动态库项目
//简单的动态库开发----报文发送 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> //定义上下文结构体 typedef struct _SCK_HANDLE{ //定义报文IP char ipaddress[30]; //定义报文端口 char port[10]; //定义报文接受数组 unsigned char * buf; //定义报文长度 int buflen; }SCK_HANDLE; //初始化上下文 _declspec(dllexport) int cltSocketInit(void **handle/*out*/){ int ERRO_MSG = 0; if (handle == NULL) { ERRO_MSG = 1; printf("handle==NULL 报文初始化失败 erro msg:%d ", ERRO_MSG); return ERRO_MSG; } //定义上下文指针 SCK_HANDLE *shandle = NULL; //分配内存 //详述:此处分配内存必须分配堆内存(malloc函数分配),这也正是malloc函数真正的用途所在 //此处不可以分配栈内存,栈内存会被系统自动回收,但是报文的发送与接受所使用的上下文SCK_HANDLE,必须长时间存在 //何时回收必须由用户决定,而不能随便的被回收 //同样使用静态区也不合适,因为无法人为回收内存空间,必须等待电脑关机,综上所述,只能使用malloc函数分配内存 shandle = (SCK_HANDLE *)malloc(sizeof(SCK_HANDLE)); //重置内存空间 memset(shandle, 0, sizeof(SCK_HANDLE)); strcpy(shandle->ipaddress, "192.168.0.128"); strcpy(shandle->port, "88"); *handle = shandle; return ERRO_MSG; } //客户端发报文 _declspec(dllexport) int cltSocketSend(void *handle/*in*/, unsigned char *buf/*in*/, int buflen/*in*/){ int ERRO_MSG = 0; if (handle == NULL) { ERRO_MSG = 1; printf("handle==NULL handle不可以为NULL erro msg :%d ", ERRO_MSG); return ERRO_MSG; } if (buf == NULL) { ERRO_MSG = 2; printf("buf==NULL buf不可以为NULL erro msg :%d ", ERRO_MSG); return ERRO_MSG; } SCK_HANDLE *sh = NULL; sh = (SCK_HANDLE *)handle; //为报文字符开辟内存空间 sh->buf = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*buflen); if (sh->buf == NULL) { ERRO_MSG = 3; printf("sh->buf==NULL 内存分配失败 erro msg :%d ", ERRO_MSG); return ERRO_MSG; } //给上下文中的报文字符赋值 //memcpy()函数详解 //函数原型 //void *memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, size_t n); //功能 //从源src所指的内存地址的起始位置开始拷贝n个字节到目标dest所指的内存地址的起始位置中 //所需头文件 //C语言:#include<string.h> //C++:#include<cstring> //返回值 //函数返回指向dest的指针。 //说明 //1.source和destin所指的内存区域可能重叠,但是如果source和destin所指的内存区域重叠, 那么这个函数并不能够确保source所在重叠区域在拷贝之前不被覆盖。而使用memmove可以用来处理重叠区域。函数返回指向destin的指针. //2.如果目标数组destin本身已有数据,执行memcpy()后,将覆盖原有数据(最多覆盖n)。如果要追加数据,则每次执行memcpy后,要将目标数组地址增加到你要追加数据的地址。 //注意:source和destin都不一定是数组,任意的可读写的空间均可。 memcpy(sh->buf, buf, buflen); sh->buflen = buflen; return ERRO_MSG; } //客户端收报文 _declspec(dllexport) int cltSocketRev(void *handle/*in*/, unsigned char **buf/*out*/, int *buflen/*out*/){ int ERRO_MSG = 0; if (handle == NULL || buf == NULL || buflen == NULL) { ERRO_MSG = 1; printf("handle == NULL || buf == NULL || buflen==NULL erro msg:%d ", ERRO_MSG); return ERRO_MSG; } //定义临时上下文变量 SCK_HANDLE *sh = NULL; sh = (SCK_HANDLE *)handle; //分配返回报文字符串内存 char *cbuf = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*sh->buflen); memcpy(cbuf, sh->buf, sh->buflen); *buf = cbuf; *buflen = sh->buflen; //释放上下文中字符串数组的内存空间(至于具体应用还是看场景) if (sh->buf != NULL) { //释放内存 free(sh->buf); //消除野指针 sh->buf = NULL; } sh->buflen = 0; return ERRO_MSG; } //客户端释放资源 _declspec(dllexport) int cltSocketDestory(void **handle){ int ERRO_MSG = 0; if (handle == NULL) { ERRO_MSG = 1; printf("handle==NULL%d ", ERRO_MSG); return ERRO_MSG; } //转换类型 SCK_HANDLE *sh = NULL; sh = (SCK_HANDLE *)(*handle); //判断字符串数组是否释放--严谨做法 if (sh->buf!=NULL) { //释放内存 free(sh->buf); //消除野指针 sh->buf = NULL; //长度置零 sh->buflen = 0; } if (sh != NULL) { //释放内存 free(sh); //消除野指针 sh = NULL; } return ERRO_MSG; }
测试项目
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include"socketclientdll.h" void main() { int ret = 0; //初始化报文 void *handle = NULL; ret = cltSocketInit(&handle); if (ret==0) { printf("报文初始化成功! "); } //发送报文 unsigned char *str = "1234567890qwertyuiop"; int buflen = 10; ret = cltSocketSend(handle, str, buflen); if (ret == 0) { printf("报文发送成功! "); } unsigned char *str2 = NULL; int buflen2 = 0; //接受报文 ret = cltSocketRev(handle, &str2, &buflen2); if (ret == 0) { unsigned char *buf3 = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*12); memset(buf3,0,sizeof(char)*12); memcpy(buf3, str2, 10); //strcpy(buf3, str2); printf("报文接受成功! "); printf("接受报文:%s;报文长度是%d ", buf3, buflen2); } //释放上下文 cltSocketDestory(&handle); printf("%p ", handle); system("pause"); }
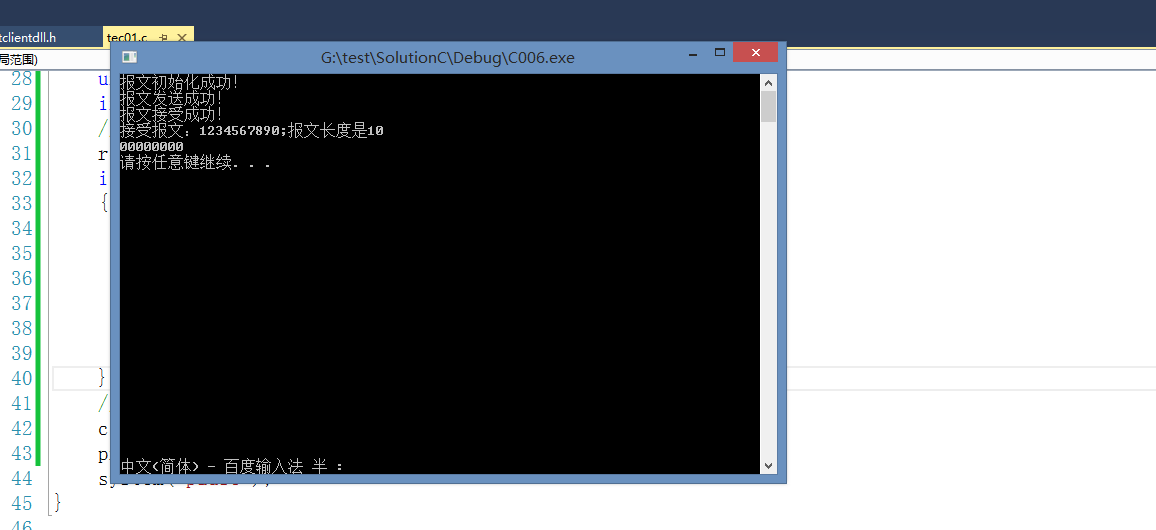
效果图