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext"); } ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment()); wac.setParent(parent); String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation(); if (configLocation != null) { wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac); return wac; }
该方法用于创建一个子IoC容器并将根IoC容器做为其父容器,接着进行配置和刷新操作用于构造相关的Bean。至此,根IoC容器以及相关Servlet的子IoC容器已经配置完成,子容器中管理的Bean一般只被该Servlet使用,因此,其中管理的Bean一般是“局部”的,如SpringMVC中需要的各种重要组件,包括Controller、Interceptor、Converter、ExceptionResolver等。相关关系如下图所示:
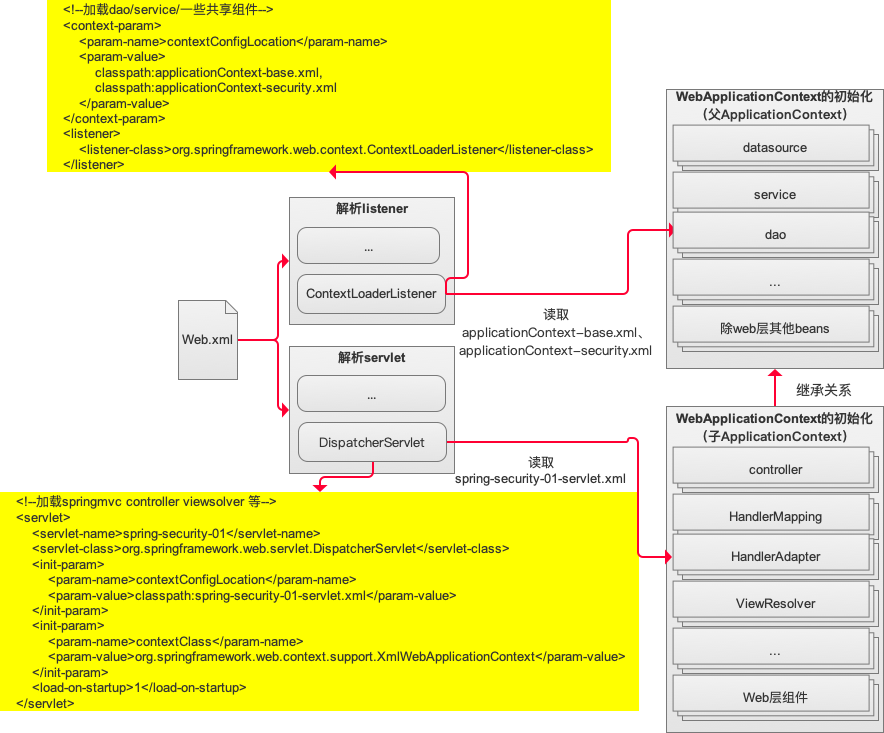
package org.springframework.web.servlet; ... @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet { ... /** * This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}. */ @Override protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); } /** * Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses. * <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects. */ protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); initHandlerMappings(context); initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); } ... }
onRefresh()方法直接调用了initStrategies()方法,源码如上,通过函数名可以判断,该方法用于初始化创建multipartResovle来支持图片等文件的上传、本地化解析器、主题解析器、HandlerMapping处理器映射器、HandlerAdapter处理器适配器、异常解析器、视图解析器、flashMap管理器等,这些组件都是SpringMVC开发中的重要组件,相关组件的初始化创建过程均在此完成。
父子容器
在学习Spring时,我们都是从读取xml配置文件来构造IoC容器,常用的类有ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类,该类存在一个初始化方法用于传入xml文件路径以及一个父容器,我们可以创建两个不同的xml配置文件并实现如下代码:
//applicationContext1.xml文件中配置一个id为baseBean的Bean //applicationContext2.xml文件中配置一个id未subBean的Bean public void testParentChhildrenIOC(){ ApplicationContext baseContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext1.xml"); Object obj1 = baseContext.getBean("baseBean"); System.out.println("baseContext Get Bean " + obj1); ApplicationContext subContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"applicationContext2.xml"}, baseContext); Object obj2 = subContext.getBean("baseBean"); System.out.println("subContext get baseContext Bean " + obj2); Object obj3 = subContext.getBean("subBean"); System.out.println("subContext get subContext Bean " + obj3); //抛出NoSuchBeanDefinitionException异常 Object obj4 = baseContext.getBean("subBean"); System.out.println("baseContext get subContext Bean " + obj4); }
1)首先创建baseContext没有为其设置父容器,接着可以成功获取id为baseBean的Bean;
2)接着创建subContext并将baseContext设置为其父容器,subContext可以成功获取baseBean以及subBean
3)最后试图使用baseContext去获取subContext中定义的subBean,此时会抛出异常NoSuchBeanDefinitionException。
由此可见,父子容器类似于类的继承关系,子类可以访问父类中的成员变量,而父类不可访问子类的成员变量,同样的,子容器可以访问父容器中定义的Bean,但父容器无法访问子容器定义的Bean。
参考
《第三章 DispatcherServlet详解 ——跟开涛学SpringMVC》
《SpringMvc之DispatcherServlet详解》
《Spring MVC入口Servlet详解(HttpServletBean,FrameworkServlet,DispatcherServlet )》