http://thinkiii.blogspot.jp/2014/02/arm64-linux-kernel-virtual-address-space.html
ARM64 Linux kernel virtual address space
Now let's talk about the Linux kernel virtual address space on 64-bit ARM CPU. You can find information about ARMv8 in ARM official website.http://www.arm.com/products/processors/armv8-architecture.php
One big problem on 32-bit CPUs is the limited 4GB limitation of virtual address spaces. The problem remains even if some PAE support since it focuses on the extension of physical address space not virtual address space. Things changes after the born of 64-bit CPUs: AMD64 and ARMv8, they can now support up to 2^64 addresses, which is uhh.. a very big number.
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM64_64K_PAGES#define VA_BITS (42)#else#define VA_BITS (39)#endif |
One good thing on ARM64 is that since we have enough virtual address bits, user space and kernel space can have their own 2^39 = 512GB virtual addresses!
All user virtual addresses have 25 leading zeros and kernel addresses have 25 leading ones. Address between user space and kernel space are not used and they are used to trap illegal accesses.
|
| ARM64 Linux virtual address space layout |
kernel space:
In arch/arm64/include/asm/memory.h, we can see the some differences: we have no lowmem zone, since the virtual address is so big that we can treat all memory of lowmem and do not have to worry about virtual address. (Yes, there is still a limit of kernel virtual address). Second, the order of different kernel virtual address changes:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM64_64K_PAGES#define VA_BITS (42)#else #define VA_BITS (39)#endif #define PAGE_OFFSET (UL(0xffffffffffffffff) << (VA_BITS - 1))#define MODULES_END (PAGE_OFFSET)#define MODULES_VADDR (MODULES_END - SZ_64M)#define EARLYCON_IOBASE (MODULES_VADDR - SZ_4M) |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
pr_notice("Virtual kernel memory layout:
" " vmalloc : 0x%16lx - 0x%16lx (%6ld MB)
"#ifdef CONFIG_SPARSEMEM_VMEMMAP " vmemmap : 0x%16lx - 0x%16lx (%6ld MB)
"#endif " modules : 0x%16lx - 0x%16lx (%6ld MB)
" " memory : 0x%16lx - 0x%16lx (%6ld MB)
" " .init : 0x%p" " - 0x%p" " (%6ld kB)
" " .text : 0x%p" " - 0x%p" " (%6ld kB)
" " .data : 0x%p" " - 0x%p" " (%6ld kB)
", MLM(VMALLOC_START, VMALLOC_END),#ifdef CONFIG_SPARSEMEM_VMEMMAP MLM((unsigned long)virt_to_page(PAGE_OFFSET), (unsigned long)virt_to_page(high_memory)),#endif MLM(MODULES_VADDR, MODULES_END), MLM(PAGE_OFFSET, (unsigned long)high_memory), MLK_ROUNDUP(__init_begin, __init_end), MLK_ROUNDUP(_text, _etext), MLK_ROUNDUP(_sdata, _edata)); |
see also:
arch/arm64/mm/init.c
arch/arm64/include/asm/pgtable.h
You can see that there is no pkmap or fixmap, it's because the kernel is assuming every memory has a valid kernel virtual address and there's no need to create pkmap/fixmap.
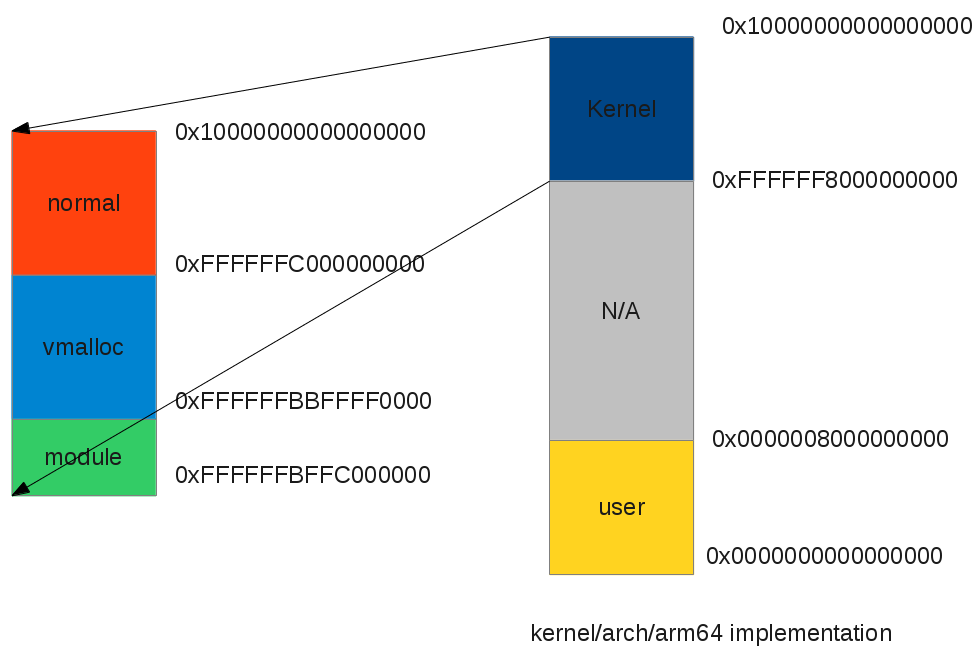
|
| ARM64 kernel virtual address space layout |
User space:
The memory layout implementation of user virtual address space looks like it does on ARM32. Since the available user space virtual address becomes 512GB, we can build a larger application on 64-bit CPUs.
One interesting topic is that ARM claims the ARMv8 is compatible with ARM 32-bit applications, all 32-bit applications can run on ARMv8 without modification.How does the 32-bit application virtual memory layout look like on a 64-bit kernel?
Actually, all process on 64-bit kernel is a 64-bit process. To run ARM 32-bit applications, Linux kernel still create a process from a 64-bit init process, but limit the user address space to 4GB. In this way, we can have both 32-bit and 64-bit application on a 64-bit Linux kernel.One interesting topic is that ARM claims the ARMv8 is compatible with ARM 32-bit applications, all 32-bit applications can run on ARMv8 without modification.How does the 32-bit application virtual memory layout look like on a 64-bit kernel?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT#define TASK_SIZE_32 UL(0x100000000)#define TASK_SIZE (test_thread_flag(TIF_32BIT) ? TASK_SIZE_32 : TASK_SIZE_64)#else#define TASK_SIZE TASK_SIZE_64#endif /* CONFIG_COMPAT */ |
64-bit ARM applications on 64-bit Linux kernel
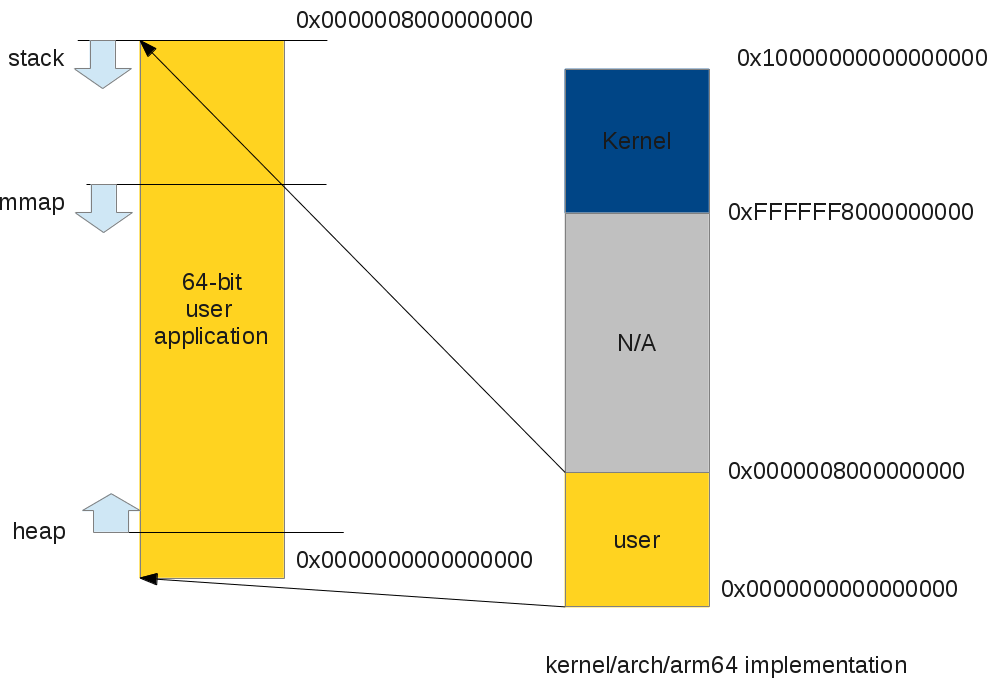
|
| ARM64 64-bit user space program virtual address space layout |
32-bit ARM applications on 64-bit Linux kernel
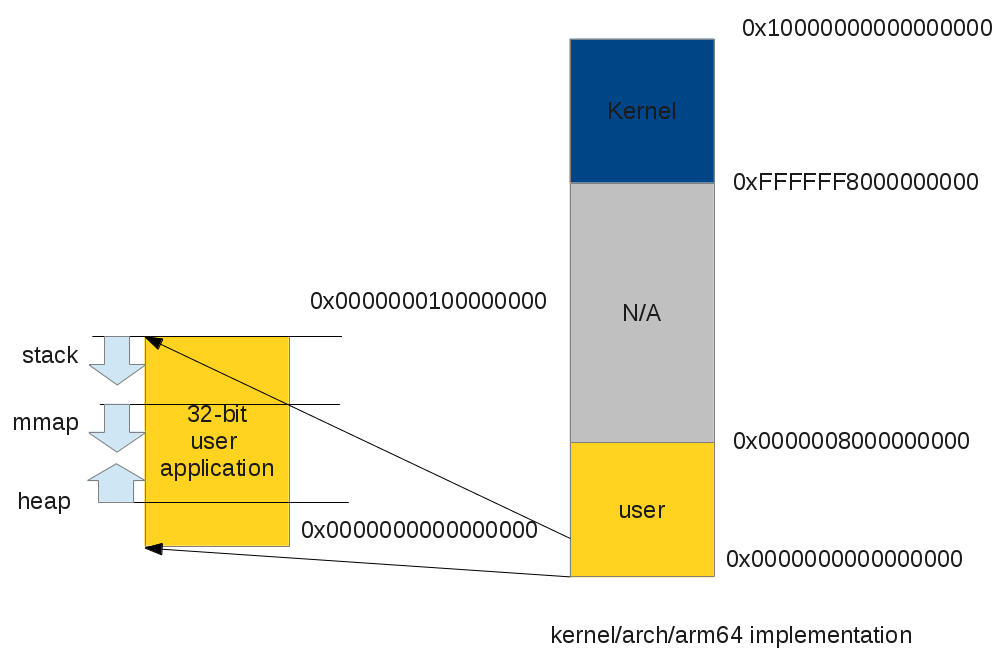
|
| ARM64 32-bit user space program virtual address space layout |
Note that the 32-bit application still have a 512GB kernel virtual address space and do not share it's own 4GB of virtual address space with kernel, the user applications have a complete 4GB of virtual address. On the other hand, 32-bit applications on 32-bit kernel have only 3GB of virtual address space.
| ARM32 Linux | ARM64 Linux | |
| 32-bit user virtual address space size | 3GB | 4GB |
| 64-bit user virtual address space size | N/A | 512GB |
| kernel virtual address space | 1GB | 512GB |