本文对 Runtime 进行简单介绍 和对 objc_msgSend 的发消息流程中的缓存查找进行探索。
更新(流程图概览):缓存查找流程图

我们知道类结构中包含了很多信息:isa superclass cache bits,cache 中缓存了我们调用的方法,具体流程见OC底层探索07. 但是方法具体时间什么时候缓存的,需要继续探究。
源码 objc_cache.mm 文件,Method cache locking 中,我们可以看到在写入之前还有一个读的过程
--> objc_msgSend* / cache_getImp:
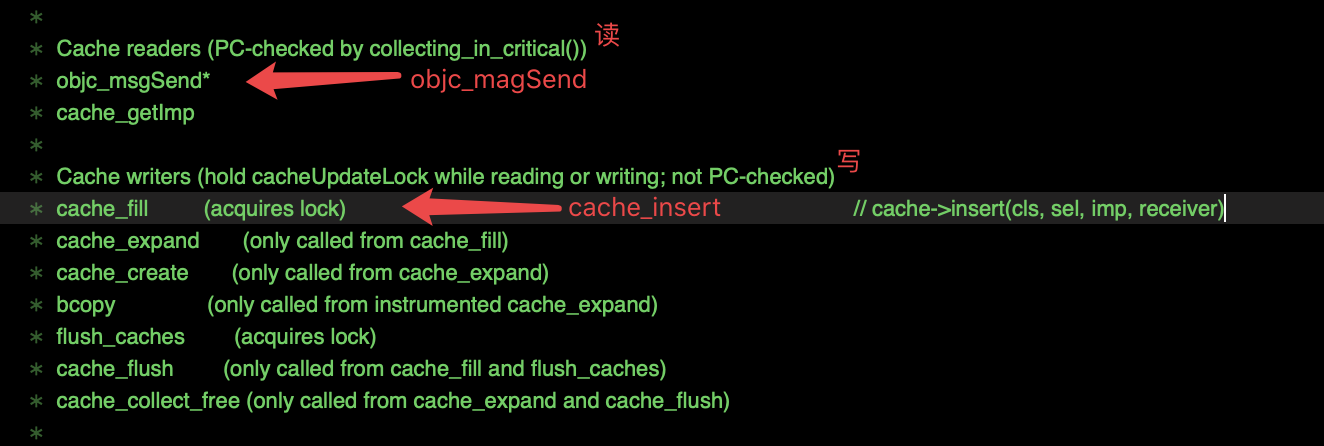
看到 objc_msgSend 就不免想到 runtime,我们先简单介绍下 runtime 是什么。
一、Runtime 简介
Runtime 是一个为我们OC语言开发中提供动态特性的一个库。
官方文档: Objective-C Runtime
/Objective-C Runtime Programming Guide

《The Objective-C language defers as many decisions as it can from compile time and link time to runtime. Whenever possible, it does things dynamically. This means that the language requires not just a compiler, but also a runtime system to execute the compiled code. The runtime system acts as a kind of operating system for the Objective-C language; it’s what makes the language work.》
OC 语言将尽可能多的决策从编译时和链接时延迟到运行时。只要有可能,它就动态地做事情。这意味着该语言不仅需要一个编译器,还需要一个运行时系统来执行编译后的代码。运行时系统作为Objective-C语言的一种操作系统;它使语言起作用。
提取信息点:一个提供动态特性的库,实现运行时作用。
1、Runtime 结构和调用方式:
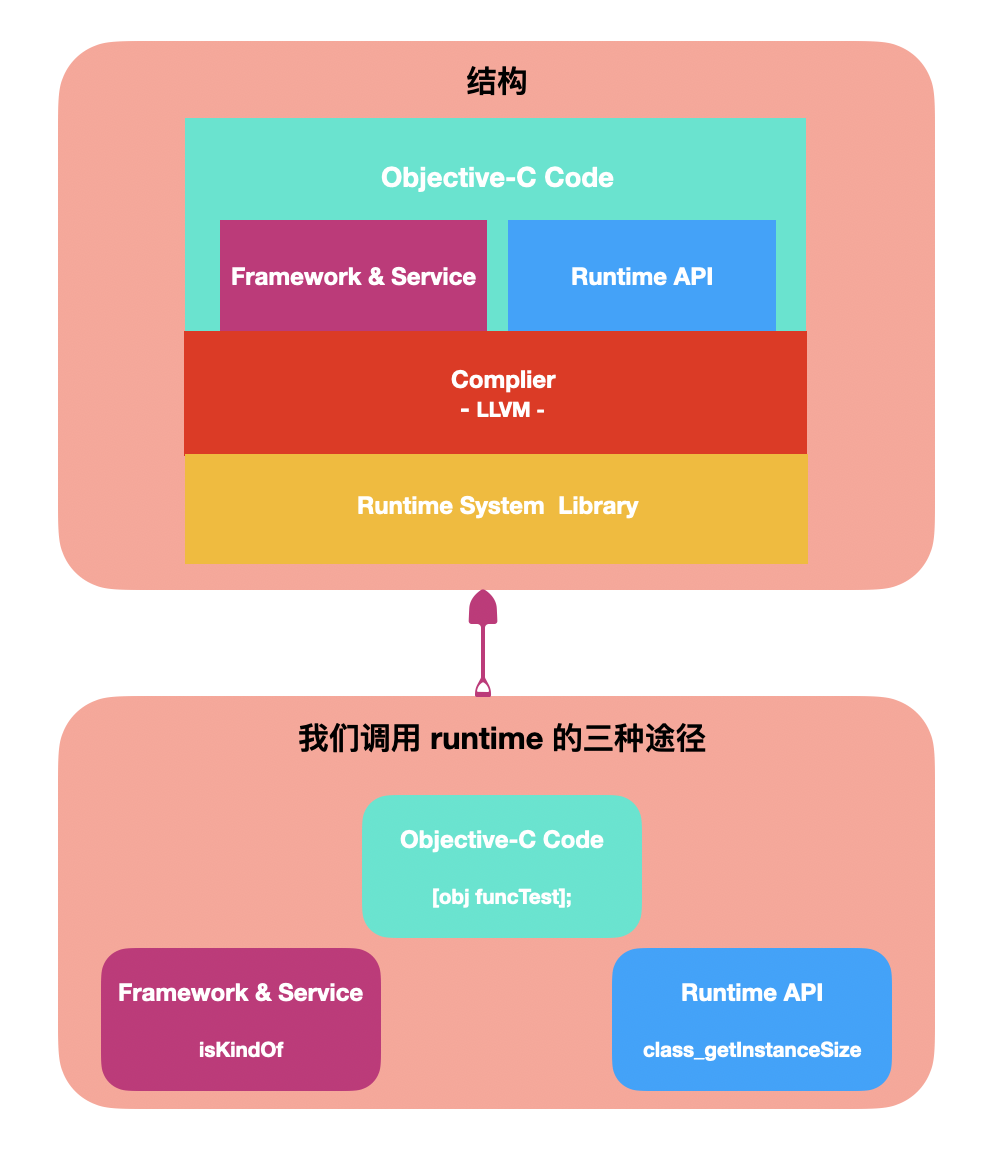
complier: 编译 --> runtime 底层所调用的并非我们写的代码,它进过了 complier 进行编译、优化。 --> LLVM
tip:编译时、链接时,一句话简介 {
编译时:
1、对我们的代码进行语法词法等分析,并给出waring、error等提示。类似一个扫描过程,将代码扫一遍;
2、将编写的高级语言(C C++ OC等)编译成机器识别的机器语言(汇编、机器语言01等),编译得到相应的二进制目标文件。
编译时并没有进行加载分配内存等操作。
链接时:
将编译得到的二进制文件和库函数等进行连接。
运行时:
代码已被装载到内存中,已运行起来了。
}
2、探索
通过clang 将 main.m 文件编译成 mian.cpp. mian函数编译结果如下:
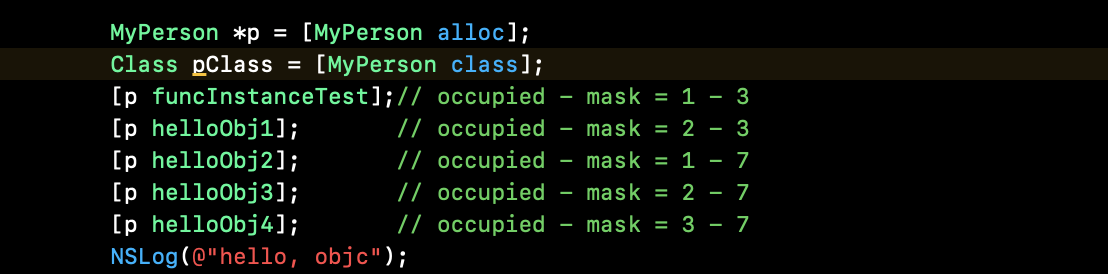
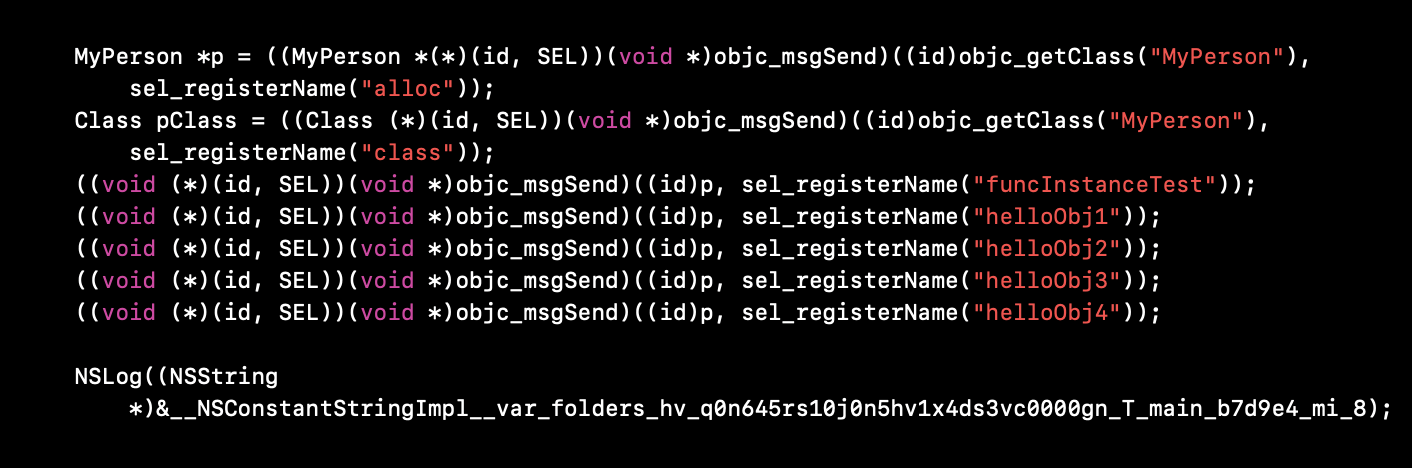
id objc_msgSend(id self, SEL _cmd, ...) :
消息接受者 self;消息体 SEL. 通过查找 objc_msgSend() 源码,我们可以发现它是使用汇编实现的,这里暂时先不探究,继续当前操作。
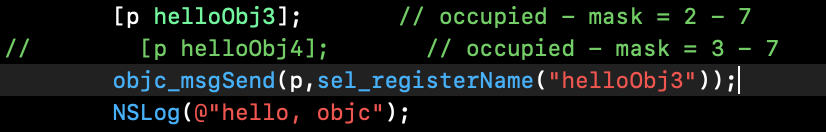
sel_registerName("helloObj1"):
注册一个方法。例: 上层的操作 @selector() / NSSelectorFromString() 都是 SEL 类型.
直接使用 API - objc_msgSend() 进行方法调用
对代码进行修改:
报错如下:
![]()
修改工程配置:Building Setting --> Preprocessing --> 将 objc_msgSend call 严格检查改为 NO.
![]()
运行结果如下,通过 objc_msgSend() 正常调用了方法 'helloObj3':

OC 方法调用 --> objc_msgSend() --> sel (方法编号) --> imp (函数指针地址) --> 函数.
sel 如何找到 imp 呢?
二、objc_msgSend 流程探索 - cache
从上面的操作,可知方法调用的本质是 发送消息,下面进行 发送消息流程的探究。
全局查找 objc_msgSend(),是通过汇编实现的
使用汇编的原因:
1、快速,方法的查找操作是很频繁的,汇编是相对底层的语言更易被机器识别,节省中间的一些编译过程。
2、语言的动态特性,C/C++ 来编写实现的话更偏向于静态,虽然也可实现会更麻烦且慢。
下面我们通过源码 注释 和 网络 对消息查找流程进行探索。
objc_msgSend 流程
消息接收者 和 sel:
消息接受者 --> 对象 --> isa --> 方法(类/元类) --> cache_t --> methodliss(bits中)
主要流程源码 CacheLookup:(汇编指令解读)
1 .macro CacheLookup 2 // 3 // Restart protocol: 4 // 5 // As soon as we're past the LLookupStart$1 label we may have loaded 6 // an invalid cache pointer or mask. 7 // 8 // When task_restartable_ranges_synchronize() is called, 9 // (or when a signal hits us) before we're past LLookupEnd$1, 10 // then our PC will be reset to LLookupRecover$1 which forcefully 11 // jumps to the cache-miss codepath which have the following 12 // requirements: 13 // 14 // GETIMP: 15 // The cache-miss is just returning NULL (setting x0 to 0) 16 // 17 // NORMAL and LOOKUP: 18 // - x0 contains the receiver 19 // - x1 contains the selector 20 // - x16 contains the isa 21 // - other registers are set as per calling conventions 22 // 23 LLookupStart$1: 24 25 // p1 = SEL, p16 = isa 26 ldr p11, [x16, #CACHE] // p11 = mask|buckets 27 28 #if CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16 29 // 真机 64 位 30 and p10, p11, #0x0000ffffffffffff // p10 = buckets 31 // p11, LSR #48: p11 >> 48 = mask --> p1 & mask 赋给 p12 32 and p12, p1, p11, LSR #48 // x12 = _cmd & mask 33 #elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_LOW_4 34 and p10, p11, #~0xf // p10 = buckets 35 and p11, p11, #0xf // p11 = maskShift 36 mov p12, #0xffff 37 lsr p11, p12, p11 // p11 = mask = 0xffff >> p11 38 and p12, p1, p11 // x12 = _cmd & mask 39 #else 40 #error Unsupported cache mask storage for ARM64. 41 #endif 42 43 // x12 << 4 --> buckets 内存平移 得到查询的 bucket - p12 44 add p12, p10, p12, LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT) 45 // p12 = buckets + ((_cmd & mask) << (1+PTRSHIFT)) // PTRSHIFT=3 46 47 ldp p17, p9, [x12] // {imp, sel} = *bucket 48 1: cmp p9, p1 // if (bucket->sel != _cmd) 49 b.ne 2f // scan more cmp不相等,跳到2 50 CacheHit $0 // call or return imp - cmp相等,找到了 51 52 2: // not hit: p12 = not-hit bucket 53 CheckMiss $0 // miss if bucket->sel == 0 54 cmp p12, p10 // wrap if bucket == buckets 判断当前的bucket是不是第一个 55 b.eq 3f // 是第一个bucket 跳3 56 ldp p17, p9, [x12, #-BUCKET_SIZE]! // {imp, sel} = *--bucket 57 b 1b // loop 跳到下面的1 58 59 3: // wrap: p12 = first bucket, w11 = mask 60 #if CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16 61 // 真机 64 位 62 add p12, p12, p11, LSR #(48 - (1+PTRSHIFT)) 63 // p12 = buckets + (mask << 1+PTRSHIFT) 64 // 将bucket手动置为buckets的最后一个 65 66 #elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_LOW_4 67 add p12, p12, p11, LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT) 68 // p12 = buckets + (mask << 1+PTRSHIFT) 69 #else 70 #error Unsupported cache mask storage for ARM64. 71 #endif 72 73 // Clone scanning loop to miss instead of hang when cache is corrupt. 74 // The slow path may detect any corruption and halt later. 75 76 ldp p17, p9, [x12] // {imp, sel} = *bucket 77 1: cmp p9, p1 // if (bucket->sel != _cmd) 判断sel和cmd是否相同 78 b.ne 2f // scan more 不同d跳到2 79 CacheHit $0 // call or return imp 80 81 2: // not hit: p12 = not-hit bucket 82 CheckMiss $0 // miss if bucket->sel == 0 83 cmp p12, p10 // wrap if bucket == buckets 84 b.eq 3f // 上一步cmp相同:bucket还是buckets的第一个,直接跳到 3 -> JumpMiss 85 ldp p17, p9, [x12, #-BUCKET_SIZE]! // {imp, sel} = *--bucket 86 // 从后向前 --bucket 回到1 继续判断 87 b 1b // loop 88 89 LLookupEnd$1: 90 LLookupRecover$1: 91 3: // double wrap 92 JumpMiss $0 // cache 中没找到方法 93 94 .endmacro