http://www.cnblogs.com/xpchild/p/3780625.html
Open_table_definitions The number of cached .frm files.
Open_tables //当前打开的表数 The number of tables that are open.
Opened_files //已经打开过了的FILE 数 The number of files that have been opened with my_open() (a mysys library function). Parts of the server that open files without using this function do not increment the count.
Opened_table_definitions The number of .frm files that have been cached.
Opened_tables The number of tables that have been opened. If Opened_tables is big, your table_open_cache value is probably too small.
mysql> show global status like 'Opened_table_definitions'; //已打开过的表定义文件数 +--------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+-------+ | Opened_table_definitions | 112 | +--------------------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> show global status like 'Open_table_definitions'; //当前打开的表定义 +------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +------------------------+-------+ | Open_table_definitions | 1 | +------------------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
table_cache 参数设置表高速缓存的数目。每个连接进来,都会至少打开一个表缓存。因此, table_cache 的大小应与 max_connections 的设置有关。例如,对于 200 个并行运行的连接,应该让表的缓存至少有 200 × N ,这里 N 是应用可以执行的查询的一个联接中表的最大数量。此外,还需要为临时表和文件保留一些额外的文件描述符。 缓存机制 当 Mysql 访问一个表时,如果该表在缓存中已经被打开,则可以直接访问缓存;如果还没有被缓存,但是在 Mysql 表缓冲区中还有空间,那么这个表就被打开并放入表缓冲区;如果表缓存满了,则会按照一定的规则将当前未用的表释放,或者临时扩大表缓存来存放,使用表缓存的好处是可以更快速地访问表中的内容。 参数调优 一般来说,可以通过查看数据库运行峰值时间的状态值 Open_tables 和 Opened_tables ,判断是否需要增加 table_cache 的值(其中 open_tables 是当前打开的表的数量, Opened_tables 则是已经打开的表的数量)。即如果open_tables接近table_cache的时候,并且Opened_tables这个值在逐步增加,那就要考虑增加这个值的大小了。还有就是Table_locks_waited比较高的时候,也需要增加table_cache。 mysql> show global status like 'open%_tables'; 如果Open_tables的值已经接近table_cache的值,且Opened_tables还在不断变大,则说明mysql正在将缓存的表释放以容纳新的表,此时可能需要加大table_cache的值。对于大多数情况, 比较适合的值: Open_tables / Opened_tables >= 0.85 Open_tables / table_cache <= 0.95 如果对此参数的把握不是很准,VPS管理百科给出一个很保守的设置建议:把MySQL数据库放在生产环境中试运行一段时间,然后把参数的值调整得比Opened_tables的数值大一些,并且保证在比较高负载的极端条件下依然比Opened_tables略大。 在mysql默认安装情况下,table_cache的值在2G内存以下的机器中的值默认时256到 512,如果机器有4G内存,则默认这个值是2048,但这决意味着机器内存越大,这个值应该越大,因为table_cache加大后,使得mysql对 SQL响应的速度更快了,不可避免的会产生更多的死锁(dead lock),这样反而使得数据库整个一套操作慢了下来,严重影响性能。所以平时维护中还是要根据库的实际情况去作出判断,找到最适合你维护的库的 table_cache值。 清空缓存 执行 mysql >flush tables; 命令将会清空当前所有缓存的表。
mysql>flush tables
mysql> show global status like 'open%_tables';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| Open_tables | 1 |
| Opened_tables | 135 |
+---------------+-------+
open_tables : 值清空为1,全局的,表示当前打开的表数量,在内存中
opened_tables:已经打开过了的表的次数,累加值
背景:
MySQL经常会遇到Too many open files,MySQL上的open_files_limit和OS层面上设置的open file limit有什么关系?
源码中也会看到不同的数据结构,TABLE, TABLE_SHARE,跟表是什么关系?
MySQL flush tables又做了些什么,这几个东西放在一起,就会比较迷惑,下面进行梳理一下:
1 数据结构
table: MySQL为每一个查询sql中的表建一个TABLE对象
table_share: MySQL为每一张表建立一个table_share对象,与frm文件对应
handler: 对应于每个TABLE对象,innodb引擎创建一个handler
dict_table_t: innodb为每一个ibd表load一个数据字典对象
简略图如下:
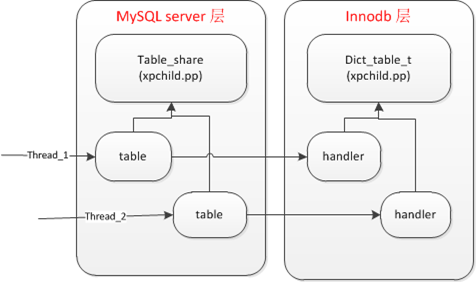
1. open table的过程
测试sql:select * from xpchild.pp
函数调用栈:
open_and_lock_tables
open_tables
open_and_process_table
open_table:打开一个table,并赋值给table_list->table
下面进入核心的逻辑:
开始锁lock_open:
1.1 table_share:
首先根据db&&table_name创建一个table_share.
函数调用栈:
get_table_share_with_discover: 创建或者查找table_share对象。
get_table_share:如果全局cache:table_def_cache中存在,就直接使用,如果不存在,就创建一个table_share
alloc_table_share: 如果不存在,先分配一个share的对象。
open_table_def: 打开frm文件。
mysql_file_open: my_open打开
inline_mysql_file_close: my_close关闭
share->ref_count++;
要点:
- MySQL server层维护了一个全局的table definition cache即table_def_cache,所以一个table_share只会创建一次,后续进行共享。
- 初始化table_share的过程中,调用文件系统打开frm文件,初始化完成后,关闭frm文件。
- share结构中ref_count来表示有多少个table关联
1.2 打开table:
open_table_from_share
step1: 初始化table中的变量,包括file handler (get_new_handler(share->db_type()))
step2: 添加各种索引,字段结构
step3: file->ha_open:ha_innobase::open 为innodb的table创建一个handler。
要点:
1. 在open table的过程中,innodb会创建一个handler,并打开ibd文件,初始化dict_table结构。
释放锁lock_open
1.3 close table:
sql执行结束之前,会调用close table
close_open_tables(thd)
table_def_unuse_table:
要点:
1.table_share维护了两个双向链表used_tables,free_tables,当close table的时候,
1.1 table->in_use=NULL,
1.2 把table从used_tables移除
1.3 加入到free_tables
2.全局参数table_cache_size,已经当前table_cache_count计数控制cache的置换策略
2. 再次执行sql
因为第一步已经完成了table_share的创建,并且cache了table,再次执行sql时,open table的过程就比较简单:
2.1: get_table_share:从cache中直接获取table_share对象
2.2:open_table_from_share:从s->free_tables中获取缓存的可以使用的table,然后增加ref计数。
if (!share->free_tables.is_empty())
table= share->free_tables.front();
++share->ref_count;
3 系统计数:
opened_tables:系统在open_table_from_share中,对新建的table,进行thd->status_var.opened_tables++计数。
opened_shares: 系统在 open_table_def的函数中,对于首次进行open的table_share进行thd->status_var.opened_shares++计数
注: 所以当系统的status:open_tables增长比较多的时候,可以适当的增加table_cache_size,用于缓存更多的table,毕竟open table的开销还是不小的。
4 status统计
使用show status命令,跟open有关的几个:
{"Open_files", (char*) &my_file_opened, SHOW_LONG_NOFLUSH}
注释:【全局变量】MySQL和innodb通过文件系统打开的文件的计数,这里包括了所有的文件,binlog,relay,alert,slow log等。
{"Open_table_definitions", (char*) &show_table_definitions, SHOW_FUNC},
注释:【全局变量】server当前打开的table_share数量,等于table_def_cache.records的数量
{"Open_tables", (char*) &show_open_tables, SHOW_FUNC}
注释:【全局变量】 server当前打开的table数量,server维护了一个全局变量table_cache_count
{"Opened_files", (char*) &my_file_total_opened, SHOW_LONG_NOFLUSH}
注释:【全局变量】 启动以来打开过的文件的总数
{"Opened_tables", (char*) offsetof(STATUS_VAR, opened_tables), SHOW_LONG_STATUS}
注释: 【线程变量】 在真正open_table_from_share的过程中,累计计数
{"Opened_table_definitions", (char*) offsetof(STATUS_VAR, opened_shares), SHOW_LONG_STATUS}
注释: 【线程变量】 在真正打开share的时候,累计计数
注: use test的过程:
在use test的过程中,会轮询把test db下的所有表的table_share都创建一遍,即open所有的frm文件,并创建table_share对象,最后close 所有的frm文件。
为了方便调试,写了一个进程监控的程序:pidmon.py
在gdb的时候,可以看到mysqld进程打开的所有文件:
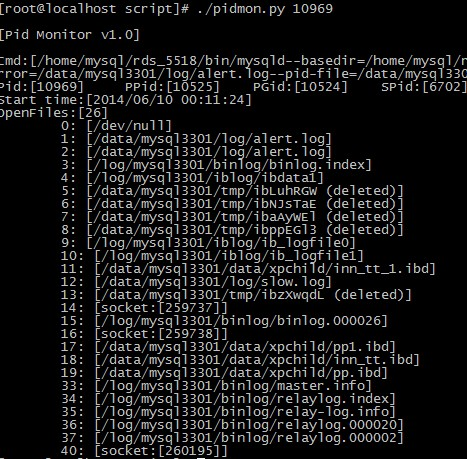
Too many open files:
这里包括了server层的open frm,和innodb层open ibd的时候,当打开的文件超过limit限制,就会报这个错误。
但这个限制牵涉到两个参数:
一个是MySQL配置的open_files_limit
一个是OS层配置的进程的open file limit