计算机程序离不开算法和数据结构,本文简单介绍栈(Stack)和队列(Queue)的实现,.NET中与之相关的数据结构,典型应用等,希望能加深自己对这两个简单数据结构的理解。
1. 基本概念
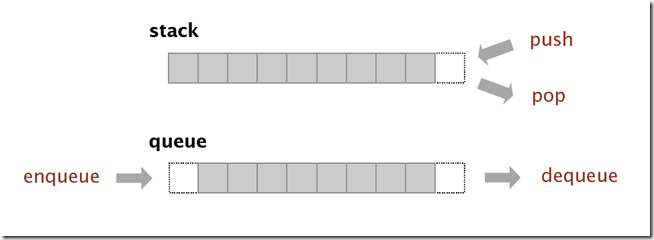
概念很简单,栈 (Stack)是一种后进先出(last in first off,LIFO)的数据结构,而队列(Queue)则是一种先进先出 (fisrt in first out,FIFO)的结构,如下图:
2. 实现
现在来看如何实现以上的两个数据结构。在动手之前,Framework Design Guidelines这本书告诉我们,在设计API或者实体类的时候,应当围绕场景编写API规格说明书。
1.1 Stack的实现
栈是一种后进先出的数据结构,对于Stack 我们希望至少要对外提供以下几个方法:
|
Stack<T>() |
创建一个空的栈 |
|
void Push(T s) |
往栈中添加一个新的元素 |
|
T Pop() |
移除并返回最近添加的元素 |
|
boolean IsEmpty() |
栈是否为空 |
|
int Size() |
栈中元素的个数 |
要实现这些功能,我们有两中方法,数组和链表,先看链表实现:
栈的链表实现:
我们首先定义一个内部类来保存每个链表的节点,该节点包括当前的值以及指向下一个的值,然后建立一个节点保存位于栈顶的值以及记录栈的元素个数;
class Node
{
public T Item{get;set;}
public Node Next { get; set; }
}
private Node first = null;
private int number = 0;
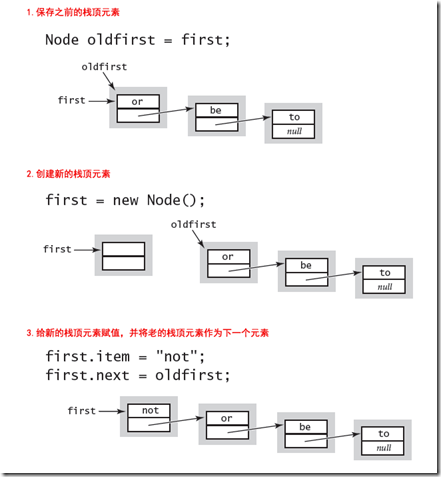
现在来实现Push方法,即向栈顶压入一个元素,首先保存原先的位于栈顶的元素,然后新建一个新的栈顶元素,然后将该元素的下一个指向原先的栈顶元素。整个Pop过程如下:
实现代码如下:
void Push(T node)
{
Node oldFirst = first;
first = new Node();
first.Item= node;
first.Next = oldFirst;
number++;
}
Pop方法也很简单,首先保存栈顶元素的值,然后将栈顶元素设置为下一个元素:
T Pop()
{
T item = first.Item;
first = first.Next;
number--;
return item;
}
基于链表的Stack实现,在最坏的情况下只需要常量的时间来进行Push和Pop操作。
栈的数组实现:
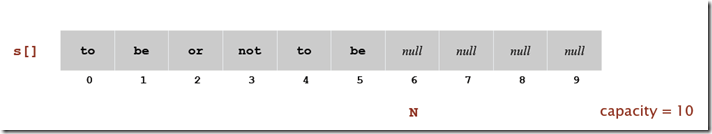
我们可以使用数组来存储栈中的元素Push的时候,直接添加一个元素S[N]到数组中,Pop的时候直接返回S[N-1].
首先,我们定义一个数组,然后在构造函数中给定初始化大小,Push方法实现如下,就是集合里添加一个元素:
T[] item;
int number = 0;
public StackImplementByArray(int capacity)
{
item = new T[capacity];
}
public void Push(T _item)
{
if (number == item.Length) Resize(2 * item.Length);
item[number++] = _item;
}
Pop方法:
public T Pop()
{
T temp = item[--number];
item[number] = default(T);
if (number > 0 && number == item.Length / 4) Resize(item.Length / 2);
return temp;
}
在Push和Pop方法中,为了节省内存空间,我们会对数组进行整理。Push的时候,当元素的个数达到数组的Capacity的时候,我们开辟2 倍于当前元素的新数组,然后将原数组中的元素拷贝到新数组中。Pop的时候,当元素的个数小于当前容量的1/4的时候,我们将原数组的大小容量减少1 /2。
Resize方法基本就是数组复制:
private void Resize(int capacity)
{
T[] temp = new T[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < item.Length; i++)
{
temp[i] = item[i];
}
item = temp;
}
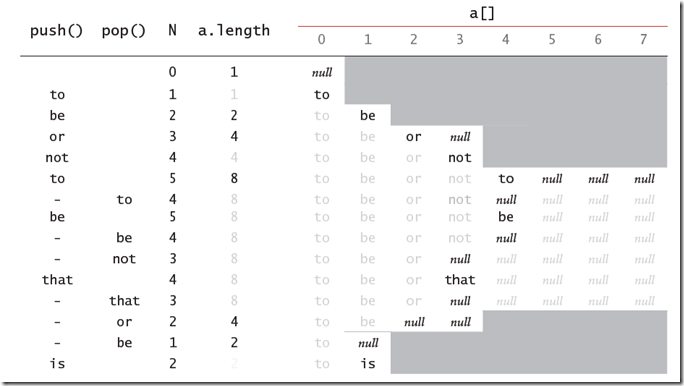
当我们缩小数组的时候,采用的是判断1/4的情况,这样效率要比1/2要高,因为可以有效避免在1/2附件插入,删除,插入,删除,从而频繁的扩大和缩小数组的情况。下图展示了在插入和删除的情况下数组中的元素以及数组大小的变化情况:
分析:1. Pop和Push操作在最坏的情况下与元素个数成比例的N的时间,时间主要花费在扩大或者缩小数组的个数时,数组拷贝上。
2. 元素在内存中分布紧凑,密度高,便于利用内存的时间和空间局部性,便于CPU进行缓存,较LinkList内存占用小,效率高。
2.2 Queue的实现
Queue是一种先进先出的数据结构,和Stack一样,他也有链表和数组两种实现,理解了Stack的实现后,Queue的实现就比较简单了。
|
Stack<T>() |
创建一个空的队列 |
|
void Enqueue(T s) |
往队列中添加一个新的元素 |
|
T Dequeue() |
移除队列中最早添加的元素 |
|
boolean IsEmpty() |
队列是否为空 |
|
int Size() |
队列中元素的个数 |
首先看链表的实现:
Dequeue方法就是返回链表中的第一个元素,这个和Stack中的Pop方法相似:
public T Dequeue()
{
T temp = first.Item;
first = first.Next;
number--;
if (IsEmpety())
last = null;
return temp;
}
Enqueue和Stack的Push方法不同,他是在链表的末尾增加新的元素:
public void Enqueue(T item)
{
Node oldLast = last;
last = new Node();
last.Item = item;
if (IsEmpety())
{
first = last;
}
else
{
oldLast.Next = last;
}
number++;
}
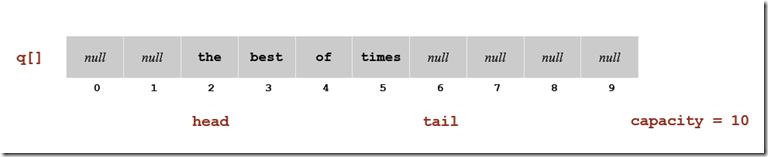
同样地,现在再来看如何使用数组来实现Queue,首先我们使用数组来保存数据,并定义变量head和tail来记录Queue的首尾元素。
和Stack的实现方式不同,在Queue中,我们定义了head和tail来记录头元素和尾元素。当enqueue的时候,tial加1,将元素放在尾部,当dequeue的时候,head减1,并返回。
public void Enqueue(T _item)
{
if ((head - tail + 1) == item.Length) Resize(2 * item.Length);
item[tail++] = _item;
}
public T Dequeue()
{
T temp = item[--head];
item[head] = default(T);
if (head > 0 && (tail - head + 1) == item.Length / 4) Resize(item.Length / 2);
return temp;
}
private void Resize(int capacity)
{
T[] temp = new T[capacity];
int index = 0;
for (int i = head; i < tail; i++)
{
temp[++index] = item[i];
}
item = temp;
}
3. .NET中的Stack和Queue
在.NET中有Stack和Queue泛型类,使用Reflector工具可以查看其具体实现。先看Stack的实现,下面是截取的部分代码,仅列出了Push,Pop方法,其他的方法希望大家自己使用Reflector查看:
可以看到.NET中的Stack的实现和我们之前写的差不多,也是使用数组来实现的。.NET中Stack的初始容量为4,在Push方法中,可以 看到当元素个数达到数组长度时,扩充2倍容量,然后将原数组拷贝到新的数组中。Pop方法和我们之前实现的基本上相同,下面是具体代码,只截取了部分:
[Serializable, ComVisible(false), DebuggerTypeProxy(typeof(System_StackDebugView<>)), DebuggerDisplay("Count = {Count}"), __DynamicallyInvokable]
public class Stack<T> : IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable
{
// Fields
private T[] _array;
private const int _defaultCapacity = 4;
private static T[] _emptyArray;
private int _size;
private int _version;
// Methods
static Stack()
{
Stack<T>._emptyArray = new T[0];
}
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public Stack()
{
this._array = Stack<T>._emptyArray;
this._size = 0;
this._version = 0;
}
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public Stack(int capacity)
{
if (capacity < 0)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.capacity, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNumRequired);
}
this._array = new T[capacity];
this._size = 0;
this._version = 0;
}
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int arrayIndex)
{
if (array == null)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.array);
}
if ((arrayIndex < 0) || (arrayIndex > array.Length))
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.arrayIndex, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNum);
}
if ((array.Length - arrayIndex) < this._size)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentException(ExceptionResource.Argument_InvalidOffLen);
}
Array.Copy(this._array, 0, array, arrayIndex, this._size);
Array.Reverse(array, arrayIndex, this._size);
}
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public T Pop()
{
if (this._size == 0)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowInvalidOperationException(ExceptionResource.InvalidOperation_EmptyStack);
}
this._version++;
T local = this._array[--this._size];
this._array[this._size] = default(T);
return local;
}
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public void Push(T item)
{
if (this._size == this._array.Length)
{
T[] destinationArray = new T[(this._array.Length == 0) ? 4 : (2 * this._array.Length)];
Array.Copy(this._array, 0, destinationArray, 0, this._size);
this._array = destinationArray;
}
this._array[this._size++] = item;
this._version++;
}
// Properties
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public int Count
{
[__DynamicallyInvokable, TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline this type of method across NGen image boundaries")]
get
{
return this._size;
}
}
}
下面再看看Queue的实现:
[Serializable, DebuggerDisplay("Count = {Count}"), ComVisible(false), DebuggerTypeProxy(typeof(System_QueueDebugView<>)), __DynamicallyInvokable]
public class Queue<T> : IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable
{
// Fields
private T[] _array;
private const int _DefaultCapacity = 4;
private static T[] _emptyArray;
private int _head;
private int _size;
private int _tail;
private int _version;
// Methods
static Queue()
{
Queue<T>._emptyArray = new T[0];
}
public Queue()
{
this._array = Queue<T>._emptyArray;
}
public Queue(int capacity)
{
if (capacity < 0)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.capacity, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNumRequired);
}
this._array = new T[capacity];
this._head = 0;
this._tail = 0;
this._size = 0;
}
public T Dequeue()
{
if (this._size == 0)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowInvalidOperationException(ExceptionResource.InvalidOperation_EmptyQueue);
}
T local = this._array[this._head];
this._array[this._head] = default(T);
this._head = (this._head + 1) % this._array.Length;
this._size--;
this._version++;
return local;
}
public void Enqueue(T item)
{
if (this._size == this._array.Length)
{
int capacity = (int)((this._array.Length * 200L) / 100L);
if (capacity < (this._array.Length + 4))
{
capacity = this._array.Length + 4;
}
this.SetCapacity(capacity);
}
this._array[this._tail] = item;
this._tail = (this._tail + 1) % this._array.Length;
this._size++;
this._version++;
}
private void SetCapacity(int capacity)
{
T[] destinationArray = new T[capacity];
if (this._size > 0)
{
if (this._head < this._tail)
{
Array.Copy(this._array, this._head, destinationArray, 0, this._size);
}
else
{
Array.Copy(this._array, this._head, destinationArray, 0, this._array.Length - this._head);
Array.Copy(this._array, 0, destinationArray, this._array.Length - this._head, this._tail);
}
}
this._array = destinationArray;
this._head = 0;
this._tail = (this._size == capacity) ? 0 : this._size;
this._version++;
}
public int Count
{
[__DynamicallyInvokable, TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline this type of method across NGen image boundaries")]
get
{
return this._size;
}
}
}
可以看到.NET中Queue的实现也是基于数组的,定义了head和tail,当长度达到数组的容量的时候,使用了SetCapacity方法来进行扩容和拷贝。
4. Stack和Queue的应用
Stack这种数据结构用途很广泛,比如编译器中的词法分析器、Java虚拟机、软件中的撤销操作、浏览器中的回退操作,编译器中的函数调用实现等等。
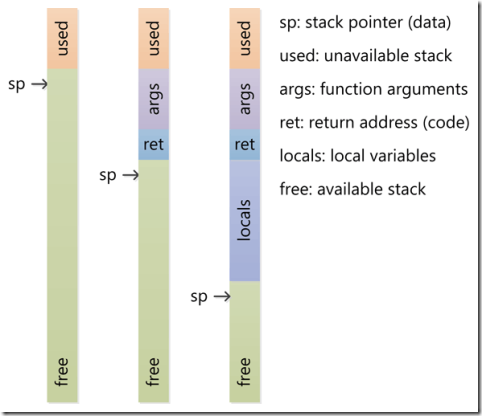
4.1 线程堆 (Thread Stack)
线程堆是 操作系型系统分配的一块内存区域。通常CPU上有一个特殊的称之为堆指针的寄存器 (stack pointer) 。在程序初始化时,该指针指向栈顶,栈顶的地址最大。CPU有特殊的指令可以将值Push到线程堆上,以及将值Pop出堆栈。每一次Push操作都将值存 放到堆指针指向的地方,并将堆指针递减。每一次Pop都将堆指针指向的值从堆中移除,然后堆指针递增,堆是向下增长的。Push到线程堆,以及从线程堆中 Pop的值都存放到CPU的寄存器中。
当发起函数调用的时候,CPU使用特殊的指令将当前的指令指针(instruction pointer),如当前执行的代码的地址压入到堆上。然后CPU通过设置指令指针到函数调用的地址来跳转到被调用的函数去执行。当函数返回值时,旧的指 令指针从堆中Pop出来,然后从该指令地址之后继续执行。
当进入到被调用的函数中时,堆指针减小来在堆上为函数中的局部变量分配更多的空间。如果函数中有一个32位的变量分配到了堆中,当函数返回时,堆指针就返回到之前的函数调用处,分配的空间就会被释放。
如果函数有参数,这些参数会在函数调用之前就被分配在堆上,函数中的代码可以从当前堆往上访问到这些参数。
线程堆是一块有一定限制的内存空间,如果调用了过多的嵌套函数,或者局部变量分配了过多的内存空间,就会产生堆栈溢出的错误。
下图简单显示了线程堆的变化情况。
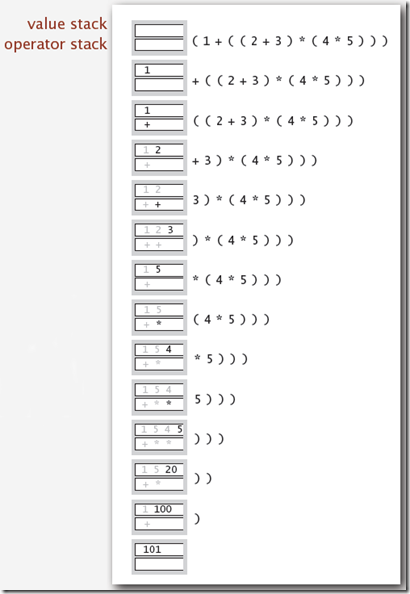
4.2 算术表达式的求值
Stack使用的一个最经典的例子就是算术表达式的求值了,这其中还包括前缀表达式和后缀表达式的求值。E. W. Dijkstra发明了使用两个Stack,一个保存操作值,一个保存操作符的方法来实现表达式的求值,具体步骤如下:
1) 当输入的是值的时候Push到属于值的栈中。
2) 当输入的是运算符的时候,Push到运算符的栈中。
3) 当遇到左括号的时候,忽略
4) 当遇到右括号的时候,Pop一个运算符,Pop两个值,然后将计算结果Push到值的栈中。
下面是在C#中的一个简单的括号表达式的求值:
/// <summary>
/// 一个简单的表达式运算
/// </summary>
/// <param name="args"></param>
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Stack<char> operation = new Stack<char>();
Stack<Double> values = new Stack<double>();
//为方便,直接使用ToChar对于两位数的数组问题
Char[] charArray = Console.ReadLine().ToCharArray();
foreach (char s in charArray)
{
if (s.Equals('(')) { }
else if (s.Equals('+')) operation.Push(s);
else if (s.Equals('*')) operation.Push(s);
else if (s.Equals(')'))
{
char op = operation.Pop();
if (op.Equals('+'))
values.Push(values.Pop() + values.Pop());
else if (op.Equals('*'))
values.Push(values.Pop() * values.Pop());
}
else values.Push(Double.Parse(s.ToString()));
}
Console.WriteLine(values.Pop());
Console.ReadKey();
}
运行结果如下:
下图演示了操作栈和数据栈的变化。
在编译器技术中,前缀表达式,后缀表达式的求值都会用到堆。
4.3 Object-C中以及OpenGL中的图形绘制
在Object-C以及OpenGL中都存在”绘图上下文”,有时候我们对局部对象的绘图不希望影响到全局的设置,所以需要保存上一次的绘图状态。下面是Object-C中绘制一个圆形的典型代码:
- (void)drawGreenCircle:(CGContextRef)ctxt {
UIGraphicsPushContext(ctxt);
[[UIColor greenColor] setFill];
// draw my circle
UIGraphicsPopContext();
}
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)aRect {
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
[[UIColor redColor] setFill];
// do some stuff
[self drawGreenCircle:context];
// do more stuff and expect fill color to be red
}
可以看到,在drawGreenCircle方法中,在设置填充颜色之前,我们Push保存了绘图上下文的信息,然后在设置当前操作的一些环境变量,绘制图形,绘制完成之后,我们Pop出之前保存的绘图上下文信息,从而不影响后面的绘图。
4.4 一些其他场景
有一个场景是利用stack 处理多余无效的请求,比如用户长按键盘,或者在很短的时间内连续按某一个功能键,我们需要过滤到这些无效的请求。一个通常的做法是将所有的请求都压入到堆中,然后要处理的时候Pop出来一个,这个就是最新的一次请求。
Queue的应用
在现实生活中Queue的应用也很广泛,最广泛的就是排队了,”先来后到” First come first service ,以及Queue这个单词就有排队的意思。
还有,比如我们的播放器上的播放列表,我们的数据流对象,异步的数据传输结构(文件IO,管道通讯,套接字等)
还有一些解决对共享资源的冲突访问,比如打印机的打印队列等。消息队列等。交通状况模拟,呼叫中心用户等待的时间的模拟等等。
5. 一点点感悟
本文简单介绍了Stack和Queue的原理及实现,并介绍了一些应用。
最后一点点感悟就是不要为了使用数据结构而使用数据结构。举个例子,之前看到过一个数组反转的问题,刚学过Stack可能会想,这个简单啊,直接将字符串挨个的Push进去,然后Pop出来就可以了,完美的解决方案。但是,这是不是最有效地呢,其实有更有效地方法,那就是以中间为对折,然后左右两边替换。
public static void Reverse(int[] array, int begin, int end)
{
while (end > begin)
{
int temp = array[begin];
array[begin] = array[end];
array[end] = temp;
begin++;
end--;
}
}