模拟退火算法SA原理及python、java、php、c++语言代码实现TSP旅行商问题,智能优化算法,随机寻优算法,全局最短路径
模拟退火算法(Simulated Annealing,SA)最早的思想是由N. Metropolis等人于1953年提出。1983 年,S. Kirkpatrick 等成功地将退火思想引入到组合优化领域。
来源于固体退火原理,将固体加温至充分高,再让其徐徐冷却,加温时,固体内部粒子随温升变为无序状,内能增大,而徐徐冷却时粒子渐趋有序,在每个温度都达到平衡态,最后在常温时达到基态,内能减为最小。
它是基于Monte-Carlo(蒙特卡洛)迭代求解策略的一种随机寻优算法,其出发点是基于物理中固体物质的退火过程与一般组合优化问题之间的相似性。
模拟退火算法从某一较高初温出发,伴随温度参数的不断下降,结合概率突跳特性在解空间中随机寻找目标函数的全局最优解,即在局部最优解能概率性地跳出并最终趋于全局最优。模拟退火算法是一种通用的优化算法,理论上算法具有概率的全局优化性能,目前已在工程中得到了广泛应用,诸如VLSI、生产调度、控制工程、机器学习、神经网络、信号处理等领域。
模拟退火算法是通过赋予搜索过程一种时变且最终趋于零的概率突跳性,从而可有效避免陷入局部极小并最终趋于全局最优的串行结构的优化算法。
这里的“一定的概率”的计算参考了金属冶炼的退火过程,这也是模拟退火算法名称的由来。
根据热力学的原理,在温度为T时,出现能量差为dE的降温的概率为P(dE),表示为:
P(dE) = exp( dE/(kT) )
其中k是一个常数,exp表示自然指数,且dE<0。这条公式说白了就是:温度越高,出现一次能量差为dE的降温的概率就越大;温度越低,则出现降温的概率就越小。又由于dE总是小于0(否则就不叫退火了),因此dE/kT < 0 ,所以P(dE)的函数取值范围是(0,1) 。
随着温度T的降低,P(dE)会逐渐降低。我们将一次向较差解的移动看做一次温度跳变过程,我们以概率P(dE)来接受这样的移动。
二、什么是智能优化算法
启发式算法,是一种具有全局优化性能、通用性强且适用于并行处理的算法。这种算法一般具有严密的理论依据,而不是单纯凭专家经验,理论上可以在一定的时间内找到最优解或近似最优解。
常用的智能优化算法
遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm, GA)
模拟退火算法(Simulated Annealing, SA)
禁忌搜索算法(Tabu Search, TS)
神经网络 (Neural Network)
蚁群算法(Ant Colony Optimization,ACO)
爬山算法(局部最优解法) ( Hill Climbing )
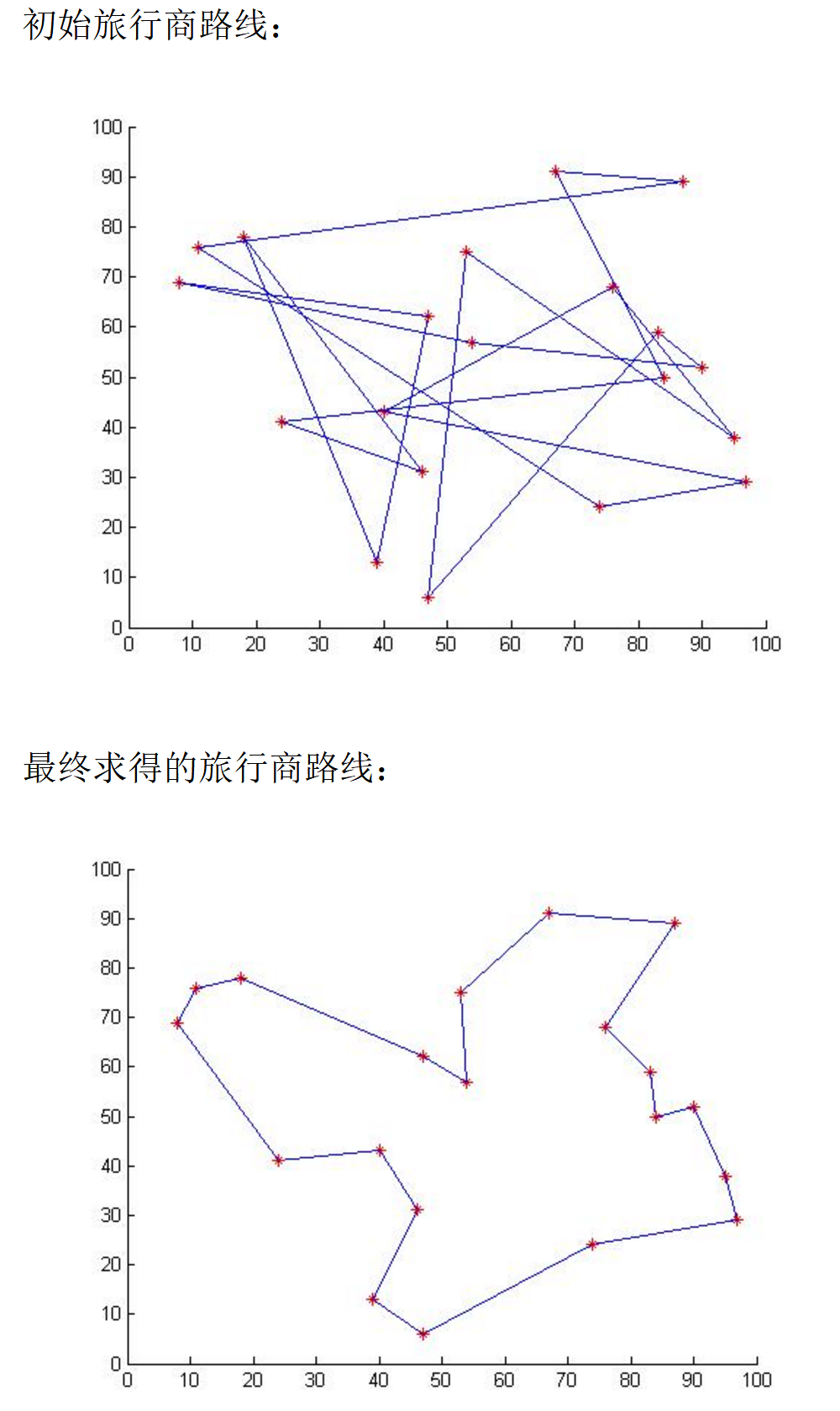
三、TSP问题描述
旅行商问题描述的是一个旅行商要在N之间游走来贩卖货物,而路费的成本与距离成正比,因此他想在N个城市之间找到仅一条最短路径,即能去所有城市一次且仅一次,最后回到出发点。
这个简单的问题被证明为NP问题,对于N个城市的问题计算量为O(N!),对于N=40时的计算量就已是目前全世界最强的计算机都难以解决。因此必须寻找其它的可行的算法(TSP问题算法目前有:爬山、禁忌、蚁群、退火、遗传算法),模拟退火算法就是其中一种。
模拟退火算法其特点是在开始搜索阶段解的质量提高比较缓慢,但是到了迭代后期,它的解的质量提高明显,所以如果在求解过程中,对迭代步数限制比较严格的话,模拟退火算法在有限的迭代步数内很难得到高质量的解。总体而言模拟退火算法比较适合用于有充足计算资源的问题求解。
根据Metropolis准则,粒子在温度T时趋于平衡的概率为exp(-ΔE/(kT)),其中E为温度T时的内能,ΔE为其改变数,k为Boltzmann常数。
若f( Y(i+1) ) <= f( Y(i) ) (即移动后得到更优解),则总是接受该移动;
若f( Y(i+1) ) > f( Y(i) ) (即移动后的解比当前解要差),则以一定的概率接受移动,而且这个概率随着时间推移逐渐降低(逐渐降低才能趋向稳定)相当于上图中,从B移向BC之间的小波峰时,每次右移(即接受一个更糟糕值)的概率在逐渐降低。如果这个坡特别长,那么很有可能最终我们并不会翻过这个坡。如果它不太长,这很有可能会翻过它,这取决于衰减 t 值的设定。
====================
模拟退火算法 伪代码
s:=s0;e:=E(s)//设定目前状态为s0,其能量E(s0)
k:=0//评估次数k
whilek<kmaxande>emax//若还有时间(评估次数k还不到kmax)且结果还不够好(能量e不够低)则:
sn:=neighbour(s)//随机选取一临近状态sn
en:=Esn)//sn的能量为E(sn)
ifrandom()<P(e,en,temp(k/kmax))then//决定是否移至临近状态sn
s:=sn;e:=en//移至临近状态sn
k:=k+1//评估完成,次数k加一
returns//回转状态s
===============
模拟退火算法python有库可以调用,实现起来很简单
Python 代码实现编辑
step1:在GitHub上下载常用的 scikit-opt [2] 库。
step2:设立目标函数并执行模拟退火算法。
def demo_func(x): x1, x2, x3 = x return x1 ** 2 + (x2 - 0.05) ** 2 + x3 ** 2 from sko.SA import SA sa = SA(func=demo_func, x0=[1, 1, 1]) x_star, y_star = sa.fit() step2(2):如果是最短路径问题(TSP) sa_tsp = SA_TSP(func=demo_func, x0=range(num_points)) best_points, best_distance = sa_tsp.fit()
====================
TSP问题的SA算法PHP实现
<?php class SimulatedAnnealing { private $map;//地图,按照矩阵的方式 private $n;//地图规模 private $T;//初始温度T private $L;//每个温度下达到降温状态的迭代次数 private $l;//降温常数小于却接近于1的常数。λ通常的取值在0.8至0.99之间。在每一温度下,实验足够多的转移次数 private $ord_temp;//降温终止条件,相当于降温到常温 private $path;//输出结果 public function __construct($_map,$_n,$_T,$_L) { $this->map = $_map; $this->n = $_n; $this->T = $_T; $this->L = $_L; $this->l = 0.95; $this->ord_temp = 1; } function randomFloat($min = 0, $max = 1) { return $min + mt_rand() / mt_getrandmax() * ($max - $min); } public function output() { foreach($this->path as $key => $value) { echo $value."->"; } } //第二个元素向右随机移动1至n-2位 public function new_S($_S) { $temp_S = $_S; $shift = rand(1,$this->n-2); $ts = $temp_S[1]; $temp_S[1] = $temp_S[1+$shift]; $temp_S[1+$shift] = $ts; return $temp_S; } public function cost($_S) { $_cost = 0; for($i=0;$i<$this->n-1;$i++) { $_cost += $this->map[$_S[$i]][$_S[$i+1]]; } $_cost += $this->map[$_S[$i]][0]; return $_cost; } public function calculate() { //初始解 $S = array(); for($i=0;$i<$this->n;$i++) { $S[$i] = $i; } $S[] = 0; $this->path = $S; //进入降温过程,初始温度为T $t = $this->T; while($t > $this->ord_temp) { for($i=0;$i<$this->L;$i++) { //产生新解 $S1 = $this->new_S($S); //判断新解的价值 $K = $this->cost($S1) - $this->cost($S); if($K < 0) { $S = $S1; if($this->cost($S) < $this->cost($this->path)) $this->path = $S; } else { //不好的解根据Metropolis准则接受 if($this->randomFloat(0,1) < exp(-$K/$t)) { $S = $S1; } } } //这里可以按照如果连续几次降温能量不变作为终止循序条件 //本例按照降温到常温终止,不计算是否能量不变,需要初始温度给定足够好 $t = $t * $this->l; } //输出结果 $this->output(); echo '<br>The min cost is '.$this->cost($this->path); } } ?>
调用过程:
$map = array( array(0,3,6,7), array(5,0,2,3), array(6,4,0,2), array(3,7,5,0), ); $n = 4; $T = 20; $L = 100; $SA = new SimulatedAnnealing($map,$n,$T,$L); $SA->calculate();
结果输出:
0->1->2->3->0->
The min cost is 10
=========================
TSP问题JAVA实现代码:
package noah; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.Random; public class SA { private int cityNum; // 城市数量,编码长度 private int N;// 每个温度迭代步长 private int T;// 降温次数 private float a;// 降温系数 private float t0;// 初始温度 private int[][] distance; // 距离矩阵 private int bestT;// 最佳出现代数 private int[] Ghh;// 初始路径编码 private int GhhEvaluation; private int[] bestGh;// 最好的路径编码 private int bestEvaluation; private int[] tempGhh;// 存放临时编码 private int tempEvaluation; private Random random; public SA() { } /** * constructor of GA * * @param cn * 城市数量 * @param t * 降温次数 * @param n * 每个温度迭代步长 * @param tt * 初始温度 * @param aa * 降温系数 * **/ public SA(int cn, int n, int t, float tt, float aa) { cityNum = cn; N = n; T = t; t0 = tt; a = aa; } // 给编译器一条指令,告诉它对被批注的代码元素内部的某些警告保持静默 @SuppressWarnings("resource") /** * 初始化Tabu算法类 * @param filename 数据文件名,该文件存储所有城市节点坐标数据 * @throws IOException */ private void init(String filename) throws IOException { // 读取数据 int[] x; int[] y; String strbuff; BufferedReader data = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader( new FileInputStream(filename))); distance = new int[cityNum][cityNum]; x = new int[cityNum]; y = new int[cityNum]; for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) { // 读取一行数据,数据格式1 6734 1453 strbuff = data.readLine(); // 字符分割 String[] strcol = strbuff.split(" "); x[i] = Integer.valueOf(strcol[1]);// x坐标 y[i] = Integer.valueOf(strcol[2]);// y坐标 } // 计算距离矩阵 // ,针对具体问题,距离计算方法也不一样,此处用的是att48作为案例,它有48个城市,距离计算方法为伪欧氏距离,最优值为10628 for (int i = 0; i < cityNum - 1; i++) { distance[i][i] = 0; // 对角线为0 for (int j = i + 1; j < cityNum; j++) { double rij = Math .sqrt(((x[i] - x[j]) * (x[i] - x[j]) + (y[i] - y[j]) * (y[i] - y[j])) / 10.0); // 四舍五入,取整 int tij = (int) Math.round(rij); if (tij < rij) { distance[i][j] = tij + 1; distance[j][i] = distance[i][j]; } else { distance[i][j] = tij; distance[j][i] = distance[i][j]; } } } distance[cityNum - 1][cityNum - 1] = 0; Ghh = new int[cityNum]; bestGh = new int[cityNum]; bestEvaluation = Integer.MAX_VALUE; tempGhh = new int[cityNum]; tempEvaluation = Integer.MAX_VALUE; bestT = 0; random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println(cityNum+","+N+","+T+","+a+","+t0); } // 初始化编码Ghh void initGroup() { int i, j; Ghh[0] = random.nextInt(65535) % cityNum; for (i = 1; i < cityNum;)// 编码长度 { Ghh[i] = random.nextInt(65535) % cityNum; for (j = 0; j < i; j++) { if (Ghh[i] == Ghh[j]) { break; } } if (j == i) { i++; } } } // 复制编码体,复制编码Gha到Ghb public void copyGh(int[] Gha, int[] Ghb) { for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) { Ghb[i] = Gha[i]; } } public int evaluate(int[] chr) { // 0123 int len = 0; // 编码,起始城市,城市1,城市2...城市n for (int i = 1; i < cityNum; i++) { len += distance[chr[i - 1]][chr[i]]; } // 城市n,起始城市 len += distance[chr[cityNum - 1]][chr[0]]; return len; } // 邻域交换,得到邻居 public void Linju(int[] Gh, int[] tempGh) { int i, temp; int ran1, ran2; for (i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) { tempGh[i] = Gh[i]; } ran1 = random.nextInt(65535) % cityNum; ran2 = random.nextInt(65535) % cityNum; while (ran1 == ran2) { ran2 = random.nextInt(65535) % cityNum; } temp = tempGh[ran1]; tempGh[ran1] = tempGh[ran2]; tempGh[ran2] = temp; } public void solve() { // 初始化编码Ghh initGroup(); copyGh(Ghh, bestGh);// 复制当前编码Ghh到最好编码bestGh bestEvaluation = evaluate(Ghh); GhhEvaluation = bestEvaluation; int k = 0;// 降温次数 int n = 0;// 迭代步数 float t = t0; float r = 0.0f; while (k < T) { n = 0; while (n < N) { Linju(Ghh, tempGhh);// 得到当前编码Ghh的邻域编码tempGhh tempEvaluation = evaluate(tempGhh); if (tempEvaluation < bestEvaluation) { copyGh(tempGhh, bestGh); bestT = k; bestEvaluation = tempEvaluation; } r = random.nextFloat(); if (tempEvaluation < GhhEvaluation || Math.exp((GhhEvaluation - tempEvaluation) / t) > r) { copyGh(tempGhh, Ghh); GhhEvaluation = tempEvaluation; } n++; } t = a * t; k++; } System.out.println("最佳长度出现代数:"); System.out.println(bestT); System.out.println("最佳长度"); System.out.println(bestEvaluation); System.out.println("最佳路径:"); for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) { System.out.print(bestGh[i] + ","); if (i % 10 == 0 && i != 0) { System.out.println(); } } } /** * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("Start...."); SA sa = new SA(48, 40, 400, 250.0f, 0.98f); sa.init("c://data.txt"); sa.solve(); } }
==================
C++实现的代码:
#include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <algorithm> #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> #include <math.h> #define N 30 //城市数量 #define T 3000 //初始温度 #define EPS 1e-8 //终止温度 #define DELTA 0.98 //温度衰减率 #define LIMIT 1000 //概率选择上限 #define OLOOP 20 //外循环次数 #define ILOOP 100 //内循环次数 using namespace std; //定义路线结构体 struct Path { int citys[N]; double len; }; //定义城市点坐标 struct Point { double x, y; }; Path bestPath; //记录最优路径 Point p[N]; //每个城市的坐标 double w[N][N]; //两两城市之间路径长度 int nCase; //测试次数 double dist(Point A, Point B) { return sqrt((A.x - B.x) * (A.x - B.x) + (A.y - B.y) * (A.y - B.y)); } void GetDist(Point p[], int n) { for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) w[i][j] = w[j][i] = dist(p[i], p[j]); } void Input(Point p[], int &n) { scanf("%d", &n); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%lf %lf", &p[i].x, &p[i].y); } void Init(int n) { nCase = 0; bestPath.len = 0; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { bestPath.citys[i] = i; if(i != n - 1) { printf("%d--->", i); bestPath.len += w[i][i + 1]; } else printf("%d ", i); } printf(" Init path length is : %.3lf ", bestPath.len); printf("----------------------------------- "); } void Print(Path t, int n) { printf("Path is : "); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(i != n - 1) printf("%d-->", t.citys[i]); else printf("%d ", t.citys[i]); } printf(" The path length is : %.3lf ", t.len); printf("----------------------------------- "); } Path GetNext(Path p, int n) { Path ans = p; int x = (int)(n * (rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0))); int y = (int)(n * (rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0))); while(x == y) { x = (int)(n * (rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0))); y = (int)(n * (rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0))); } swap(ans.citys[x], ans.citys[y]); ans.len = 0; for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) ans.len += w[ans.citys[i]][ans.citys[i + 1]]; cout << "nCase = " << nCase << endl; Print(ans, n); nCase++; return ans; } void SA(int n) { double t = T; srand((unsigned)(time(NULL))); Path curPath = bestPath; Path newPath = bestPath; int P_L = 0; int P_F = 0; while(1) //外循环,主要更新参数t,模拟退火过程 { for(int i = 0; i < ILOOP; i++) //内循环,寻找在一定温度下的最优值 { newPath = GetNext(curPath, n); double dE = newPath.len - curPath.len; if(dE < 0) //如果找到更优值,直接更新 { curPath = newPath; P_L = 0; P_F = 0; } else { double rd = rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0); //如果找到比当前更差的解,以一定概率接受该解,并且这个概率会越来越小 if(exp(dE / t) > rd && exp(dE / t) < 1) curPath = newPath; P_L++; } if(P_L > LIMIT) { P_F++; break; } } if(curPath.len < bestPath.len) bestPath = curPath; if(P_F > OLOOP || t < EPS) break; t *= DELTA; } } int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { freopen("TSP.data", "r", stdin); int n; Input(p, n); GetDist(p, n); Init(n); SA(n); Print(bestPath, n); printf("Total test times is : %d ", nCase); return 0; }