As you know, every birthday party has a cake! This time, Babaei is going to prepare the very special birthday party's cake.
Simple cake is a cylinder of some radius and height. The volume of the simple cake is equal to the volume of corresponding cylinder. Babaei has n simple cakes and he is going to make a special cake placing some cylinders on each other.
However, there are some additional culinary restrictions. The cakes are numbered in such a way that the cake number i can be placed only on the table or on some cake number j where j < i. Moreover, in order to impress friends Babaei will put the cake i on top of the cake j only if the volume of the cake i is strictly greater than the volume of the cake j.
Babaei wants to prepare a birthday cake that has a maximum possible total volume. Help him find this value.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of simple cakes Babaei has.
Each of the following n lines contains two integers ri and hi (1 ≤ ri, hi ≤ 10 000), giving the radius and height of the i-th cake.
Print the maximum volume of the cake that Babaei can make. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6.
Namely: let's assume that your answer is a, and the answer of the jury is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct, if 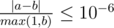 .
.
2
100 30
40 10
942477.796077000
4
1 1
9 7
1 4
10 7
3983.539484752
In first sample, the optimal way is to choose the cake number 1.
In second sample, the way to get the maximum volume is to use cakes with indices 1, 2 and 4.
思路:一般的dp写法会tle,需要线段树进行维护,由于条件a[i]<a[j]&&i<j,故要sort先一下,可以保证a[i]<a[j],而这些值插入线段树是按照i<j的顺序插入的,所以答案才正确,一开始总想不通这点,后来在纸上找了一个数组演绎了一下就明白了;
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long const double PI=acos(-1.0); using namespace std; const int N=1e5+7; double r[N],h[N],v[N],a[N],dp[N]; struct nod { int l,r; double sum; }; nod tree[4*N]; int build(int node,int le,int ri) { tree[node].l=le; tree[node].r=ri; if(le==ri) { tree[node].sum=0; return 0; } int mid=(le+ri)/2; build(2*node,le,mid); build(2*node+1,mid+1,ri); tree[node].sum=max(tree[2*node].sum,tree[2*node+1].sum); } double query(int node,int le,int ri) { if(tree[node].l>=le&&tree[node].r<=ri)return tree[node].sum; else { int mid=(tree[node].l+tree[node].r)/2; if(ri<=mid)return query(2*node,le,ri); else if(le>mid)return query(2*node+1,le,ri); else return max(query(2*node,le,ri),query(2*node+1,le,ri)); } } int update(int node,int posi,double x) { if(tree[node].l==posi&&tree[node].r==posi) { tree[node].sum=max(tree[node].sum,x); return 0; } int mid=(tree[node].l+tree[node].r)/2; if(posi<=mid)update(2*node,posi,x); else update(2*node+1,posi,x); tree[node].sum=max(tree[2*node].sum,tree[2*node+1].sum); } int main() { int n; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%lf%lf",&r[i],&h[i]); a[i]=v[i]=r[i]*r[i]*h[i]; } sort(a+1,a+n+1); build(1,1,n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { int pos=lower_bound(a+1,a+n+1,v[i])-a; if(pos==1)dp[i]=v[i]; else { dp[i]=query(1,1,pos-1)+v[i]; } update(1,pos,dp[i]); } printf("%.12lf",query(1,1,n)*PI); return 0; }