C#WinForm国际化的简单实现
软件行业发展到今天,国际化问题一直都占据非常重要的位置,而且应该越来越被重视。对于开发人员而言,在编写程序之前,国际化问题是首先要考虑的一个问题,也许有时候这个问题已经在设计者的考虑范围之内,但终归要开发人员去做实现的。因此,如何实现国际化,是开发人员必须掌握的一项基本技能。
今天,这里要讲的就是,在利用C#进行WinForm开发时,国际化是怎么实现的。鉴于时间及篇幅关系,这里仅仅介绍一种简单的国际化实现方法,可能这里提到的方法已经有非常多人提到过,但笔者还是不厌其烦地介绍一下。
要在C#中实现国际化,需要相关资源文件,比如要在一个软件中支持英文、中文两种语言,那么就必须有这两种语言的资源文件,这在C#中可以采用资源文件(后缀名为.resx)来实现,我们不妨定义英文资源文件名称为Resource.en-US,中文资源文件名称为Resource.zh-CN,两种资源文件所涉及的ID都应该是一样的(这对于其他更多的资源文件均是一样的),只不过是展示的名称不同罢了。
有了这两种资源文件,接下来就要考虑如何做的问题了。为了适应多处使用的情形,这里笔者单独编写了一个类ResourceCulture,该类包含了一些静态方法,主要作用是用来设置当前语言及返回当前的语言的相关字符串。该类代码如下:
- using System.Reflection;
- using System.Resources;
- using System.Threading;
- using System.Globalization;
- namespace GlobalizationTest
- {
- class ResourceCulture
- {
- /// <summary>
- /// Set current culture by name
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="name">name</param>
- public static void SetCurrentCulture(string name)
- {
- if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(name))
- {
- name = "en-US";
- }
- Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture = new CultureInfo(name);
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// Get string by id
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="id">id</param>
- /// <returns>current language string</returns>
- public static string GetString(string id)
- {
- string strCurLanguage = "";
- try
- {
- ResourceManager rm = new ResourceManager("GlobalizationTest.Resource", Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly());
- CultureInfo ci = Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture;
- strCurLanguage = rm.GetString(id, ci);
- }
- catch
- {
- strCurLanguage = "No id:" + id + ", please add.";
- }
- return strCurLanguage;
- }
- }
- }
在Form1中的代码如下:
- /**
- * This project is just a example to show how to do the globalization in C# winform.
- * You and rebuild and/or modify it by yourself if you want.
- * Specially, this project was created in Visual Studio 2010.
- *
- * Project Name : GlobalizationTest
- * Create Date : April 29th, 2010
- * */
- using System;
- using System.Windows.Forms;
- namespace GlobalizationTest
- {
- public partial class Form1 : Form
- {
- public Form1()
- {
- InitializeComponent();
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// Set the resource culture
- /// </summary>
- private void SetResourceCulture()
- {
- // Set the form title text
- this.Text = ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_frmText");
- // Set the groupbox text
- this.gbLanguageView.Text = ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_gbLanguageViewText");
- this.gbLanguageSelection.Text = ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_gbLanguageSelectionText");
- // Set the label text
- this.lblCurLanguageText.Text = ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_lblCurLanguageText");
- this.lblNameText.Text = ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_lblNameText");
- this.lblPhoneText.Text = ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_lblPhoneText");
- // Set the button text
- this.btnMsgShow.Text = ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_btnMsgShowText");
- // Set radiobutton text
- this.rbEnglish.Text = ResourceCulture.GetString("Language_EnglishText");
- this.rbChinese.Text = ResourceCulture.GetString("Language_ChineseText");
- // Set the current language text
- if (rbEnglish.Checked)
- {
- this.lblCurLanguage.Text = ResourceCulture.GetString("Language_EnglishText");
- }
- else if (rbChinese.Checked)
- {
- this.lblCurLanguage.Text = ResourceCulture.GetString("Language_ChineseText");
- }
- }
- private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- // Set the default language
- ResourceCulture.SetCurrentCulture("en-US");
- this.SetResourceCulture();
- }
- private void btnMsgShow_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtName.Text))
- {
- MessageBox.Show(ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_msgbox_nameText"), ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_msgbox_TitleText"),
- MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Exclamation);
- return;
- }
- if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtPhone.Text))
- {
- MessageBox.Show(ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_msgbox_phoneText"), ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_msgbox_TitleText"),
- MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Exclamation);
- return;
- }
- MessageBox.Show(ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_msgbox_InfoText") + txtName.Text + ", " + txtPhone.Text,
- ResourceCulture.GetString("Form1_msgbox_TitleText"), MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
- }
- private void rbEnglish_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- ResourceCulture.SetCurrentCulture("en-US");
- this.SetResourceCulture();
- }
- private void rbChinese_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- ResourceCulture.SetCurrentCulture("zh-CN");
- this.SetResourceCulture();
- }
- }
- }
最终的效果如下图1和图2所示: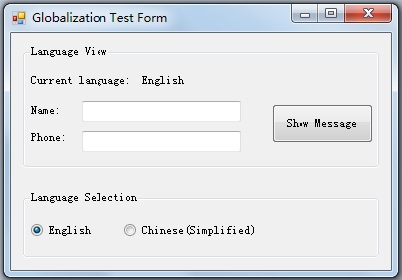
图1
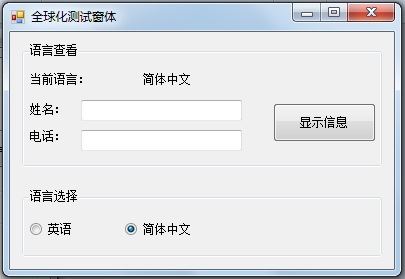
图2
归结起来,要在C#的WinForm中实现国际化,至少需要做好以下几点:
(1)准备所需资源文件(如本文中提到的英文和中文资源文件);
(2)引入命名空间(包括:System.Reflection、System.Resources、System.Threading和System.Globalization);
(3)实例化资源管理器(即ResourceManager);
(4)设置当前进程的语言区域;
(5)通过资源管理器从指定的资源文件中获取所需值。
通过上述的方法即可简单实现国际化。