一:文档
官方文档地址:1.x版本和2.x版本
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/guide/index.html
硬件要求:
1、内存,官方推荐64G,但是自己使用32G或16G也可以
2、CPU,核心越多越好
3、硬盘,越快越好,不建议使用NAS网络存储,官方建议使用RAID 0
4、网络,千兆或以上
5、JVM,建议使用比较新的版本,可以是openJDK或oracle的Java JDK
6、文件描述符,即可以打开的最大文件数,一定要改大
7、cluster 同一个集群要一样,集群被的各node name不能相同
8、组播和单播设置
9、JDK 内存设置不要超过32G,可以关闭Swap分区
10、锁住内存设置
动态改变配置:
PUT /_cluster/settings { "persistent" : { "discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes" : 2 }, "transient" : { "indices.store.throttle.max_bytes_per_sec" : "50mb" } }
滚动升级或维护:
1、尽量不写新的数据,就不产生新的索引
2、关闭自动分片:
PUT /_cluster/settings { "transient" : { "cluster.routing.allocation.enable" : "none" } }
3、关闭当前节点:
停止后会在集群当中找其他的几点并提升为主节点,并将被停止的节点的分片分配给其他节点,并将数据同步到其他节点。
POST /_cluster/nodes/_local/_shutdown
4、执行升级或维护操作
5、重启节点,会自动加入到集群
6、开启当前节点的分片功能
注意:即分片同步需要一段时间,需要等待集群状态转换为绿色即集群可用状态。
Shard rebalancing may take some time. Wait until the cluster has returned to status green before continuing.
7、对集群当中的其他节点做2-6步骤的操作
数据备份--->快照备份:curl
1、创建备份目录,节点之间需要共享一个目录,共享的文件系统需要每个节点都可以访问,并且每个节点可挂载的路径要一致
支持的共享系统:
Shared filesystem, such as a NAS
Amazon S3
HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System)
Azure Cloud
执行挂载目录的命令:
PUT _snapshot/my_backup { "type": "fs", "settings": { "location": "/mount/backups/my_backup" } }
2、创建快照:
POST _snapshot/my_backup/ { "type": "fs", "settings": { "location": "/mount/backups/my_backup", "max_snapshot_bytes_per_sec" : "50mb", "max_restore_bytes_per_sec" : "50mb" } }
ELK的工作原理:
使用多播进行机器发现同一个集群内的节点,并汇总各个节点的返回组成一个集群,主节点要读取各个节点的状态,在关键的时候进行数据的恢复,主节点会坚持各个节点的状态,并决定每个分片的位置,通过ping的request检测各失效的节点
三:安装logstash:
官网下载地址:
https://www.elastic.co/downloads/logstash
1、安装:
tar xvf logstash-1.5.3.zip
mv logstash-1.5.3 /usr/local/logstash
2、测试:
[root@node6 ~]# /usr/local/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{} }' test Logstash startup completed 2016-04-09T18:14:47.891Z node6.a.com test
3、使用ruby进行更详细的输出:
需要主机能解析自己的主机名,可以在hosts文件解析:
[root@node6 ~]# /usr/local/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{codec => rubydebug}}' asd Logstash startup completed { "message" => "asd", "@version" => "1", "@timestamp" => "2016-04-09T18:13:51.250Z", "host" => "node6.a.com" }
4、通过logstas将输出交给elasticsearch:
启动:
[root@node6 ~]# /usr/local/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { host => "192.168.10.206" protocol => "http"} }' '[DEPRECATED] use `require 'concurrent'` instead of `require 'concurrent_ruby'` Logstash startup completed
5、通过logstash直接输出到屏幕:
#配置文件如下:
input { stdin{ } } output { stdout { codec => rubydebug } }
测试标准输出:
[root@elk-server2 conf.d]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/03.conf
"message" => "{"@timestamp":"2016-05-14T11:24:45+08:00","host":"192.168.0.22","clientip":"36.104.21.88","size":650,"responsetime":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"webapi.weather.com.cn","url":"/data/","domain":"webapi.weather.com.cn","xff":"-","referer":"-","status":"200"}", "@version" => "1", "@timestamp" => "2016-05-14T03:25:04.068Z", "host" => "elk-server2"
6、输入一个hello word! 以进行测试:
[root@node6 ~]# /usr/local/logstash/bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { host => "192.168.10.206" protocol => "http"} }' '[DEPRECATED] use `require 'concurrent'` instead of `require 'concurrent_ruby'` Logstash startup completed hello word!
7、查看集群管理软件head的状态:
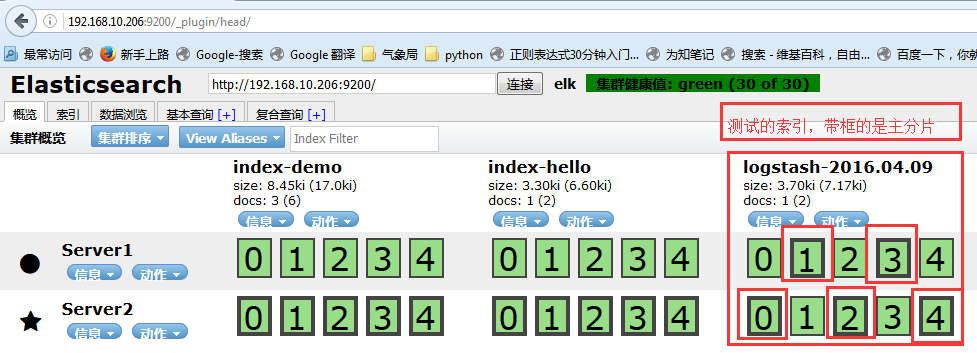
8、进行基本查询:

9、配置文件格式:
input { file { path => "/var/log/messages" type => "syslog" } file { path => "/var/log/apache/access.log" type => "apache" } }
10、数组类型--->多个文件:
path => [ "/var/log/messages", "/var/log/*.log" ] #通过*匹配多个文件 path => "/data/mysql/mysql.log"
11、bool类型:
ssl_enable => true
12、字节设置:
my_bytes => "1113" # 1113 bytes my_bytes => "10MiB" # 10485760 bytes my_bytes => "100kib" # 102400 bytes my_bytes => "180 mb" # 180000000 bytes
13、codec:
codec => "json"
14、Hash:
match => { "field1" => "value1" "field2" => "value2" ... }
15、Number--->数字:
port => 33
16、Path--->密码:
my_password => "password"
17、Path---->路径:
my_path => "/tmp/logstash"
18、string-->字符串:
name => "Hello world"
四:logstash的input使用语法:
1、input,默认不支持目录的递归,即目录中还有文件是不支持直接读取的,但是可以使用*/*进行匹配。
2、exclude--->排除文件,
exclude => "*.gz"
3、sincedb_path,记录读取的时候位置,默认是一个隐藏文件
4、sincedb_write_interval,记录sincedb_path文件的写间隔,默认是15秒
5、start_position,从这个文件的什么位置开始读,默认是end,可以改成beginning
6、stat_interval,多久检测一次此文件的更新状态
五:logstash的output使用及插件:
1、可以输出到文件、rendis等
2、gzip,是否压缩,默认为false,压缩是安装数据流一点点增量压缩的
3、message_format,消息的格式
六:logstash --> file -->elasticsearch:
通过logstash输出到文件在输入到elasticsearch:
1、启动脚本:
vim /etc/init.d/logstash
[root@node6 tmp]# cat /etc/init.d/logstash #!/bin/sh # Init script for logstash # Maintained by Elasticsearch # Generated by pleaserun. # Implemented based on LSB Core 3.1: # * Sections: 20.2, 20.3 # ### BEGIN INIT INFO # Provides: logstash # Required-Start: $remote_fs $syslog # Required-Stop: $remote_fs $syslog # Default-Start: 2 3 4 5 # Default-Stop: 0 1 6 # Short-Description: # Description: Starts Logstash as a daemon. ### END INIT INFO PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/logstash/bin/ export PATH if [ `id -u` -ne 0 ]; then echo "You need root privileges to run this script" exit 1 fi name=logstash pidfile="/var/run/$name.pid" export JAVA_HOME=/opt/jdk1.8.0_45 export JRE_HOME=/opt/jdk1.8.0_45/jre export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar:$JRE_HOME/lib:$CLASSPATH export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH LS_USER=root LS_GROUP=root LS_HOME=/usr/local/logstash LS_HEAP_SIZE="512m" LS_LOG_DIR=/usr/local/logstash LS_LOG_FILE="${LS_LOG_DIR}/$name.log" LS_CONF_DIR=/etc/logstash.conf LS_OPEN_FILES=16384 LS_NICE=19 LS_OPTS="" [ -r /etc/default/$name ] && . /etc/default/$name [ -r /etc/sysconfig/$name ] && . /etc/sysconfig/$name program=/usr/local/logstash/bin/logstash args="agent -f ${LS_CONF_DIR} -l ${LS_LOG_FILE} ${LS_OPTS}" quiet() { "$@" > /dev/null 2>&1 return $? } start() { LS_JAVA_OPTS="${LS_JAVA_OPTS} -Djava.io.tmpdir=${LS_HOME}" HOME=${LS_HOME} export PATH HOME LS_HEAP_SIZE LS_JAVA_OPTS LS_USE_GC_LOGGING # chown doesn't grab the suplimental groups when setting the user:group - so we have to do it for it. # Boy, I hope we're root here. SGROUPS=$(id -Gn "$LS_USER" | tr " " "," | sed 's/,$//'; echo '') if [ ! -z $SGROUPS ] then EXTRA_GROUPS="--groups $SGROUPS" fi # set ulimit as (root, presumably) first, before we drop privileges ulimit -n ${LS_OPEN_FILES} # Run the program! nice -n ${LS_NICE} chroot --userspec $LS_USER:$LS_GROUP $EXTRA_GROUPS / sh -c " cd $LS_HOME ulimit -n ${LS_OPEN_FILES} exec "$program" $args " > "${LS_LOG_DIR}/$name.stdout" 2> "${LS_LOG_DIR}/$name.err" & # Generate the pidfile from here. If we instead made the forked process # generate it there will be a race condition between the pidfile writing # and a process possibly asking for status. echo $! > $pidfile echo "$name started." return 0 } stop() { # Try a few times to kill TERM the program if status ; then pid=`cat "$pidfile"` echo "Killing $name (pid $pid) with SIGTERM" kill -TERM $pid # Wait for it to exit. for i in 1 2 3 4 5 ; do echo "Waiting $name (pid $pid) to die..." status || break sleep 1 done if status ; then if [ "$KILL_ON_STOP_TIMEOUT" -eq 1 ] ; then echo "Timeout reached. Killing $name (pid $pid) with SIGKILL. This may result in data loss." kill -KILL $pid echo "$name killed with SIGKILL." else echo "$name stop failed; still running." fi else echo "$name stopped." fi fi } status() { if [ -f "$pidfile" ] ; then pid=`cat "$pidfile"` if kill -0 $pid > /dev/null 2> /dev/null ; then # process by this pid is running. # It may not be our pid, but that's what you get with just pidfiles. # TODO(sissel): Check if this process seems to be the same as the one we # expect. It'd be nice to use flock here, but flock uses fork, not exec, # so it makes it quite awkward to use in this case. return 0 else return 2 # program is dead but pid file exists fi else return 3 # program is not running fi } force_stop() { if status ; then stop status && kill -KILL `cat "$pidfile"` fi } configtest() { # Check if a config file exists if [ ! "$(ls -A ${LS_CONF_DIR}/* 2> /dev/null)" ]; then echo "There aren't any configuration files in ${LS_CONF_DIR}" return 1 fi HOME=${LS_HOME} export PATH HOME JAVA_OPTS LS_HEAP_SIZE LS_JAVA_OPTS LS_USE_GC_LOGGING test_args="-f ${LS_CONF_DIR} --configtest ${LS_OPTS}" $program ${test_args} [ $? -eq 0 ] && return 0 # Program not configured return 6 } case "$1" in start) status code=$? if [ $code -eq 0 ]; then echo "$name is already running" else start code=$? fi exit $code ;; stop) stop ;; force-stop) force_stop ;; status) status code=$? if [ $code -eq 0 ] ; then echo "$name is running" else echo "$name is not running" fi exit $code ;; restart) quiet configtest RET=$? if [ ${RET} -ne 0 ]; then echo "Configuration error. Not restarting. Re-run with configtest parameter for details" exit ${RET} fi stop && start ;; configtest) configtest exit $? ;; *) echo "Usage: $SCRIPTNAME {start|stop|force-stop|status|restart|configtest}" >&2 exit 3 ;; esac exit $?
2、设置开机启动:
chmod a+x /etc/init.d/logstash chkconfig --add logstash
3、编辑配置文件:
[root@node6 tmp]# vim /etc/logstash.conf
input { file { path => "/var/log/messages" } } output { file { path => "/tmp/log-%{+YYYY-MM-dd}messages.gz" gzip => true } }
4、测试:
[root@node6 tmp]# echo "Apr 12 14:03:53 HTC-Server2 snmpd[1573]: Connection from UDP: [60.195.252.107]:31001->[192.168.0.116]" >> /var/log/messages
测试结果:
[root@node6 tmp]# ls /tmp/ hsperfdata_root log-2016-04-09.messages.gz
5、把输出直接传输到elasticsearch:
[root@node6 ~]# vim /etc/logstash.conf
input { file { path => "/var/log/messages" } } output { file { path => "/tmp/log-%{+YYYY-MM-dd}.messages.gz" gzip => true } elasticsearch { host => ["192.168.10.206"] protocol => "http" index => "system-message-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } }
6、在集群管理平台查看结果:
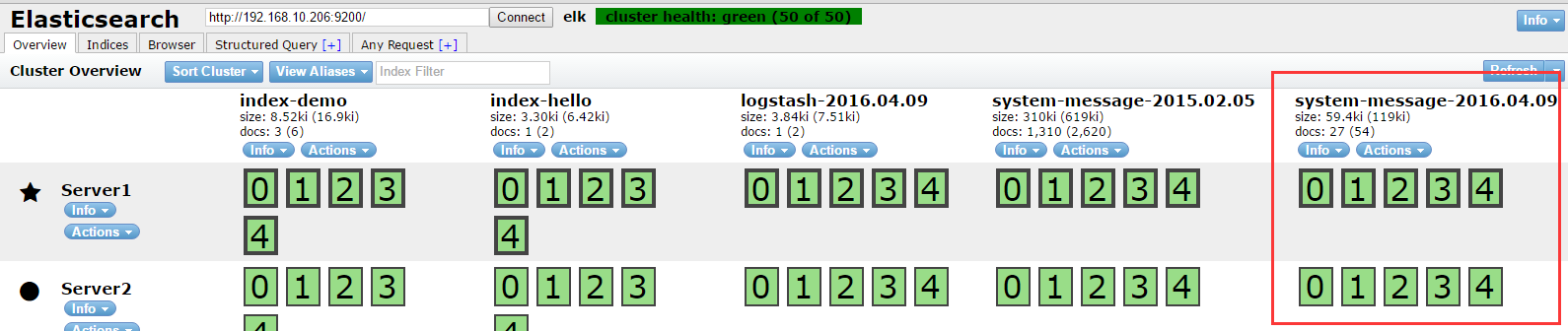
七:将logstash输出给redis:
1、基本语法:
db:使用的数据库,默认为0,也可以使用其他的,但是redis主从不支持其他数据库同步。
host: redis服务器的地址
key:key的名称
password:redis服务器的redis连接密码
port:redis端口,默认6379
data_type:数据类型,支持string和list,我们使用list
2、重启logstash
3、向logstash监控的文件写入数据
[root@node6 yum.repos.d]# echo "Apr 12 14:03:53 HTC-Server2 snmpd[1573]: Connection from UDP: [60.195.252.107]:31001->[192.168.0.116]" >> /var/log/messages [root@node6 yum.repos.d]# echo "Apr 12 14:03:53 HTC-Server2 snmpd[1573]: Connection from UDP: [60.195.252.107]:31001->[192.168.0.116]" >> /var/log/messages [root@node6 yum.repos.d]# echo "Apr 12 14:03:53 HTC-Server2 snmpd[1573]: Connection from UDP: [60.195.252.107]:31001->[192.168.0.116]" >> /var/log/messages [root@node6 yum.repos.d]# echo "Apr 12 14:03:53 HTC-Server2 snmpd[1573]: Connection from UDP: [60.195.252.107]:31001->[192.168.0.116]" >> /var/log/messages [root@node6 yum.repos.d]# echo "Apr 12 14:03:53 HTC-Server2 snmpd[1573]: Connection from UDP: [60.195.252.107]:31001->[192.168.0.116]" >> /var/log/messages [root@node6 yum.repos.d]# echo "Apr 12 14:03:53 HTC-Server2 snmpd[1573]: Connection from UDP: [60.195.252.107]:31001->[192.168.0.116]" >> /var/log/messages
4、到redis查看结果:
[root@node5 ~]# redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> KEYS * 1) "system-message-jack" #已经生成数据 127.0.0.1:6379> LLEN system-message-jack #查看key的长度 (integer) 681 127.0.0.1:6379> LINDEX system-message-jack -1 #查看最后一行数据 "{"message":"Apr 12 14:03:53 HTC-Server2 snmpd[1573]: Connection from UDP: [60.195.252.107]:31001->[192.168.0.116]","@version":"1","@timestamp":"2016-04-12T08:37:51.025Z","host":"node6.a.com","path":"/var/log/messages"}"
5、在重新找一台机器安装logstash,步骤参考之前的步骤:
6、另外一台logstash的配置文件:
input { #读取redis的数据 redis { data_type => "list" key => "system-message-jack" host => "192.168.10.205" port => "6379" db => "0" } } output { #将读取到的reids的数据写入到elasticsearch elasticsearch { host => ["192.168.10.206"] protocol => "http" index => "redis-message-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } }
7、向message文件写入数据,写入的数据会读取到redis,reids的数据则会被传输给
[root@node6 yum.repos.d]# echo "Apr 12 14:03:53 HTC-Server2 snmpd[1573]: Connection from UDP: [60.195.252.107]:31001->[192.168.0.116]" >> /var/log/messages [root@node6 yum.repos.d]# echo "Apr 12 14:03:53 HTC-Server2 snmpd[1573]: Connection from UDP: [60.195.252.107]:31001->[192.168.0.116]" >> /var/log/messages [root@node6 yum.repos.d]# echo "Apr 12 14:03:53 HTC-Server2 snmpd[1573]: Connection from UDP: [60.195.252.107]:31001->[192.168.0.116]" >> /var/log/messages [root@node6 yum.repos.d]# echo "Apr 12 14:03:53 HTC-Server2 snmpd[1573]: Connection from UDP: [60.195.252.107]:31001->[192.168.0.116]" >> /var/log/messages
8、在集群管理平台查看:

9、 查看索引:

八:分析的日志类型:
1、系统日志:/var/log下的所有的内容,google每一个文件的内容 2、通过ELS分析某一个访问记录 3、错误日志,收集后反馈给开发 4、系统运行日志 5、其他类型的日志
九:日志的字段划分:
1、grok模块:通过正则表达式,比较复杂,而且当数据大的时候会占用CPU
2、json,简单易用
3、将nginx的日志设置为json模式:
安装nginx:可以编译或yum安装,省略
4、日志配置部分:
http { include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; # log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; log_format logstash_json '{"@timestamp":"$time_iso8601",' #定义日志格式logstash_json '"host":"$server_addr",' '"clientip":"$remote_addr",' '"size":$body_bytes_sent,' '"responsetime":$request_time,' '"upstreamtime":"$upstream_response_time",' '"upstreamhost":"$upstream_addr",' '"http_host":"$host",' '"url":"$uri",' '"domain":"$host",' '"xff":"$http_x_forwarded_for",' '"referer":"$http_referer",' '"agent":"$http_user_agent",' '"status":"$status"}'; sendfile on; serevr配置: # server { listen 9009; server_name localhost; #charset koi8-r; access_log /var/log/nginx/json.access.log logstash_json; #日志文件保存路径及使用上面定义的日志格式logstash_json # Load configuration files for the default server block. include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; location / { root /usr/share/nginx/html; index index.html index.htm; } error_page 404 /404.html; location = /404.html { root /usr/share/nginx/html; } # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root /usr/share/nginx/html; }
5、使用ab访问nginx测试日志:
[root@node5 nginx]# ab -n1000 -c10 http://192.168.10.205:9009/ #一共1000个请求,每次并发10个,即100次请求完成
6、查看日志是否有内容:
[root@node5 nginx]# tail /var/log/nginx/json.access.log {"@timestamp":"2016-04-12T18:21:31+08:00","host":"192.168.10.205","clientip":"192.168.10.205","size":3698,"responsetime":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"192.168.10.205","url":"/index.html","domain":"192.168.10.205","xff":"-","referer":"-","agent":"ApacheBench/2.3","status":"200"} {"@timestamp":"2016-04-12T18:21:31+08:00","host":"192.168.10.205","clientip":"192.168.10.205","size":3698,"responsetime":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"192.168.10.205","url":"/index.html","domain":"192.168.10.205","xff":"-","referer":"-","agent":"ApacheBench/2.3","status":"200"} {"@timestamp":"2016-04-12T18:21:31+08:00","host":"192.168.10.205","clientip":"192.168.10.205","size":3698,"responsetime":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"192.168.10.205","url":"/index.html","domain":"192.168.10.205","xff":"-","referer":"-","agent":"ApacheBench/2.3","status":"200"} {"@timestamp":"2016-04-12T18:21:31+08:00","host":"192.168.10.205","clientip":"192.168.10.205","size":3698,"responsetime":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"192.168.10.205","url":"/index.html","domain":"192.168.10.205","xff":"-","referer":"-","agent":"ApacheBench/2.3","status":"200"} {"@timestamp":"2016-04-12T18:21:31+08:00","host":"192.168.10.205","clientip":"192.168.10.205","size":3698,"responsetime":0.001,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"192.168.10.205","url":"/index.html","domain":"192.168.10.205","xff":"-","referer":"-","agent":"ApacheBench/2.3","status":"200"} {"@timestamp":"2016-04-12T18:21:31+08:00","host":"192.168.10.205","clientip":"192.168.10.205","size":3698,"responsetime":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"192.168.10.205","url":"/index.html","domain":"192.168.10.205","xff":"-","referer":"-","agent":"ApacheBench/2.3","status":"200"} {"@timestamp":"2016-04-12T18:21:31+08:00","host":"192.168.10.205","clientip":"192.168.10.205","size":3698,"responsetime":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"192.168.10.205","url":"/index.html","domain":"192.168.10.205","xff":"-","referer":"-","agent":"ApacheBench/2.3","status":"200"} {"@timestamp":"2016-04-12T18:21:31+08:00","host":"192.168.10.205","clientip":"192.168.10.205","size":3698,"responsetime":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"192.168.10.205","url":"/index.html","domain":"192.168.10.205","xff":"-","referer":"-","agent":"ApacheBench/2.3","status":"200"} {"@timestamp":"2016-04-12T18:21:31+08:00","host":"192.168.10.205","clientip":"192.168.10.205","size":3698,"responsetime":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"192.168.10.205","url":"/index.html","domain":"192.168.10.205","xff":"-","referer":"-","agent":"ApacheBench/2.3","status":"200"} {"@timestamp":"2016-04-12T18:21:31+08:00","host":"192.168.10.205","clientip":"192.168.10.205","size":3698,"responsetime":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"192.168.10.205","url":"/index.html","domain":"192.168.10.205","xff":"-","referer":"-","agent":"ApacheBench/2.3","status":"200"}
7、配置logstash手机nginx的json日志并写入到redis:
[root@node5 logstash]# cat /etc/logstash.conf input { # redis { # data_type => "list" # key => "system-message-jack" # host => "192.168.10.205" # port => "6379" # db => "0" # } file { path => "/var/log/nginx/json.access.log" #读取指定的json格式的日志 codec => "json" #指定json格式 } } output { # elasticsearch { # host => ["192.168.10.206"] # protocol => "http" # index => "redis-message-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" # } redis { data_type => "list" key => "nginx-json-log" #nginx的json格式日志的key名称 host => "192.168.10.205" #写入到redis服务器 port => "6379" db => "1" #使用redis的数据库1 } }
8、重启logstash服务,并使用ab重新访问web地址,以产生新的日志写入redis:
[root@node5 nginx]# ab -n1000 -c10 http://192.168.10.205:9009/
9、在redis查询是否有当前key的日志:
[root@node5 nginx]# redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> SELECT 1 OK 127.0.0.1:6379[1]> KEYS * 1) "nginx-json-log" #已有日志 127.0.0.1:6379[1]> LLEN nginx-json-log #日志长度 (integer) 1000
10、配置logstash当前redis日志并输出至elasticsearch:
[root@node5 nginx]# grep "#" -v /etc/logstash.conf input { redis { data_type => "list" key => "nginx-json-log" host => "192.168.10.205" port => "6379" db => "1" } } output { elasticsearch { host => ["192.168.10.206"] protocol => "http" index => "nginx-json-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } }
11、重启logstash并使用ab批量访问web,再查看elasticsearch集群管理界面是否有nginx的json定义的nginx-json-log的key出现:
