A Knight's Journey
Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 131072/65536K (Java/Other)
Total Submission(s) : 66 Accepted Submission(s) : 27
Problem Description
 Background
Background The knight is getting bored of seeing the same black and white squares again and again and has decided to make a journey
around the world. Whenever a knight moves, it is two squares in one direction and one square perpendicular to this. The world of a knight is the chessboard he is living on. Our knight lives on a chessboard that has a smaller area than a regular 8 * 8 board, but it is still rectangular. Can you help this adventurous knight to make travel plans?
Problem
Find a path such that the knight visits every square once. The knight can start and end on any square of the board.
Input
The input begins with a positive integer n in the first line. The following lines contain n test cases. Each test case consists of a single line with two positive integers p and q, such that 1 <= p * q <= 26. This represents a p * q chessboard, where p describes how many different square numbers 1, . . . , p exist, q describes how many different square letters exist. These are the first q letters of the Latin alphabet: A, . . .
Output
The output for every scenario begins with a line containing "Scenario #i:", where i is the number of the scenario starting at 1. Then print a single line containing the lexicographically first path that visits all squares of the chessboard with knight moves followed by an empty line. The path should be given on a single line by concatenating the names of the visited squares. Each square name consists of a capital letter followed by a number.
If no such path exist, you should output impossible on a single line.
If no such path exist, you should output impossible on a single line.
Sample Input
3
1 1
2 3
4 3
Sample Output
Scenario #1:
A1
Scenario #2:
impossible
Scenario #3:
A1B3C1A2B4C2A3B1C3A4B2C4
Source
PKU
题意:
 View Code
View Code
给出一个国际棋盘的大小,判断马能否不重复的走过所有格,并记录下其中按字典序排列的第一种路径。经典的“骑士游历”问题。
思路:
1、 题目要求以"lexicographically"方式输出,也就是字典序...要以字典序输出路径,那么搜索的方向(我的程序是path()函数)就要以特殊的顺序排列了...这样只要每次从dfs(A,1)开始搜索,第一个成功遍历的路径一定是以字典序排列...
下图是搜索的次序,马的位置为当前位置,序号格为测试下一步的位置的测试先后顺序
按这个顺序测试,那么第一次成功周游的顺序就是字典序
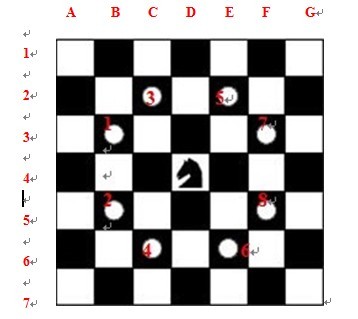
2、国际象棋的棋盘,行为数字a;列为字母b
这一题一定程度上考验了做题者的模拟思想,利用了DFS+回溯;
AC代码:

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstdlib> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #include<cstring> 6 #include<string> 7 #include<cmath> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 12 int s[10][10]={0}; 13 int number=1; 14 int a; 15 int b; 16 17 18 void path(int &x,int &y,int i,int j,int num) 19 { 20 switch(num) 21 { 22 case 1:{x=i-1;y=j-2;break;} 23 case 2:{x=i+1;y=j-2;break;} 24 case 3:{x=i-2;y=j-1;break;} 25 case 4:{x=i+2;y=j-1;break;} 26 case 5:{x=i-2;y=j+1;break;} 27 case 6:{x=i+2;y=j+1;break;} 28 case 7:{x=i-1;y=j+2;break;} 29 case 8:{x=i+1;y=j+2;break;} 30 } 31 return; 32 } 33 34 void dfsz(int row,int cow) 35 { 36 char c=(char)(cow-1+'A'); 37 cout<<c<<row; 38 if(number==a*b){//当number=a*b的时候则证明输出完毕 39 return; 40 } 41 number++;//自己后的number代表着该输出第number个点了 42 int x,y; 43 for(int i=1;i<=8;i++)//寻找第number个点 44 { 45 path(x,y,row,cow,i); 46 if(s[x][y]==number) 47 break; 48 } 49 dfsz(x,y);//输出(x,y)这个点; 50 return; 51 } 52 53 54 bool dfs(int row,int cow)//表示行进到了(row,cow)这个点 55 { 56 if(row<=0||row>a)//横坐标超界 57 return false;//竖坐标超界 58 if(cow<=0||cow>b) 59 return false; 60 if(s[row][cow])//该点已经被访问过 61 return false; 62 number++; 63 s[row][cow]=number;//该点是第number个点 64 if(number==a*b){//当number=a*b的时候则证明输出完毕 65 return true; 66 } 67 int i; 68 for(i=1;i<=8;i++){ 69 int x,y; 70 path(x,y,row,cow,i);//计算下一步的坐标(x,y) 71 bool a=dfs(x,y);//判断点(x,y) 72 if(a){ 73 return true; 74 } 75 } 76 s[row][cow]=0;//这一步访问点(row,cow)不行 77 number--; 78 return false; 79 } 80 81 82 83 int main() 84 { 85 // freopen("1.txt","r",stdin); 86 int test; 87 cin>>test; 88 int k=1; 89 while(k<=test){ 90 cin>>a>>b; 91 number=0; 92 memset(s,0,sizeof(s));//每一个样例都要初始化,我就在这WA好几次 93 bool sgin=false; 94 for(int i=1;i<=a;i++){ 95 for(int j=1;j<=b;j++){ 96 sgin=dfs(i,j); 97 if(sgin){ 98 number=1; 99 cout<<"Scenario #"<<k<<":"<<endl; 100 dfsz(i,j); 101 cout<<endl<<endl;//输出结束后有一个空行 102 break; 103 } 104 s[i][j]=0; 105 } 106 if(sgin) 107 break; 108 } 109 if(!sgin){ 110 cout<<"Scenario #"<<k<<":"<<endl<<"impossible"<<endl<<endl;//输出结束后有一个空行,切记! 111 } 112 k++; 113 } 114 return 0; 115 }
