原型模式
-
原型模式:用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝原型创建新的对象(Specify the kinds of objects to create using a prototypical instance, and create objects by copying this prototype)。
- 原型模式的核心是clone()方法,通过该方法进行对象的拷贝,实现Cloneable接口,其通用类图如下:
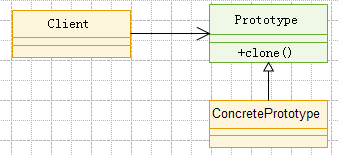
-
- 通用源码如下:
-
public class Prototype implements Cloneable{ public Prototype clone(){ Prototype prototype= null; try { prototype = (Prototype) super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return prototype; } }
-
原型模式的优点
- 性能较好:原型模式是在内存二进制流的拷贝,要比直接new一个对象性能好很多,特别是在一个循环体内产生大量的对象时,原型模式可以更好地体现其优点。
- 逃避构造函数的约束:这既是它的优点也是缺点,直接在内存中拷贝,构造函数不会执行。
-
原型模式的使用场景
- 资源优化场景:类初始化需要大量的数据、硬件资源时。
- 性能和安全要求场景:通过new产生一个对象需要非常频繁的数据准备或访问权限,则可以使用原型模型。
- 一个对象多个修改者:一个对象需要提供给其他对象访问,而且各个调用者可能都需要修改其值时,可以利用原型模式拷贝多个对象供调用者使用。
- 原型模型经常和工厂方法模式配合使用。
-
原型模型中的深拷贝和浅拷贝
原型模型clone()方法只负责拷贝本对象,其对象内部的数组、引用、引用对象等都不拷贝,还是指向原生对象的内部元素地址,这就叫做浅拷贝。通过对对象内部的数组、引用、引用对象执行clone()方法实现这些变量的深拷贝。当一个对象有大量的引用情况时,建议深拷贝和浅拷贝分开实现。
public class ConcretePrototype implements Cloneable{ private ArrayList<String> name = new ArrayList<String>(); public ConcretePrototype clone(){ ConcretePrototype concretePrototype = null; try { concretePrototype = (ConcretePrototype ) super.clone(); cloneName(concretePrototype); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return concretePrototype ; } private void cloneName(ConcretePrototype concretePrototype){ concretePrototype.name = (ArrayList<String>) this.name.clone(); } }