在整个Java.io包中最重要的就是5个类和一个接口。
5个类指的是
- File
- OutputStream
- InputStream
- Writer
- Reader
一个接口指的是
- Serializable
掌握了这些IO的核心操作那么对于Java中的IO体系也就有了一个初步的认识了
Java I/O主要包括如下几个层次,包含三个部分:
1.流式部分――IO的主体部分;
2.非流式部分――主要包含一些辅助流式部分的类,如:File类、RandomAccessFile类和FileDescriptor等类;
3.其他类--文件读取部分的与安全相关的类,如:SerializablePermission类,以及与本地操作系统相关的文件系统的类,如:FileSystem类和Win32FileSystem类和WinNTFileSystem类。
Java I/O主要的类
1. File(文件特征与管理):用于文件或者目录的描述信息,例如生成新目录,修改文件名,删除文件,判断文件所在路径等。
2. InputStream(二进制格式操作):抽象类,基于字节的输入操作,是所有输入流的父类。定义了所有输入流都具有的共同特征。
3. OutputStream(二进制格式操作):抽象类。基于字节的输出操作。是所有输出流的父类。定义了所有输出流都具有的共同特征。
Java中字符是采用Unicode标准,一个字符是16位,即一个字符使用两个字节来表示。为此,JAVA中引入了处理字符的流。
4. Reader(文件格式操作):抽象类,基于字符的输入操作。
5. Writer(文件格式操作):抽象类,基于字符的输出操作。
6. RandomAccessFile(随机文件操作):它的功能丰富,可以从文件的任意位置进行存取(输入输出)操作。
Java.IO流类库
1. io流的四个基本类
java.io包中包含了流式I/O所需要的所有类。
在java.io包中有四个基本类:
- InputStream
- OutputStream
- Reader
- Writer类
它们分别处理字节流和字符流
| 字节流 | 字符流 | 输入流 | 输出流 |
| Inputstream | Reader | OutputStream | Writer |
Java中其他多种多样变化的流均是由它们派生出来的:
JDK1.4版本开始引入了新I/O类库,它位于java.nio包中,新I/O类库利用通道和缓冲区等来提高I/O操作的效率。
在java.io包中, java.io.InputStream 表示字节输入流, java.io.OutputStream表示字节输出流,处于java.io包最顶层。这两个类均为抽象类,也就是说它们不能被实例化,必须生成子类之后才能实现一定的功能。
io流几种分类
第一种:按I/O类型来总体分类
1. Memory 1)从/向内存数组读写数据: CharArrayReader、 CharArrayWriter、ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream
2)从/向内存字符串读写数据 StringReader、StringWriter、StringBufferInputStream
2. Pipe管道 实现管道的输入和输出(进程间通信): PipedReader、PipedWriter、PipedInputStream、PipedOutputStream
3. File 文件流。对文件进行读、写操作 :FileReader、FileWriter、FileInputStream、FileOutputStream
4. ObjectSerialization 对象输入、输出 :ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream
5. DataConversion数据流 按基本数据类型读、写(处理的数据是Java的基本类型(如布尔型,字节,整数和浮点数)):DataInputStream、DataOutputStream
6. Printing 包含方便的打印方法 :PrintWriter、PrintStream
7. Buffering缓冲 在读入或写出时,对数据进行缓存,以减少I/O的次数:BufferedReader、BufferedWriter、BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream
8. Filtering 滤流,在数据进行读或写时进行过滤:FilterReader、FilterWriter、FilterInputStream、FilterOutputStream过
9. Concatenation合并输入 把多个输入流连接成一个输入流 :SequenceInputStream
10. Counting计数 在读入数据时对行记数 :LineNumberReader、LineNumberInputStream
11. Peeking Ahead 通过缓存机制,进行预读 :PushbackReader、PushbackInputStream
12. Converting between Bytes and Characters 按照一定的编码/解码标准将字节流转换为字符流,或进行反向转换(Stream到Reader,Writer的转换类):InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter
第二种:按数据来源(去向)分类
1、File(文件): FileInputStream, FileOutputStream, FileReader, FileWriter
2、byte[]:ByteArrayInputStream, ByteArrayOutputStream
3、Char[]: CharArrayReader, CharArrayWriter
4、String: StringBufferInputStream, StringReader, StringWriter
5、网络数据流:InputStream, OutputStream, Reader, Writer
6. 字节流 InputStream/OutputStream
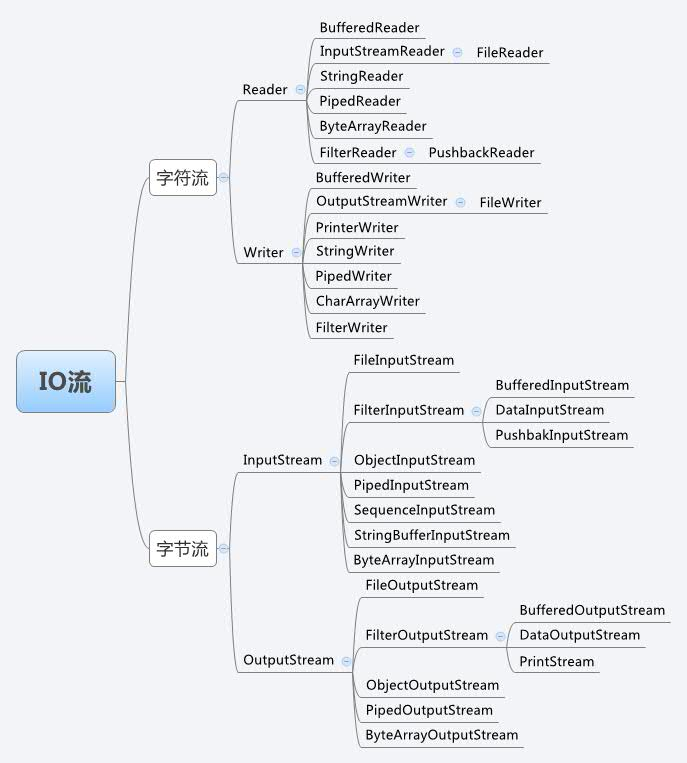
Java中IO流的体系结构如图:
非流式文件类--File类
代码如下:
public class File extends Object implements Serializable,Comparable {}
File类共提供了三个不同的构造函数,以不同的参数形式灵活地接收文件和目录名信息。
构造函数:
1)File (String pathname)
2)File (String parent , String child)
3)File (File parent , String child)
例: File f4 = new File("\dir3");
File f5 = new File(f4,"FileTest5.txt");
2)public boolean isFile( ) 判断是文件还是目录
3)public boolean isDirectory( ) 判断是文件还是目录
4)public String getName( ) 返回文件名或目录名
5)public String getPath( ) 返回文件或目录的路径。
6)public long length( ) 获取文件的长度
7)public String[ ] list ( ) 将目录中所有文件名保存在字符串数组中返回。
1) public boolean renameTo( File newFile ); 重命名文件
2) public void delete( ); 删除文件
3) public boolean mkdir( ); 创建目录
import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; public class TestFile { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { File dir = new File("\root"); File f1 = new File(dir, "fileOne.txt"); File f2 = new File(dir, "fileTwo.java"); // 文件对象创建后,指定的文件或目录不一定物理上存在 if (!dir.exists()) dir.mkdir(); if (!f1.exists()) f1.createNewFile(); if (!f2.exists()) f2.createNewFile(); System.out.println("f1's AbsolutePath= " + f1.getAbsolutePath()); System.out.println("f1 Canread=" + f1.canRead()); System.out.println("f1's len= " + f1.length()); String[] FL; int count = 0; FL = dir.list(); for (int i = 0; i < FL.length; i++) { count++; System.out.println(FL[i] + "is in \root"); } System.out.println("there are" + count + "file in //root"); } }
(1) exists()测试磁盘中指定的文件或目录是否存在
(2) mkdir()创建文件对象指定的目录(单层目录)
(3) createNewFile()创建文件对象指定的文件
文件字节流的操作
InputStream 为字节输入流,它本身为一个抽象类,必须依靠其子类实现各种功能,此抽象类是表示字节输入流的所有类的超类。 继承自InputStream 的流都是向程序中输入数据的,且数据单位为字节(8bit);
InputStream是输入字节数据用的类,所以InputStream类提供了3种重载的read方法.Inputstream类中的常用方法:
(1) public abstract int read( ):读取一个byte的数据,返回值是高位补0的int类型值。若返回值=-1说明没有读取到任何字节读取工作结束。
(2) public int read(byte b[ ]):读取b.length个字节的数据放到b数组中。返回值是读取的字节数。该方法实际上是调用下一个方法实现的
(3) public int read(byte b[ ], int off, int len):从输入流中最多读取len个字节的数据,存放到偏移量为off的b数组中。
(4) public int available( ):返回输入流中可以读取的字节数。注意:若输入阻塞,当前线程将被挂起,如果InputStream对象调用这个方法的话,它只会返回0,这个方法必须由继承InputStream类的子类对象调用才有用,
(5) public long skip(long n):忽略输入流中的n个字节,返回值是实际忽略的字节数, 跳过一些字节来读取
(6) public int close( ) :我们在使用完后,必须对我们打开的流进行关闭.
主要的子类: 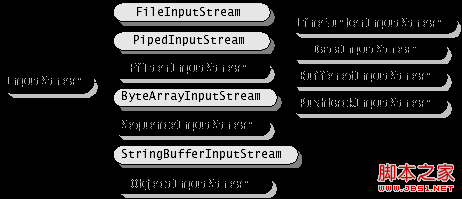
1) FileInputStream把一个文件作为InputStream,实现对文件的读取操作
2) ByteArrayInputStream:把内存中的一个缓冲区作为InputStream使用
3) StringBufferInputStream:把一个String对象作为InputStream
4) PipedInputStream:实现了pipe的概念,主要在线程中使用
5) SequenceInputStream:把多个InputStream合并为一个InputStream
1. public void write(byte b[ ]):将参数b中的字节写到输出流。
2. public void write(byte b[ ], int off, int len) :将参数b的从偏移量off开始的len个字节写到输出流。
3. public abstract void write(int b) :先将int转换为byte类型,把低字节写入到输出流中。
4. public void flush( ) : 将数据缓冲区中数据全部输出,并清空缓冲区。
5. public void close( ) : 关闭输出流并释放与流相关的系统资源。
主要的子类: 
1) ByteArrayOutputStream:把信息存入内存中的一个缓冲区中
2) FileOutputStream:把信息存入文件中
3) PipedOutputStream:实现了pipe的概念,主要在线程中使用
4) SequenceOutputStream:把多个OutStream合并为一个OutStream
流结束的判断:方法read()的返回值为-1时;readLine()的返回值为null时。
3. 文件输入流: FileInputStream类FileInputStream可以使用read()方法一次读入一个字节,并以int类型返回,或者是使用read()方法时读入至一个byte数组,byte数组的元素有多少个,就读入多少个字节。在将整个文件读取完成或写入完毕的过程中,这么一个byte数组通常被当作缓冲区,因为这么一个byte数组通常扮演承接数据的中间角色。

作用:以文件作为数据输入源的数据流。或者说是打开文件,从文件读数据到内存的类。
使用方法(1)
File fin=new File("d:/abc.txt"); FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream( fin);
使用方法(2)
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(“d: /abc.txt”);
程序举例:
将InputFromFile.java的程序的内容显示在显示器上
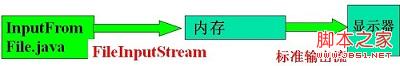
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.FileInputStream; public class TestFile { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { try{ FileInputStream rf=new FileInputStream("InputFromFile.java"); int n=512; byte buffer[]=new byte[n]; while((rf.read(buffer,0,n)!=-1)&&(n>0)){ System.out.println(new String(buffer) ); } System.out.println(); rf.close(); } catch(IOException IOe){ System.out.println(IOe.toString()); } } }
FileOutputStream类用来处理以文件作为数据输出目的数据流;一个表示文件名的字符串,也可以是File或FileDescriptor对象。
创建一个文件流对象有两种方法:
方式1:
File f=new File (“d:/myjava/write.txt "); FileOutputStream out= new FileOutputStream (f);
方式2:
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(“d:/myjava/write.txt ");
方式3:构造函数将 FileDescriptor()对象作为其参数。
FileDescriptor() fd=new FileDescriptor(); FileOutputStream f2=new FileOutputStream(fd);
方式4:构造函数将文件名作为其第一参数,将布尔值作为第二参数。
FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("d:/abc.txt",true);
注意:(1)文件中写数据时,若文件已经存在,则覆盖存在的文件;(2)的读/写操作结束时,应调用close方法关闭流。
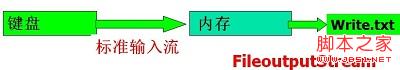
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; public class TestFile { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { try { System.out.println("please Input from Keyboard"); int count, n = 512; byte buffer[] = new byte[n]; count = System.in.read(buffer); FileOutputStream wf = new FileOutputStream("d:/myjava/write.txt"); wf.write(buffer, 0, count); wf.close(); // 当流写操作结束时,调用close方法关闭流。 System.out.println("Save to the write.txt"); } catch (IOException IOe) { System.out.println("File Write Error!"); } } }
import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.FileInputStream; public class TestFile { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { try { File inFile = new File("copy.java"); File outFile = new File("copy2.java"); FileInputStream finS = new FileInputStream(inFile); FileOutputStream foutS = new FileOutputStream(outFile); int c; while ((c = finS.read()) != -1) { foutS.write(c); } finS.close(); foutS.close(); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("FileStreamsTest: " + e); } } }
计算机访问外部设备非常耗时。访问外存的频率越高,造成CPU闲置的概率就越大。为了减少访问外存的次数,应该在一次对外设的访问中,读写更多的数据。为此,除了程序和流节点间交换数据必需的读写机制外,还应该增加缓冲机制。缓冲流就是每一个数据流分配一个缓冲区,一个缓冲区就是一个临时存储数据的内存。这样可以减少访问硬盘的次数,提高传输效率。
BufferedInputStream:当向缓冲流写入数据时候,数据先写到缓冲区,待缓冲区写满后,系统一次性将数据发送给输出设备。
BufferedOutputStream :当从向缓冲流读取数据时候,系统先从缓冲区读出数据,待缓冲区为空时,系统再从输入设备读取数据到缓冲区。
将BufferedInputStream与FileInputStream相接
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream( “file1.txt ” ); BufferedInputStream bin=new BufferedInputStream( in);
2)将内存写入文件:
将BufferedOutputStream与 FileOutputStream相接】
FileOutputStreamout=new FileOutputStream(“file1.txt”); BufferedOutputStream bin=new BufferedInputStream(out);
3)键盘输入流读到内存
InputStreamReader sin=new InputStreamReader (System.in) ; BufferedReader bin=new BufferedReader(sin);
import java.io.*; public class ReadWriteToFile { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { InputStreamReader sin = new InputStreamReader(System.in); BufferedReader bin = new BufferedReader(sin); FileWriter out = new FileWriter("myfile.txt"); BufferedWriter bout = new BufferedWriter(out); String s; while ((s = bin.readLine()).length() > 0) { bout.write(s, 0, s.length()); } } }
从键盘读入字符,并写入到文件中BufferedReader类的方法:String readLine()
作用:读一行字符串,以回车符为结束。
BufferedWriter类的方法:bout.write(String s,offset,len)
作用:从缓冲区将字符串s从offset开始,len长度的字符串写到某处。
文件字符流操作
Java中字符是采用Unicode标准,一个字符是16位,即一个字符使用两个字节来表示。为此,JAVA中引入了处理字符的流。
1). Reader抽象类
用于读取字符流的抽象类。子类必须实现的方法只有 read(char[], int, int) 和 close()。但是,多数子类将重写此处定义的一些方法,以提供更高的效率和/或其他功能。 
1) FileReader :与FileInputStream对应
主要用来读取字符文件,使用缺省的字符编码,有三种构造函数:
(1)将文件名作为字符串 :
FileReader f=new FileReader(“c:/temp.txt”);
(2)构造函数将File对象作为其参数。
File f=new file(“c:/temp.txt”); FileReader f1=new FileReader(f);
(3) 构造函数将FileDescriptor对象作为参数
FileDescriptor() fd=new FileDescriptor() FileReader f2=new FileReader(fd);
(1) 用指定字符数组作为参数:CharArrayReader(char[])
(2) 将字符数组作为输入流:CharArrayReader(char[], int, int)
读取字符串,构造函数如下: public StringReader(String s);
2) CharArrayReader:与ByteArrayInputStream对应
3) StringReader : 与StringBufferInputStream对应
4) InputStreamReader
从输入流读取字节,在将它们转换成字符:Public inputstreamReader(inputstream is);
5) FilterReader: 允许过滤字符流
protected filterReader(Reader r);
6) BufferReader :接受Reader对象作为参数,并对其添加字符缓冲器,使用readline()方法可以读取一行。
Public BufferReader(Reader r);
主要方法:
(1) public int read() throws IOException; //读取一个字符,返回值为读取的字符
(2) public int read(char cbuf[]) throws IOException; /*读取一系列字符到数组cbuf[]中,返回值为实际读取的字符的数量*/
(3) public abstract int read(char cbuf[],int off,int len) throws IOException;
/*读取len个字符,从数组cbuf[]的下标off处开始存放,返回值为实际读取的字符数量,该方法必须由子类实现*/
2) Writer抽象类
写入字符流的抽象类。子类必须实现的方法仅有 write(char[], int, int)、flush() 和 close()。但是,多数子类将重写此处定义的一些方法,以提供更高的效率和/或其他功能。 其子类如下:
1) FileWrite: 与FileOutputStream对应
将字符类型数据写入文件,使用缺省字符编码和缓冲器大小。
Public FileWrite(file f);
2) chararrayWrite:与ByteArrayOutputStream对应 ,将字符缓冲器用作输出。
Public CharArrayWrite();
3) PrintWrite:生成格式化输出
public PrintWriter(outputstream os);
4) filterWriter:用于写入过滤字符流
protected FilterWriter(Writer w);
5) PipedWriter:与PipedOutputStream对应
6) StringWriter:无与之对应的以字节为导向的stream
主要方法:
(1) public void write(int c) throws IOException; //将整型值c的低16位写入输出流
(2) public void write(char cbuf[]) throws IOException; //将字符数组cbuf[]写入输出流
(3) public abstract void write(char cbuf[],int off,int len) throws IOException; //将字符数组cbuf[]中的从索引为off的位置处开始的len个字符写入输出流
(4) public void write(String str) throws IOException; //将字符串str中的字符写入输出流
(5) public void write(String str,int off,int len) throws IOException; //将字符串str 中从索引off开始处的len个字符写入输出流
(6) flush( ) //刷空输出流,并输出所有被缓存的字节。
(7)close() 关闭流 public abstract void close() throws IOException
InputStream与Reader差别 OutputStream与Writer差别
Reader与Writer处理的是字符流,在处理字符流时涉及了字符编码的转换问题
import java.io.*; public class EncodeTest { private static void readBuff(byte [] buff) throws IOException { ByteArrayInputStream in =new ByteArrayInputStream(buff); int data; while((data=in.read())!=-1) System.out.print(data+" "); System.out.println(); in.close(); } public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { System.out.println("内存中采用unicode字符编码:" ); char c='好'; int lowBit=c&0xFF; int highBit=(c&0xFF00)>>8; System.out.println(""+lowBit+" "+highBit); String s="好"; System.out.println("本地操作系统默认字符编码:"); readBuff(s.getBytes()); System.out.println("采用GBK字符编码:"); readBuff(s.getBytes("GBK")); System.out.println("采用UTF-8字符编码:"); readBuff(s.getBytes("UTF-8")); } }
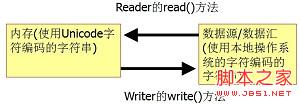
Reader类能够将输入流中采用其他编码类型的字符转换为Unicode字符,然后在内存中为其分配内存
Writer类能够将内存中的Unicode字符转换为其他编码类型的字符,再写到输出流中。
文件IOException异常类
1.public class EOFException :
非正常到达文件尾或输入流尾时,抛出这种类型的异常。
2.public class FileNotFoundException:
当文件找不到时,抛出的异常。
3.public class InterruptedIOException:
当I/O操作被中断时,抛出这种类型的异常。