Spring MVC提供了以下几种途径输出模型数据:
1)ModelAndView:处理方法返回值类型为ModelAndView时,方法体即可通过该对象添加模型数据;
2)Map及Model:处理方法入参为org.springframework.ui.Model、org.springframework.ui.ModelMap或java.util.Map时,处理方法返回时,Map中的数据会自动被添加到模型中;
3)@SessionAttributes:将模型中的某个属性暂存到HttpSeession中,以便多个请求之间可以共享这个属性;
4)@ModelAttribute:方法入参标注该注解后,入参的对象就会放到数据模型中。
ModelAndView
用法示例:
添加TestModelAndView.java handler类:
package com.dx.springlearn.hanlders; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; @Controller public class TestModelData { private final String SUCCESS = "success"; @RequestMapping("/testModelAndView") public ModelAndView testModelAndView() { String viewName = SUCCESS; ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(viewName); modelAndView.addObject("currentTime", new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())); return modelAndView; } }
修改index.jsp,添加链接:
<a href="testModelAndView">test ModelAndView</a> <br />
修改/WEB-INF/views/success.jsp,编辑添加内容:
current time:${requestScope.currentTime} <br>
点击链接地址,显示结果:
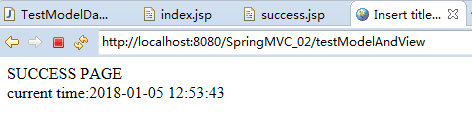
对TestModelAndView.java中“ modelAndView.addObject("currentTime", new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));”该行添加断点,进行调试:
根据调试信息,索引到DispatcherServlet的doDispatcher方法中:
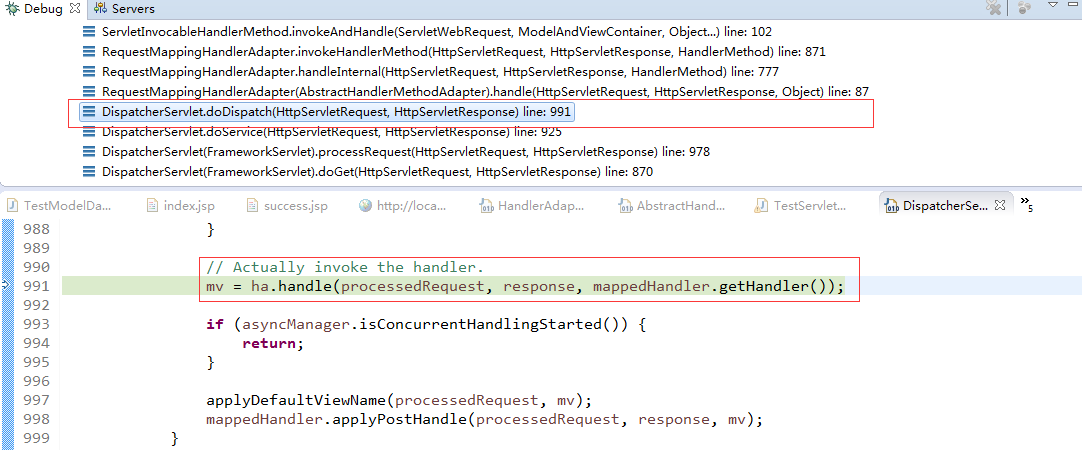
DispatcherServlet的doDispatcher方法源代码为:
1 /** 2 * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. 3 * <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order. 4 * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters 5 * to find the first that supports the handler class. 6 * <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers 7 * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. 8 * @param request current HTTP request 9 * @param response current HTTP response 10 * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure 11 */ 12 protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 13 HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; 14 HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; 15 boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; 16 17 WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); 18 19 try { 20 ModelAndView mv = null; 21 Exception dispatchException = null; 22 23 try { 24 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); 25 multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); 26 27 // Determine handler for the current request. 28 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); 29 if (mappedHandler == null) { 30 noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); 31 return; 32 } 33 34 // Determine handler adapter for the current request. 35 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); 36 37 // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. 38 String method = request.getMethod(); 39 boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); 40 if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { 41 long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 42 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 43 logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); 44 } 45 if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { 46 return; 47 } 48 } 49 50 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { 51 return; 52 } 53 54 // Actually invoke the handler. 55 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 56 57 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 58 return; 59 } 60 61 applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); 62 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); 63 } 64 catch (Exception ex) { 65 dispatchException = ex; 66 } 67 catch (Throwable err) { 68 // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, 69 // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. 70 dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); 71 } 72 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); 73 } 74 catch (Exception ex) { 75 triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); 76 } 77 catch (Throwable err) { 78 triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, 79 new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); 80 } 81 finally { 82 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 83 // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion 84 if (mappedHandler != null) { 85 mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); 86 } 87 } 88 else { 89 // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. 90 if (multipartRequestParsed) { 91 cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); 92 } 93 } 94 } 95 }
结合第20行和第55行,我们可以得知:不管SpringMVC的handler类方法返回值是ModelAndView、String,也不管SpringMVC的handler类方法的入参是Map、Model、MapModel等,在SpringMVC内部都会把请求返回结果封装为一个ModelAndView。
ModelAndView实际上内部存储结构就是一个Map<String,Object>,具体请查看ModelAndView源代码

1 /* 2 * Copyright 2002-2017 the original author or authors. 3 * 4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at 7 * 8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 9 * 10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 14 * limitations under the License. 15 */ 16 17 package org.springframework.web.servlet; 18 19 import java.util.Map; 20 21 import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; 22 import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; 23 import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap; 24 import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils; 25 26 /** 27 * Holder for both Model and View in the web MVC framework. 28 * Note that these are entirely distinct. This class merely holds 29 * both to make it possible for a controller to return both model 30 * and view in a single return value. 31 * 32 * <p>Represents a model and view returned by a handler, to be resolved 33 * by a DispatcherServlet. The view can take the form of a String 34 * view name which will need to be resolved by a ViewResolver object; 35 * alternatively a View object can be specified directly. The model 36 * is a Map, allowing the use of multiple objects keyed by name. 37 * 38 * @author Rod Johnson 39 * @author Juergen Hoeller 40 * @author Rob Harrop 41 * @author Rossen Stoyanchev 42 * @see DispatcherServlet 43 * @see ViewResolver 44 * @see HandlerAdapter#handle 45 * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller#handleRequest 46 */ 47 public class ModelAndView { 48 49 /** View instance or view name String */ 50 @Nullable 51 private Object view; 52 53 /** Model Map */ 54 @Nullable 55 private ModelMap model; 56 57 /** Optional HTTP status for the response */ 58 @Nullable 59 private HttpStatus status; 60 61 /** Indicates whether or not this instance has been cleared with a call to {@link #clear()} */ 62 private boolean cleared = false; 63 64 65 /** 66 * Default constructor for bean-style usage: populating bean 67 * properties instead of passing in constructor arguments. 68 * @see #setView(View) 69 * @see #setViewName(String) 70 */ 71 public ModelAndView() { 72 } 73 74 /** 75 * Convenient constructor when there is no model data to expose. 76 * Can also be used in conjunction with {@code addObject}. 77 * @param viewName name of the View to render, to be resolved 78 * by the DispatcherServlet's ViewResolver 79 * @see #addObject 80 */ 81 public ModelAndView(String viewName) { 82 this.view = viewName; 83 } 84 85 /** 86 * Convenient constructor when there is no model data to expose. 87 * Can also be used in conjunction with {@code addObject}. 88 * @param view View object to render 89 * @see #addObject 90 */ 91 public ModelAndView(View view) { 92 this.view = view; 93 } 94 95 /** 96 * Create a new ModelAndView given a view name and a model. 97 * @param viewName name of the View to render, to be resolved 98 * by the DispatcherServlet's ViewResolver 99 * @param model Map of model names (Strings) to model objects 100 * (Objects). Model entries may not be {@code null}, but the 101 * model Map may be {@code null} if there is no model data. 102 */ 103 public ModelAndView(String viewName, @Nullable Map<String, ?> model) { 104 this.view = viewName; 105 if (model != null) { 106 getModelMap().addAllAttributes(model); 107 } 108 } 109 110 /** 111 * Create a new ModelAndView given a View object and a model. 112 * <emphasis>Note: the supplied model data is copied into the internal 113 * storage of this class. You should not consider to modify the supplied 114 * Map after supplying it to this class</emphasis> 115 * @param view View object to render 116 * @param model Map of model names (Strings) to model objects 117 * (Objects). Model entries may not be {@code null}, but the 118 * model Map may be {@code null} if there is no model data. 119 */ 120 public ModelAndView(View view, @Nullable Map<String, ?> model) { 121 this.view = view; 122 if (model != null) { 123 getModelMap().addAllAttributes(model); 124 } 125 } 126 127 /** 128 * Create a new ModelAndView given a view name and HTTP status. 129 * @param viewName name of the View to render, to be resolved 130 * by the DispatcherServlet's ViewResolver 131 * @param status an HTTP status code to use for the response 132 * (to be set just prior to View rendering) 133 * @since 4.3.8 134 */ 135 public ModelAndView(String viewName, HttpStatus status) { 136 this.view = viewName; 137 this.status = status; 138 } 139 140 /** 141 * Create a new ModelAndView given a view name, model, and HTTP status. 142 * @param viewName name of the View to render, to be resolved 143 * by the DispatcherServlet's ViewResolver 144 * @param model Map of model names (Strings) to model objects 145 * (Objects). Model entries may not be {@code null}, but the 146 * model Map may be {@code null} if there is no model data. 147 * @param status an HTTP status code to use for the response 148 * (to be set just prior to View rendering) 149 * @since 4.3 150 */ 151 public ModelAndView(@Nullable String viewName, @Nullable Map<String, ?> model, @Nullable HttpStatus status) { 152 this.view = viewName; 153 if (model != null) { 154 getModelMap().addAllAttributes(model); 155 } 156 this.status = status; 157 } 158 159 /** 160 * Convenient constructor to take a single model object. 161 * @param viewName name of the View to render, to be resolved 162 * by the DispatcherServlet's ViewResolver 163 * @param modelName name of the single entry in the model 164 * @param modelObject the single model object 165 */ 166 public ModelAndView(String viewName, String modelName, Object modelObject) { 167 this.view = viewName; 168 addObject(modelName, modelObject); 169 } 170 171 /** 172 * Convenient constructor to take a single model object. 173 * @param view View object to render 174 * @param modelName name of the single entry in the model 175 * @param modelObject the single model object 176 */ 177 public ModelAndView(View view, String modelName, Object modelObject) { 178 this.view = view; 179 addObject(modelName, modelObject); 180 } 181 182 183 /** 184 * Set a view name for this ModelAndView, to be resolved by the 185 * DispatcherServlet via a ViewResolver. Will override any 186 * pre-existing view name or View. 187 */ 188 public void setViewName(@Nullable String viewName) { 189 this.view = viewName; 190 } 191 192 /** 193 * Return the view name to be resolved by the DispatcherServlet 194 * via a ViewResolver, or {@code null} if we are using a View object. 195 */ 196 @Nullable 197 public String getViewName() { 198 return (this.view instanceof String ? (String) this.view : null); 199 } 200 201 /** 202 * Set a View object for this ModelAndView. Will override any 203 * pre-existing view name or View. 204 */ 205 public void setView(@Nullable View view) { 206 this.view = view; 207 } 208 209 /** 210 * Return the View object, or {@code null} if we are using a view name 211 * to be resolved by the DispatcherServlet via a ViewResolver. 212 */ 213 @Nullable 214 public View getView() { 215 return (this.view instanceof View ? (View) this.view : null); 216 } 217 218 /** 219 * Indicate whether or not this {@code ModelAndView} has a view, either 220 * as a view name or as a direct {@link View} instance. 221 */ 222 public boolean hasView() { 223 return (this.view != null); 224 } 225 226 /** 227 * Return whether we use a view reference, i.e. {@code true} 228 * if the view has been specified via a name to be resolved by the 229 * DispatcherServlet via a ViewResolver. 230 */ 231 public boolean isReference() { 232 return (this.view instanceof String); 233 } 234 235 /** 236 * Return the model map. May return {@code null}. 237 * Called by DispatcherServlet for evaluation of the model. 238 */ 239 @Nullable 240 protected Map<String, Object> getModelInternal() { 241 return this.model; 242 } 243 244 /** 245 * Return the underlying {@code ModelMap} instance (never {@code null}). 246 */ 247 public ModelMap getModelMap() { 248 if (this.model == null) { 249 this.model = new ModelMap(); 250 } 251 return this.model; 252 } 253 254 /** 255 * Return the model map. Never returns {@code null}. 256 * To be called by application code for modifying the model. 257 */ 258 public Map<String, Object> getModel() { 259 return getModelMap(); 260 } 261 262 /** 263 * Set the HTTP status to use for the response. 264 * <p>The response status is set just prior to View rendering. 265 * @since 4.3 266 */ 267 public void setStatus(@Nullable HttpStatus status) { 268 this.status = status; 269 } 270 271 /** 272 * Return the configured HTTP status for the response, if any. 273 * @since 4.3 274 */ 275 @Nullable 276 public HttpStatus getStatus() { 277 return this.status; 278 } 279 280 281 /** 282 * Add an attribute to the model. 283 * @param attributeName name of the object to add to the model 284 * @param attributeValue object to add to the model (never {@code null}) 285 * @see ModelMap#addAttribute(String, Object) 286 * @see #getModelMap() 287 */ 288 public ModelAndView addObject(String attributeName, Object attributeValue) { 289 getModelMap().addAttribute(attributeName, attributeValue); 290 return this; 291 } 292 293 /** 294 * Add an attribute to the model using parameter name generation. 295 * @param attributeValue the object to add to the model (never {@code null}) 296 * @see ModelMap#addAttribute(Object) 297 * @see #getModelMap() 298 */ 299 public ModelAndView addObject(Object attributeValue) { 300 getModelMap().addAttribute(attributeValue); 301 return this; 302 } 303 304 /** 305 * Add all attributes contained in the provided Map to the model. 306 * @param modelMap a Map of attributeName -> attributeValue pairs 307 * @see ModelMap#addAllAttributes(Map) 308 * @see #getModelMap() 309 */ 310 public ModelAndView addAllObjects(@Nullable Map<String, ?> modelMap) { 311 getModelMap().addAllAttributes(modelMap); 312 return this; 313 } 314 315 316 /** 317 * Clear the state of this ModelAndView object. 318 * The object will be empty afterwards. 319 * <p>Can be used to suppress rendering of a given ModelAndView object 320 * in the {@code postHandle} method of a HandlerInterceptor. 321 * @see #isEmpty() 322 * @see HandlerInterceptor#postHandle 323 */ 324 public void clear() { 325 this.view = null; 326 this.model = null; 327 this.cleared = true; 328 } 329 330 /** 331 * Return whether this ModelAndView object is empty, 332 * i.e. whether it does not hold any view and does not contain a model. 333 */ 334 public boolean isEmpty() { 335 return (this.view == null && CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.model)); 336 } 337 338 /** 339 * Return whether this ModelAndView object is empty as a result of a call to {@link #clear} 340 * i.e. whether it does not hold any view and does not contain a model. 341 * <p>Returns {@code false} if any additional state was added to the instance 342 * <strong>after</strong> the call to {@link #clear}. 343 * @see #clear() 344 */ 345 public boolean wasCleared() { 346 return (this.cleared && isEmpty()); 347 } 348 349 350 /** 351 * Return diagnostic information about this model and view. 352 */ 353 @Override 354 public String toString() { 355 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("ModelAndView: "); 356 if (isReference()) { 357 sb.append("reference to view with name '").append(this.view).append("'"); 358 } 359 else { 360 sb.append("materialized View is [").append(this.view).append(']'); 361 } 362 sb.append("; model is ").append(this.model); 363 return sb.toString(); 364 } 365 366 }
、ModelMap源代码

1 /* 2 * Copyright 2002-2017 the original author or authors. 3 * 4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at 7 * 8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 9 * 10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 14 * limitations under the License. 15 */ 16 17 package org.springframework.ui; 18 19 import java.util.Collection; 20 import java.util.LinkedHashMap; 21 import java.util.Map; 22 23 import org.springframework.core.Conventions; 24 import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; 25 import org.springframework.util.Assert; 26 27 /** 28 * Implementation of {@link java.util.Map} for use when building model data for use 29 * with UI tools. Supports chained calls and generation of model attribute names. 30 * 31 * <p>This class serves as generic model holder for Servlet MVC but is not tied to it. 32 * Check out the {@link Model} interface for an interface variant. 33 * 34 * @author Rob Harrop 35 * @author Juergen Hoeller 36 * @since 2.0 37 * @see Conventions#getVariableName 38 * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView 39 */ 40 @SuppressWarnings("serial") 41 public class ModelMap extends LinkedHashMap<String, Object> { 42 43 /** 44 * Construct a new, empty {@code ModelMap}. 45 */ 46 public ModelMap() { 47 } 48 49 /** 50 * Construct a new {@code ModelMap} containing the supplied attribute 51 * under the supplied name. 52 * @see #addAttribute(String, Object) 53 */ 54 public ModelMap(String attributeName, Object attributeValue) { 55 addAttribute(attributeName, attributeValue); 56 } 57 58 /** 59 * Construct a new {@code ModelMap} containing the supplied attribute. 60 * Uses attribute name generation to generate the key for the supplied model 61 * object. 62 * @see #addAttribute(Object) 63 */ 64 public ModelMap(Object attributeValue) { 65 addAttribute(attributeValue); 66 } 67 68 69 /** 70 * Add the supplied attribute under the supplied name. 71 * @param attributeName the name of the model attribute (never {@code null}) 72 * @param attributeValue the model attribute value (can be {@code null}) 73 */ 74 public ModelMap addAttribute(String attributeName, @Nullable Object attributeValue) { 75 Assert.notNull(attributeName, "Model attribute name must not be null"); 76 put(attributeName, attributeValue); 77 return this; 78 } 79 80 /** 81 * Add the supplied attribute to this {@code Map} using a 82 * {@link org.springframework.core.Conventions#getVariableName generated name}. 83 * <p><emphasis>Note: Empty {@link Collection Collections} are not added to 84 * the model when using this method because we cannot correctly determine 85 * the true convention name. View code should check for {@code null} rather 86 * than for empty collections as is already done by JSTL tags.</emphasis> 87 * @param attributeValue the model attribute value (never {@code null}) 88 */ 89 public ModelMap addAttribute(Object attributeValue) { 90 Assert.notNull(attributeValue, "Model object must not be null"); 91 if (attributeValue instanceof Collection && ((Collection<?>) attributeValue).isEmpty()) { 92 return this; 93 } 94 return addAttribute(Conventions.getVariableName(attributeValue), attributeValue); 95 } 96 97 /** 98 * Copy all attributes in the supplied {@code Collection} into this 99 * {@code Map}, using attribute name generation for each element. 100 * @see #addAttribute(Object) 101 */ 102 public ModelMap addAllAttributes(@Nullable Collection<?> attributeValues) { 103 if (attributeValues != null) { 104 for (Object attributeValue : attributeValues) { 105 addAttribute(attributeValue); 106 } 107 } 108 return this; 109 } 110 111 /** 112 * Copy all attributes in the supplied {@code Map} into this {@code Map}. 113 * @see #addAttribute(String, Object) 114 */ 115 public ModelMap addAllAttributes(@Nullable Map<String, ?> attributes) { 116 if (attributes != null) { 117 putAll(attributes); 118 } 119 return this; 120 } 121 122 /** 123 * Copy all attributes in the supplied {@code Map} into this {@code Map}, 124 * with existing objects of the same name taking precedence (i.e. not getting 125 * replaced). 126 */ 127 public ModelMap mergeAttributes(@Nullable Map<String, ?> attributes) { 128 if (attributes != null) { 129 attributes.forEach((key, value) -> { 130 if (!containsKey(key)) { 131 put(key, value); 132 } 133 }); 134 } 135 return this; 136 } 137 138 /** 139 * Does this model contain an attribute of the given name? 140 * @param attributeName the name of the model attribute (never {@code null}) 141 * @return whether this model contains a corresponding attribute 142 */ 143 public boolean containsAttribute(String attributeName) { 144 return containsKey(attributeName); 145 } 146 147 }
、LinkedHashMap源代码

1 /* 2 * Copyright (c) 1997, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. 3 * ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms. 4 * 5 * 6 * 7 * 8 * 9 * 10 * 11 * 12 * 13 * 14 * 15 * 16 * 17 * 18 * 19 * 20 * 21 * 22 * 23 * 24 */ 25 26 package java.util; 27 28 import java.util.function.Consumer; 29 import java.util.function.BiConsumer; 30 import java.util.function.BiFunction; 31 import java.io.IOException; 32 33 /** 34 * <p>Hash table and linked list implementation of the <tt>Map</tt> interface, 35 * with predictable iteration order. This implementation differs from 36 * <tt>HashMap</tt> in that it maintains a doubly-linked list running through 37 * all of its entries. This linked list defines the iteration ordering, 38 * which is normally the order in which keys were inserted into the map 39 * (<i>insertion-order</i>). Note that insertion order is not affected 40 * if a key is <i>re-inserted</i> into the map. (A key <tt>k</tt> is 41 * reinserted into a map <tt>m</tt> if <tt>m.put(k, v)</tt> is invoked when 42 * <tt>m.containsKey(k)</tt> would return <tt>true</tt> immediately prior to 43 * the invocation.) 44 * 45 * <p>This implementation spares its clients from the unspecified, generally 46 * chaotic ordering provided by {@link HashMap} (and {@link Hashtable}), 47 * without incurring the increased cost associated with {@link TreeMap}. It 48 * can be used to produce a copy of a map that has the same order as the 49 * original, regardless of the original map's implementation: 50 * <pre> 51 * void foo(Map m) { 52 * Map copy = new LinkedHashMap(m); 53 * ... 54 * } 55 * </pre> 56 * This technique is particularly useful if a module takes a map on input, 57 * copies it, and later returns results whose order is determined by that of 58 * the copy. (Clients generally appreciate having things returned in the same 59 * order they were presented.) 60 * 61 * <p>A special {@link #LinkedHashMap(int,float,boolean) constructor} is 62 * provided to create a linked hash map whose order of iteration is the order 63 * in which its entries were last accessed, from least-recently accessed to 64 * most-recently (<i>access-order</i>). This kind of map is well-suited to 65 * building LRU caches. Invoking the {@code put}, {@code putIfAbsent}, 66 * {@code get}, {@code getOrDefault}, {@code compute}, {@code computeIfAbsent}, 67 * {@code computeIfPresent}, or {@code merge} methods results 68 * in an access to the corresponding entry (assuming it exists after the 69 * invocation completes). The {@code replace} methods only result in an access 70 * of the entry if the value is replaced. The {@code putAll} method generates one 71 * entry access for each mapping in the specified map, in the order that 72 * key-value mappings are provided by the specified map's entry set iterator. 73 * <i>No other methods generate entry accesses.</i> In particular, operations 74 * on collection-views do <i>not</i> affect the order of iteration of the 75 * backing map. 76 * 77 * <p>The {@link #removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry)} method may be overridden to 78 * impose a policy for removing stale mappings automatically when new mappings 79 * are added to the map. 80 * 81 * <p>This class provides all of the optional <tt>Map</tt> operations, and 82 * permits null elements. Like <tt>HashMap</tt>, it provides constant-time 83 * performance for the basic operations (<tt>add</tt>, <tt>contains</tt> and 84 * <tt>remove</tt>), assuming the hash function disperses elements 85 * properly among the buckets. Performance is likely to be just slightly 86 * below that of <tt>HashMap</tt>, due to the added expense of maintaining the 87 * linked list, with one exception: Iteration over the collection-views 88 * of a <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> requires time proportional to the <i>size</i> 89 * of the map, regardless of its capacity. Iteration over a <tt>HashMap</tt> 90 * is likely to be more expensive, requiring time proportional to its 91 * <i>capacity</i>. 92 * 93 * <p>A linked hash map has two parameters that affect its performance: 94 * <i>initial capacity</i> and <i>load factor</i>. They are defined precisely 95 * as for <tt>HashMap</tt>. Note, however, that the penalty for choosing an 96 * excessively high value for initial capacity is less severe for this class 97 * than for <tt>HashMap</tt>, as iteration times for this class are unaffected 98 * by capacity. 99 * 100 * <p><strong>Note that this implementation is not synchronized.</strong> 101 * If multiple threads access a linked hash map concurrently, and at least 102 * one of the threads modifies the map structurally, it <em>must</em> be 103 * synchronized externally. This is typically accomplished by 104 * synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the map. 105 * 106 * If no such object exists, the map should be "wrapped" using the 107 * {@link Collections#synchronizedMap Collections.synchronizedMap} 108 * method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental 109 * unsynchronized access to the map:<pre> 110 * Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new LinkedHashMap(...));</pre> 111 * 112 * A structural modification is any operation that adds or deletes one or more 113 * mappings or, in the case of access-ordered linked hash maps, affects 114 * iteration order. In insertion-ordered linked hash maps, merely changing 115 * the value associated with a key that is already contained in the map is not 116 * a structural modification. <strong>In access-ordered linked hash maps, 117 * merely querying the map with <tt>get</tt> is a structural modification. 118 * </strong>) 119 * 120 * <p>The iterators returned by the <tt>iterator</tt> method of the collections 121 * returned by all of this class's collection view methods are 122 * <em>fail-fast</em>: if the map is structurally modified at any time after 123 * the iterator is created, in any way except through the iterator's own 124 * <tt>remove</tt> method, the iterator will throw a {@link 125 * ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of concurrent 126 * modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than risking 127 * arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined time in the future. 128 * 129 * <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed 130 * as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the 131 * presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators 132 * throw <tt>ConcurrentModificationException</tt> on a best-effort basis. 133 * Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this 134 * exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators 135 * should be used only to detect bugs.</i> 136 * 137 * <p>The spliterators returned by the spliterator method of the collections 138 * returned by all of this class's collection view methods are 139 * <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em>, 140 * <em>fail-fast</em>, and additionally report {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}. 141 * 142 * <p>This class is a member of the 143 * <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html"> 144 * Java Collections Framework</a>. 145 * 146 * @implNote 147 * The spliterators returned by the spliterator method of the collections 148 * returned by all of this class's collection view methods are created from 149 * the iterators of the corresponding collections. 150 * 151 * @param <K> the type of keys maintained by this map 152 * @param <V> the type of mapped values 153 * 154 * @author Josh Bloch 155 * @see Object#hashCode() 156 * @see Collection 157 * @see Map 158 * @see HashMap 159 * @see TreeMap 160 * @see Hashtable 161 * @since 1.4 162 */ 163 public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> 164 extends HashMap<K,V> 165 implements Map<K,V> 166 { 167 168 /* 169 * Implementation note. A previous version of this class was 170 * internally structured a little differently. Because superclass 171 * HashMap now uses trees for some of its nodes, class 172 * LinkedHashMap.Entry is now treated as intermediary node class 173 * that can also be converted to tree form. The name of this 174 * class, LinkedHashMap.Entry, is confusing in several ways in its 175 * current context, but cannot be changed. Otherwise, even though 176 * it is not exported outside this package, some existing source 177 * code is known to have relied on a symbol resolution corner case 178 * rule in calls to removeEldestEntry that suppressed compilation 179 * errors due to ambiguous usages. So, we keep the name to 180 * preserve unmodified compilability. 181 * 182 * The changes in node classes also require using two fields 183 * (head, tail) rather than a pointer to a header node to maintain 184 * the doubly-linked before/after list. This class also 185 * previously used a different style of callback methods upon 186 * access, insertion, and removal. 187 */ 188 189 /** 190 * HashMap.Node subclass for normal LinkedHashMap entries. 191 */ 192 static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> { 193 Entry<K,V> before, after; 194 Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { 195 super(hash, key, value, next); 196 } 197 } 198 199 private static final long serialVersionUID = 3801124242820219131L; 200 201 /** 202 * The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list. 203 */ 204 transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head; 205 206 /** 207 * The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list. 208 */ 209 transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail; 210 211 /** 212 * The iteration ordering method for this linked hash map: <tt>true</tt> 213 * for access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order. 214 * 215 * @serial 216 */ 217 final boolean accessOrder; 218 219 // internal utilities 220 221 // link at the end of list 222 private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) { 223 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail; 224 tail = p; 225 if (last == null) 226 head = p; 227 else { 228 p.before = last; 229 last.after = p; 230 } 231 } 232 233 // apply src's links to dst 234 private void transferLinks(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> src, 235 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> dst) { 236 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> b = dst.before = src.before; 237 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> a = dst.after = src.after; 238 if (b == null) 239 head = dst; 240 else 241 b.after = dst; 242 if (a == null) 243 tail = dst; 244 else 245 a.before = dst; 246 } 247 248 // overrides of HashMap hook methods 249 250 void reinitialize() { 251 super.reinitialize(); 252 head = tail = null; 253 } 254 255 Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) { 256 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = 257 new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e); 258 linkNodeLast(p); 259 return p; 260 } 261 262 Node<K,V> replacementNode(Node<K,V> p, Node<K,V> next) { 263 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> q = (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)p; 264 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> t = 265 new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(q.hash, q.key, q.value, next); 266 transferLinks(q, t); 267 return t; 268 } 269 270 TreeNode<K,V> newTreeNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { 271 TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>(hash, key, value, next); 272 linkNodeLast(p); 273 return p; 274 } 275 276 TreeNode<K,V> replacementTreeNode(Node<K,V> p, Node<K,V> next) { 277 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> q = (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)p; 278 TreeNode<K,V> t = new TreeNode<K,V>(q.hash, q.key, q.value, next); 279 transferLinks(q, t); 280 return t; 281 } 282 283 void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> e) { // unlink 284 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = 285 (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after; 286 p.before = p.after = null; 287 if (b == null) 288 head = a; 289 else 290 b.after = a; 291 if (a == null) 292 tail = b; 293 else 294 a.before = b; 295 } 296 297 void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest 298 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first; 299 if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) { 300 K key = first.key; 301 removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true); 302 } 303 } 304 305 void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last 306 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last; 307 if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) { 308 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = 309 (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after; 310 p.after = null; 311 if (b == null) 312 head = a; 313 else 314 b.after = a; 315 if (a != null) 316 a.before = b; 317 else 318 last = b; 319 if (last == null) 320 head = p; 321 else { 322 p.before = last; 323 last.after = p; 324 } 325 tail = p; 326 ++modCount; 327 } 328 } 329 330 void internalWriteEntries(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException { 331 for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) { 332 s.writeObject(e.key); 333 s.writeObject(e.value); 334 } 335 } 336 337 /** 338 * Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance 339 * with the specified initial capacity and load factor. 340 * 341 * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity 342 * @param loadFactor the load factor 343 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative 344 * or the load factor is nonpositive 345 */ 346 public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { 347 super(initialCapacity, loadFactor); 348 accessOrder = false; 349 } 350 351 /** 352 * Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance 353 * with the specified initial capacity and a default load factor (0.75). 354 * 355 * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity 356 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative 357 */ 358 public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) { 359 super(initialCapacity); 360 accessOrder = false; 361 } 362 363 /** 364 * Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance 365 * with the default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75). 366 */ 367 public LinkedHashMap() { 368 super(); 369 accessOrder = false; 370 } 371 372 /** 373 * Constructs an insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with 374 * the same mappings as the specified map. The <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> 375 * instance is created with a default load factor (0.75) and an initial 376 * capacity sufficient to hold the mappings in the specified map. 377 * 378 * @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map 379 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null 380 */ 381 public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { 382 super(); 383 accessOrder = false; 384 putMapEntries(m, false); 385 } 386 387 /** 388 * Constructs an empty <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with the 389 * specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode. 390 * 391 * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity 392 * @param loadFactor the load factor 393 * @param accessOrder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for 394 * access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order 395 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative 396 * or the load factor is nonpositive 397 */ 398 public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, 399 float loadFactor, 400 boolean accessOrder) { 401 super(initialCapacity, loadFactor); 402 this.accessOrder = accessOrder; 403 } 404 405 406 /** 407 * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the 408 * specified value. 409 * 410 * @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested 411 * @return <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the 412 * specified value 413 */ 414 public boolean containsValue(Object value) { 415 for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) { 416 V v = e.value; 417 if (v == value || (value != null && value.equals(v))) 418 return true; 419 } 420 return false; 421 } 422 423 /** 424 * Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, 425 * or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key. 426 * 427 * <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key 428 * {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null : 429 * key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise 430 * it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.) 431 * 432 * <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i> 433 * indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also 434 * possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}. 435 * The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to 436 * distinguish these two cases. 437 */ 438 public V get(Object key) { 439 Node<K,V> e; 440 if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null) 441 return null; 442 if (accessOrder) 443 afterNodeAccess(e); 444 return e.value; 445 } 446 447 /** 448 * {@inheritDoc} 449 */ 450 public V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) { 451 Node<K,V> e; 452 if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null) 453 return defaultValue; 454 if (accessOrder) 455 afterNodeAccess(e); 456 return e.value; 457 } 458 459 /** 460 * {@inheritDoc} 461 */ 462 public void clear() { 463 super.clear(); 464 head = tail = null; 465 } 466 467 /** 468 * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map should remove its eldest entry. 469 * This method is invoked by <tt>put</tt> and <tt>putAll</tt> after 470 * inserting a new entry into the map. It provides the implementor 471 * with the opportunity to remove the eldest entry each time a new one 472 * is added. This is useful if the map represents a cache: it allows 473 * the map to reduce memory consumption by deleting stale entries. 474 * 475 * <p>Sample use: this override will allow the map to grow up to 100 476 * entries and then delete the eldest entry each time a new entry is 477 * added, maintaining a steady state of 100 entries. 478 * <pre> 479 * private static final int MAX_ENTRIES = 100; 480 * 481 * protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) { 482 * return size() > MAX_ENTRIES; 483 * } 484 * </pre> 485 * 486 * <p>This method typically does not modify the map in any way, 487 * instead allowing the map to modify itself as directed by its 488 * return value. It <i>is</i> permitted for this method to modify 489 * the map directly, but if it does so, it <i>must</i> return 490 * <tt>false</tt> (indicating that the map should not attempt any 491 * further modification). The effects of returning <tt>true</tt> 492 * after modifying the map from within this method are unspecified. 493 * 494 * <p>This implementation merely returns <tt>false</tt> (so that this 495 * map acts like a normal map - the eldest element is never removed). 496 * 497 * @param eldest The least recently inserted entry in the map, or if 498 * this is an access-ordered map, the least recently accessed 499 * entry. This is the entry that will be removed it this 500 * method returns <tt>true</tt>. If the map was empty prior 501 * to the <tt>put</tt> or <tt>putAll</tt> invocation resulting 502 * in this invocation, this will be the entry that was just 503 * inserted; in other words, if the map contains a single 504 * entry, the eldest entry is also the newest. 505 * @return <tt>true</tt> if the eldest entry should be removed 506 * from the map; <tt>false</tt> if it should be retained. 507 */ 508 protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) { 509 return false; 510 } 511 512 /** 513 * Returns a {@link Set} view of the keys contained in this map. 514 * The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are 515 * reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified 516 * while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through 517 * the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation), the results of 518 * the iteration are undefined. The set supports element removal, 519 * which removes the corresponding mapping from the map, via the 520 * <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>, <tt>Set.remove</tt>, 521 * <tt>removeAll</tt>, <tt>retainAll</tt>, and <tt>clear</tt> 522 * operations. It does not support the <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt> 523 * operations. 524 * Its {@link Spliterator} typically provides faster sequential 525 * performance but much poorer parallel performance than that of 526 * {@code HashMap}. 527 * 528 * @return a set view of the keys contained in this map 529 */ 530 public Set<K> keySet() { 531 Set<K> ks = keySet; 532 if (ks == null) { 533 ks = new LinkedKeySet(); 534 keySet = ks; 535 } 536 return ks; 537 } 538 539 final class LinkedKeySet extends AbstractSet<K> { 540 public final int size() { return size; } 541 public final void clear() { LinkedHashMap.this.clear(); } 542 public final Iterator<K> iterator() { 543 return new LinkedKeyIterator(); 544 } 545 public final boolean contains(Object o) { return containsKey(o); } 546 public final boolean remove(Object key) { 547 return removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true) != null; 548 } 549 public final Spliterator<K> spliterator() { 550 return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED | 551 Spliterator.ORDERED | 552 Spliterator.DISTINCT); 553 } 554 public final void forEach(Consumer<? super K> action) { 555 if (action == null) 556 throw new NullPointerException(); 557 int mc = modCount; 558 for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) 559 action.accept(e.key); 560 if (modCount != mc) 561 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 562 } 563 } 564 565 /** 566 * Returns a {@link Collection} view of the values contained in this map. 567 * The collection is backed by the map, so changes to the map are 568 * reflected in the collection, and vice-versa. If the map is 569 * modified while an iteration over the collection is in progress 570 * (except through the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation), 571 * the results of the iteration are undefined. The collection 572 * supports element removal, which removes the corresponding 573 * mapping from the map, via the <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>, 574 * <tt>Collection.remove</tt>, <tt>removeAll</tt>, 575 * <tt>retainAll</tt> and <tt>clear</tt> operations. It does not 576 * support the <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt> operations. 577 * Its {@link Spliterator} typically provides faster sequential 578 * performance but much poorer parallel performance than that of 579 * {@code HashMap}. 580 * 581 * @return a view of the values contained in this map 582 */ 583 public Collection<V> values() { 584 Collection<V> vs = values; 585 if (vs == null) { 586 vs = new LinkedValues(); 587 values = vs; 588 } 589 return vs; 590 } 591 592 final class LinkedValues extends AbstractCollection<V> { 593 public final int size() { return size; } 594 public final void clear() { LinkedHashMap.this.clear(); } 595 public final Iterator<V> iterator() { 596 return new LinkedValueIterator(); 597 } 598 public final boolean contains(Object o) { return containsValue(o); } 599 public final Spliterator<V> spliterator() { 600 return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED | 601 Spliterator.ORDERED); 602 } 603 public final void forEach(Consumer<? super V> action) { 604 if (action == null) 605 throw new NullPointerException(); 606 int mc = modCount; 607 for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) 608 action.accept(e.value); 609 if (modCount != mc) 610 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 611 } 612 } 613 614 /** 615 * Returns a {@link Set} view of the mappings contained in this map. 616 * The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are 617 * reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified 618 * while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through 619 * the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation, or through the 620 * <tt>setValue</tt> operation on a map entry returned by the 621 * iterator) the results of the iteration are undefined. The set 622 * supports element removal, which removes the corresponding 623 * mapping from the map, via the <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>, 624 * <tt>Set.remove</tt>, <tt>removeAll</tt>, <tt>retainAll</tt> and 625 * <tt>clear</tt> operations. It does not support the 626 * <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt> operations. 627 * Its {@link Spliterator} typically provides faster sequential 628 * performance but much poorer parallel performance than that of 629 * {@code HashMap}. 630 * 631 * @return a set view of the mappings contained in this map 632 */ 633 public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { 634 Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es; 635 return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new LinkedEntrySet()) : es; 636 } 637 638 final class LinkedEntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> { 639 public final int size() { return size; } 640 public final void clear() { LinkedHashMap.this.clear(); } 641 public final Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() { 642 return new LinkedEntryIterator(); 643 } 644 public final boolean contains(Object o) { 645 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) 646 return false; 647 Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o; 648 Object key = e.getKey(); 649 Node<K,V> candidate = getNode(hash(key), key); 650 return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e); 651 } 652 public final boolean remove(Object o) { 653 if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { 654 Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o; 655 Object key = e.getKey(); 656 Object value = e.getValue(); 657 return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null; 658 } 659 return false; 660 } 661 public final Spliterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> spliterator() { 662 return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED | 663 Spliterator.ORDERED | 664 Spliterator.DISTINCT); 665 } 666 public final void forEach(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) { 667 if (action == null) 668 throw new NullPointerException(); 669 int mc = modCount; 670 for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) 671 action.accept(e); 672 if (modCount != mc) 673 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 674 } 675 } 676 677 // Map overrides 678 679 public void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) { 680 if (action == null) 681 throw new NullPointerException(); 682 int mc = modCount; 683 for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) 684 action.accept(e.key, e.value); 685 if (modCount != mc) 686 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 687 } 688 689 public void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) { 690 if (function == null) 691 throw new NullPointerException(); 692 int mc = modCount; 693 for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) 694 e.value = function.apply(e.key, e.value); 695 if (modCount != mc) 696 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 697 } 698 699 // Iterators 700 701 abstract class LinkedHashIterator { 702 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> next; 703 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> current; 704 int expectedModCount; 705 706 LinkedHashIterator() { 707 next = head; 708 expectedModCount = modCount; 709 current = null; 710 } 711 712 public final boolean hasNext() { 713 return next != null; 714 } 715 716 final LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> nextNode() { 717 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = next; 718 if (modCount != expectedModCount) 719 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 720 if (e == null) 721 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 722 current = e; 723 next = e.after; 724 return e; 725 } 726 727 public final void remove() { 728 Node<K,V> p = current; 729 if (p == null) 730 throw new IllegalStateException(); 731 if (modCount != expectedModCount) 732 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 733 current = null; 734 K key = p.key; 735 removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false); 736 expectedModCount = modCount; 737 } 738 } 739 740 final class LinkedKeyIterator extends LinkedHashIterator 741 implements Iterator<K> { 742 public final K next() { return nextNode().getKey(); } 743 } 744 745 final class LinkedValueIterator extends LinkedHashIterator 746 implements Iterator<V> { 747 public final V next() { return nextNode().value; } 748 } 749 750 final class LinkedEntryIterator extends LinkedHashIterator 751 implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> { 752 public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextNode(); } 753 } 754 755 756 }
继续调试,找到DispatcherServlet的doDispatcher第72行并进入processDispatchResult方法:
1 /** 2 * Handle the result of handler selection and handler invocation, which is 3 * either a ModelAndView or an Exception to be resolved to a ModelAndView. 4 */ 5 private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, 6 @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv, 7 @Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception { 8 9 boolean errorView = false; 10 11 if (exception != null) { 12 if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { 13 logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); 14 mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); 15 } 16 else { 17 Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); 18 mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); 19 errorView = (mv != null); 20 } 21 } 22 23 // Did the handler return a view to render? 24 if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { 25 render(mv, request, response); 26 if (errorView) { 27 WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); 28 } 29 } 30 else { 31 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 32 logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + 33 "': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling"); 34 } 35 } 36 37 if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 38 // Concurrent handling started during a forward 39 return; 40 } 41 42 if (mappedHandler != null) { 43 mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); 44 } 45 }
继续调试,找到DispatcherServlet的processDispatchResult第25行并进入render方法:
1 /** 2 * Render the given ModelAndView. 3 * <p>This is the last stage in handling a request. It may involve resolving the view by name. 4 * @param mv the ModelAndView to render 5 * @param request current HTTP servlet request 6 * @param response current HTTP servlet response 7 * @throws ServletException if view is missing or cannot be resolved 8 * @throws Exception if there's a problem rendering the view 9 */ 10 protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 11 // Determine locale for request and apply it to the response. 12 Locale locale = 13 (this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale()); 14 response.setLocale(locale); 15 16 View view; 17 String viewName = mv.getViewName(); 18 if (viewName != null) { 19 // We need to resolve the view name. 20 view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request); 21 if (view == null) { 22 throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() + 23 "' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); 24 } 25 } 26 else { 27 // No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object. 28 view = mv.getView(); 29 if (view == null) { 30 throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " + 31 "View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); 32 } 33 } 34 35 // Delegate to the View object for rendering. 36 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 37 logger.debug("Rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); 38 } 39 try { 40 if (mv.getStatus() != null) { 41 response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value()); 42 } 43 view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response); 44 } 45 catch (Exception ex) { 46 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 47 logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + 48 getServletName() + "'", ex); 49 } 50 throw ex; 51 } 52 }
继续调试,找到是View接口类的render接口方法,CTRL+T查找引用类结构:
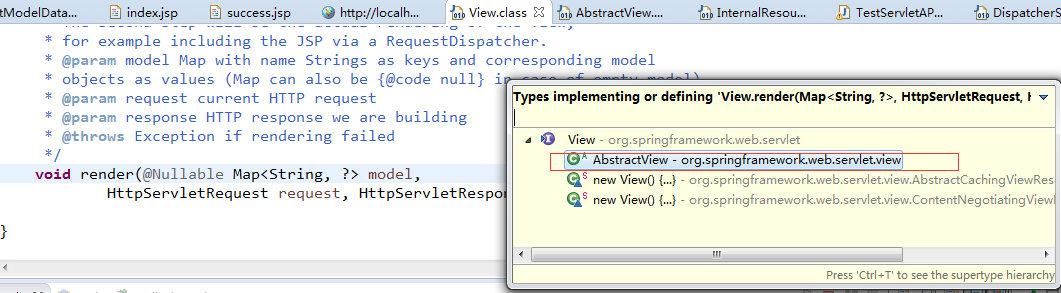
进入AbstractView抽象类,找到render方法:
1 /** 2 * Prepares the view given the specified model, merging it with static 3 * attributes and a RequestContext attribute, if necessary. 4 * Delegates to renderMergedOutputModel for the actual rendering. 5 * @see #renderMergedOutputModel 6 */ 7 @Override 8 public void render(@Nullable Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, 9 HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 10 11 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 12 logger.trace("Rendering view with name '" + this.beanName + "' with model " + model + 13 " and static attributes " + this.staticAttributes); 14 } 15 16 Map<String, Object> mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response); 17 prepareResponse(request, response); 18 renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response); 19 }
找到第18行方法renderMergedOutputModel方法,并进入该方法:
protected abstract void renderMergedOutputModel( Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
此方法是AbstractView的一个抽象方法,CTRL+T:
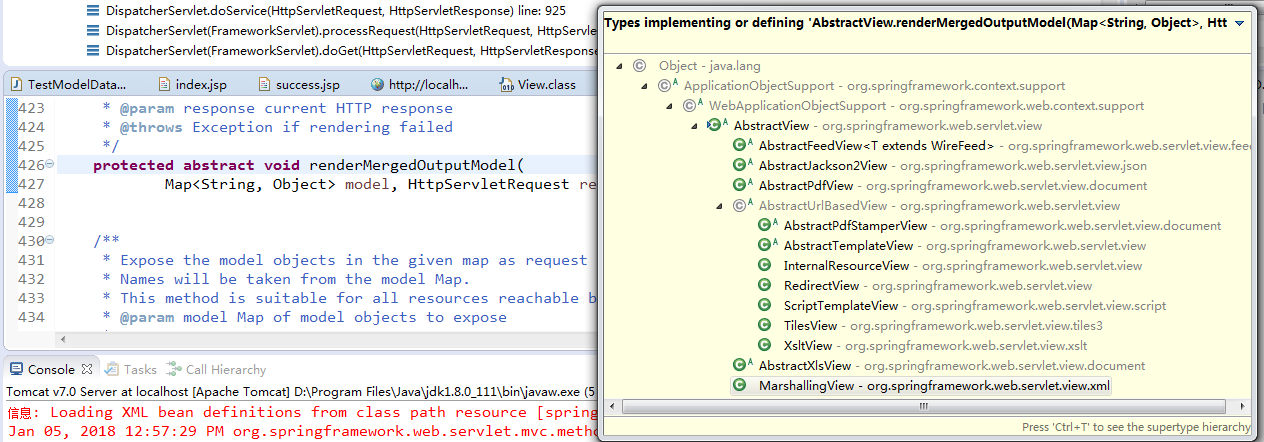
从上图中我们可以发现renderMergedOutputModel的实现类中包含了InternalResourceView,而我们的web.xml配置的springDispatcherServlet指定的类就是该类,因此直接查看InternalResourceView类即可。
进入InternalResourceView类renderMergedOutputModel方法:
1 @Override 2 protected void renderMergedOutputModel( 3 Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 4 5 // Expose the model object as request attributes. 6 exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, request); 7 8 // Expose helpers as request attributes, if any. 9 exposeHelpers(request); 10 11 // Determine the path for the request dispatcher. 12 String dispatcherPath = prepareForRendering(request, response); 13 14 // Obtain a RequestDispatcher for the target resource (typically a JSP). 15 RequestDispatcher rd = getRequestDispatcher(request, dispatcherPath); 16 if (rd == null) { 17 throw new ServletException("Could not get RequestDispatcher for [" + getUrl() + 18 "]: Check that the corresponding file exists within your web application archive!"); 19 } 20 21 // If already included or response already committed, perform include, else forward. 22 if (useInclude(request, response)) { 23 response.setContentType(getContentType()); 24 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 25 logger.debug("Including resource [" + getUrl() + "] in InternalResourceView '" + getBeanName() + "'"); 26 } 27 rd.include(request, response); 28 } 29 30 else { 31 // Note: The forwarded resource is supposed to determine the content type itself. 32 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 33 logger.debug("Forwarding to resource [" + getUrl() + "] in InternalResourceView '" + getBeanName() + "'"); 34 } 35 rd.forward(request, response); 36 } 37 }
找到第6行exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, request);方法并进入,此时进入方法归属类为AbstractView:
1 /** 2 * Expose the model objects in the given map as request attributes. 3 * Names will be taken from the model Map. 4 * This method is suitable for all resources reachable by {@link javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher}. 5 * @param model Map of model objects to expose 6 * @param request current HTTP request 7 */ 8 protected void exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(Map<String, Object> model, 9 HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { 10 11 model.forEach((modelName, modelValue) -> { 12 if (modelValue != null) { 13 request.setAttribute(modelName, modelValue); 14 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 15 logger.debug("Added model object '" + modelName + "' of type [" + modelValue.getClass().getName() + 16 "] to request in view with name '" + getBeanName() + "'"); 17 } 18 } 19 else { 20 request.removeAttribute(modelName); 21 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 22 logger.debug("Removed model object '" + modelName + 23 "' from request in view with name '" + getBeanName() + "'"); 24 } 25 } 26 }); 27 }
从该方法中我们可以总结出一个结论:
不管SpringMVC的handler类方法返回值是ModelAndView、String,也不管SpringMVC的handler类方法的入参是Map、Model、MapModel等,这些参数信息都会被存放到SpringMVC的request请求域中,这也是为什么success.jsp中显示currentTime时,采用${requestScope.currentTime}的原因。
