编写测试用例
HttpRunner v3.x支持三种测试用例格式:pytest、YAML和JSON。非常推荐用pytest格式编写和维护测试用例,而不是以前的YAML/JSON格式。
格式关系说明如下:

记录并生成测试用例
如果SUT(被测系统)准备好了,最有效的方法是首先捕获HTTP流量,然后用HAR文件生成测试用例。参考Record & Generate testcase了解更多细节。
根据生成的pytest测试用例,您可以根据需要进行一些调整,因此您需要知道测试用例格式的细节。
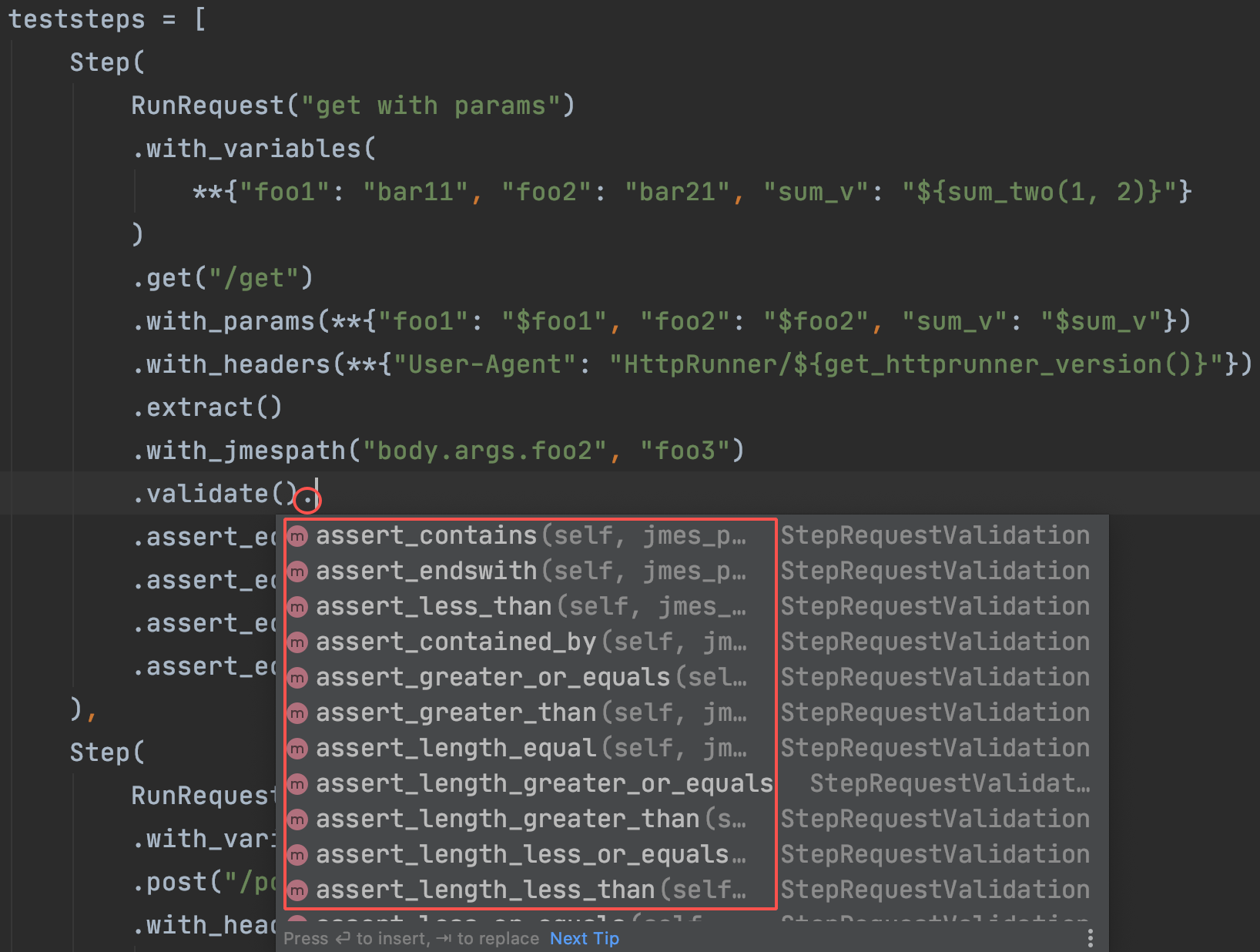
测试用例结构
每个测试用例都是HttpRunner的一个子类,必须有两个类属性:config和teststeps。
配置测试用例级别的设置,包括base_url、验证、变量、导出。
teststeps: teststep的列表(list [Step]),每一步都对应一个API请求或另一个测试用例引用调用。此外,还支持variables/extract/validate/hooks机制来创建极其复杂的测试场景。
from httprunner import HttpRunner, Config, Step, RunRequest, RunTestCase
class TestCaseRequestWithFunctions(HttpRunner):
config = (
Config("request methods testcase with functions")
.variables(
**{
"foo1": "config_bar1",
"foo2": "config_bar2",
"expect_foo1": "config_bar1",
"expect_foo2": "config_bar2",
}
)
.base_url("https://postman-echo.com")
.verify(False)
.export(*["foo3"])
)
teststeps = [
Step(
RunRequest("get with params")
.with_variables(
**{"foo1": "bar11", "foo2": "bar21", "sum_v": "${sum_two(1, 2)}"}
)
.get("/get")
.with_params(**{"foo1": "$foo1", "foo2": "$foo2", "sum_v": "$sum_v"})
.with_headers(**{"User-Agent": "HttpRunner/${get_httprunner_version()}"})
.extract()
.with_jmespath("body.args.foo2", "foo3")
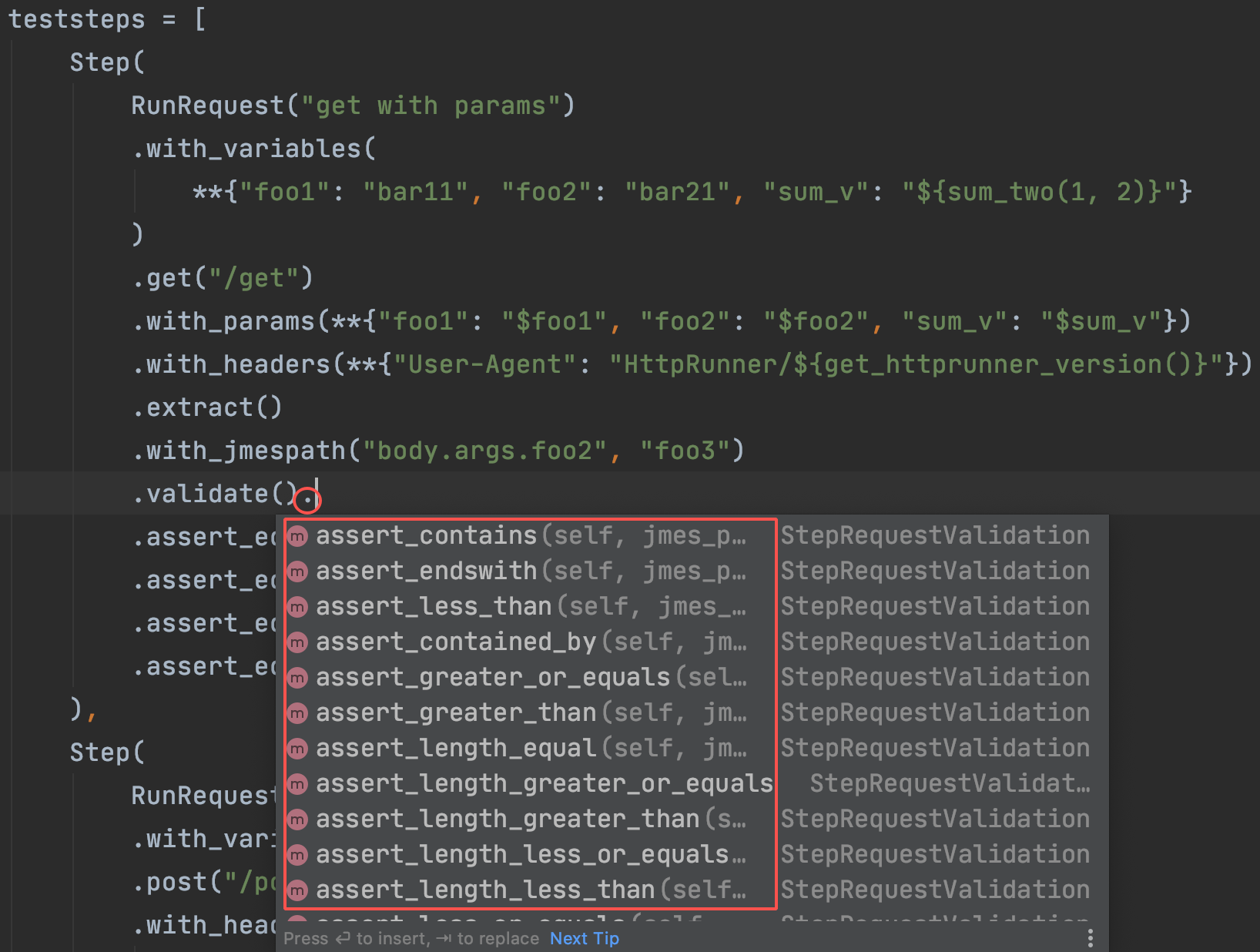
.validate()
.assert_equal("status_code", 200)
.assert_equal("body.args.foo1", "bar11")
.assert_equal("body.args.sum_v", "3")
.assert_equal("body.args.foo2", "bar21")
),
Step(
RunRequest("post form data")
.with_variables(**{"foo2": "bar23"})
.post("/post")
.with_headers(
**{
"User-Agent": "HttpRunner/${get_httprunner_version()}",
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
}
)
.with_data("foo1=$foo1&foo2=$foo2&foo3=$foo3")
.validate()
.assert_equal("status_code", 200)
.assert_equal("body.form.foo1", "$expect_foo1")
.assert_equal("body.form.foo2", "bar23")
.assert_equal("body.form.foo3", "bar21")
),
]
if __name__ == "__main__":
TestCaseRequestWithFunctions().test_start()
链调用
HttpRunner v3.x最令人惊叹的特性之一是链调用,使用它您不需要记住任何测试用例格式细节,而且当您在IDE中编写测试用例时,您可以获得智能补全。

配置
每个testcase应该有一个配置部分,您可以在其中配置testcase级别的设置。
name (必须的)
指定testcase的名字。这将显示在执行日志和测试报告中。
base_url(可选)
指定SUT的通用模式和主机部分,例如https://postman-echo.com。如果指定了base_url, teststep中的url只能设置相对路径部分。如果您想要在不同的SUT环境之间切换,这一点特别有用。
variables(可选)
指定testcase的常用变量。每个teststep都可以引用没有在step变量中设置的配置变量。换句话说,步骤变量比配置变量具有更高的优先级。
verify(可选)
指定是否验证服务器的TLS证书。如果我们想要记录testcase执行的HTTP流量,这就特别有用,因为如果verify没有设置或者被设置为True,就会发生SSLError。
证书验证失败:证书链中的自签名证书(_ssl.c:1076)'))
export (可选)
指定导出的testcase会话变量。将每个testcase看作一个黑盒,配置变量是输入部分,而配置导出是输出部分。特别是,当一个testcase在另一个testcase的步骤中被引用,并且将被提取一些会话变量用于后续的teststeps中,那么提取的会话变量应该在配置导出部分进行配置。
teststeps 测试步骤
每个测试用例应该有一个或多个有序的测试步骤(List[Step]),每个步骤对应于一个API请求或另一个测试用例引用调用。
注意:为了简化,HttpRunner v2.x中的API概念已经不推荐使用。您可以将API看作只有一个请求步骤的testcase。
RunRequest(name)
RunRequest在一个步骤中用于向API发出请求,并为响应执行一些提取或验证。
RunRequest的参数名称用于指定teststep名称,该名称将显示在执行日志和测试报告中。
.with_variables
指定teststep变量。每个步骤的变量是独立的,因此如果你想在多个步骤中共享变量,你应该在配置变量中定义变量。此外,步骤变量将覆盖配置变量中具有相同名称的变量。
.method (url)
指定HTTP方法和SUT的url。它们对应于request. request的方法和url参数。
如果在配置中设置了base_url, url只能设置相对路径部分。
.with_params
为请求url指定查询字符串。这对应于request. request的params参数。
.with_headers
指定请求的HTTP头。这对应于request. request的header参数。
.with_cookies
指定HTTP请求cookie。这对应于request. request的cookie参数。
.with_data
指定HTTP请求主体。这对应于request. request的data参数。
.with_json
用json指定HTTP请求主体。这对应于request. request的json参数。
extract
.WITH_JMESPATH
使用jmespath提取JSON响应体 .
with_jmespath(jmes_path: Text, var_name: Text)
jmes_path: jmespath表达式,更多细节请参考jmespath教程
var_name:存储提取值的变量名,后续测试步骤可以引用它
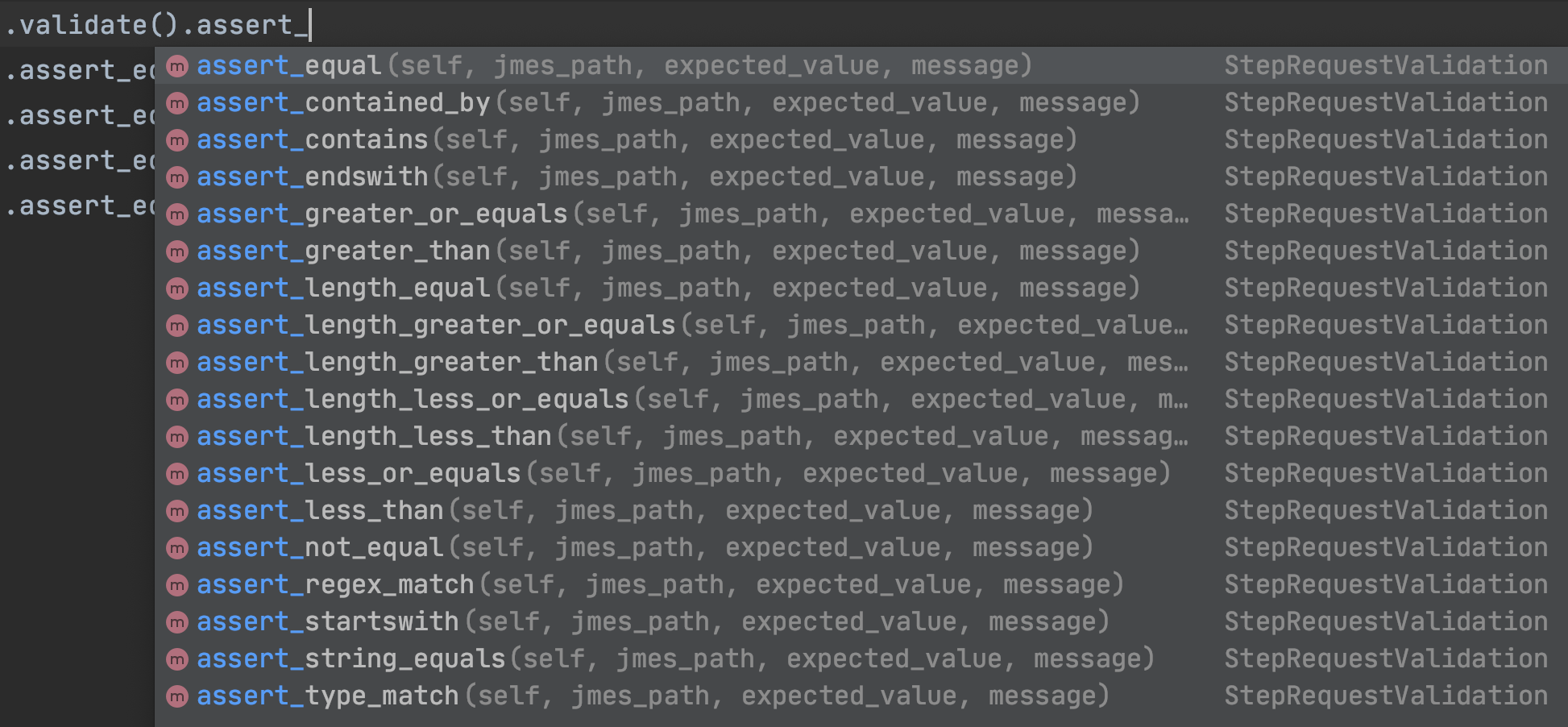
validate
.ASSERT_XXX
使用jmespath提取JSON响应体,并使用期望值进行验证。
assert_XXX(jmes_path: Text, expected_value: Any, message: Text = "")
- jmes_path: jmespath表达式,更多细节请参考jmespath教程
- expected_value:指定的期望值、变量或函数引用也可以在这里使用
- message(可选):用于指示断言错误的原因
下面的图片显示了HttpRunner内置验证器。
RunTestCase(name)
在步骤中使用RunTestCase来引用另一个testcase调用。
RunTestCase的参数名称用于指定teststep名称,该名称将显示在执行日志和测试报告中。
.with_variables
与RunRequest的.with_variables相同。
.call
指定引用的testcase类。
.export
指定要从引用的testcase导出的会话变量名。导出的变量可以被后续的测试步骤引用。
import os
import sys
sys.path.insert(0, os.getcwd())
from httprunner import HttpRunner, Config, Step, RunRequest, RunTestCase
from examples.postman_echo.request_methods.request_with_functions_test import (
TestCaseRequestWithFunctions as RequestWithFunctions,
)
class TestCaseRequestWithTestcaseReference(HttpRunner):
config = (
Config("request methods testcase: reference testcase")
.variables(
**{
"foo1": "testsuite_config_bar1",
"expect_foo1": "testsuite_config_bar1",
"expect_foo2": "config_bar2",
}
)
.base_url("https://postman-echo.com")
.verify(False)
)
teststeps = [
Step(
RunTestCase("request with functions")
.with_variables(
**{"foo1": "testcase_ref_bar1", "expect_foo1": "testcase_ref_bar1"}
)
.call(RequestWithFunctions)
.export(*["foo3"])
),
Step(
RunRequest("post form data")
.with_variables(**{"foo1": "bar1"})
.post("/post")
.with_headers(
**{
"User-Agent": "HttpRunner/${get_httprunner_version()}",
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
}
)
.with_data("foo1=$foo1&foo2=$foo3")
.validate()
.assert_equal("status_code", 200)
.assert_equal("body.form.foo1", "bar1")
.assert_equal("body.form.foo2", "bar21")
),
]
if __name__ == "__main__":
TestCaseRequestWithTestcaseReference().test_start()