在多线程编程过程中,遇到这样的情况,主线程需要等待多个子线程的处理结果,才能继续运行下去。个人给这样的子线程任务取了个名字叫并行任务。对于这种任务,每次去编写代码加锁控制时序,觉得太麻烦,正好朋友提到CountDownLatch这个类,于是用它来编写了个小工具。
首先,要处理的是多个任务,于是定义了一个接口
package com.zyj.thread; import com.zyj.exception.ChildThreadException; /** * 多任务处理 * @author zengyuanjun */ public interface MultiThreadHandler { /** * 添加任务 * @param tasks */ void addTask(Runnable... tasks); /** * 执行任务 * @throws ChildThreadException */ void run() throws ChildThreadException; }
要处理的是并行任务,需要用到CountDownLatch来统计所有子线程执行结束,还要一个集合记录所有任务,另外加上我自定义的ChildThreadException类来记录子线程中的异常,通知主线程是否所有子线程都执行成功,便得到了下面这个抽象类AbstractMultiParallelThreadHandler。在这个类中,我顺便完成了addTask这个方法。
package com.zyj.thread.parallel; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import com.zyj.exception.ChildThreadException; import com.zyj.thread.MultiThreadHandler; /** * 并行线程处理 * @author zengyuanjun */ public abstract class AbstractMultiParallelThreadHandler implements MultiThreadHandler { /** * 子线程倒计数锁 */ protected CountDownLatch childLatch; /** * 任务列表 */ protected List<Runnable> taskList; /** * 子线程异常 */ protected ChildThreadException childThreadException; public AbstractMultiParallelThreadHandler() { taskList = new ArrayList<Runnable>(); childThreadException = new ChildThreadException(); } public void setCountDownLatch(CountDownLatch latch) { this.childLatch = latch; } /** * {@inheritDoc} */ @Override public void addTask(Runnable... tasks) { if (null == tasks) { taskList = new ArrayList<Runnable>(); } for (Runnable task : tasks) { taskList.add(task); } } /** * {@inheritDoc} */ @Override public abstract void run() throws ChildThreadException; }
具体的实现,则是下面这个类。实现原理也很简单,主线程根据并行任务数创建一个CountDownLatch,传到子线程中,并运行所有子线程,然后await等待。子线程执行结束后调用CountDownLatch的countDown()方法,当所有子线程执行结束后,CountDownLatch计数清零,主线程被唤醒继续执行。
package com.zyj.thread.parallel; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import com.zyj.exception.ChildThreadException; /** * 并行任务处理工具 * * @author zengyuanjun * */ public class MultiParallelThreadHandler extends AbstractMultiParallelThreadHandler { /** * 无参构造器 */ public MultiParallelThreadHandler() { super(); } /** * 根据任务数量运行任务 */ @Override public void run() throws ChildThreadException { if (null == taskList || taskList.size() == 0) { return; } else if (taskList.size() == 1) { runWithoutNewThread(); } else if (taskList.size() > 1) { runInNewThread(); } } /** * 新建线程运行任务 * * @throws ChildThreadException */ private void runInNewThread() throws ChildThreadException { childLatch = new CountDownLatch(taskList.size()); childThreadException.clearExceptionList(); for (Runnable task : taskList) { invoke(new MultiParallelRunnable(new MultiParallelContext(task, childLatch, childThreadException))); } taskList.clear(); try { childLatch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { childThreadException.addException(e); } throwChildExceptionIfRequired(); } /** * 默认线程执行方法 * * @param command */ protected void invoke(Runnable command) { if(command.getClass().isAssignableFrom(Thread.class)){ Thread.class.cast(command).start(); }else{ new Thread(command).start(); } } /** * 在当前线程中直接运行 * * @throws ChildThreadException */ private void runWithoutNewThread() throws ChildThreadException { try { taskList.get(0).run(); } catch (Exception e) { childThreadException.addException(e); } throwChildExceptionIfRequired(); } /** * 根据需要抛出子线程异常 * * @throws ChildThreadException */ private void throwChildExceptionIfRequired() throws ChildThreadException { if (childThreadException.hasException()) { childExceptionHandler(childThreadException); } } /** * 默认抛出子线程异常 * @param e * @throws ChildThreadException */ protected void childExceptionHandler(ChildThreadException e) throws ChildThreadException { throw e; } }
并行任务是要运行的子线程,只要实现Runnable接口就行,并没有CountDownLatch对象,所以我用MultiParallelRunnable类对它封装一次,MultiParallelRunnable类里有个属性叫 MultiParallelContext,MultiParallelContext里面就是保存的子线程task、倒计数锁CountDownLatch和ChildThreadException这些参数。MultiParallelRunnable类完成运行子线程、记录子线程异常和倒计数锁减一。
package com.zyj.thread.parallel; /** * 并行线程对象 * * @author zengyuanjun * */ public class MultiParallelRunnable implements Runnable { /** * 并行任务参数 */ private MultiParallelContext context; /** * 构造函数 * @param context */ public MultiParallelRunnable(MultiParallelContext context) { this.context = context; } /** * 运行任务 */ @Override public void run() { try { context.getTask().run(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); context.getChildException().addException(e); } finally { context.getChildLatch().countDown(); } } }
package com.zyj.thread.parallel; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import com.zyj.exception.ChildThreadException; /** * 并行任务参数 * @author zengyuanjun * */ public class MultiParallelContext { /** * 运行的任务 */ private Runnable task; /** * 子线程倒计数锁 */ private CountDownLatch childLatch; /** * 子线程异常 */ private ChildThreadException childException; public MultiParallelContext() { } public MultiParallelContext(Runnable task, CountDownLatch childLatch, ChildThreadException childException) { this.task = task; this.childLatch = childLatch; this.childException = childException; } public Runnable getTask() { return task; } public void setTask(Runnable task) { this.task = task; } public CountDownLatch getChildLatch() { return childLatch; } public void setChildLatch(CountDownLatch childLatch) { this.childLatch = childLatch; } public ChildThreadException getChildException() { return childException; } public void setChildException(ChildThreadException childException) { this.childException = childException; } }
这里提一下ChildThreadException这个自定义异常,跟普通异常不一样,我在里面加了个List<Exception> exceptionList,用来保存子线程的异常。因为有多个子线程,抛出的异常可能有多个。
package com.zyj.exception; import java.io.PrintStream; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; import com.zyj.exception.util.ExceptionMessageFormat; import com.zyj.exception.util.factory.ExceptionMsgFormatFactory; /** * 子线程异常,子线程出现异常时抛出 * @author zengyuanjun */ public class ChildThreadException extends Exception { /** * serialVersionUID */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 5682825039992529875L; /** * 子线程的异常列表 */ private List<Exception> exceptionList; /** * 异常信息格式化工具 */ private ExceptionMessageFormat formatter; /** * 锁 */ private Lock lock; public ChildThreadException() { super(); initial(); } public ChildThreadException(String message) { super(message); initial(); } public ChildThreadException(String message, StackTraceElement[] stackTrace) { this(message); setStackTrace(stackTrace); } private void initial() { exceptionList = new ArrayList<Exception>(); lock = new ReentrantLock(); formatter = ExceptionMsgFormatFactory.getInstance().getFormatter(ExceptionMsgFormatFactory.STACK_TRACE); } /** * 子线程是否有异常 * @return */ public boolean hasException() { return exceptionList.size() > 0; } /** * 添加子线程的异常 * @param e */ public void addException(Exception e) { try { lock.lock(); e.setStackTrace(e.getStackTrace()); exceptionList.add(e); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } /** * 获取子线程的异常列表 * @return */ public List<Exception> getExceptionList() { return exceptionList; } /** * 清空子线程的异常列表 */ public void clearExceptionList() { exceptionList.clear(); } /** * 获取所有子线程异常的堆栈跟踪信息 * @return */ public String getAllStackTraceMessage() { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); for (Exception e : exceptionList) { sb.append(e.getClass().getName()); sb.append(": "); sb.append(e.getMessage()); sb.append(" "); sb.append(formatter.formate(e)); } return sb.toString(); } /** * 打印所有子线程的异常的堆栈跟踪信息 */ public void printAllStackTrace() { printAllStackTrace(System.err); } /** * 打印所有子线程的异常的堆栈跟踪信息 * @param s */ public void printAllStackTrace(PrintStream s) { for (Exception e : exceptionList) { e.printStackTrace(s); } } }
·有没有问题试一下才知道,写了个类来测试:TestCase 为并行任务子线程,resultMap为并行任务共同完成的结果集。假设resultMap由5部分组成,main方法中启动5个子线程分别完成一个部分,等5个子线程处理完后,main方法将结果resultMap打印出来。
package com.zyj.thread.test; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import com.zyj.exception.ChildThreadException; import com.zyj.thread.MultiThreadHandler; import com.zyj.thread.parallel.MultiParallelThreadHandler; import com.zyj.thread.parallel.ParallelTaskWithThreadPool; public class TestCase implements Runnable { private String name; private Map<String, Object> result; public TestCase(String name, Map<String, Object> result) { this.name = name; this.result = result; } @Override public void run() { // 模拟线程执行1000ms try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 模拟线程1和线程3抛出异常 // if(name.equals("1") || name.equals("3")) // throw new RuntimeException(name + ": throw exception"); result.put(name, "complete part " + name + "!"); } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("main begin ================="); Map<String, Object> resultMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(8, 1); MultiThreadHandler handler = new MultiParallelThreadHandler(); // ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); // MultiThreadHandler handler = new ParallelTaskWithThreadPool(service); TestCase task = null; // 启动5个子线程作为要处理的并行任务,共同完成结果集resultMap for(int i=1; i<=5 ; i++){ task = new TestCase("" + i, resultMap); handler.addTask(task); } try { handler.run(); } catch (ChildThreadException e) { System.out.println(e.getAllStackTraceMessage()); } System.out.println(resultMap); // service.shutdown(); System.out.println("main end ================="); } }
运行main方法,测试结果如下
main begin ================= {3=complete part 3!, 2=complete part 2!, 1=complete part 1!, 5=complete part 5!, 4=complete part 4!} main end =================
将模拟线程1和线程3抛出异常的注释打开,测试结果如下
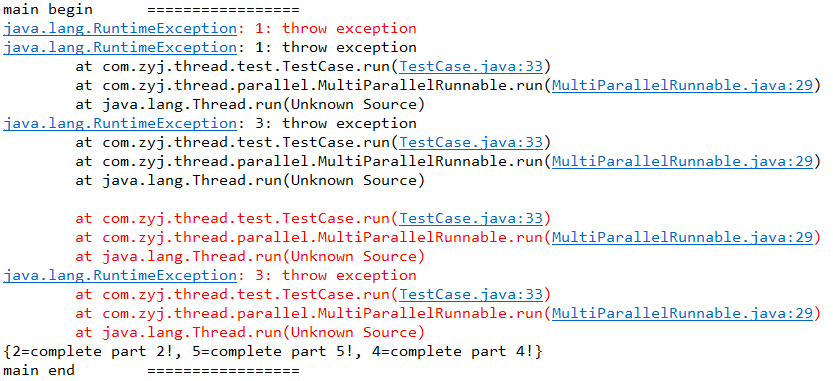
红色的打印是子线程中捕获异常打印的堆栈跟踪信息,黑色的异常信息是主线程main方法中打印的,这说明主线程能够监视到子线程的出错,以便采取对应的处理。由于线程1和线程3出现了异常,未能完成任务,所以打印的resultMap只有第2、4、5三个部分完成。
为了便于扩展,我把MultiParallelThreadHandler类中的invoke方法和childExceptionHandler方法定义为protected类型。invoke方法中是具体的线程执行,childExceptionHandler方法是子线程抛出异常后的处理,可以去继承,重写为自己想要的,比如我想用线程池去运行子线程,就可以去继承并重写invoke方法,得到下面的这个类
package com.zyj.thread.parallel; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; /** * 使用线程池运行并行任务 * @author zengyuanjun * */ public class ParallelTaskWithThreadPool extends MultiParallelThreadHandler { private ExecutorService service; public ParallelTaskWithThreadPool() { } public ParallelTaskWithThreadPool(ExecutorService service) { this.service = service; } public ExecutorService getService() { return service; } public void setService(ExecutorService service) { this.service = service; } /** * 使用线程池运行 */ @Override protected void invoke(Runnable command) { if(null != service){ service.execute(command); }else{ super.invoke(command); } } }
测试就在上面的测试类中,只不过被注释掉了,测试结果是一样的,就不多说了。