题意
你初始位于((0,0)),然后你想要到((x,y))去,第(i)步的步长是(2^{i-1}),要求用最少的步数走到((x,y))。
解题思路
首先可以推出,走(i)步可以走到一个正方形范围内横纵坐标之和为奇数的所有点。
如,走3步可以走到所有红色直线围成的正方形内横纵坐标之和为奇数的点。
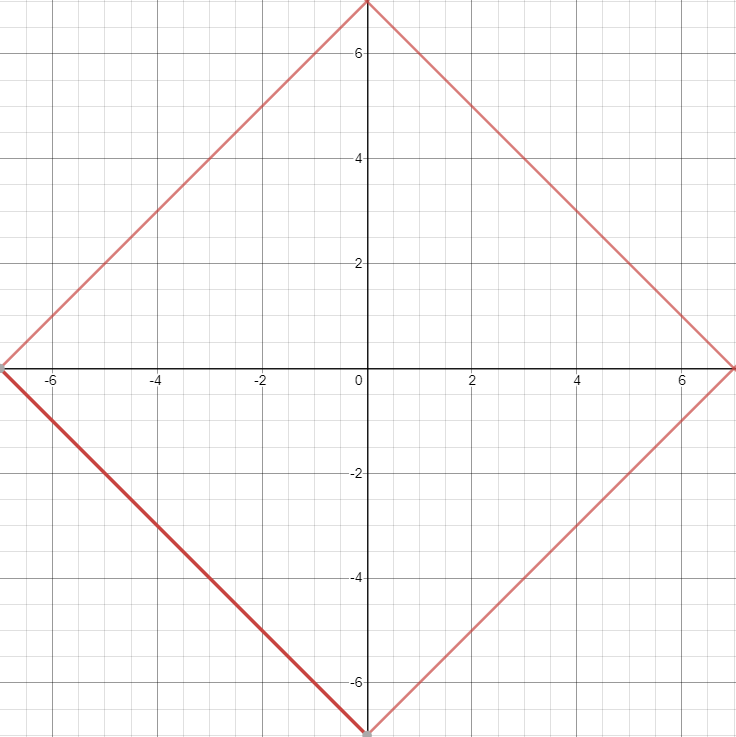
这样,我们就可以直接算出是否可达以及若可达最少步数是多少。
然后考虑从最后一步开始从((x,y))往((0,0))走,枚举4个方向,向这个方向走了这一步之后到达的点的最少步数也可以算出来,如果最少步数减少那么就表示可行,然后就完成这一步,继续枚举下一步的方向,直至走到((0,0))。
AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// #include <ext/rope>
// using namespace __gnu_cxx;
// #include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
// #include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
// using namespace __gnu_pbds;
// typedef ll key_type;
// typedef null_mapped_type value_type;
// typedef tree<key_type, value_type, less<key_type>, rb_tree_tag, tree_order_statistics_node_update> rbtree;
// typedef __gnu_pbds::priority_queue<pi,greater<pi>,pairing_heap_tag > heap;
// mt19937 rng(chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());
// int rnd(int l,int r){return l+rng()%(r-l+1);}
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef vector<int> VI;
#define rep(i,_,__) for (int i=_; i<__; ++i)
#define per(i,_,__) for (int i=_-1; i>=__; --i)
#define eb emplace_back
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define x1 _x
#define x2 __x
#define y1 _y
#define y2 __y
#define SZ(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define rall(x) (x).rbegin(),(x).rend()
#define endl '
'
const double pi = acos(-1.0);
namespace IO{
bool REOF = 1; //为0表示文件结尾
inline char nc() {
static char buf[1 << 20], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
return p1 == p2 && REOF && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2) ? (REOF = 0, EOF) : *p1++;
}
template<class T>
inline bool read(T &x) {
char c = nc();bool f = 0; x = 0;
while (c<'0' || c>'9')c == '-' && (f = 1), c = nc();
while (c >= '0'&&c <= '9')x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c ^ 48), c = nc();
if(f)x=-x;
return REOF;
}
template<class T>
inline void write(T x){
if(x > 9) write(x / 10);
putchar('0'+x%10);
}
template<typename T, typename... T2>
inline bool read(T &x, T2 &... rest) {
read(x);
return read(rest...);
}
inline bool need(char &c) { return ((c >= 'a') && (c <= 'z')) || ((c >= '0') && (c <= '9')) || ((c >= 'A') && (c <= 'Z')); }
// inline bool need(char &c) { return ((c >= 'a') && (c <= 'z')) || ((c >= '0') && (c <= '9')) || ((c >= 'A') && (c <= 'Z')) || c==' '; }
inline bool read_str(char *a) {
while ((*a = nc()) && need(*a) && REOF)++a; *a = '�';
return REOF;
}
inline bool read_db(double &x){
bool f = 0; char ch = nc(); x = 0;
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {f|=(ch=='-');ch=nc();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10.0+(ch^48);ch=nc();}
if(ch == '.') {
double tmp = 1; ch = nc();
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){tmp=tmp/10.0;x=x+tmp*(ch^48);ch=nc();}
}
if(f)x=-x;
return REOF;
}
template<class TH>
inline void _dbg(const char *sdbg, TH h){ cerr<<sdbg<<'='<<h<<endl; }
template<class TH, class... TA>
inline void _dbg(const char *sdbg, TH h, TA... a) {
while(*sdbg!=',')cerr<<*sdbg++;
cerr<<'='<<h<<','<<' '; _dbg(sdbg+1, a...);
}
template<class T>
ostream &operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> V) {
os << "[ "; for (auto vv : V) os << vv << ","; return os << " ]";
}
template<class T>
ostream &operator<<(ostream& os, set<T> V) {
os << "[ "; for (auto vv : V) os << vv << ","; return os << " ]";
}
template<class T>
ostream &operator<<(ostream& os, map<T,T> V) {
os << "[ "; for (auto vv : V) os << vv << ","; return os << " ]";
}
template<class L, class R>
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, pair<L,R> P) {
return os << "(" << P.x << "," << P.y << ")";
}
#ifdef BACKLIGHT
#define debug(...) _dbg(#__VA_ARGS__, __VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...)
#endif
}
using namespace IO;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
const int M = 5e5 + 5;
const int MAXV = 1e6 + 5;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; // 998244353 1e9+7
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // 1e9+7 0x3f3f3f3f
const ll LLINF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; // 1e18+9 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f
const double eps = 1e-8;
// int dx[4] = { 0, 1, 0, -1 };
// int dx[8] = { 1, 0, -1, 1, -1, 1, 0, -1 };
// int dy[4] = { 1, 0, -1, 0 };
// int dy[8] = { 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1 };
// ll qp(ll a, ll b) {
// ll res = 1;
// a %= mod;
// assert(b >= 0);
// while(b){
// if(b&1)
// res = res * a % mod;
// a = a * a % mod;
// b >>= 1;
// }
// return res;
// }
// ll inv(ll x) {return qp(x, mod - 2);}
// ll factor[N], finv[N];
// void init() {
// factor[0]=1;
// for(int i=1; i<N; i++) factor[i] = factor[i-1] * i % mod;
// finv[N-1] = qp(factor[N-1], mod - 2);
// for(int i=N-2; i>=0; i--) finv[i] = finv[i+1] * (i+1) % mod;
// }
// ll c(ll n, ll m) {
// return factor[n] * finv[m] % mod * finv[n-m] % mod;
// }
// #define ls (x<<1)
// #define rs (x<<1|1)
// #define mid ((l+r)>>1)
// #define lson ls,l,mid
// #define rson rs,mid+1,r
// #define fore(_, __) for(int _ = head[__]; _; _=e[_].nxt)
// int head[N], tot = 1;
// struct Edge {
// int v, nxt;
// Edge(){}
// Edge(int _v, int _nxt):v(_v), nxt(_nxt) {}
// }e[N << 1];
// void addedge(int u, int v) {
// e[tot] = Edge(v, head[u]); head[u] = tot++;
// e[tot] = Edge(u, head[v]); head[v] = tot++;
// }
/**
* ********** Backlight **********
* 仔细读题
* 注意边界条件
* 记得注释输入流重定向
* 没有思路就试试逆向思维
* 我不打了,能不能把我的分还给我
*/
int dis(ll x, ll y) {
ll sum = abs(x) + abs(y);
if(x==0 && y==0) return 0;
if((x+y)%2==0) return INF;
rep(i, 1, 33) {
if(sum <= (1LL<<i)-1) return i;
}
return INF;
}
ll x, y;
void solve(int Case) {
read(x, y);
if(dis(x,y)==INF) {
printf("Case #%d: IMPOSSIBLE
", Case);
return;
}
string ans = "";
int d = dis(x, y);
per(i, d, 0) {
ll D = 1LL << i;
if(dis(x-D, y)<=i) ans+='E', x-=D;
else if(dis(x+D, y)<=i) ans+='W', x+=D;
else if(dis(x, y-D)<=i) ans+='N', y-=D;
else if(dis(x, y+D)<=i) ans+='S', y+=D;
else assert(false);
}
reverse(all(ans));
printf("Case #%d: %s
", Case, ans.c_str());
}
int main()
{
#ifdef BACKLIGHT
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int _T; read(_T); for (int _ = 1; _ <= _T; _++) solve(_);
// int _T=1; while(read(n)) solve(_T), _T++;
// solve(1);
return 0;
}