在工作中,使用mybatis操作数据库,只需要提供一个接口类,定义一些方法,然后调用接口里面的方法就可以CRUD,感觉是牛了一逼!
该篇就是记录一下,mybatis是如何完成这波骚操作的,即分析我们测试代码的第4行。
FemaleMapper femaleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(FemaleMapper.class);
由上篇可知,sqlSession的真实类型是DefaultSqlSession. 所以,我们直接是看DefaultSqlSession#getMapper(Class<T> type)方法,当然,断点也是少不了的!
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) { return configuration.getMapper(type, this); }
是不是有点熟悉。。。。 接着走。。。
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); }
再接着走。。。。
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type); if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); } try { return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e); } }
看到上面这段代码 ,肯定有反应了。 在上上篇中,我们说到解析xml配置时,会将Mapper接口缓存到MapperRegistry#knownMappers集合中,key是Mapper接口全路径,
Value是该Mapper接口的一个代理工厂类MapperProxyFactory, 源代码就是MapperRegistry#addMapper(Class<T> type)方法,代码如下:
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) { try { knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type)); } finally { } }
回归正题,此时getMapper()就是根据Mapper接口类型,去knownMappers集合中拿到其对应的代理工厂类。然后通过这个代理工厂类去创建Mapper接口的代理对象。
请看MapperProxyFactory#newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession)方法
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); return newInstance(mapperProxy); }
又new了个MapperProxy, 看框架就是麻烦 ,封装了一层又一层, 但是还得看, 因为MapperProxy才是真正干事的!
然后就是下面这个方法,创建代理类
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); }
debug 看一下,感觉不用debug完全活不下去了。。。
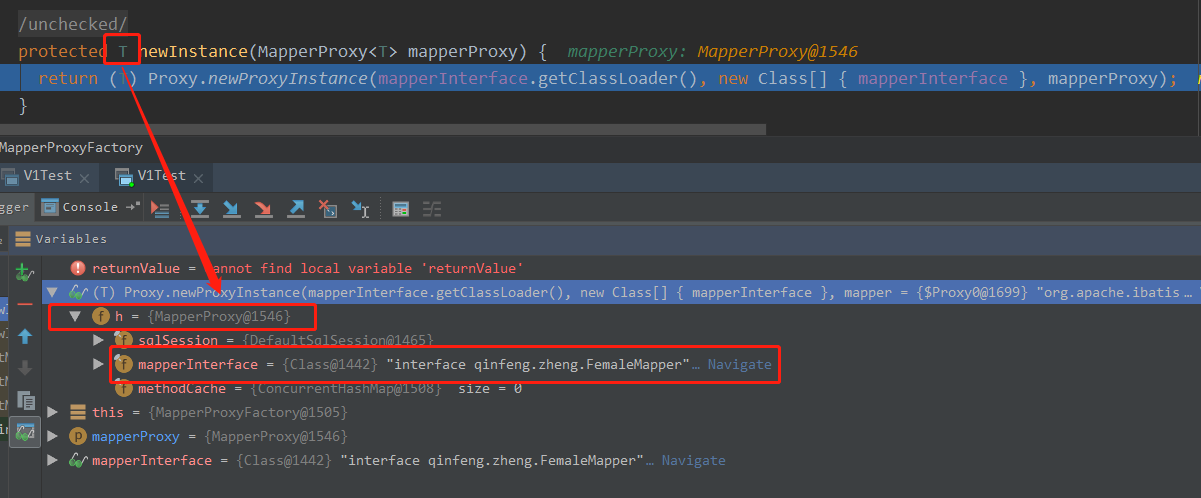
看到没有, 返回的是一个MapperProxy@1546
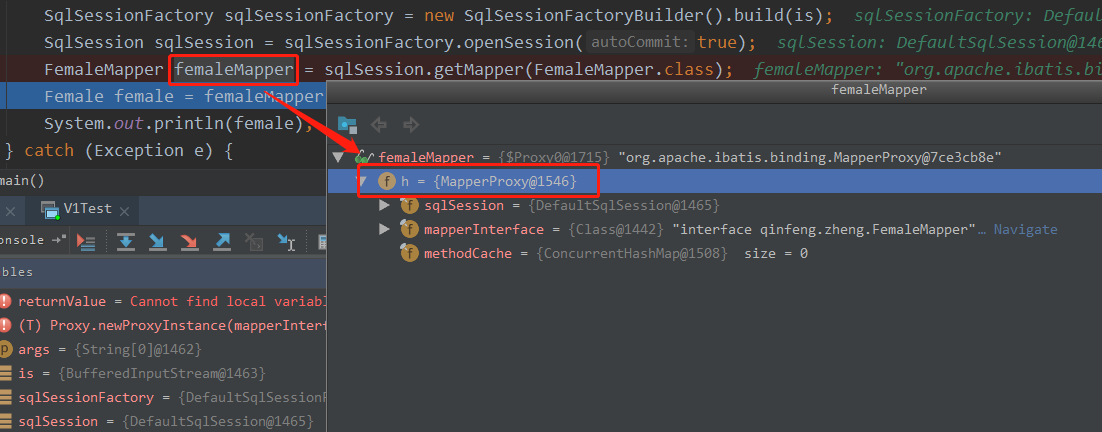
好,测试代码 FemaleMapper femaleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(FemaleMapper.class) 这一句执行完毕,返回了一个MapperProxy代码对象,即然是代理,那肯定是
要去看看它的invoke()方法了, 这才是重头戏。
而当程序执行 Female female = femaleMapper.getFemaleById(1) 这行代理时,就会调用MapperProxy#invoke()方法。
MapperProxy#invoke()方法,源码如下:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { return method.invoke(this, args); } else if (method.isDefault()) { return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args); } } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method); return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); }
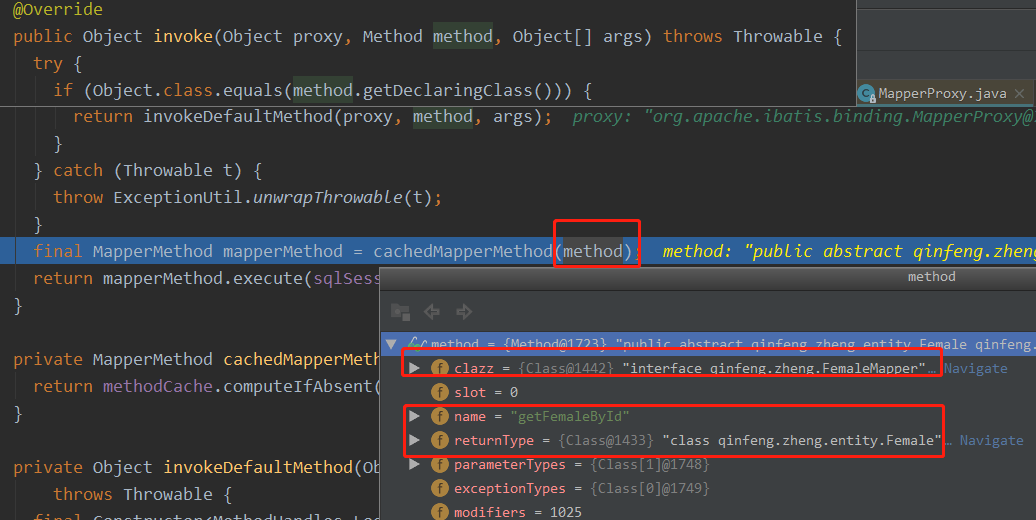
所以,应该去看看cachedMapperMethod(method)在干啥?
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) { return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, k -> new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration())); }
创建 MapperMethod,并缓存起来,所以说,mybatis也没那么傻,并不是每次都去构造MapperMethod实例 ,这个实例干嘛呢? 接着看!
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) { this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method); this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method); }
这里就不具体说了,代码也很简单。
<1> SqlCommand两个属性,一个name,一个type, debug一下,啥都明白了

<2> MethodSignature 方法签名,就是对方法的返回值判断,还有比如@Param注解等处理。。。

MapperProxy#invoke()方法的最后就是调用MapperMethod#execute(sqlSession,args)方法,该方法最终就是调用Executor类中方法操作数据库。
<1> MapperMethod#execute()
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Object result; switch (command.getType()) { case INSERT: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param)); break; } case UPDATE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param)); break; } case DELETE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param)); break; } case SELECT: if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) { executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args); result = null; } else if (method.returnsMany()) { result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args); } else if (method.returnsMap()) { result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args); } else if (method.returnsCursor()) { result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args); } else { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param); if (method.returnsOptional() && (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) { result = Optional.ofNullable(result); } } break; case FLUSH: result = sqlSession.flushStatements(); break; default: throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName()); } if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) { throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ")."); } return result; }
该方法就是根据sql的类型,执行具体的逻辑 ,咱们的测试代码是SELECT,所以会走到这儿

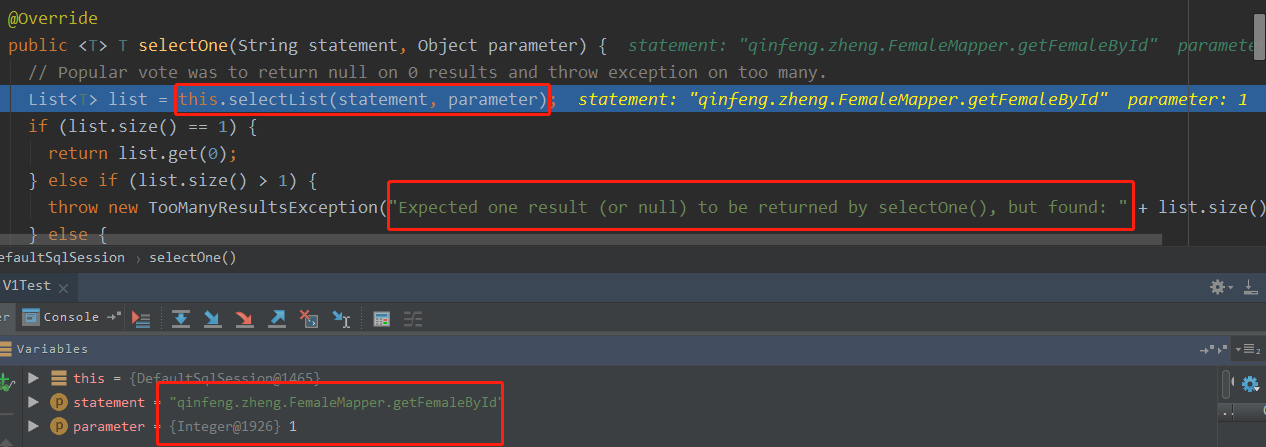
selectOne底层还是调用的selectList,只是取的get(0) , 还有这个异常,工作中也是很常见的呀,原来是这儿抛出来的!
接着看selectList()方法
@Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) { return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT); }
RowBounds, mybatis提供的分页功能,不过这里使用的是DEFAULT,即是偏移量是0,limit 是 Integer.MAX_VALUE, 没啥用,如果我们想使用RowBounds分页,传一个自定义的RowBounds对象即可!
一路往前奔。。。 终于来到这儿。。。
@Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
前文说过,跟数据库sql相关的东西都封装在MappedStatement 对象中,最终操作数据库的都是Executor实例 ,这儿可以得到证明!
到这儿就差不多了,剩下的就是jdbc操作数据库那一套了。
总结:
1. mybatis创建了一个MapperProxy的代理,用于操作Mapper接口的方法,从而做到CRUD, 在此过程中需要用到的一些实例,前期都已经准备好了!
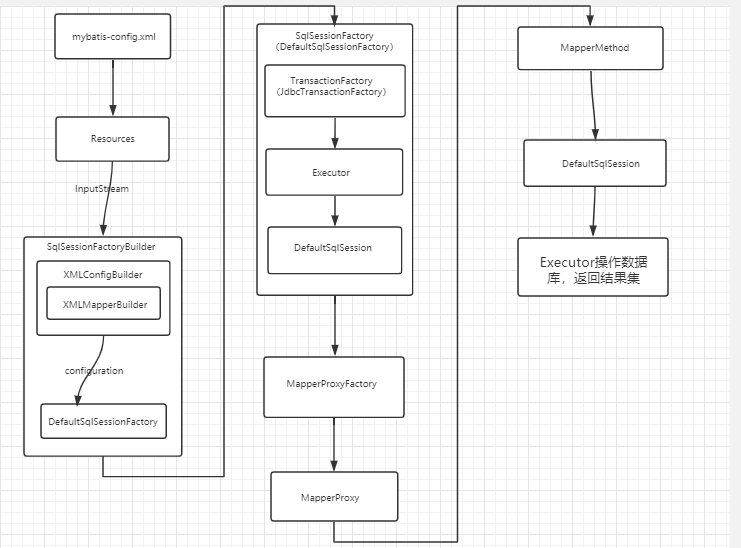
2. 流程图