1、Number:数字型(整型和浮点型)
(1)不同的进制
八进制:数字前加0表示八进制
<script>
var num1=010;
console.log(num1);
</script>
十六进制:0x开头表示十六进制
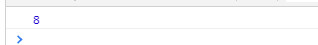
<script>
var num=0xff;
console.log(num);
</script>

(2)最大值与最小值
<script>
console.log(Number.MAX_VALUE);
console.log(Number.MIN_VALUE);
</script>
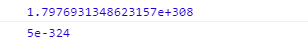
与java中调用包装类的静态方法获取最大值最小值相似
(3)无穷
<script> console.log(Number.MAX_VALUE*3); console.log(-Number.MIN_VALUE*4); </script>
(4)NaN
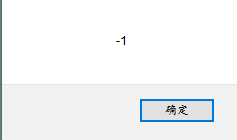
console.log('zahi'-1);

(5)浮点数计算不精确的问题
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Java Script</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function welcome() {
console.log(0.01+0.09)
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="welcome()" bgcolor="aquamarine">
<center>
<h1>你好</h1>
</center>
</body>
</html>
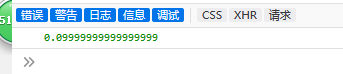
和java相似,浮点数相加会存在不精确的问题。
(6)判断是否为数字,是数字返回false,不是返回true:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Java Script</title>
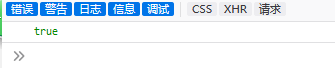
<script type="text/javascript">
function welcome() {
console.log(isNaN("as"));
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="welcome()" bgcolor="aquamarine">
<center>
<h1>你好</h1>
</center>
</body>
</html>
(7) 函数的运用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Java Script</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function test() {
alert(Math.cos(Math.PI));
}
</script>
</head>
<body bgcolor="aquamarine">
<center>
<button onclick="test()">点击这里</button>
</center>
</body>
</html>
(8)类型判断
<script>
var num=12;
console.log(typeof num);
</script>

2、字符串型
(1)类型检测与定义
<script>
var string1="12333";
console.log(typeof string1);
var string2='hello';
console.log(typeof string1);
</script>

可以用单引号也可以用双引号
(2)字符串的拼接
与java类似在字符串中“+”具有连接作用,但是要保证有字符串,如果是两个数值型的数据则进行的是相加操作
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Java Script</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
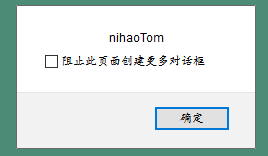
function test() {
var String1="nihao"+"Tom";
alert(String1);
}
</script>
</head>
<body bgcolor="aquamarine">
<center>
<button onclick="test()">点击这里</button>
</center>
</body>
</html>
(3)基本函数的使用
length属性:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Java Script</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function test() {
var String1="nihao";
alert(String1.length);
}
</script>
</head>
<body bgcolor="aquamarine">
<center>
<button onclick="test()">点击这里</button>
</center>
</body>
</html>
获取字符串中的某个字符:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Java Script</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function test() {
var String1="nihao";
alert(String1.charAt(1));
}
</script>
</head>
<body bgcolor="aquamarine">
<center>
<button onclick="test()">点击这里</button>
</center>
</body>
</html>
(4)字符串转义字符
<script>
var string1="12333
hello";
console.log(string1);
</script>

3、布尔型
(1)类型测试
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Java Script</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
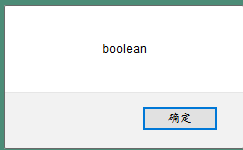
function test() {
var String1=true;
alert(typeof String1);
}
</script>
</head>
<body bgcolor="aquamarine">
<center>
<button onclick="test()">点击这里</button>
</center>
</body>
</html>
(2)数学运算
<script>
var flag=true;
console.log(flag+1);
</script>

在进行数学运算的时候true的值为1
<script>
var flag=false;
console.log(flag+1);
</script>

false的默认值为0
4、undefined类型
(1)类型测试
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Java Script</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function test() {
var String1;
alert(typeof String1);
}
</script>
</head>
<body bgcolor="aquamarine">
<center>
<button onclick="test()">点击这里</button>
</center>
</body>
</html>
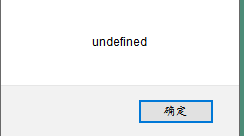
即定义了但未赋值
5、null类型
(1)类型测试
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Java Script</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function test() {
num=null;
alert(typeof(num));
}
</script>
</head>
<body bgcolor="aquamarine">
<center>
<button onclick="test()">点击这里</button>
</center>
</body>
</html>
访问的对象不存在(未声明)。
(2)与数字和字符串的运算
<script>
var num;
console.log(num+'string');
console.log(num+1);
var str=null;
console.log(str+'string');
console.log(str+1);
</script>
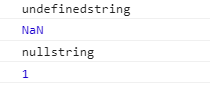
6、数据类型间的转换
(1)数字转换为字符串:
<script>
var num=123;
console.log(typeof num.toString());
console.log(typeof String(num));
console.log(typeof (num+ ''));
</script>

(2)转换为数字型
<script>
var num='123';
console.log(typeof parseInt(num));
console.log(typeof parseFloat(num));
console.log(typeof Number(num));
console.log(typeof (num-0));
</script>
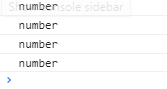
(3)转换为布尔型
<script> console.log(typeof Boolean(0)); console.log(typeof Boolean(NaN)); console.log(typeof Boolean(null)); console.log(typeof Boolean(undefined)); console.log(Boolean(0)); console.log(Boolean(NaN)); console.log(Boolean(null)); console.log(Boolean(undefined)); console.log('---------------'); console.log(typeof Boolean(12)); console.log(typeof Boolean('str')); console.log( Boolean(12)); console.log( Boolean('str')); </script>
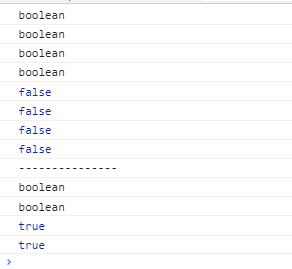
代表空、否定的值会转换为false,其他的转化为true
总结:
- 声明变量用var+变量名即可,var是varible的缩写,声明之后会自动为该变量分配内存空间
- 不同的数据所占的存储空间是不同的,为了便于把数据分成所需内存大小不同的数据,充分利用存储空间,定义了不同的数据类型
- js是一种弱类型的语言,不用提前声明变量的类型,在程序运行中会根据值来自动确定,例如:java语言有byte、short、int、long、float、double等,在声明变量的时候必须指定变量的类型,但是在js中一律用var指定
<script>
var uname="zhai";
console.log(uname);
var uname=123;
console.log(uname);
</script>
- typeof可以检测变量的数据类型