第一 : ArrayList(非泛型集合) 与List(泛型集合)
ArrayList 是数组的复杂版本。ArrayList 类提供在大多数 Collections 类中提供但不在 Array 类中提供的一些功能:
1.Array 的容量是固定的,而 ArrayList 的容量是根据需要自动扩展的。
2.ArrayList 提供添加、插入或移除某一范围元素的方法。在 Array 中,您只能一次获取或设置一个元素的值。
3.使用 Synchronized 方法可以很容易地创建 ArrayList 的同步版本。而 Array 将一直保持它直到用户实现同步为止。
4.ArrayList 提供将只读和固定大小包装返回到集合的方法。而 Array 不提供。
5.Array 提供 ArrayList 所不具有的某些灵活性:
a.可以设置 Array 的下限,但 ArrayList 的下限始终为零。
b.Array 可以具有多个维度,而 ArrayList 始终只是一维的。
c.特定类型(不包括 Object)的 Array 的性能比 ArrayList 好,这是因为 ArrayList 的元素属于 Object 类型,所以在存储或检索值类型时通常发生装箱和取消装箱。
d.要求一个数组的大多数情况也可以代之以使用 ArrayList。它更易于使用,并且通常具有与 Object 类型的数组类似的性能。
一:ArrayList:
ArrayList可以不用指定维数 可动态赋值 赋不同类型值
ArrayList arrayList1 = new ArrayList();
arrayList1.
arrayList1.Add("a");
arrayList1.Add(1);
arrayList1.Add("b");
Response.Write(arrayList1[1]);
二:Array:
Array的容量是固定的 先指定大小 在赋值
Array arrayList2 = Array.CreateInstance(typeof(string), 6);
arrayList2.SetValue("a", 0);
arrayList2.SetValue("b", 1);
Response.Write(arrayList2.GetValue(1));
List泛型集合:
泛型集合List<T>
泛型最重要的应用就是集合操作,使用泛型集合可以提高代码重用性,类型安全和更佳的性能。
List<T>的用法和ArrayList相似,List<T>有更好的类型安全性,无须拆,装箱。
在泛型定义中,泛型类型参数“<T>”是必须指定的,其中T是定义泛型类时的占位符,其并不是一种类型,仅代表某种可能的类型。在定义时T会被使用的类型代替。泛型集合List<T>中只能有一个参数类型,“<T>”中的T可以对集合中的元素类型进行约束。
eg:
List<T>添加、删除、检索元素的方法和ArrayList相似,明显的特点是不需要像ArrayList那样装箱和拆箱。
List < Student > students = new List < Student > ();
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.Name = "陆小凤";
stu1.Number = "0801";
stu1.Score = 20;
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.Name = "西门吹雪";
stu2.Number = "0802";
stu2.Score = 23;
students.Add(stu1);
students.Add(stu2);
Console.WriteLine("集合中的元素个数为{0}", students.Count);
foreach (Student stu in students)
{
Console.WriteLine("/t{0}/t{1}/t{2}", stu.Name, stu.Number, stu.Score);
}
students.Remove(stu1);
Console.WriteLine("集合中的元素个数为{0}", students.Count);
Console.ReadLine();
List<T>和ArrayList的区别
List<T>和ArrayList的相同点:添加元素、删除元素、通过索引访问元素方法相同。
List<T>和ArrayList的不同点:
ArrayList可以添加任意类型元素;List<T>对添加的元素具有类型约束;
ArratList添加时装箱,读取时拆箱;List<T>不需要装箱,拆箱操作;
//创建Person对象
Person p1 = new Person("张三", 30);
Person p2 = new Person("李四", 20);
Person p3 = new Person("王五", 50);
//创建类型为Person的对象集合
List < Person > persons = new List < Person > ();
//将Person对象放入集合
persons.Add(p1);
persons.Add(p2);
persons.Add(p3);
//输出第2个人的姓名
Console.WriteLine(persons[1].Name);
foreach (Person p in persons)
{
Console.WriteLine("/t{0}/t{1}", p.Name, p.Age);
}
第二 :HashTable(非泛型集合)对应Dictionary(泛型集合)
Hashtable 和 Dictionary <K, V> 类型
1:单线程程序中推荐使用 Dictionary, 有泛型优势, 且读取速度较快, 容量利用更充分.
2:多线程程序中推荐使用 Hashtable, 默认的 Hashtable 允许单线程写入, 多线程读取, 对 Hashtable 进一步调用 Synchronized() 方法可以获得完全线程安全的类型. 而 Dictionary 非线程安全, 必须人为使用 lock 语句进行保护, 效率大减.
3:Dictionary 有按插入顺序排列数据的特性 (注: 但当调用 Remove() 删除过节点后顺序被打乱), 因此在需要体现顺序的情境中使用 Dictionary 能获得一定方便.
Hashtable 类和 Dictionary<(Of <(TKey, TValue>)>) 泛型类实现 IDictionary 接口
Dictionary<(Of <(TKey, TValue>)>) 泛型类还实现 IDictionary<(Of <(TKey, TValue>)>) 泛型接口。因此,这些集合中的每个元素都是一个键/值对。
Dictionary<(Of <(TKey, TValue>)>) 类与 Hashtable 类的功能相同
对于值类型,特定类型(不包括 Object)的 Dictionary<(Of <(TKey, TValue>)>) 的性能优于 Hashtable,这是因为 Hashtable 的元素属于 Object 类型,所以在存储或检索值类型时通常发生装箱和取消装箱操作。
eg:
HashTable ht=new HashTable();//实现 IDictionary接口
ht.Add(1,"A");
ht.Add(2,"B");
ht.Add(3,"c");
foreach(DictionaryEntry de in ht)//HashTable返回的是DictionaryEntry类型
{
de.Key;
de.Value;
}
Dictionary<int,string> myDictionary=new Dictionary<int,string>();//实现IDictionary接口,IDictionary<T key,T value>类
myDictionary.Add(1,"a");
myDictionary.Add(2,"b");
myDictionary.Add(3,"c");
foreach(int i in myDictionary.Keys)
{
Console.WriteLine("Key="+i+"Value="+myDictionary);
}
Or
foreach(KeyValuePair<string, double> temp in myDictionary)//返回的是KeyValuePair<string, double>泛型数组
{
temp.Key;
temp.Value;
}
一:HashTable:
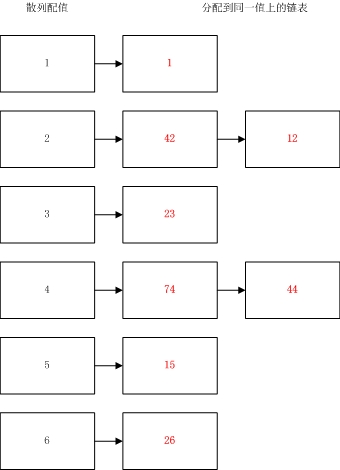
1.HashTable是一种散列表,他内部维护很多对Key-Value键值对,其还有一个类似索引的值叫做散列值(HashCode),它是根据GetHashCode方法对Key通过一定算法获取得到的,所有的查找操作定位操作都是基于散列值来实现找到对应的Key和Value值的。
2.我们需要使用一个算法让散列值对应HashTable的空间地址尽量不重复,这就是散列函数(GetHashCode)需要做的事。
3.当一个HashTable被占用一大半的时候我们通过计算散列值取得的地址值可能会重复指向同一地址,这就是哈希冲突。
4.在.Net中键值对在HashTable中的位置Position= (HashCode& 0x7FFFFFFF) % HashTable.Length,.net中是通过探测法解决哈希冲突的,当通过散列值取得的位置Postion以及被占用的时候,就会增加一个位移x值判断下一个位置Postion+x是否被占用,如果仍然被占用就继续往下位移x判断Position+2*x位置是否被占用,如果没有被占用则将值放入其中。当HashTable中的可用空间越来越小时,则获取得到可用空间的难度越来越大,消耗的时间就越多。
5..当前HashTable中的被占用空间达到一个百分比的时候就将该空间自动扩容,在.net中这个百分比是72%,也叫.net中HashTable的填充因子为0.72。例如有一个HashTable的空间大小是100,当它需要添加第73个值的时候将会扩容此HashTable.
6.这个自动扩容的大小是多少呢?答案是当前空间大小的两倍最接近的素数,例如当前HashTable所占空间为素数71,如果扩容,则扩容大小为素数131.

二:Dictionary
1.Dictionary是一种变种的HashTable,它采用一种分离链接散列表的数据结构来解决哈希冲突的问题。
2.分离链接散列表是当散列到同一个地址的值存为一个链表中。
3.这个变种HashTable的填充因子是1
eg:本文将以代码的形式探索HashTable和Dictionary的插入和三种读取方式的效率(for/foreach/GetEnumerator)
public class HashTableTest
{
static Hashtable _Hashtable;
static Dictionary<string, object> _Dictionary;
static void Main()
{
Compare(10);
Compare(10000);
Compare(5000000);
Console.ReadLine();
}
public static void Compare(int dataCount)
{
Console.WriteLine("-------------------------------------------------
");
_Hashtable = new Hashtable();
_Dictionary = new Dictionary<string, object>();
Stopwatch stopWatch = new Stopwatch();
//HashTable插入dataCount条数据需要时间
stopWatch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < dataCount; i++)
{
_Hashtable.Add("Str" + i.ToString(), "Value");
}
stopWatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(" HashTable插入" + dataCount + "条数据需要时间:" + stopWatch.Elapsed);
//Dictionary插入dataCount条数据需要时间
stopWatch.Reset();
stopWatch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < dataCount; i++)
{
_Dictionary.Add("Str" + i.ToString(), "Value");
}
stopWatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(" Dictionary插入" + dataCount + "条数据需要时间:" + stopWatch.Elapsed);
//Dictionary插入dataCount条数据需要时间
stopWatch.Reset();
int si = 0;
stopWatch.Start();
for(int i=0;i<_Hashtable.Count;i++)
{
si++;
}
stopWatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(" HashTable遍历时间:" + stopWatch.Elapsed + " ,遍历采用for方式");
//Dictionary插入dataCount条数据需要时间
stopWatch.Reset();
si = 0;
stopWatch.Start();
foreach (var s in _Hashtable)
{
si++;
}
stopWatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(" HashTable遍历时间:" + stopWatch.Elapsed + " ,遍历采用foreach方式");
//Dictionary插入dataCount条数据需要时间
stopWatch.Reset();
si = 0;
stopWatch.Start();
IDictionaryEnumerator _hashEnum = _Hashtable.GetEnumerator();
while (_hashEnum.MoveNext())
{
si++;
}
stopWatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(" HashTable遍历时间:" + stopWatch.Elapsed + " ,遍历采用HashTable.GetEnumerator()方式");
//Dictionary插入dataCount条数据需要时间
stopWatch.Reset();
si = 0;
stopWatch.Start();
for(int i=0;i<_Dictionary.Count;i++)
{
si++;
}
stopWatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(" Dictionary遍历时间:" + stopWatch.Elapsed + " ,遍历采用for方式");
//Dictionary插入dataCount条数据需要时间
stopWatch.Reset();
si = 0;
stopWatch.Start();
foreach (var s in _Dictionary)
{
si++;
}
stopWatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(" Dictionary遍历时间:" + stopWatch.Elapsed + " ,遍历采用foreach方式");
//Dictionary插入dataCount条数据需要时间
stopWatch.Reset();
si = 0;
stopWatch.Start();
_hashEnum = _Dictionary.GetEnumerator();
while (_hashEnum.MoveNext())
{
si++;
}
stopWatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(" Dictionary遍历时间:" + stopWatch.Elapsed + " ,遍历采用Dictionary.GetEnumerator()方式");
Console.WriteLine("
-------------------------------------------------");
}
}
四:从上面的结果可以看出
1.HashTable大数据量插入数据时需要花费比Dictionary大的多的时间。
2.for方式遍历HashTable和Dictionary速度最快。
3.在foreach方式遍历时Dictionary遍历速度更快。
五:在单线程的时候使用Dictionary更好一些,多线程的时候使用HashTable更好。
因为HashTable可以通过Hashtable tab = Hashtable.Synchronized(new Hashtable());获得线程安全的对象。
eg: hashtable
public static Hashtable List()
{
Hashtable h = new Hashtable();
h.Add(1,"asdasdsad");
h.Add("dasda","dsadsa");
return h;
}
Hashtable list=List();
foreach(Object item in list.Keys){
Console.WriteLine(item);
Console.WriteLine(list[item]);
}
三:遍历方式:
Dictionary的几种遍历方式:
Dictionary<string, int> list = new Dictionary<string, int>();
list.Add("d", 1);
//一:通过key值遍历:
foreach (string key in list.Keys) {
Console.WriteLine(key + list[key]);
}
//二:通过value值遍历:
foreach (int val in list.Values){
Console.WriteLine(val);
}
//三:通过key和value遍历:
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, int> kv in list){
Console.WriteLine(kv.Key + kv.Value);
}
//四:3.0以上版本
foreach (var item in list){
Console.WriteLine(item.Key + item.Value);
}
HashTable的遍历方式:
static void Main(string[] args)
2 {
3 Person person1 = new Person();
4 person1.Age = 34;
5 person1.Name = "Jacky";
6 person1.Email = "Jacky@gmail.com";
7
8 Person person2 = new Person();
9 person2.Age = 23;
10 person2.Name = "Ajay";
11 person2.Email = "Ajay@gmail.com";
12
13 Person person3 = new Person();
14 person3.Age = 12;
15 person3.Name = "Bill";
16 person3.Email = "Bill@gmail.com";
17
18 Person person4 = new Person();
19 person4.Age = 23;
20 person4.Name = "Gace";
21 person4.Email = "Gace@gmail.com";
22
23 Person person5 = new Person();
24 person5.Age = 45;
25 person5.Name = "Jim";
26 person5.Email = "Jim@gmail.com";
27
28 Hashtable ht = new Hashtable();
29 ht.Add("1", person1);
30 ht.Add("2", person2);
31 ht.Add("3", person3);
32 ht.Add("4", person4);
33 ht.Add("5", person5);
34 Console.WriteLine("请输入你的查询的用户名:");
35 string strName = Console.ReadLine();
36 //第一种方法 key值
37 foreach (string item in ht.Keys)
38 {
39 Person p = (Person)ht[item];
40 if (strName == p.Name)
41 {
42 Console.WriteLine("查询后的结果是:" + p.Name + " " + p.Email + " " + p.Age);
43 }
44 }
45
46
47
48 //第二种方法 value值
49 foreach (Person item in ht.Values)
50 {
51 if (item.Name == strName)
52 {
53 Console.WriteLine("查询后的结果是:" + item.Name + " " + item.Email + " " + item.Age);
54 }
55
56 }
57 //第三种方法 key和value值
58 foreach (DictionaryEntry item in ht)
59 {
60 if (strName == ((Person)item.Value).Name)
61 {
62 Console.WriteLine("查询后的结果是:" + ((Person)item.Value).Name + " " + ((Person)item.Value).Email + " " + ((Person)item.Value).Age);
63 }
64 }
65
66 //第四种方法
67 IDictionaryEnumerator id = ht.GetEnumerator();
68 while (id.MoveNext())
69 {
70 Person p = (Person)ht[id.Key];
71 if (p.Name == strName)
72 {
73 Console.WriteLine("查询后的结果是:" + p.Name + " " + p.Email + " " + p.Age);
74 }
75 }
76
77 }
第四:Queue集合和Stack
Queue:它是一个先进先出的集合(它存储于队列中),先进先出的意思也就是最先放进集合的数据,拿数据的时候从最初放进去的数据开始拿。
Stack:它是一个后进先出的集合(它存储于栈中),后进先出的意思顾名思义,也就是说取数据只能从最后放进去的那个数据开始取。
以下代码实例了分别使用Stack和Queue打印数字0~9。
//写入数据到Queue中
2. Queue q = new Queue();
3. for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
4. {
5. q.Enqueue(i);
6. }
7.
8.
9. //循环输出Queue所有数据
10. Console.WriteLine("开始输出Queue数据");
11. while (q.Count > 0)
12. {
13. Console.WriteLine(q.Dequeue());
14. }
15.
16. //-------------------------------------分割线------------------------------------//
17.
18. //写入数据到Stack中
19. Stack s = new Stack();
20. for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
21. {
22. s.Push(i);
23. }
24.
25. //循环输出所有Stack数据
26. Console.WriteLine("开始输出Stack数据");
27. while (s.Count > 0)
28. {
29. Console.WriteLine(s.Pop());
30. }
基于以下代码对Queue 与 Stack进行了性能测试,他们的性能都比数组要高大约2~倍。
Stopwatch sw_queue = new Stopwatch();
2. sw_queue.Start();
3.
4. //写入数据到Queue中
5. Queue q = new Queue();
6. for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
7. {
8. q.Enqueue(i);
9. }
10.
11. //循环输出Queue所有数据
12. while (q.Count > 0)
13. {
14. q.Dequeue();
15. }
16.
17. sw_queue.Stop(); // 停止监视
18. Console.WriteLine("Queue 100万数据写入读取消耗时间:{0}毫秒", sw_queue.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds.ToString());
19.
20. //---------------------------------分割线--------------------------------//
21.
22. Stopwatch sw_stack = new Stopwatch();
23. sw_stack.Start();
24.
25.
26. //写入数据到Stack中
27. Stack s = new Stack();
28. for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
29. {
30. s.Push(i);
31. }
32.
33. //循环输出所有Stack数据
34. while (s.Count > 0)
35. {
36. s.Pop();
37. }
38.
39. sw_stack.Stop(); // 停止监视
40. Console.WriteLine("Stack 100万数据写入读取消耗时间:{0}毫秒", sw_stack.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds.ToString());
41.
42.
43. Console.R
eadKey();
测试结果:
1、SortedList定义
System.Collections.SortedList类表示键/值对的集合,这些键值对按键排序并可按照键和索引访问。SortedList 在内部维护两个数组以存储列表中的元素;即,一个数组用于键,另一个数组用于相关联的值。每个元素都是一个可作为DictionaryEntry 对象进行访问的键/值对。键不能为null,但值可以。
2.优点
1、SortedList 允许通过相关联键或通过索引对值进行访问,可提供更大的灵活性。
2、可根据需要自动增大容量。
3.注意点:
1、SortedList 的容量是 SortedList 可以保存的元素数。SortedList 的默认初始容量为 0。随着元素添加到 SortedList 中,在需要时可以通过重新分配自动增加容量。可通过调用 TrimToSize方法 或通过显式设置 Capacity 属性减少容量。
2、SortedList 中不允许重复键。
3、SortedList的索引顺序基于排序顺序。当添加元素时,元素将按正确的排序顺序插入 SortedList,同时索引会相应地进行调整。当移除元素时,索引也会相应地进行调整。因此,当在 SortedList 中添加或移除元素时,特定键/值对的索引可能会更改。
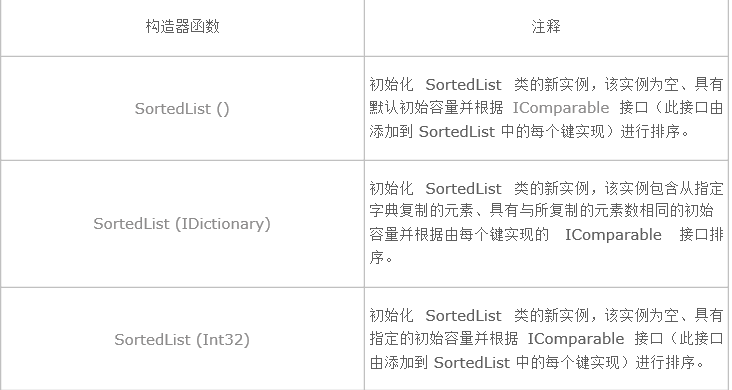
4. SortedList的构造器
5、SortedList的属性

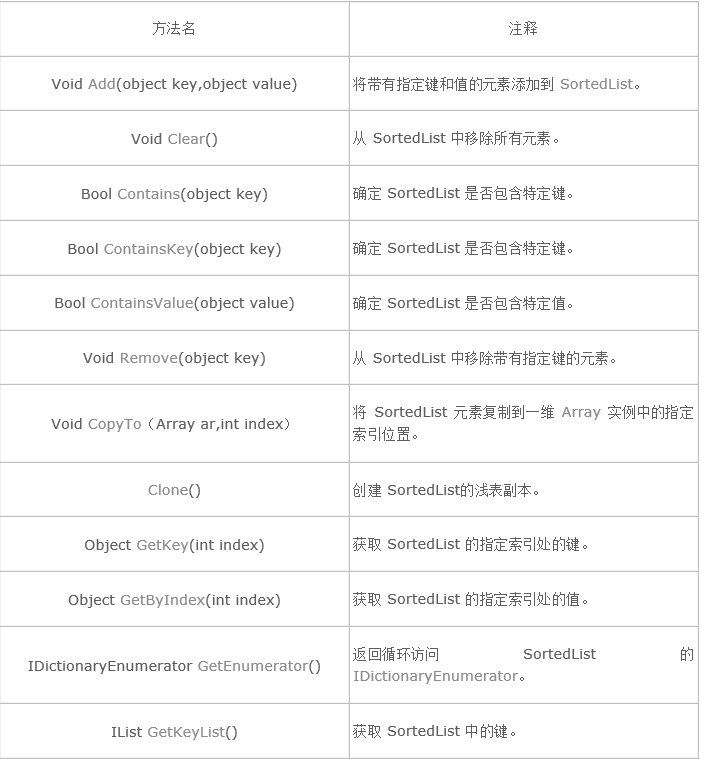
6.SortedList的方法

泛型集合SortedList<TKey,TValue>:
下面的例子创建一个有序表,其中键和值都是string类型。默认的构造函数创建了一个空表,再用Add()方法添加两本书。使用重载的构造函数,可以定义有序表的容量,传送执行了IComparer<TKey>接口的对象,用于给有序表中得元素排序。
Add()方法的第一个参数是键(书名),第二个参数是值(ISBN号)。除了使用Add()方法之外,还可以使用索引器将元素添加到有序表中。索引器需要把键作为索引参数。如果键已存在,那么Add()方法就抛出一个ArgumentException类型的异常。如果索引器使用相同的键,就用新值替代旧值。
static void Main(string[] args)
06. {
07. // 创建一个SortedList对象
08. SortedList mySortedList = new SortedList();
09. mySortedList.Add("First", "Hello");
10. mySortedList.Add("Second", "World");
11. mySortedList.Add("Third", "!");
12. mySortedList.Add("Four", "{1}quot;);
13.
14. //列举SortedList的属性、键、值
15. Console.WriteLine("MySortedList");
16. Console.WriteLine(" Count: {0}", mySortedList.Count);
17. Console.WriteLine(" Capacity: {0}", mySortedList.Capacity);
18. Console.WriteLine(" Keys and Values:");
19. PrintIndexAndKeysAndValues(mySortedList);
20.
21. #region SortedList获得键、值列表
22. SortedList mySortedList1 = new SortedList();
23. mySortedList1.Add(1.3, "fox");
24. mySortedList1.Add(1.4, "jumped");
25. mySortedList1.Add(1.5, "over");
26. mySortedList1.Add(1.2, "brown");
27. mySortedList1.Add(1.1, "quick");
28. mySortedList1.Add(1.0, "The");
29. mySortedList1.Add(1.6, "the");
30. mySortedList1.Add(1.8, "dog");
31. mySortedList1.Add(1.7, "lazy");
32.
33. //获得指定索引处的键和值
34. int myIndex = 3;
35. // 获取 System.Collections.SortedList 对象的指定索引处的键
36. Console.WriteLine("The key at index {0} is {1}.", myIndex, mySortedList1.GetKey(myIndex));
37. // 获取 System.Collections.SortedList 对象的指定索引处的值
38. Console.WriteLine("The value at index {0} is {1}.", myIndex, mySortedList1.GetByIndex(myIndex));
39.
40. // 获得SortedList中的键列表和值列表
41. IList myKeyList = mySortedList1.GetKeyList();
42. IList myValueList = mySortedList1.GetValueList();
43. // Prints the keys in the first column and the values in the second column.
44. Console.WriteLine(" -KEY- -VALUE-");
45. for (int i = 0; i < mySortedList1.Count; i++)
46. Console.WriteLine(" {0} {1}", myKeyList[i], myValueList[i]);
47.
48. #endregion
49.
50. #region 为SortedList中的元素重新赋值
51. // Creates and initializes a new SortedList.
52. SortedList mySortedList2 = new SortedList();
53. mySortedList2.Add(2, "two");
54. mySortedList2.Add(3, "three");
55. mySortedList2.Add(1, "one");
56. mySortedList2.Add(0, "zero");
57. mySortedList2.Add(4, "four");
58. // 打印显示列表的键和值
59. Console.WriteLine("The SortedList contains the following values:");
60. PrintIndexAndKeysAndValues(mySortedList2);
61.
62. // 获得指定键的索引
63. int myKey = 2;
64. Console.WriteLine("The key "{0}" is at index {1}.", myKey, mySortedList2.IndexOfKey(myKey));
65. // 获得指定值的索引
66. String myValue = "three";
67. Console.WriteLine("The value "{0}" is at index {1}.", myValue, mySortedList2.IndexOfValue(myValue));
68. // 重新设置指定索引处的值
69. mySortedList2.SetByIndex(3, "III"); // SetByIndex:替换 System.Collections.SortedList 对象中指定索引处的值
70. mySortedList2.SetByIndex(4, "IV");
71. //打印显示列表的键和值
72. Console.WriteLine("After replacing the value at index 3 and index 4,");
73. PrintIndexAndKeysAndValues(mySortedList2);
74. #endregion
75. Console.ReadKey();
76. }
77.
78. //打印SortedList中的键和值
79. public static void PrintIndexAndKeysAndValues(SortedList myList)
80. {
81. Console.WriteLine(" -INDEX- -KEY- -VALUE-");
82. for (int i = 0; i < myList.Count; i++)
83. {
84. Console.WriteLine(" [{0}]: {1} {2}", i, myList.GetKey(i), myList.GetByIndex(i));
85. }
86. Console.WriteLine();
87. }
88. }
