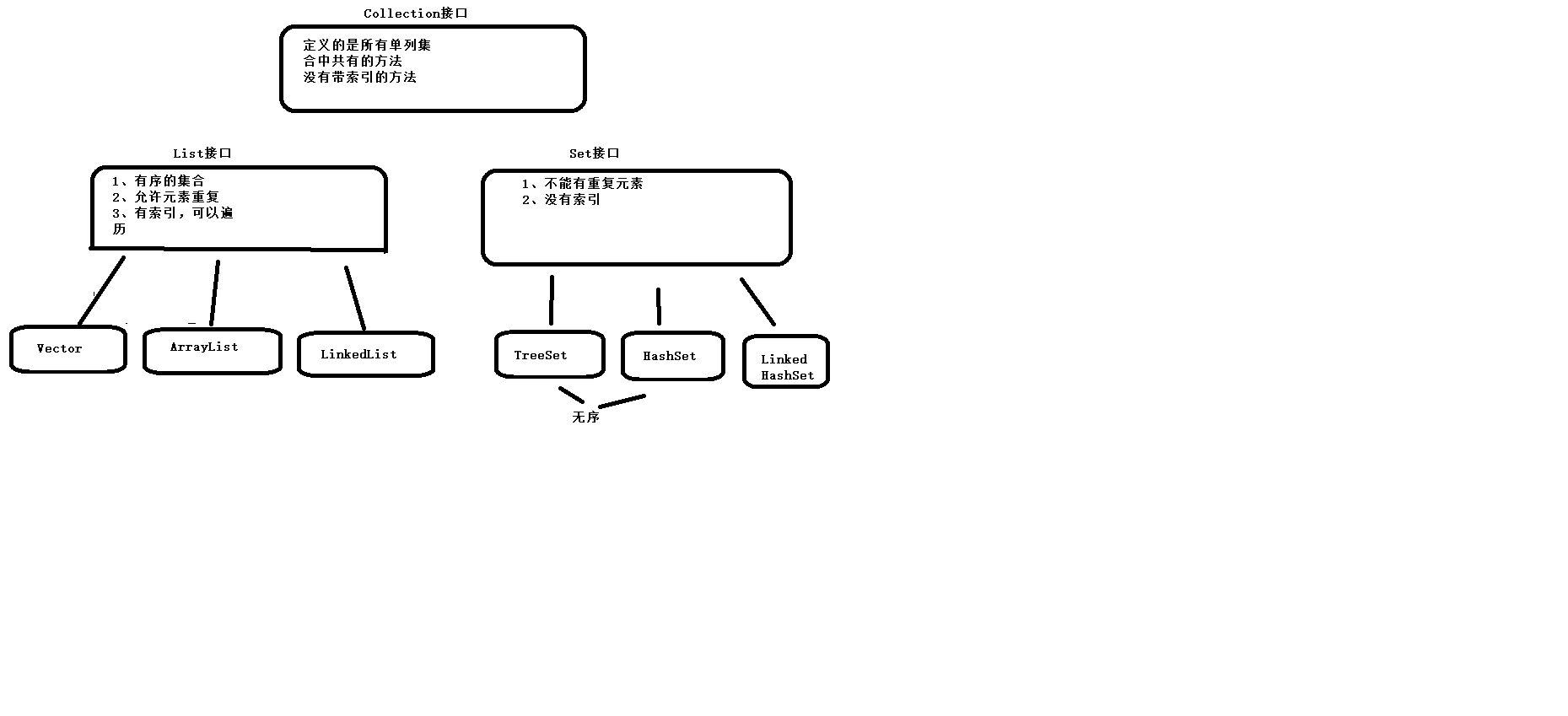
Collection集合。
java.util.Collection 接口。 没有索引
是所有单列集合的最顶层的接口,里面定义了所有单列集合共性的方法。
任意的单列集合都可以使用Collecion接口中的方法。
共性的方法:
............................
Iterator接口
java.util.Iterator
迭代器,Collection集合元素的通用取出方式。对集合遍历。 也是有泛型的,跟着集合走
常用方法: boolean hasNext() 还有没有元素可以迭代。
next()取出集合的下一个元素。
获取实现类的方式比较特殊:
在Collection接口中有一个方法叫 Iterator,这个方法的返回就是迭代器的实现类对象。
使用步骤:重点
1、使用集合中的方法,Iterator()获取迭代器的实现类对象,使用Iterator接口接收(多态)
2、使用hasnext方法,判断是否还有下一个
3、使用next,取出下一个元素
代码实现:
public static void main(String[] args) { Collection<String> collection=new ArrayList<>(); collection.add("科比"); collection.add("姚明"); collection.add("乔丹"); Iterator<String> iterator =collection.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } }
Java的foreach:
内部也是迭代器,简化迭代器的使用:
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr={1,2,3,4}; for(int i : arr){ System.out.println(i); } }
List接口。
List 接口 extends Collection类。
List接口的特点:
1、有序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序是一致的。
2、有索引,包含了一些索引的方法。
3、允许重复元素。
List接口特有的方法:
注意:操作索引要注意越界问题。
public static void main(String[] args) { /* 创建一个List集合对象,多态。 */ List<String> list=new ArrayList<>(); //add 添加元素。 list.add("a"); list.add("b"); list.add("a"); //可重复 System.out.println(list); //重写了tostring方法。 // public void add(int index, E elemet); list.add(2,"c"); System.out.println(list); //public E remove (int index) 移除指定位置元素, //并返回该元素。 String remove=list.remove(3); System.out.println(list); System.out.println(remove); //public E set(int index, E element) //替换指定位置的元素,并返回被替换的值。 String update=list.set(2,"update"); System.out.println(list); System.out.println(update); //List集合遍历有三种方式。 //1、for //2、迭代器。 //3、foreach }
LinkedList 集合:
java.util.LinkedList 集合 implements List 接口。
特有特点:
链表结构,查询慢,但增删快。
有大量操作首位元素的方法。
public static void main(String[] args) { //Public void addFirst(E e) =public void push(E e) LinkedList<String> linkedList=new LinkedList<>(); linkedList.add("b"); linkedList.add("c"); linkedList.addFirst("a"); System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.push("push an element"); System.out.println(linkedList); //public void addLast(E e) = add() linkedList.addLast("d"); System.out.println(linkedList); //获取元素。 //getFirst getLast //移除 // removeFirst = pop removeLast }
Set接口:
特点:
java.util.Set extends Collection
不允许重复
没有索引,不能用普通的for遍历
java.util.HashSet 集合 implement Set 接口
HashSet特点:
1、无序集合,存元素和取元素的顺序有可能不一致。
2、底层是哈希表结构 查询速度快。
哈希表:
哈希值:是一个十进制的整数,由系统随机给出(就是对象的地址值,是一个逻辑
地址,是模拟出来的地址看,不是数据实际存储的物理地址)
Object类有一个方法能获取对象的哈希值。
int hashCode() 返回该对象的哈希值。
源码: public native int hashCode()
native 代表该方法调用的是本地操作系统的方法。
String类的哈希值:
重写了Object类的hashCode方法。
哈希表:
jdk1.8之前,哈希表=数组+链表 jdk1.8之后, 哈希表还=数组+红黑树(查询快)
Set不允许重复元素的原理:
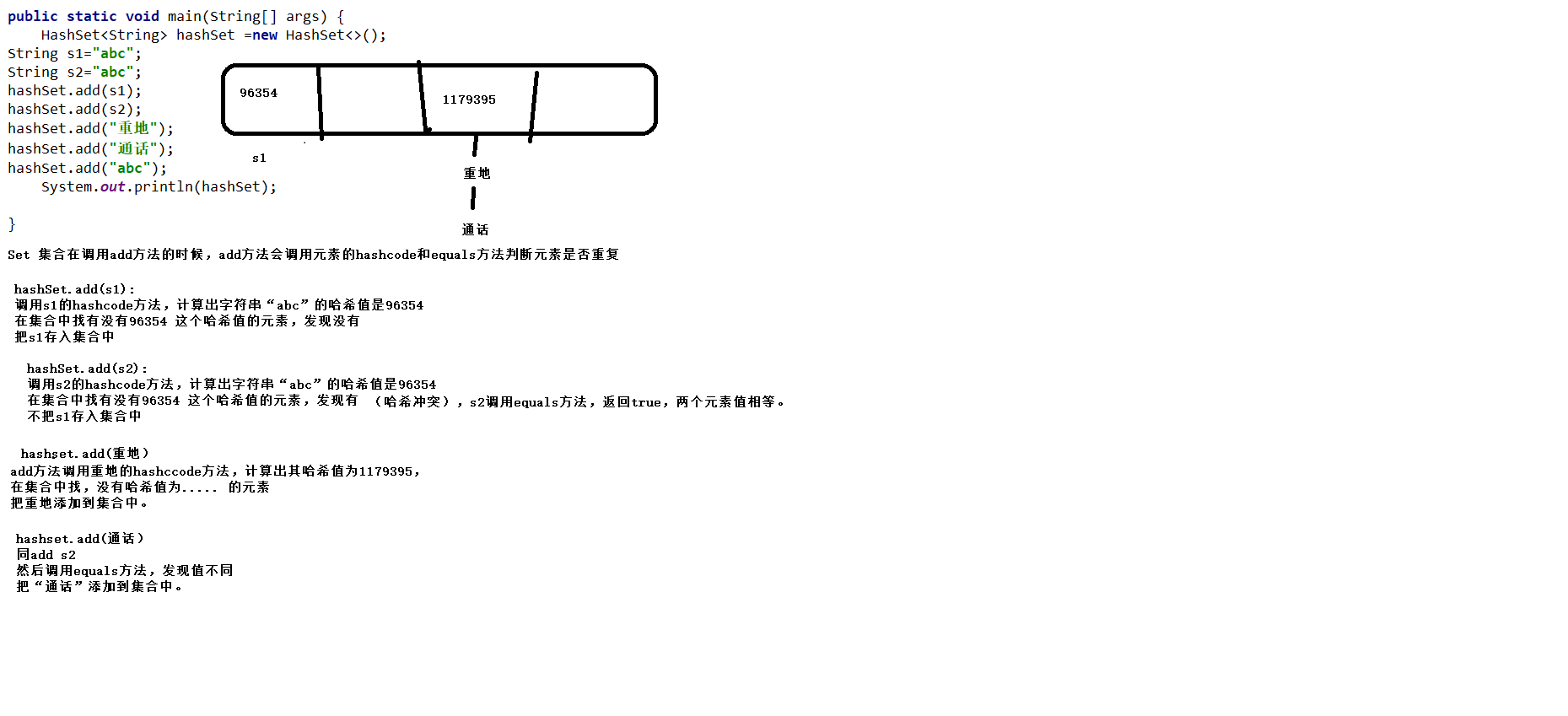
Hash Set存储自定义类型元素:
需要重写对象中的hashcode 和 equals方法,建立自己的比较方式,
才能保证 HashSet中的对象唯一。
//需求: //同名同龄的人,视为同一个人,只能存储一次。 public class main { public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<Person> set=new HashSet<>(); Person p1=new Person("Sam",18); Person p2=new Person("Sam",18); Person p3=new Person("Penny",19); set.add(p1); set.add(p2); set.add(p3); System.out.println(set); //[Person{name='Sam', age=18}, Person{name='Penny', age=19}, Person{name='Sam', age=18}] System.out.println(p1.hashCode()); System.out.println(p2.hashCode()); //1355531311 //1967205423 } }
重写方法后:
public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<Person> set=new HashSet<>(); Person p1=new Person("Sam",18); Person p2=new Person("Sam",18); Person p3=new Person("Penny",19); set.add(p1); set.add(p2); set.add(p3); System.out.println(set); System.out.println(p1.hashCode()); System.out.println(p2.hashCode()); //[Person{name='Sam', age=18}, Person{name='Penny', age=19}] //2570228 // 2570228 }
LinkedHashSet:
extends HashSet
特点:
底层是哈希表(数组+链表/红黑色) + 链表(用来记录元素的存储顺序)。
public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<String> set=new HashSet<>(); set.add("c"); set.add("a"); set.add("b"); System.out.println(set);// 无序,不允许重复。 LinkedHashSet<String> linked=new LinkedHashSet<>(); linked.add("a"); linked.add("b"); linked.add("c"); System.out.println(linked);//有序,不允许重复 //[a, b, c] //[a, b, c] }
可变参数:
jdk 1.5 之后出现。
前提: 参数列表的数据类型已确定,但参数个数不确定时。
格式:
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名 (数据类型...变量名){}
可变参数原理:
底层:数组,根据参数个数不同,来创建不同长度的数组,来存储参数。
参数个数: 0个-多个。
注意事项:
1、一个方法的参数列表,只能有一个可变参数。
2、如果参数有多个,可变参数放最后。
可变参数的终极写法 : method(Object...obj)
public static void main(String[] args) { int sum=add(10,20,30);//创建一个长度为三的数组 System.out.println(sum); } //计算多个整数的和。 public static int add(int...arr){ int sum=0; for(int i:arr) sum+=i; return sum; }
Collections 工具类:
java.utils.Collections 是集合工具类,用来对集合进行操作。
public static void main(String[] args) { //public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<T> c,T...elements) //往集合添加多个元素。 //public static void shuffle(List<T> list) //打乱集合顺序。 ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(list,"a","b","c","d"); System.out.println(list);//[a, b, c, d] Collections.shuffle(list); System.out.println(list);//[c, d, b, a] }
public static void main(String[] args) { //public static <T> void sort(List<T> list) //对集合排序,默认升序。 ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>(); Collections.addAll(list, 1,3,2); Collections.sort(list); System.out.println(list); }
sort方法的使用前提:
被排序的集合里边存储的元素,必须实现Comparable,重写接口中的compareTo
定义排序的规则。
Compareble 的排序规则:this - 参数 升序 反之。
public static void main(String[] args) { //对Person类型的集合排序。 ArrayList<Person> personList=new ArrayList<>(); personList.add(new Person("张三",17)); personList.add(new Person("李四",19)); personList.add(new Person("王麻子",15)); Collections.sort(personList); System.out.println(personList); //[Person{name='王麻子', age=15}, Person{name='张三', age=17}, Person{name='李四', age=19}] }
Person类:
@Override public int compareTo(Person o) { //return 0; 认为元素都是相同的。 //自定义比较规则,比较两个人的年龄(this,参数Person) return this.getAge()-o.getAge(); //年龄升序排序 }
Comparator 接口:
public static void main(String[] args) { //public static <T> void sort(List<T> list,Comparator<? super T>) //将集合中的元素按指定规则排序。 //Comparator和 Comparable的区别: //Comparable : 自己 this 和别人(参数)比较, //自己需要实现Comparable接口,重写compareto 方法 //Comparator:相当于找一个第三方裁判,来比较两个。 ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(list,1,3,2); System.out.println(list); Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Integer>() { @Override public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) { return o1-o2;//升序。 } }); System.out.println(list); // Person 类型的集合排序。 ArrayList<Person> personList=new ArrayList<>(); personList.add(new Person("张三",17)); personList.add(new Person("b李四",19)); personList.add(new Person("a王麻子",19)); //一个规则 // Collections.sort(personList, new Comparator<Person>() { // @Override // public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) { // //年龄升序 // return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge(); // } // }); //多个规则: Collections.sort(personList, new Comparator<Person>() { @Override public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) { int result=o1.getAge()-o2.getAge(); if (result==0){ result=o1.getName().charAt(0)-o2.getName().charAt(0); } return result; } }); System.out.println(personList); }