201771010137 赵栋《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十一周学习总结
一:理论部分。
1.数据结构:分为a.线性数据结构,如线性表、栈、队列、串、数组和文件。
b.非线性数据结构,如树和图。
1)所有数据元素在同一个线性表中必须是相同的数据类型。
线性表按其存储结构可分为顺序表和链表。
2)栈:也是一种特殊的线性表,是一种后进先出(LIFO)的结构。
栈是限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除运算的线性表,表尾称为栈顶,表头称为栈底。
3)队列:限定所有的插入只能在表的一端进行,而所有的删除都在表的另一端进行的线性表。是一种先进先出(FIFO)的结构。
表中允许插入的一端称为队尾,允许删除的一端称为队头。
2.集合:(容器)是一种包含多个元素并提供对所包含元素操作方法的类,其包含的元素可以由同一类型的对象组成,也可以由不同类型的对象组成。
1)集合框架:JAVA集合类库的统一架构。
2)集合类的作用(包含在java.util包中):提供一些基本数据结构的支持,如Vector、Hashtable、Stack等。
3)集合类的特点:a.只容纳对象;
b.集合类容纳的对象都是Object类的实例(一旦把一个对象置入集合类中,它的类信息将丢失)
4)Vector类:类似长度可变的数组。它只能存放对象,其元素通过下标进行访问。
5)Stack类(Vector的子类):它描述堆栈数据结构。(所有对象都有一个散列码,可以通过Object类的hashCode方法获得。)
3.集合框架中的基本接口:a.Collection(构造类集框架的基础):集合层次中的根接口,JDK未提供这个接口的直接实现类。
b.Set:不能包含重复的元素,即元素必须唯一。对象可能不是按存放的次序存放。(实 现 Set 接口的类有HashSet,TreeSet)
c.List:有序的集合,可以包含重复的元素。提供了按索引访问的方式。实现它的类有ArrayList和LinkedLis(如ArrayList:能够自动增长容量的数组)
d.Map:Map接口映射唯一关键字到值。包含了key-value对。Map不能包含重复的key。SortedMap是一个按照升序排列key的Map。
二:实验部分。
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握Vetor、Stack、Hashtable三个类的用途及常用API;
(2) 了解java集合框架体系组成;
(3) 掌握ArrayList、LinkList两个类的用途及常用API。
(4) 了解HashSet类、TreeSet类的用途及常用API。
(5)了解HashMap、TreeMap两个类的用途及常用API;
(6) 结对编程(Pair programming)练习,体验程序开发中的两人合作。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第9章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 使用JDK命令运行编辑、运行以下三个示例程序,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握Vetor、Stack、Hashtable三个类的用途及常用API。
示例程序1:
import java.util.Vector;
class Cat {
private int catNumber;
Cat(int i) {
catNumber = i;
}
void print() {
System.out.println("Cat #" + catNumber);
}
}
class Dog {
private int dogNumber;
Dog(int i) {
dogNumber = i;
}
void print() {
System.out.println("Dog #" + dogNumber);
}
}
public class CatsAndDogs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector cats = new Vector();
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
cats.addElement(new Cat(i));
cats.addElement(new Dog(7));
for (int i = 0; i < cats.size(); i++)
((Cat) cats.elementAt(i)).print();//进行强制类型转化
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
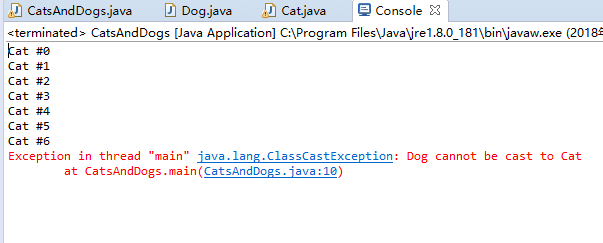
由程序运行结果可知,程序在强制转换类型时出现异常,更改后程序如下:
import java.util.Vector;
class Cat {
private int catNumber;
Cat(int i) {
catNumber = i;
}
void print() {
System.out.println("Cat #" + catNumber);
}
}
class Dog {
private int dogNumber;
Dog(int i) {
dogNumber = i;
}
void print() {
System.out.println("Dog #" + dogNumber);
}
}
public class CatsAndDogs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector cats = new Vector();
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
cats.addElement(new Cat(i));
cats.addElement(new Dog(7));
for (int i = 0; i < cats.size(); i++)
if (cats.elementAt(i) instanceof Cat) //判断是否能进行强制类型转换
{
((Cat) cats.elementAt(i)).print();//能进行强制类型转换,输出为Cat型
} else {
((Dog) cats.elementAt(i)).print();//不能进行强制类型转化,输出为Dog型
}
}
}
程序运行结果如下:

示例程序2:
import java.util.*;
public class 333{
static String[] months = { "1", "2", "3", "4" };
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stk = new Stack();
for (int i = 0; i < months.length; i++)
stk.push(months[i]);//进栈
System.out.println(stk);
System.out.println("element 2=" + stk.elementAt(2));
while (!stk.empty())
System.out.println(stk.pop());//输出出栈元素
}
}
程序运行结果如下: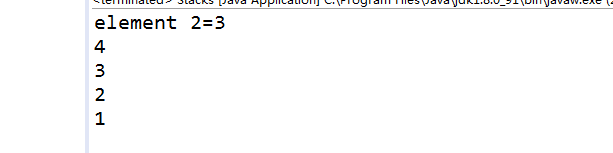
示例程序3:
import java.util.*;
class Counter {
int i = 1;
public String toString()
{
return Integer.toString(i);
}
}
public class Statistics {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Integer r = new Integer((int) (Math.random() * 20));
if (ht.containsKey(r))
((Counter) ht.get(r)).i++;
else
ht.put(r, new Counter());
}
System.out.println(ht);
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
测试程序2:
使用JDK命令编辑运行ArrayListDemo和LinkedListDemo两个程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
ArrayListDemo:
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayListDemo
{
public static void main(String[] argv) {
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(new Integer(11));
al.add(new Integer(12));
al.add(new Integer(13));
al.add(new String("hello"));
// First print them out using a for loop.
System.out.println("Retrieving by index:");
for (int i = 0; i < al.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("Element " + i + " = " + al.get(i));
}
}
}
程序运行结果如下: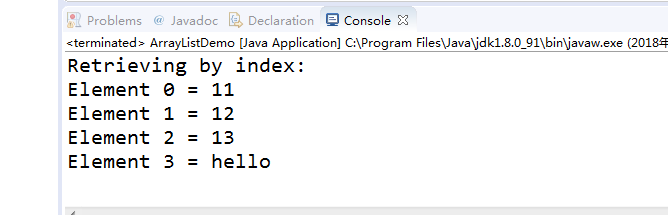
LinkedListDemo:
程序运行结果如下:
l 在Elipse环境下编辑运行调试教材360页程序9-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握ArrayList、LinkList两个类的用途及常用API。
程序如下:
import java.util.*;
/**
* This program demonstrates operations on linked lists.
* @version 1.11 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class LinkedListTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List<String> a = new LinkedList<>();
a.add("Amy");
a.add("Carl");
a.add("Erica");
List<String> b = new LinkedList<>();
b.add("Bob");
b.add("Doug");
b.add("Frances");
b.add("Gloria");
ListIterator<String> aIter = a.listIterator();
Iterator<String> bIter = b.iterator();
while (bIter.hasNext())
{
if (aIter.hasNext()) aIter.next();
aIter.add(bIter.next());
}
System.out.println(a);
bIter = b.iterator();
while (bIter.hasNext())
{
bIter.next();
if (bIter.hasNext())
{
bIter.next();
bIter.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(b);
a.removeAll(b);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
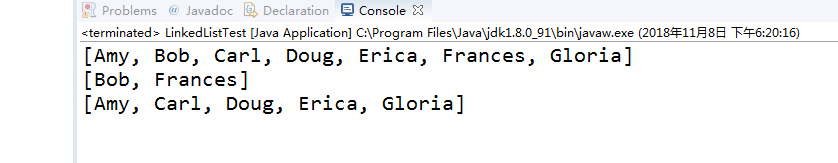
测试程序3:
l 运行SetDemo程序,结合运行结果理解程序;
程序如下:
import java.util.*;
public class SetDemo {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
HashSet h = new HashSet(); //也可以 Set h=new HashSet()
h.add("One");
h.add("Two");
h.add("One");
h.add("Three");
Iterator it = h.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
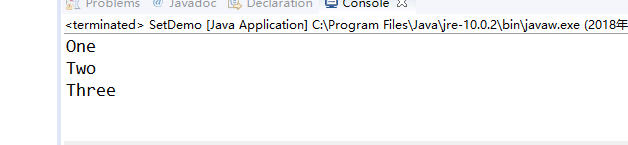
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材367页-368程序9-3、9-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;了解TreeSet类的用途及常用API。
9—3:
import java.util.*;
/**
* An item with a description and a part number.
*/
public class Item implements Comparable<Item>
{
private String description;
private int partNumber;
/**
* Constructs an item.
*
* @param aDescription
* the item's description
* @param aPartNumber
* the item's part number
*/
public Item(String aDescription, int aPartNumber)
{
description = aDescription;
partNumber = aPartNumber;
}
/**
* Gets the description of this item.
*
* @return the description
*/
public String getDescription()
{
return description;
}
public String toString()
{
return "[description=" + description + ", partNumber=" + partNumber + "]";
}
public boolean equals(Object otherObject)
{
if (this == otherObject) return true;
if (otherObject == null) return false;
if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false;
Item other = (Item) otherObject;
return Objects.equals(description, other.description) && partNumber == other.partNumber;
}
public int hashCode()
{
return Objects.hash(description, partNumber);
}
public int compareTo(Item other)
{
int diff = Integer.compare(partNumber, other.partNumber);
return diff != 0 ? diff : description.compareTo(other.description);
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
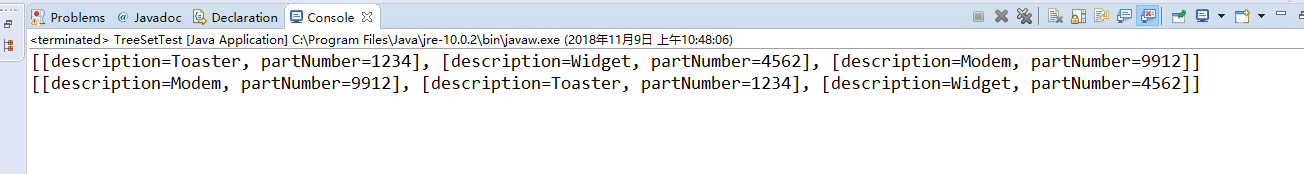
9—4:
import java.util.*;
/**
* This program sorts a set of item by comparing their descriptions.
* @version 1.12 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class TreeSetTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<Item> parts = new TreeSet<>();
parts.add(new Item("Toaster", 1234));
parts.add(new Item("Widget", 4562));
parts.add(new Item("Modem", 9912));
System.out.println(parts);
NavigableSet<Item> sortByDescription = new TreeSet<>(
Comparator.comparing(Item::getDescription));
sortByDescription.addAll(parts);
System.out.println(sortByDescription);
}
}
程序运行结果如图:
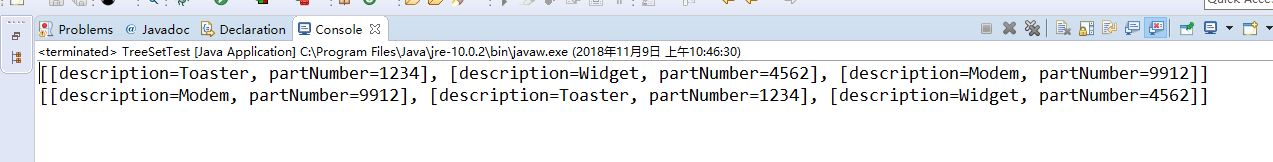
测试程序4:
l 使用JDK命令运行HashMapDemo程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
程序如下:
import java.util.*;
public class HashMapDemo
{
public static void main(String[] argv) {
HashMap h = new HashMap();
// 哈希映射从公司名称到地址
h.put("Adobe", "Mountain View, CA");
h.put("IBM", "White Plains, NY");
h.put("Sun", "Mountain View, CA");
String queryString = "Adobe";
String resultString = (String)h.get(queryString);
System.out.println("They are located in: " + resultString);
}
}
程序运行结果:
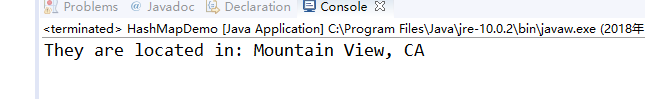
在Elipse环境下调试教材373页程序9-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
了解HashMap、TreeMap两个类的用途及常用API。
程序如下:
import java.util.*;
/**
* This program demonstrates the use of a map with key type String and value type Employee.
* @version 1.12 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
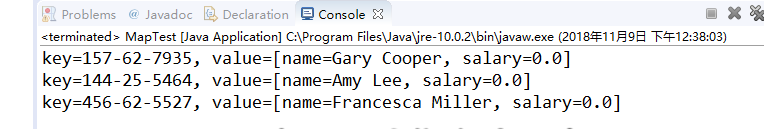
public class MapTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Map<String, Employee> staff = new HashMap<>();
staff.put("144-25-5464", new Employee("Amy Lee"));
staff.put("567-24-2546", new Employee("Harry Hacker"));
staff.put("157-62-7935", new Employee("Gary Cooper"));
staff.put("456-62-5527", new Employee("Francesca Cruz"));
System.out.println(staff);
staff.remove("567-24-2546");
staff.put("456-62-5527", new Employee("Francesca Miller"));
System.out.println(staff.get("157-62-7935"));
staff.forEach((k, v) ->
System.out.println("key=" + k + ", value=" + v));
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
实验2:结对编程练习:
l 关于结对编程:以下图片是一个结对编程场景:两位学习伙伴坐在一起,面对着同一台显示器,使用着同一键盘,同一个鼠标,他们一起思考问题,一起分析问题,一起编写程序。
l 关于结对编程的阐述可参见以下链接:
http://www.cnblogs.com/xinz/archive/2011/08/07/2130332.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pair_programming
l 对于结对编程中代码设计规范的要求参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/xinz/archive/2011/11/20/2255971.html
以下实验,就让我们来体验一下结对编程的魅力。
l 确定本次实验结对编程合作伙伴:东文才
l 各自运行合作伙伴实验九编程练习1,结合使用体验对所运行程序提出完善建议;
1 import java.io.BufferedReader;
2 import java.io.File;
3 import java.io.FileInputStream;
4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
5 import java.io.IOException;
6 import java.io.InputStreamReader;
7 import java.util.ArrayList;
8 import java.util.Arrays;
9 import java.util.Collections;
10 import java.util.Scanner;
11
12 public class ee {
13 private static ArrayList<Student> studentlist;
14 public static void main(String[] args) {
15
16 studentlist = new ArrayList<>();
17 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
18 File file = new File("F:\java\身份证号.txt");
19 try {
20 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
21 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
22 String temp = null;
23 while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) {
24
25 Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp);
26
27 linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
28 String name = linescanner.next();
29 String number = linescanner.next();
30 String sex = linescanner.next();
31 String age = linescanner.next();
32 String province =linescanner.nextLine();
33 Student student = new Student();
34 student.setName(name);
35 student.setnumber(number);
36 student.setsex(sex);
37 int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
38 student.setage(a);
39 student.setprovince(province);
40 studentlist.add(student);
41
42 }
43 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
44 System.out.println("找不到学生的信息文件");
45 e.printStackTrace();
46 } catch (IOException e) {
47 System.out.println("学生信息文件读取错误");
48 e.printStackTrace();
49 }
50 boolean isTrue = true;
51 while (isTrue) {
52 System.out.println("选择你的操作, ");
53 System.out.println("1.字典排序 ");
54 System.out.println("2.输出年龄最大和年龄最小的人 ");
55 System.out.println("3.寻找同乡 ");
56 System.out.println("4.寻找年龄相近的人 ");
57 System.out.println("5.退出 ");
58 String m = scanner.next();
59 switch (m) {
60 case "1":
61 Collections.sort(studentlist);
62 System.out.println(studentlist.toString());
63 break;
64 case "2":
65 int max=0,min=100;
66 int j,k1 = 0,k2=0;
67 for(int i=1;i<studentlist.size();i++)
68 {
69 j=studentlist.get(i).getage();
70 if(j>max)
71 {
72 max=j;
73 k1=i;
74 }
75 if(j<min)
76 {
77 min=j;
78 k2=i;
79 }
80
81 }
82 System.out.println("年龄最大:"+studentlist.get(k1));
83 System.out.println("年龄最小:"+studentlist.get(k2));
84 break;
85 case "3":
86 System.out.println("地址?");
87 String find = scanner.next();
88 String place=find.substring(0,3);
89 for (int i = 0; i <studentlist.size(); i++)
90 {
91 if(studentlist.get(i).getprovince().substring(1,4).equals(place))
92 System.out.println("同乡"+studentlist.get(i));
93 }
94 break;
95
96 case "4":
97 System.out.println("年龄:");
98 int yourage = scanner.nextInt();
99 int near=agenear(yourage);
100 int value=yourage-studentlist.get(near).getage();
101 System.out.println(""+studentlist.get(near));
102 break;
103 case "5 ":
104 isTrue = false;
105 System.out.println("退出程序!");
106 break;
107 default:
108 System.out.println("输入有误");
109
110 }
111 }
112 }
113 public static int agenear(int age) {
114 int j=0,min=53,value=0,ok=0;
115 for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++)
116 {
117 value=studentlist.get(i).getage()-age;
118 if(value<0) value=-value;
119 if (value<min)
120 {
121 min=value;
122 ok=i;
123 }
124 }
125 return ok;
126 }
127 }
1 public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
2
3 private String name;
4 private String number ;
5 private String sex ;
6 private int age;
7 private String province;
8
9 public String getName() {
10 return name;
11 }
12 public void setName(String name) {
13 this.name = name;
14 }
15 public String getnumber() {
16 return number;
17 }
18 public void setnumber(String number) {
19 this.number = number;
20 }
21 public String getsex() {
22 return sex ;
23 }
24 public void setsex(String sex ) {
25 this.sex =sex ;
26 }
27 public int getage() {
28
29 return age;
30 }
31 public void setage(int age) {
32 // int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
33 this.age= age;
34 }
35
36 public String getprovince() {
37 return province;
38 }
39 public void setprovince(String province) {
40 this.province=province ;
41 }
42
43 public int compareTo(Student o) {
44 return this.name.compareTo(o.getName());
45 }
46
47 public String toString() {
48 return name+" "+sex+" "+age+" "+number+" "+province+"
";
49 }
50 }
1 package ww;
2 import java.io.BufferedReader;
3 import java.io.File;
4 import java.io.FileInputStream;
5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
6 import java.io.IOException;
7 import java.io.InputStreamReader;
8 import java.util.ArrayList;
9 import java.util.Arrays;
10 import java.util.Collections;
11 import java.util.Scanner;
12
13
14 public class hhh{
15
16 private static ArrayList<Person> Personlist1;
17 public static void main(String[] args) {
18
19 Personlist1 = new ArrayList<>();
20
21 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
22 File file = new File("E:\面向对象程序设计Java\实验\实验六\身份证号.txt");
23
24 try {
25 FileInputStream F = new FileInputStream(file);
26 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(F));
27 String temp = null;
28 while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) {
29
30 Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp);
31
32 linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
33 String name = linescanner.next();
34 String id = linescanner.next();
35 String sex = linescanner.next();
36 String age = linescanner.next();
37 String place =linescanner.nextLine();
38 Person Person = new Person();
39 Person.setname(name);
40 Person.setid(id);
41 Person.setsex(sex);
42 int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
43 Person.setage(a);
44 Person.setbirthplace(place);
45 Personlist1.add(Person);
46
47 }
48 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
49 System.out.println("查找不到信息");
50 e.printStackTrace();
51 } catch (IOException e) {
52 System.out.println("信息读取有误");
53 e.printStackTrace();
54 }
55 boolean isTrue = true;
56 while (isTrue) {
57 System.out.println("******************************************");
58 System.out.println("1:按姓名字典顺序输出信息;");
59 System.out.println("2:查询最大年龄与最小年龄人员信息;");
60 System.out.println("3:按省份找你的同乡;");
61 System.out.println("4:输入你的年龄,查询年龄与你最近人的信息;");
62 System.out.println("5:退出");
63 System.out.println("******************************************");
64 int type = scanner.nextInt();
65 switch (type) {
66 case 1:
67 Collections.sort(Personlist1);
68 System.out.println(Personlist1.toString());
69 break;
70 case 2:
71
72 int max=0,min=100;int j,k1 = 0,k2=0;
73 for(int i=1;i<Personlist1.size();i++)
74 {
75 j=Personlist1.get(i).getage();
76 if(j>max)
77 {
78 max=j;
79 k1=i;
80 }
81 if(j<min)
82 {
83 min=j;
84 k2=i;
85 }
86
87 }
88 System.out.println("年龄最大:"+Personlist1.get(k1));
89 System.out.println("年龄最小:"+Personlist1.get(k2));
90 break;
91 case 3:
92 System.out.println("place?");
93 String find = scanner.next();
94 String place=find.substring(0,3);
95 String place2=find.substring(0,3);
96 for (int i = 0; i <Personlist1.size(); i++)
97 {
98 if(Personlist1.get(i).getbirthplace().substring(1,4).equals(place))
99 {
100 System.out.println("你的同乡:"+Personlist1.get(i));
101 }
102 }
103
104 break;
105 case 4:
106 System.out.println("年龄:");
107 int yourage = scanner.nextInt();
108 int close=ageclose(yourage);
109 int d_value=yourage-Personlist1.get(close).getage();
110 System.out.println(""+Personlist1.get(close));
111
112 break;
113 case 5:
114 isTrue = false;
115 System.out.println("再见!");
116 break;
117 default:
118 System.out.println("输入有误");
119 }
120 }
121 }
122 public static int ageclose(int age) {
123 int m=0;
124 int max=53;
125 int d_value=0;
126 int k=0;
127 for (int i = 0; i < Personlist1.size(); i++)
128 {
129 d_value=Personlist1.get(i).getage()-age;
130 if(d_value<0) d_value=-d_value;
131 if (d_value<max)
132 {
133 max=d_value;
134 k=i;
135 }
136
137 } return k;
138
139 }
140
1 package Second;
2
3
4 public class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
5
6 private String name;
7 private String id;
8 private int age;
9 private String sex;
10 private String birthplace;
11
12
13 public String getname() {
14 return name;
15 }
16 public void setname(String name) {
17 this.name = name;
18 }
19 public String getid() {
20 return id;
21 }
22 public void setid(String id) {
23 this.id= id;
24 }
25 public int getage() {
26
27 return age;
28 }
29 public void setage(int age) {
30 //int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
31 this.age= age;
32 }
33 public String getsex() {
34 return sex;
35 }
36 public void setsex(String sex) {
37 this.sex= sex;
38 }
39 public String getbirthplace() {
40 return birthplace;
41 }
42 public void setbirthplace(String birthplace) {
43 this.birthplace= birthplace;
44 }
45
46 public int compareTo(Person o) {
47 return this.name.compareTo(o.getname());
48
49 }
50
51 public String toString() {
52 return name+" "+sex+" "+age+" "+id+" ";


结合使用体验对所运行程序提出完善建议;
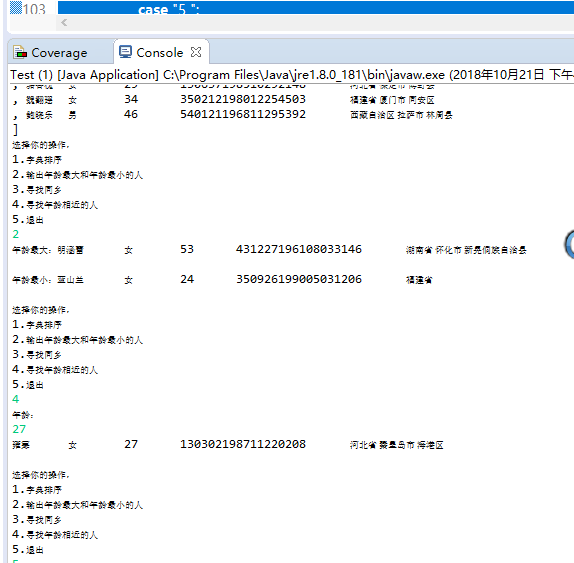
l 各自运行合作伙伴实验十编程练习2,
1 package Zhao;
2
3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
4 import java.io.PrintWriter;
5 import java.util.Scanner;
6
7 //import org.w3c.dom.css.Counter;
8
9
10 public class Main{
11 public static void main(String[] args) {
12
13 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
14 counter Counter=new counter();
15 PrintWriter output = null;
16 try {
17 output = new PrintWriter("result.txt");
18 } catch (Exception e) {
19 //e.printStackTrace();
20 }
21 int sum = 0;
22
23 for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {
24 int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
25 int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
26 int type = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 4);
27
28
29 switch(type)
30 {
31 case 1:
32
33 System.out.println(i+": "+a+"/"+b+"=");
34 while(b== 0&& a%b!=0)
35 {
36 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
37 a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
38 }
39
40 int c = in.nextInt();
41 output.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c);
42 if (c == Counter.Chu(a, b))
43 {
44 sum += 10;
45 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确!");
46 }
47 else {
48 System.out.println("答案错误!");
49 }
50 break;
51
52 case 2:
53 System.out.println(i+": "+a+"*"+b+"=");
54 int c1 = in.nextInt();
55 output.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c1);
56 if (c1 == Counter.Cheng(a, b)) {
57 sum += 10;
58 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确!");
59 }
60 else {
61 System.out.println("答案错误!");
62 }
63 break;
64 case 3:
65 System.out.println(i+": "+a+"+"+b+"=");
66 int c2 = in.nextInt();
67 output.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c2);
68
69 if (c2 == Counter.Jia(a, b)) {
70 sum += 10;
71 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确!");
72 }
73 else {
74 System.out.println("答案错误!");
75 }
76 break ;
77
78
79 case 4:
80
81 while (a < b) {
82 int x=0;
83 x=b;
84 b=a;
85 a=x;
86 }
87 System.out.println(i+": "+a+"-"+b+"=");
88 int c3 = in.nextInt();
89 output.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c3);
90 if (c3 == Counter.Jian(a, b))
91 {
92 sum += 10;
93 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确!");
94 }
95 else {
96 System.out.println("答案错误!");
97 }
98 break ;
99
100 }
101
102 }
103 System.out.println("成绩"+sum);
104 output.println("成绩:"+sum);
105 output.close();
106
107 }
108 }
1 package Zhao;
2
3
4 public class counter<T>{
5 private T a;
6 private T b;
7
8 public counter(T a, T b) {
9 this.a = a;
10 this.b = b;
11 }
12
13 public counter() {
14 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
15 }
16
17 public int Jia(int a,int b)
18 {
19 return a+b;
20 }
21 public int Jian(int a,int b)
22 {
23 return a-b;
24
25
26 }
27 public int Cheng(int a,int b)
28 {
29 return a*b;
30 }
31 public int Chu(int a,int b)
32 {
33 if (b!= 0 && a%b==0)
34 return a / b;
35 else
36 return 0;
37
38 }
39
40
41 }

结合使用体验对所运行程序提出完善建议;
实验十
1.没有全面考虑小学生的实际状况:减法算法结果可能出现负数的情况,以及除法的运算结果直接取整输出,都不符合小学生的学习范围;
2.编程过程中,关于变量的使用混乱问题;
3.结果没有输出到文件中;
l 采用结对编程方式,与学习伙伴合作完成实验九编程练习1;
1 package First;
2 import java.io.BufferedReader;
3 import java.io.File;
4 import java.io.FileInputStream;
5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
6 import java.io.IOException;
7 import java.io.InputStreamReader;
8 import java.util.ArrayList;
9 import java.util.Arrays;
10 import java.util.Collections;
11 import java.util.Scanner;
12
13
14 public class Search{
15
16 private static ArrayList<Person> Personlist1;
17 public static void main(String[] args) {
18
19 Personlist1 = new ArrayList<>();
20
21 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
22 File file = new File("E:\面向对象程序设计Java\实验\实验六\身份证号.txt");
23
24 try {
25 FileInputStream F = new FileInputStream(file);
26 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(F));
27 String temp = null;
28 while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) {
29
30 Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp);
31
32 linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
33 String name = linescanner.next();
34 String id = linescanner.next();
35 String sex = linescanner.next();
36 String age = linescanner.next();
37 String place =linescanner.nextLine();
38 Person Person = new Person();
39 Person.setname(name);
40 Person.setid(id);
41 Person.setsex(sex);
42 int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
43 Person.setage(a);
44 Person.setbirthplace(place);
45 Personlist1.add(Person);
46
47 }
48 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
49 System.out.println("查找不到信息");
50 e.printStackTrace();
51 } catch (IOException e) {
52 System.out.println("信息读取有误");
53 e.printStackTrace();
54 }
55 boolean isTrue = true;
56 while (isTrue) {
57 System.out.println("******************************************");
58 System.out.println("1:按姓名字典顺序输出信息;");
59 System.out.println("2:查询最大年龄与最小年龄人员信息;");
60 System.out.println("3:按省份找你的同乡;");
61 System.out.println("4:输入你的年龄,查询年龄与你最近人的信息;");
62 System.out.println("5:退出");
63 System.out.println("******************************************");
64 int type = scanner.nextInt();
65 switch (type) {
66 case 1:
67 Collections.sort(Personlist1);
68 System.out.println(Personlist1.toString());
69 break;
70 case 2:
71
72 int max=0,min=100;int j,k1 = 0,k2=0;
73 for(int i=1;i<Personlist1.size();i++)
74 {
75 j=Personlist1.get(i).getage();
76 if(j>max)
77 {
78 max=j;
79 k1=i;
80 }
81 if(j<min)
82 {
83 min=j;
84 k2=i;
85 }
86
87 }
88 System.out.println("年龄最大:"+Personlist1.get(k1));
89 System.out.println("年龄最小:"+Personlist1.get(k2));
90 break;
91 case 3:
92 System.out.println("place?");
93 String find = scanner.next();
94 String place=find.substring(0,3);
95 String place2=find.substring(0,3);
96 for (int i = 0; i <Personlist1.size(); i++)
97 {
98 if(Personlist1.get(i).getbirthplace().substring(1,4).equals(place))
99 {
100 System.out.println("你的同乡:"+Personlist1.get(i));
101 }
102 }
103
104 break;
105 case 4:
106 System.out.println("年龄:");
107 int yourage = scanner.nextInt();
108 int close=ageclose(yourage);
109 int d_value=yourage-Personlist1.get(close).getage();
110 System.out.println(""+Personlist1.get(close));
111
112 break;
113 case 5:
114 isTrue = false;
115 System.out.println("再见!");
116 break;
117 default:
118 System.out.println("输入有误");
119 }
120 }
121 }
122 public static int ageclose(int age) {
123 int m=0;
124 int max=53;
125 int d_value=0;
126 int k=0;
127 for (int i = 0; i < Personlist1.size(); i++)
128 {
129 d_value=Personlist1.get(i).getage()-age;
130 if(d_value<0) d_value=-d_value;
131 if (d_value<max)
132 {
133 max=d_value;
134 k=i;
135 }
136
137 } return k;
138
139 }
140 }
1 package FFF;
2
3
4 public class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
5
6
7 private String name;
8 private String id;
9 private int age;
10 private String sex;
11 private String birthplace;
12
13 public String getname() {
14 return name;
15 }
16 public void setname(String name) {
17 this.name = name;
18 }
19 public String getid() {
20 return id;
21 }
22 public void setid(String id) {
23 this.id= id;
24 }
25 public int getage() {
26
27 return age;
28 }
29 public void setage(int age) {
30 //int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
31 this.age= age;
32 }
33 public String getsex() {
34 return sex;
35 }
36 public void setsex(String sex) {
37 this.sex= sex;
38 }
39 public String getbirthplace() {
40 return birthplace;
41 }
42 public void setbirthplace(String birthplace) {
43 this.birthplace= birthplace;
44 }
45
46 public int compareTo(Person o) {
47 return this.name.compareTo(o.getname());
48
49 }
50
51 public String toString() {
52 return name+" "+sex+" "+age+" "+id+" ";

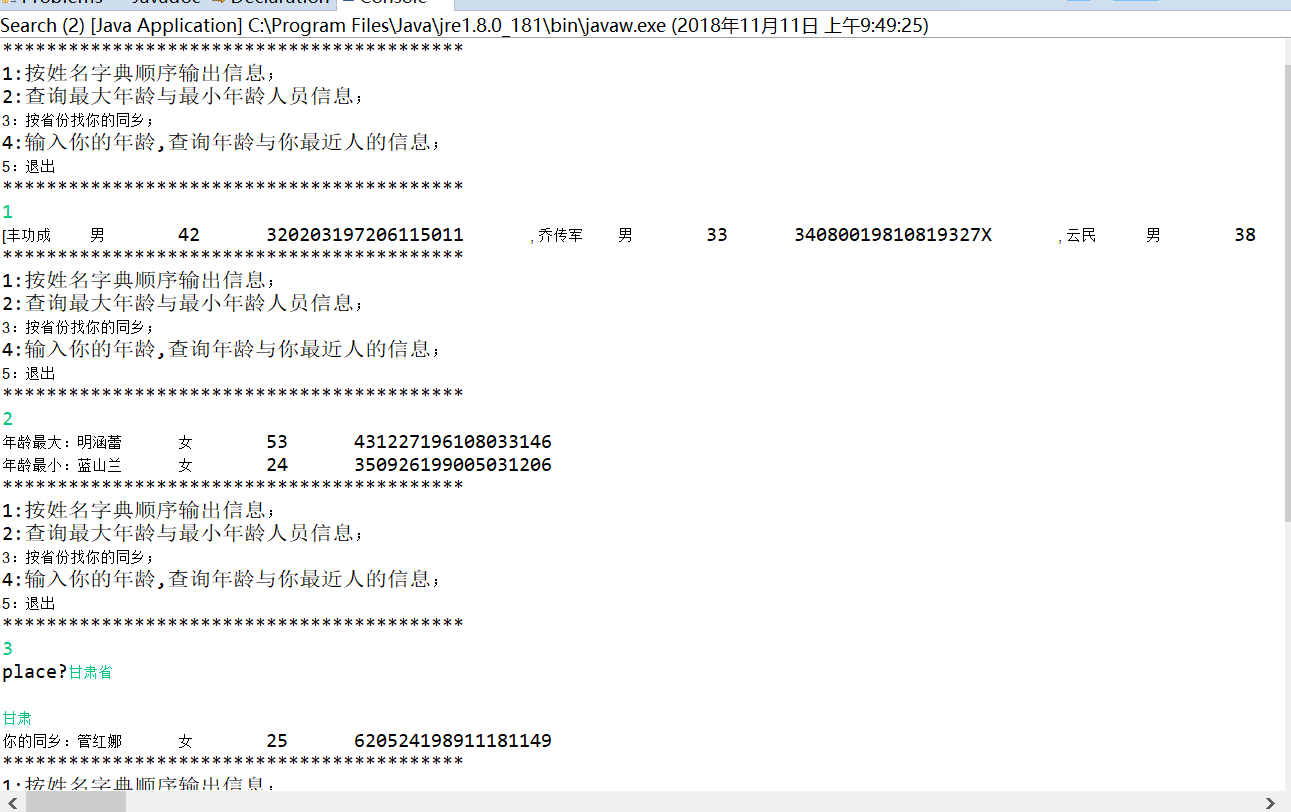
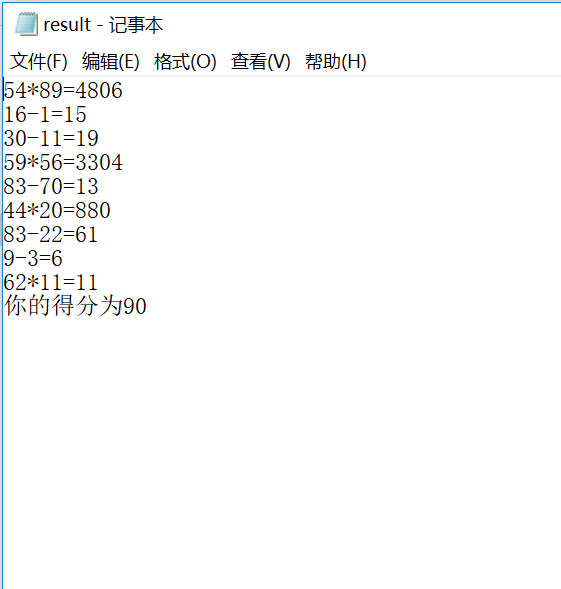
采用结对编程方式,与学习伙伴合作完成实验十编程练习2。
1 package PP;
2
3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
4 import java.io.IOException;
5 import java.io.PrintWriter;
6 import java.util.Scanner;
7 public class Main {
8
9 public static void main(String[] args) {
10 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
11 counter min=new counter();
12 PrintWriter out = null;
13 try {
14 out = new PrintWriter("result.txt");
15 int sum = 0;
16 for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {
17 int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
18 int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
19 int menu = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3);
20 switch (menu) {
21 case 0:
22 System.out.println(i+":"+a + "+" + b + "=");
23 int c1 = in.nextInt();
24 out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + c1);
25 if (c1 == (a + b)) {
26 sum += 10;
27 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确");
28 } else {
29 System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误");
30 }
31 break;
32 case 1:
33 while (a < b) {
34 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
35 }
36 System.out.println(i+":"+a + "-" + b + "=");
37 int c2 = in.nextInt();
38 out.println(a + "-" + b + "=" + c2);
39 if (c2 == (a - b)) {
40 sum += 10;
41 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确");
42 } else {
43 System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误");
44 }
45
46 break;
47 case 2:
48 System.out.println(i+":"+a + "*" + b + "=");
49 int c3 = in.nextInt();
50 out.println(a + "*" + b + "=" + c3);
51 if (c3 == a * b) {
52 sum += 10;
53 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确");
54 } else {
55 System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误");
56 }
57
58 break;
59 case 3:
60 while(b == 0){
61 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
62 }
63 while(a % b != 0){
64 a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
65
66 }
67 System.out.println(i+":"+a + "/" + b + "=");
68 int c4 = in.nextInt();
69 if (c4 == a / b) {
70 sum += 10;
71 System.out.println("恭喜,答案正确");
72 } else {
73 System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误");
74 }
75
76 break;
77 }
78 }
79 System.out.println("你的得分为" + sum);
80 out.println("你的得分为" + sum);
81 out.close();
82 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
83 e.printStackTrace();
84 }
85 }
86 }
1 package PP;
2
3 public class counter<T> {
4 private T a;
5 private T b;
6 public counter() {
7 a=null;
8 b=null;
9 }
10 public counter(T a,T b) {
11 this.a=a;
12 this.b=b;
13 }
14 public int count1(int a,int b) {
15 return a+b;
16 }
17 public int count2(int a,int b) {
18 return a-b;
19 }
20 public int count3(int a,int b) {
21 return a*b;
22 }
23 public int count4(int a,int b) {
24 return a/b;
25 }
26 }

实验总结:
通过本周学习,我进一步复习了一些有关数据结构的知识,另外初步了解了java集合类,也了解了Vector类,Stack类以及Hashtable类。除此以外,此次实验第一次采用结对编程的方法,通过和合作伙伴互相运行程序,相互讨论交流,从中学到了很多东西。希望以后多采取这种方法,在合作中互相学习进步。
