1、java8介绍
是Java语言历史上变化最大的一个版本,其调整java编程向函数式风格迈进,不会对老版本产生影响
2、Lambda表达式介绍
为什么需要Lambda表达式?
(1)在java中无法将函数作为参数传递给一个方法,也无法声明返回一个函数的方法
(2)在JS中,函数参数是一个函数,返回值是另一个函数的情况是常见的,js是一门非常典型的函数式语言
3、lambda表达式
(1)匿名内部类: 为按钮注册事件监听器
public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame jFrame=new JFrame("My JFrame"); JButton jButton=new JButton("My JButton"); jButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { System.out.println("Button Pressed!!"); } }); jFrame.add(jButton); jFrame.pack(); jFrame.setVisible(true); jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); }
可以用lambda表达式代替:
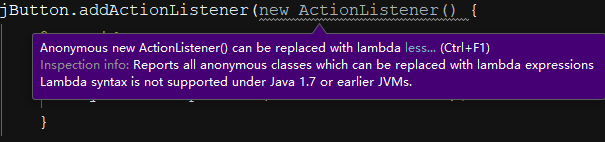
(2)用lambda表达式代替:
public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame jFrame=new JFrame("My JFrame"); JButton jButton=new JButton("My JButton"); jButton.addActionListener(Event->System.out.println("Button Pressed!!")); jFrame.add(jButton); jFrame.pack(); jFrame.setVisible(true); jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); }
4、函数式接口
(1)一个接口里面只有一个抽象的方法
(2)要求:
* <li> The type is an interface type and not an annotation type, enum, or class. * <li> The annotated type satisfies the requirements of a functional interface.
(3)如果在某一个接口上声明了@FunctionalInterface注解,那么编译器就会按函数式接口的定义来要求该接口
@FunctionalInterface public interface Consumer<T> {
(4)如果一个接口只有一个抽象方法,但我们并没有添加@FunctionalInterface注解,那么编译器依旧会将该接口当做函数式接口
(5)如果一个接口声明了一个抽象方法,但是该抽象方法重写了Object类的方法,那么不会使得接口的抽象方法数量加一:
书写一个接口:
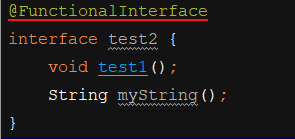
修改为: 错误消失
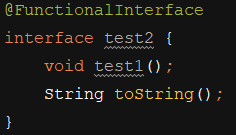
匿名内部类方式:
@FunctionalInterface interface MyInterface { void test1(); String toString(); } public class test2 { public void Mytest(MyInterface myInterface) { System.out.println("111"); myInterface.test1(); System.out.println("2222"); } public static void main(String[] args) { test2 test=new test2(); test.Mytest(new MyInterface() { @Override public void test1() { System.out.println("mytest"); } }); } }
lambda表达式:
public static void main(String[] args) { test2 test=new test2(); test.Mytest(()->{ System.out.println("mytest"); }); }
执行结果是一样的:
111
mytest
2222
5、默认方法:在接口里面定义的实现过的方法
在 interface Iterable<T> 中有如下方法:实现该接口的类默认继承该方法
default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); for (T t : this) { action.accept(t); } }
6、凡是将函数式接口作为函数参数的时候,都可以用lambar表达式的方式进行替换
public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list= Arrays.asList(1,2,45,32,234,3); list.forEach(new Consumer<Integer>() { @Override public void accept(Integer integer) { System.out.println(integer); } }); } }
public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list= Arrays.asList(1,2,45,32,234,3); list.forEach(i-> { System.out.println(i); }); }
i 没有加类型声明是因为存在类型推断
public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list= Arrays.asList(1,2,45,32,234,3); list.forEach((Integer i)-> { System.out.println(i); }); }
7、lambda表达式的作用
(1)Lambda表达式为java添加了缺失的函数式编程特性,使我们能将函数当做一个公民来看待
(2)在将函数作为一等公民的语言(python)中,lanbda表达式的类型是函数。但是在java中,它是对象,他们必须依赖于一类特别的对象模型(函数式接口)