You are given an array a with n distinct integers. Construct an array b by permuting a such that for every non-empty subset of indices S = {x1, x2, ..., xk} (1 ≤ xi ≤ n, 0 < k < n) the sums of elements on that positions in a and b are different, i. e.
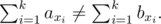
The first line contains one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 22) — the size of the array.
The second line contains n space-separated distinct integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the elements of the array.
If there is no such array b, print -1.
Otherwise in the only line print n space-separated integers b1, b2, ..., bn. Note that b must be a permutation of a.
If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
2
1 2
2 1
4
1000 100 10 1
100 1 1000 10
An array x is a permutation of y, if we can shuffle elements of y such that it will coincide with x.
Note that the empty subset and the subset containing all indices are not counted.
题目大意:给定一个数组a,将a中的元素调换位置变成b数组,使得对于每一个下标子集,a中对应下标的元素和不等于b中对应下标的元素和.
分析:构造题.如果第i位的数是第j大的,那么就把第j+1大的放在第i位,如果已经是最大的了,就把最小的放在第i位,这样一定是对的.证明的话就是看是否选最大的那个数.
这个数据范围真的是让人分分钟想到状压......
#include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <queue> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; int n, a[30]; struct node { int x, id; }e[30]; bool cmp(node a, node b) { return a.x < b.x; } int main() { scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%d", &e[i].x); e[i].id = i; } sort(e + 1, e + 1 + n, cmp); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[e[i].id] = i; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { int t = (a[i] + 1) % n; if (t == 0) t = n; printf("%d ", e[t].x); } return 0; }