选择排序之C++实现
一、源代码:SelectSort.cpp
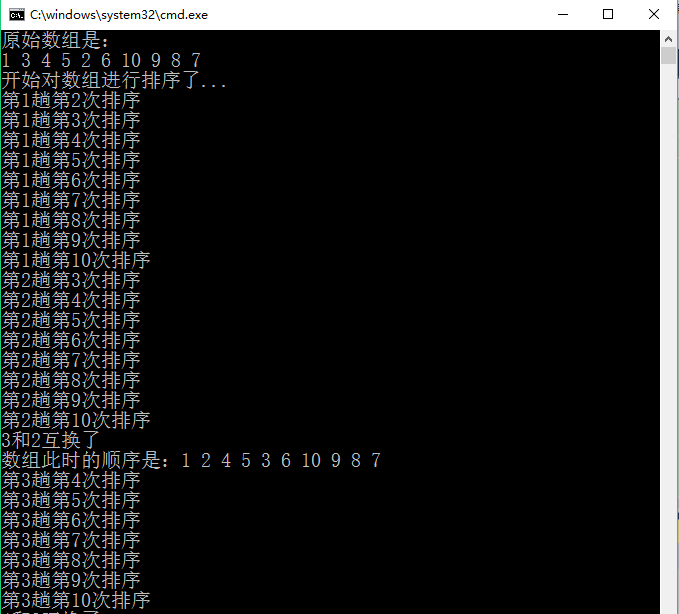
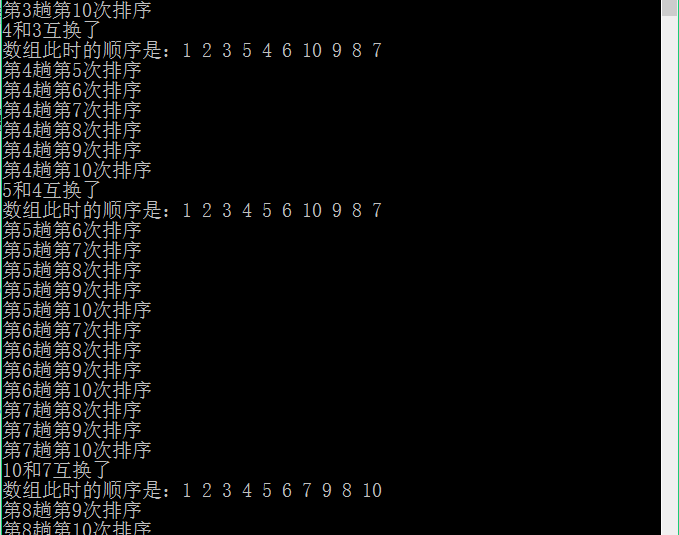
1 /* 2 选择排序(从小到大)的基本思想是,首先,选出最小的数,放在第一个位置; 3 然后,选出第二小的数,放在第二个位置; 4 以此类推,直到所有的数从小到大排序。 5 在实现上,我们通常是先确定第i小的数所在的位置,然后,将其与第i个数进行交换。 6 */ 7 #include<iostream> 8 using namespace std; 9 /*定义输出一维数组的函数*/ 10 void print(int array[], int n) 11 { 12 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 13 { 14 cout << array[i] << " "; 15 } 16 cout << endl; 17 } 18 19 int selectSort(int array[], int n) 20 { 21 //定义变量,记录交换次数 22 int count = 0; 23 //假设最小值所在的位置,默认为0,即第一个元素 24 int min_index = 0; 25 //定义中间变量,存储临时数据 26 int temp; 27 //遍历数组(进行排序) 28 cout << "开始对数组进行排序了..." << endl; 29 for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) 30 { 31 //假设当前的元素是第i小的元素,保存当前位置 32 min_index = i; 33 for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) 34 { 35 cout << "第" << (i + 1) << "趟第" << (j + 1) << "次排序" << endl; 36 //判断当前的元素是否小于假设的第i小元素 37 if (array[min_index]>array[j]) 38 { 39 //重新设置第i小的元素位置 40 min_index = j; 41 } 42 } 43 //判断当前位置的元素是否等于假设的第i小元素,如果不等于则交换这两个元素 44 if (min_index != i) 45 { 46 temp = array[min_index]; 47 array[min_index] = array[i]; 48 array[i] = temp; 49 cout << array[min_index] << "和" << array[i] << "互换了" << endl; 50 //输出此时数组的顺序 51 cout << "数组此时的顺序是:"; 52 print(array, 10); 53 //每交换一次,记录数加1 54 count++; 55 } 56 } 57 cout << "数组排序结束了..." << endl; 58 return count; 59 } 60 61 int main() 62 { 63 //定义待排序的一维数组 64 int array[] = { 1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 6, 10, 9, 8, 7 }; 65 //输出原始数组 66 cout << "原始数组是:" << endl; 67 print(array, 10); 68 //对数组进行排序 69 int count = selectSort(array, 10); 70 //输出排序后的数组 71 cout << "排序后的数组是:" << endl; 72 print(array, 10); 73 cout << "共交换" << count << "次" << endl; 74 return 0; 75 }
二、运行效果