1、遍历字符串
SQL中不提供迭代操作,所以要连接一张用来作为遍历指针的表,来实现这个过程
1 select substr(e.ename, iter.pos, 1) as C 2 from (select ename from emp where ename = 'KING') e, 3 (select id as pos from t10) iter 4 where iter.pos <= length(e.ename);
t10中有十条数据,id从1-10。
from子句提供了笛卡尔积,结果表类似于下图
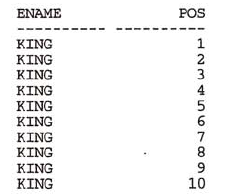
where子句限制pos范围。
另一个例子:
1 select substr(f.title, iter.pos) as C, 2 substr(f.title, length(f.title) -iter.pos + 1) as D 3 from (select title from film where film_id = 1) f, 4 (select id as pos from t10) iter 5 where iter.pos <= length(f.title);
2、字符串中的单引号
需要用两个单引号转义。
1 select 't''1' from t10;
3、计算字符在字符串中出现的次数
首先计算出原串长度,计算出然后把目标字符替换掉的字符串的长度,最后做差。
1 select length(f.title) - length(replace(f.title, 'A', '')) as cnt 2 from film f 3 where f.film_id = 1;
多个字符时,要除一下目标串的长度:
1 select length(f.title) - length(replace(f.title, 'A', ''))/length('A') as cnt 2 from film f 3 where f.film_id = 1;
4、判断字符串是不是字母数字型的
1 select title 2 from film 3 where title regexp '[^0-9a-zA-Z[:blank:]]' = 0;
整个表达式的意思是,返回“除数字、空格和字母外,还有其他字符”这一条件为假的行。
5、按字符串中的部分内容排序
1 select title 2 from film 3 where film_id <= 50 4 order by substr(title, 5);
6、组内字符串连接
使用group_concat
1 select substr(title, 1, 1) as word, 2 group_concat(title, '|') as titles 3 from film 4 group by substr(title, 1, 1)G
7、按字母顺序排列字符串
先将title拆成单个字母,然后使用原标题group起来,接着排序,最后使用group_concat连接字符串
1 select title, 2 group_concat(c order by c separator '') as new_title 3 from ( 4 select title, substr(a.title, iter.pos, 1) c 5 from film a, 6 (select id as pos from t10) iter 7 where iter.pos <= length(a.title) 8 ) x 9 group by title;
8、分解IP地址
将127.0.0.1按.分解
select substring_index(substring_index(y.ip, '.', 1), '.', -1) a, substring_index(substring_index(y.ip, '.', 2), '.', -1) b, substring_index(substring_index(y.ip, '.', 3), '.', -1) c, substring_index(substring_index(y.ip, '.', 4), '.', -1) d from (select '127.0.0.1' as ip from t10 limit 1) y;