本文继续衔接 OC 底层探索 14、类的加载2 探索分类的加载。调试源码
一、分类的本质
分类的结构查看方法
1).cpp 文件
在 main.m 中任意添加一个分类信息的 .h .m 文件信息,编译生成cpp文件 clang -rewrite-objc main.m -o main.cpp
如下tu:

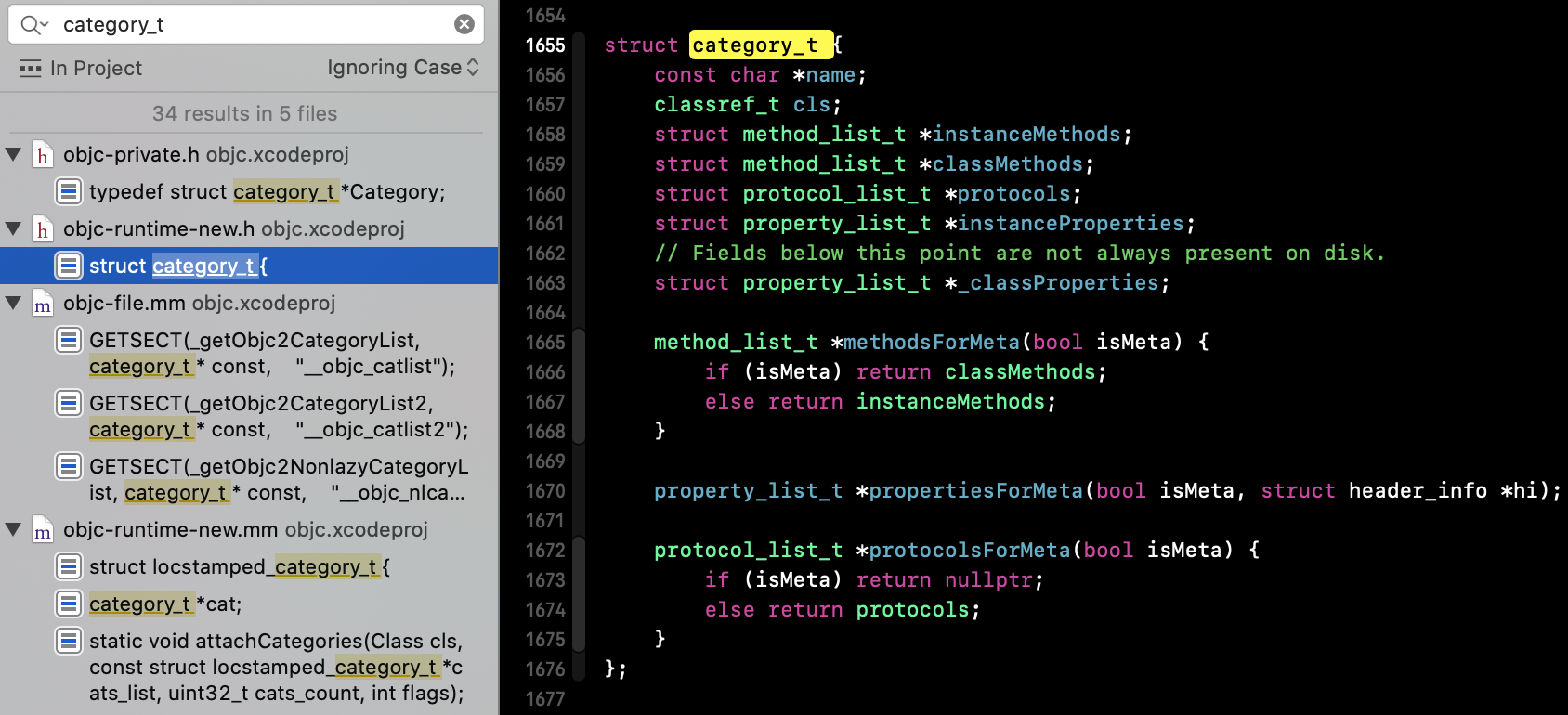
category_t 结构:
1 struct _category_t { 2 const char *name; 3 struct _class_t *cls; 4 const struct _method_list_t *instance_methods; 5 const struct _method_list_t *class_methods; 6 const struct _protocol_list_t *protocols; 7 const struct _prop_list_t *properties; 8 };
有 2 个 _method_list_t 分类的方法是要 attach 到本类cls上由本类进行调用的,分类是不存在元类的说法的。
2)objc 源码搜索 category_t
2、分类的方法 list
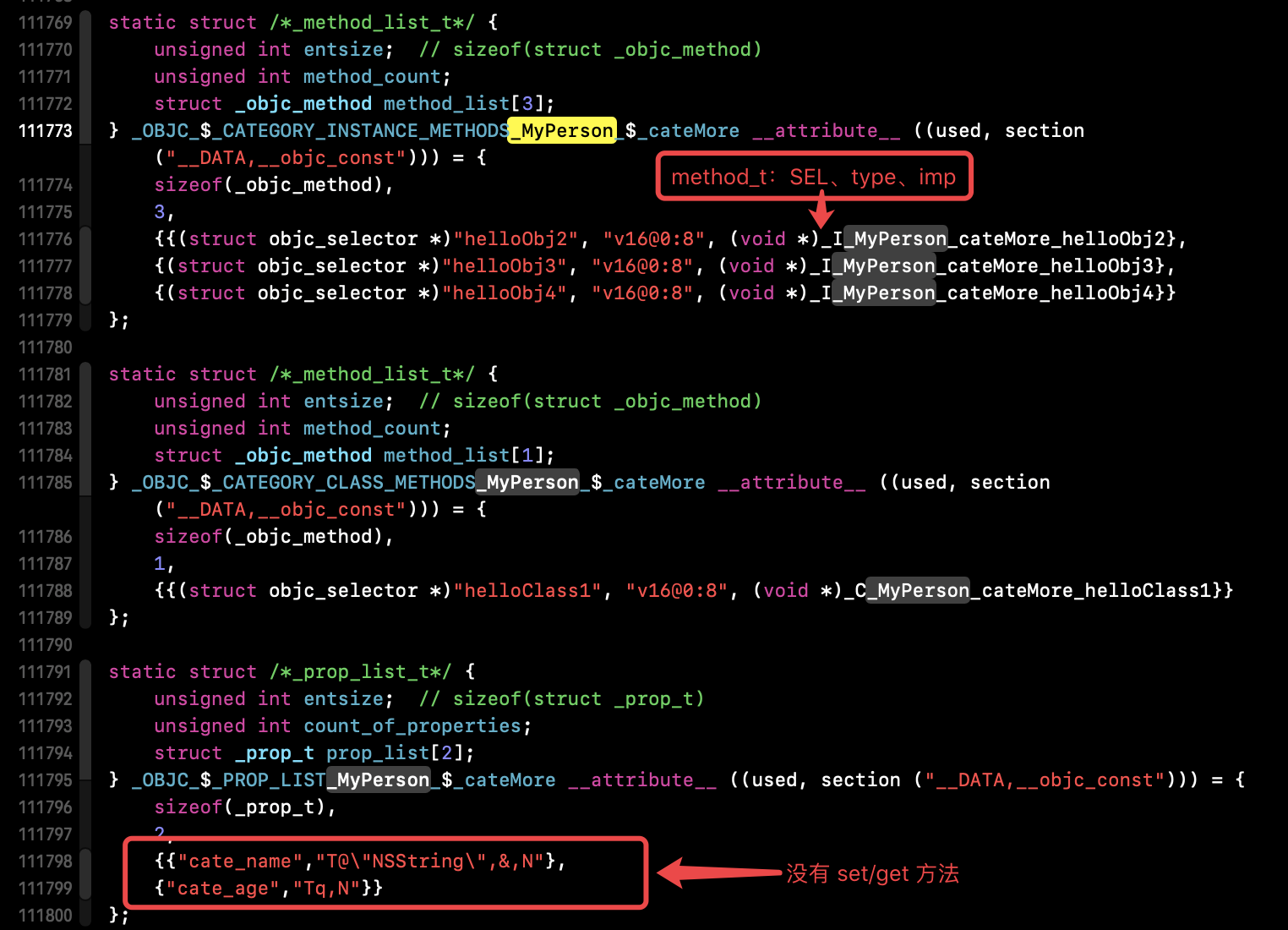
分类添加的属性系统不会给其生成 set/get 方法,我们可通过runtime 的 associate 进行set/get 方法的动态关联。
二、分类的加载
1、源码分析
继续OC 底层探索 14、类的加载2 对 methodizeClass() 源码分析,首先给 MyPerson 添加分类,并添加如下方法:

1、运行工程,方法 list 中只有本类的 2 个方法,并没有分类中的方法,见下图:
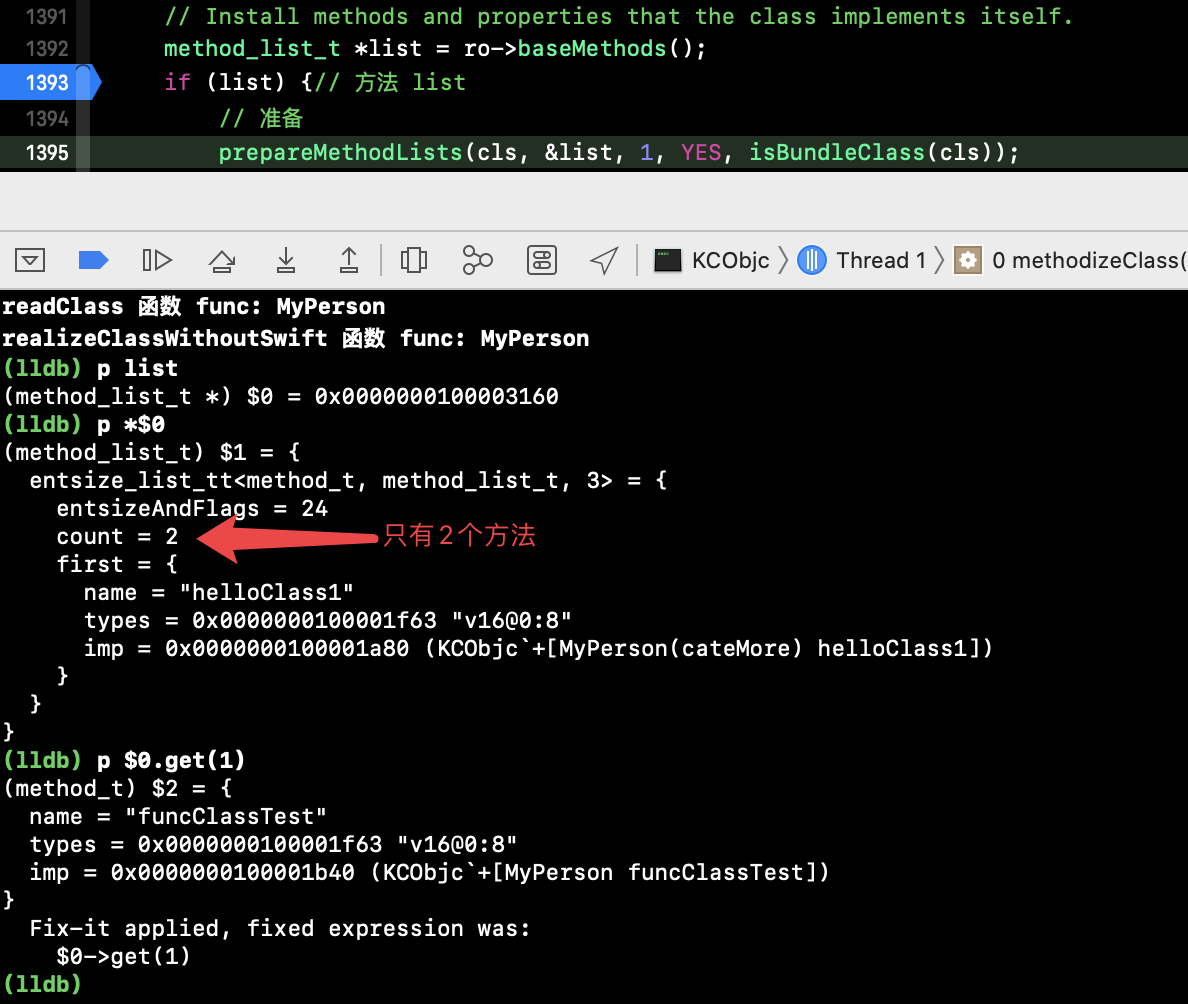
继续执行代码到 源码2的 47 行起,category 分类的 attach,此时 list 仍是有 2 个方法:
2、objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass() 代码如下,源码1:
1 void attachToClass(Class cls, Class previously, int flags) 2 { 3 runtimeLock.assertLocked(); 4 ASSERT((flags & ATTACH_CLASS) || 5 (flags & ATTACH_METACLASS) || 6 (flags & ATTACH_CLASS_AND_METACLASS)); 7 8 9 // 我加的调试代码 10 const char *mangledName = cls->mangledName(); 11 const char *myPersonName = "MyPerson"; 12 if (strcmp(mangledName, myPersonName) == 0) { 13 printf("%s 函数 func: %s ",__func__,mangledName); 14 } 15 16 auto &map = get(); 17 auto it = map.find(previously); 18 19 if (it != map.end()) { 20 category_list &list = it->second; 21 if (flags & ATTACH_CLASS_AND_METACLASS) { 22 int otherFlags = flags & ~ATTACH_CLASS_AND_METACLASS; 23 attachCategories(cls, list.array(), list.count(), otherFlags | ATTACH_CLASS); 24 attachCategories(cls->ISA(), list.array(), list.count(), otherFlags | ATTACH_METACLASS); 25 } else { 26 attachCategories(cls, list.array(), list.count(), flags); 27 } 28 map.erase(it); 29 } 30 }
但是运行并未走进 attachCategories 源码1的20行代码,我们跳进 attachCategories() 方法并对其进行断点(下面源码2的第41行):
1 // Attach method lists and properties and protocols from categories to a class. 2 // Assumes the categories in cats are all loaded and sorted by load order, 3 // oldest categories first. 4 static void 5 attachCategories(Class cls, const locstamped_category_t *cats_list, uint32_t cats_count, 6 int flags) 7 { 8 if (slowpath(PrintReplacedMethods)) { 9 printReplacements(cls, cats_list, cats_count); 10 } 11 if (slowpath(PrintConnecting)) { 12 _objc_inform("CLASS: attaching %d categories to%s class '%s'%s", 13 cats_count, (flags & ATTACH_EXISTING) ? " existing" : "", 14 cls->nameForLogging(), (flags & ATTACH_METACLASS) ? " (meta)" : ""); 15 } 16 17 /* 18 * Only a few classes have more than 64 categories during launch. 19 * This uses a little stack, and avoids malloc. 20 * 21 * Categories must be added in the proper order, which is back 22 * to front. To do that with the chunking, we iterate cats_list 23 * from front to back, build up the local buffers backwards, 24 * and call attachLists on the chunks. attachLists prepends the 25 * lists, so the final result is in the expected order. 26 */ 27 constexpr uint32_t ATTACH_BUFSIZ = 64; 28 method_list_t *mlists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ]; 29 property_list_t *proplists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ]; 30 protocol_list_t *protolists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ]; 31 32 uint32_t mcount = 0; 33 uint32_t propcount = 0; 34 uint32_t protocount = 0; 35 bool fromBundle = NO; 36 bool isMeta = (flags & ATTACH_METACLASS); 37 auto rwe = cls->data()->extAllocIfNeeded();// rwe 初始化 --> 要对copy出的干净内存进行方法插入操作 38 39 40 // 我加的调试代码 41 const char *mangledName = cls->mangledName(); 42 const char *myPersonName = "MyPerson"; 43 if (strcmp(mangledName, myPersonName) == 0) { 44 printf("%s 函数 func: %s ",__func__,mangledName); 45 } 46 47 // 遍历 分类数据的准备(method property protocol) 48 for (uint32_t i = 0; i < cats_count; i++) { 49 auto& entry = cats_list[i]; 50 51 method_list_t *mlist = entry.cat->methodsForMeta(isMeta); 52 if (mlist) { 53 if (mcount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ) { 54 prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists, mcount, NO, fromBundle); 55 rwe->methods.attachLists(mlists, mcount); 56 mcount = 0; 57 } 58 mlists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++mcount] = mlist;// mlists 添加数据 mlist --> 从后向前 倒序插入 64-1 64-2... (二维数组) 59 fromBundle |= entry.hi->isBundle(); 60 } 61 62 property_list_t *proplist = 63 entry.cat->propertiesForMeta(isMeta, entry.hi); 64 if (proplist) { 65 if (propcount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ) { 66 rwe->properties.attachLists(proplists, propcount); 67 propcount = 0; 68 } 69 proplists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++propcount] = proplist; 70 } 71 72 protocol_list_t *protolist = entry.cat->protocolsForMeta(isMeta); 73 if (protolist) { 74 if (protocount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ) { 75 rwe->protocols.attachLists(protolists, protocount); 76 protocount = 0; 77 } 78 protolists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++protocount] = protolist; 79 } 80 } 81 // 分类方法的 排序、附着关联 82 if (mcount > 0) { 83 prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount, mcount, NO, fromBundle);// 排序 84 rwe->methods.attachLists(mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount, mcount);// attach 85 if (flags & ATTACH_EXISTING) flushCaches(cls); 86 } 87 88 rwe->properties.attachLists(proplists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - propcount, propcount); 89 90 rwe->protocols.attachLists(protolists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - protocount, protocount); 91 }
tip:rwe 的初始化 开辟:extAllocIfNeeded(),在以下几种场景(我们可操作的):
-
static IMP addMethod()
- static SEL * addMethods()
-
BOOL class_addProtocol()
-
static bool _class_addProperty()
- 分类
4、继续源码分析
1 void attachLists(List* const * addedLists, uint32_t addedCount) { 2 if (addedCount == 0) return; 3 4 if (hasArray()) { 5 // many lists -> many lists 多+多 6 uint32_t oldCount = array()->count; 7 uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount; 8 setArray((array_t *)realloc(array(), array_t::byteSize(newCount)));// 扩容 9 array()->count = newCount; 10 memmove(array()->lists + addedCount, array()->lists, 11 oldCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));// 移动旧的去后面 12 memcpy(array()->lists, addedLists, 13 addedCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));// cpy 新的在前面 14 } 15 else if (!list && addedCount == 1) { 16 // 0 lists -> 1 list 17 // 0到1 - list 没有数据第一次 - 第0个元素给list,此时 list 是一维的 18 list = addedLists[0]; 19 } 20 else { 21 // 1 list -> many lists 22 // 1+many - 举例 many lists 是3个 23 List* oldList = list; 24 uint32_t oldCount = oldList ? 1 : 0; 25 uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount;// 容量计算,旧+新的和 1+3=4 26 setArray((array_t *)malloc(array_t::byteSize(newCount)));// 开辟总大小的空间 newCount 27 array()->count = newCount;// array 的数量:是新的添加 manylists 后的数量 28 if (oldList) array()->lists[addedCount] = oldList;// 旧的list 放最后面 第3个位置 29 // memcpy(位置, 放谁, 大小) 30 // 把新的 lists 从起始位置0开始放 31 memcpy(array()->lists, addedLists, 32 addedCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0])); 33 } 34 }
分类的 attachLists 过程:
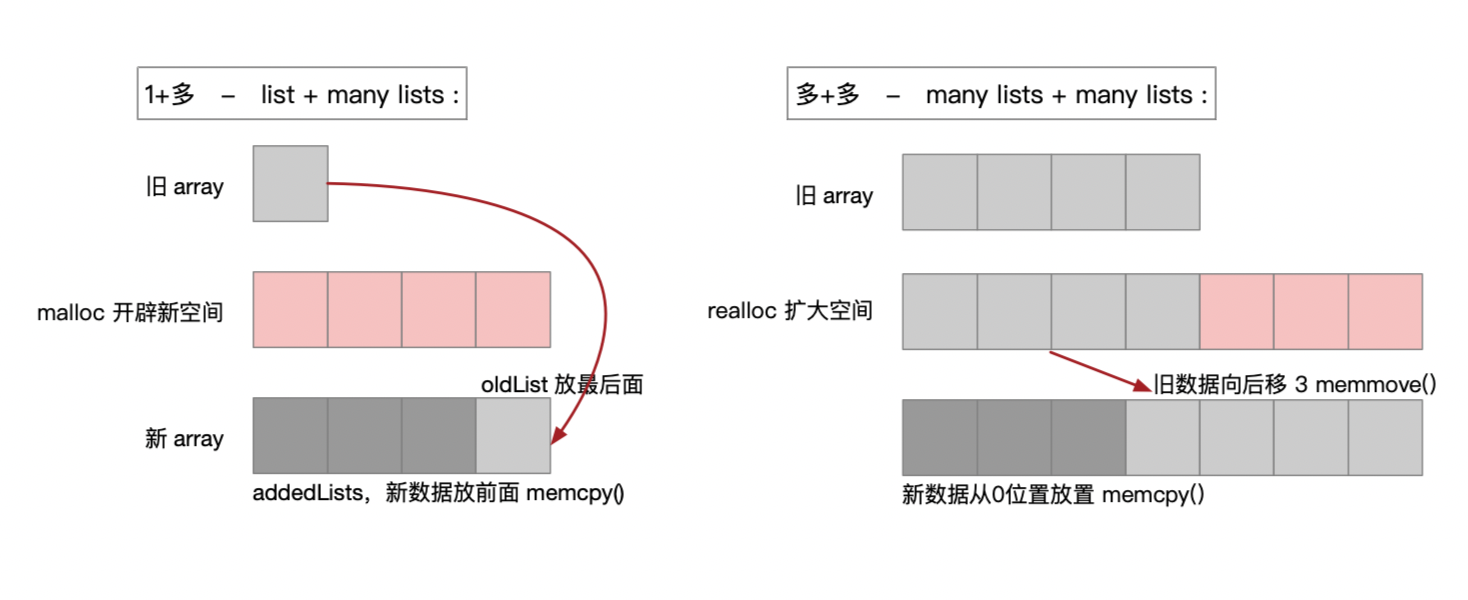
这里其实也可验证,为何我们天津爱的分类方法会优于本类方法调用 --> 本类方法并非被覆盖而是在后面了。
2、源码验证
运行工程验证,如何走进 attachCategories() 呢?
给分类也添加 +load 方法,运行可以走了进去:
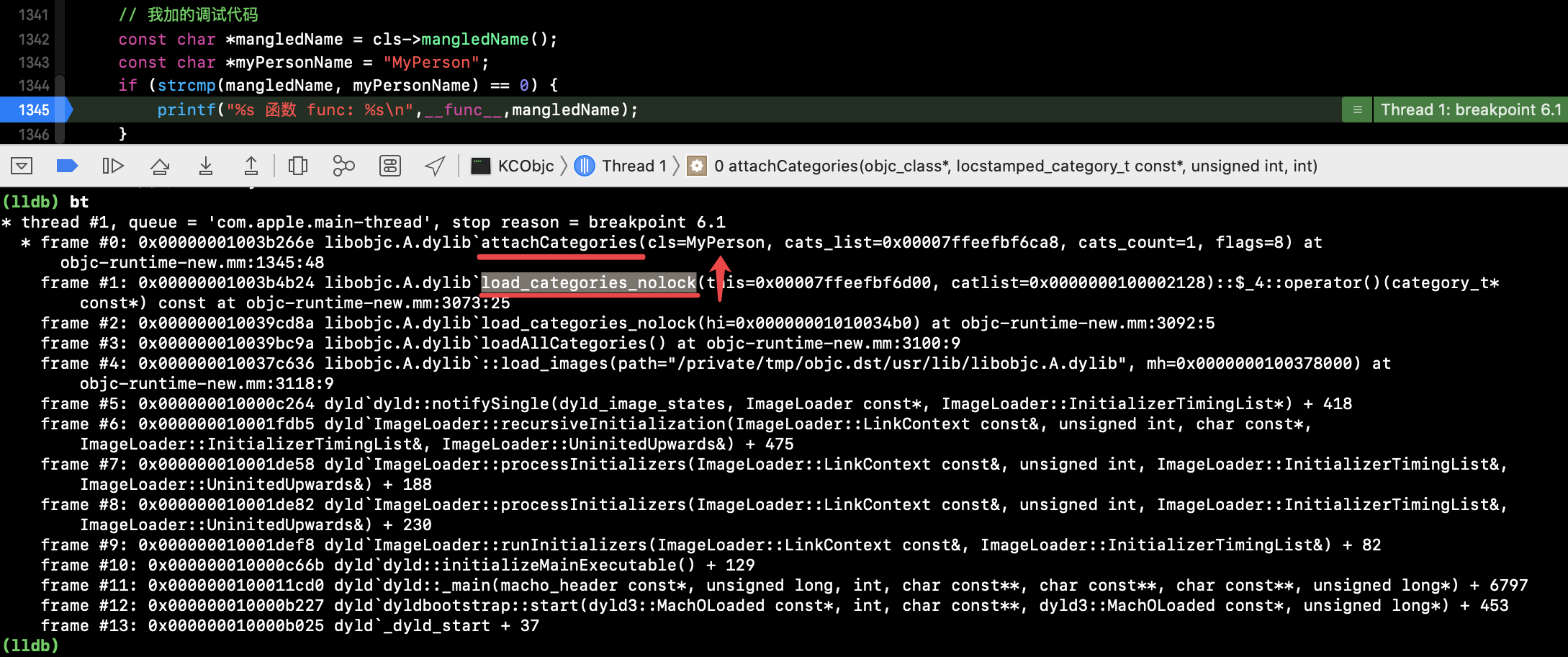
1、何时调用 attachCategories() 呢?
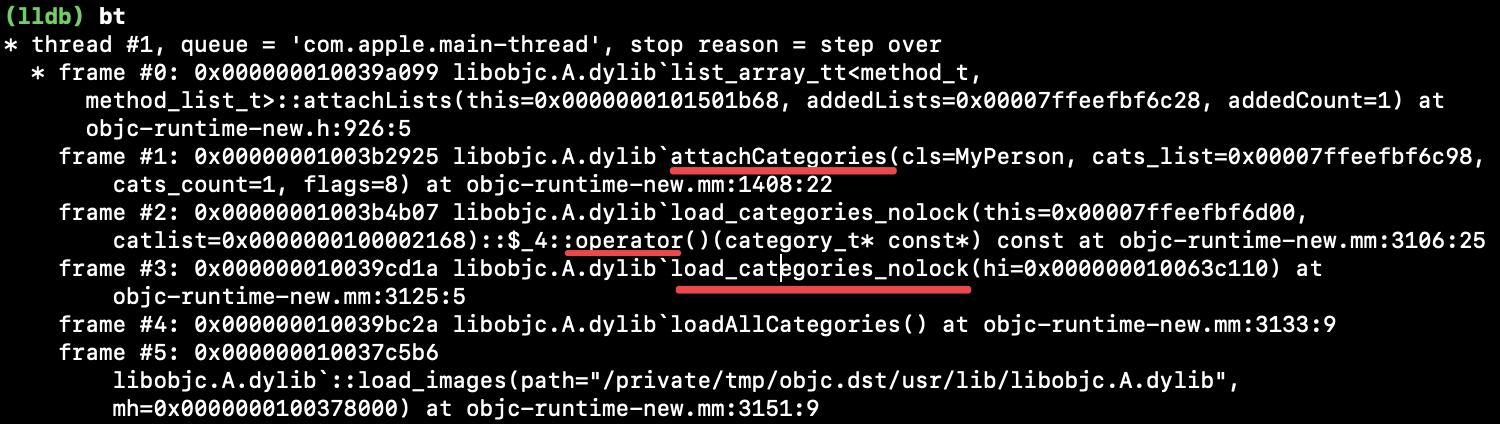
1.1. 断点 - 看堆栈信息
可以看到 load_categories_nolock() 之后走进了attachCategories(),搜索load_categories_nolock:
_read_images() 和 loadAllCategories() 两处 调了 load_categories_nolock(hi); 断点,重新运行工程,断点只走了 loadAllCategories():
--> loadAllCategories() 是在 load_images() 时调用,map_images 已经走完了。
1.2. 反推
已知必然会调 attachCategories(),全局搜索 attachCategories,找到下面两处进行了调用:
- attachToClass()
- load_categories_nolock()
通过断点调试发现走到了 load_categories_nolock().
attachCategories 调用流程图:
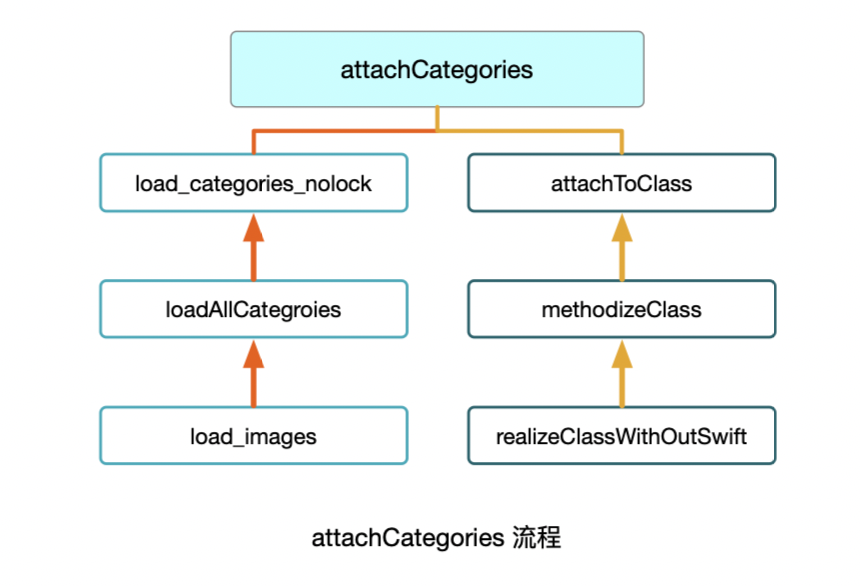
问题:我们创建多个分类,只在 本类和其中一个分类中添加load方法 其他分类不加,那么不加load方法的分类是懒加载还是非懒加载处理呢?--> 下面的 ‘3’ 进行分析。
2、attachList 源码执行
执行到上面源码2的84行(同时见下图源码):
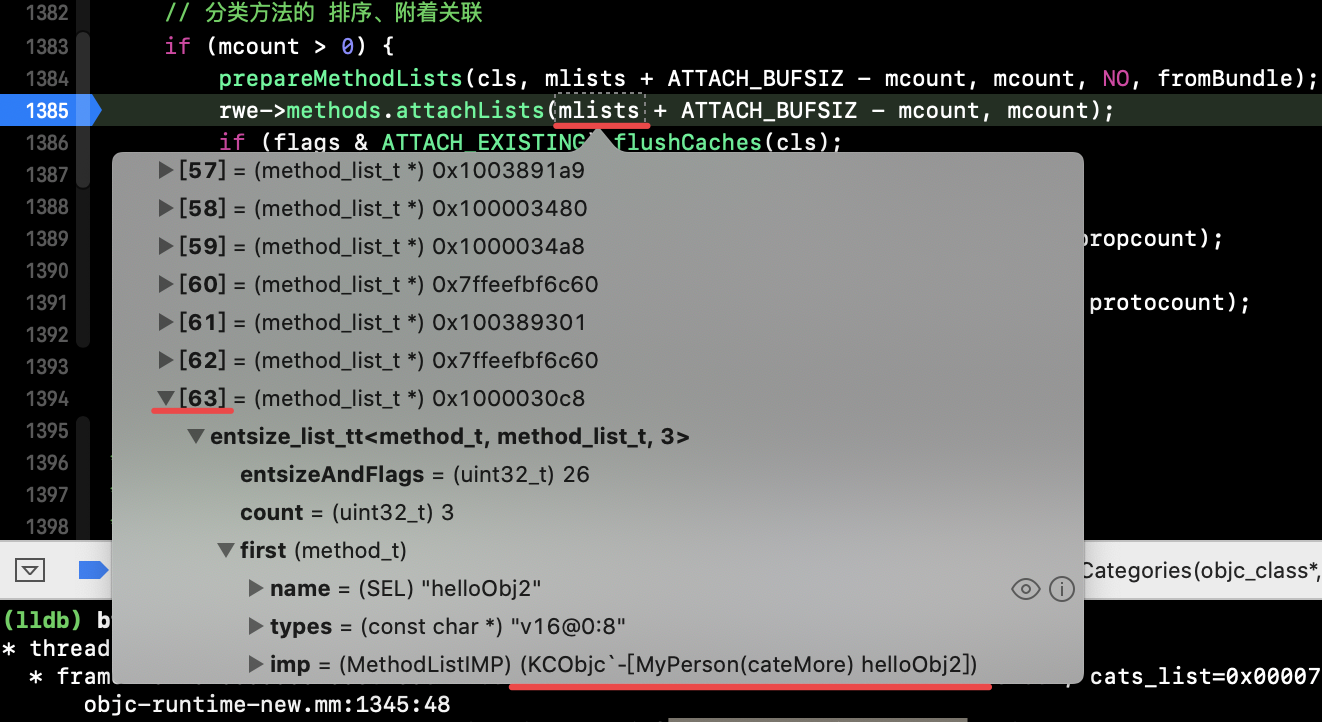
ATTACH_BUFSIZ = 64 mcount = 1 --> 内存平移 --> 平移到最后位置。
分类的 attachLists(),走进了条件 1+多 :
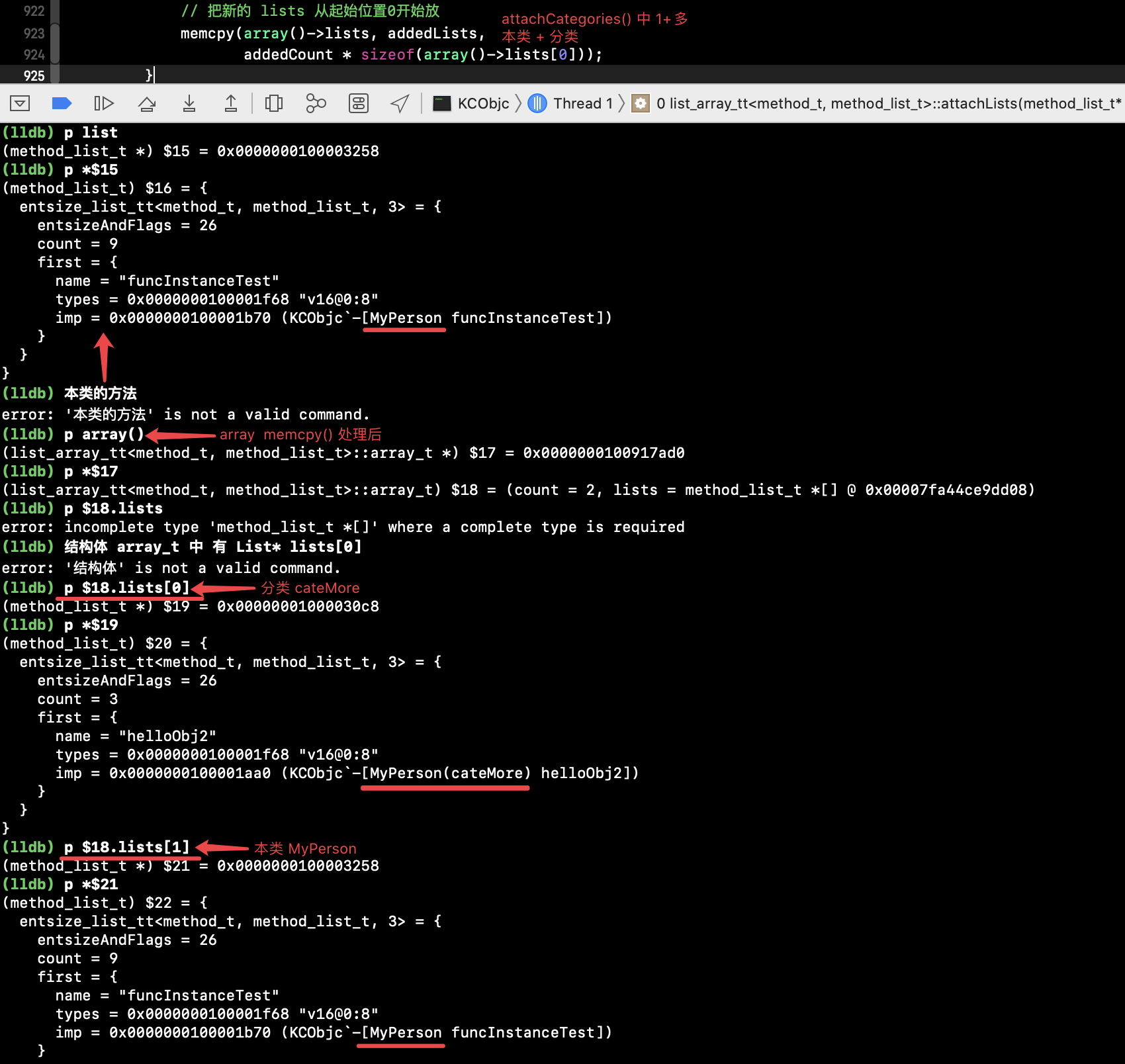
3、分类加载的几种情况
1)本类、分类均实现 load
上面的流程即使如此,全部走了 load_images() 加载到数据,文章上面的过程已可验证。
2)本类实现 load 方法非懒加载,分类都不实现 load
运行见下图,methodizeClass() 方法执行,2个分类的方法数据都在 data() 里面了。(rwe 为 NULL 未开辟脏内存,data 在 macho 中)

上图 lldb 出的信息,排序:对3者相同的方法名的排序 - 后加的分类 方法在前,本类在最后。
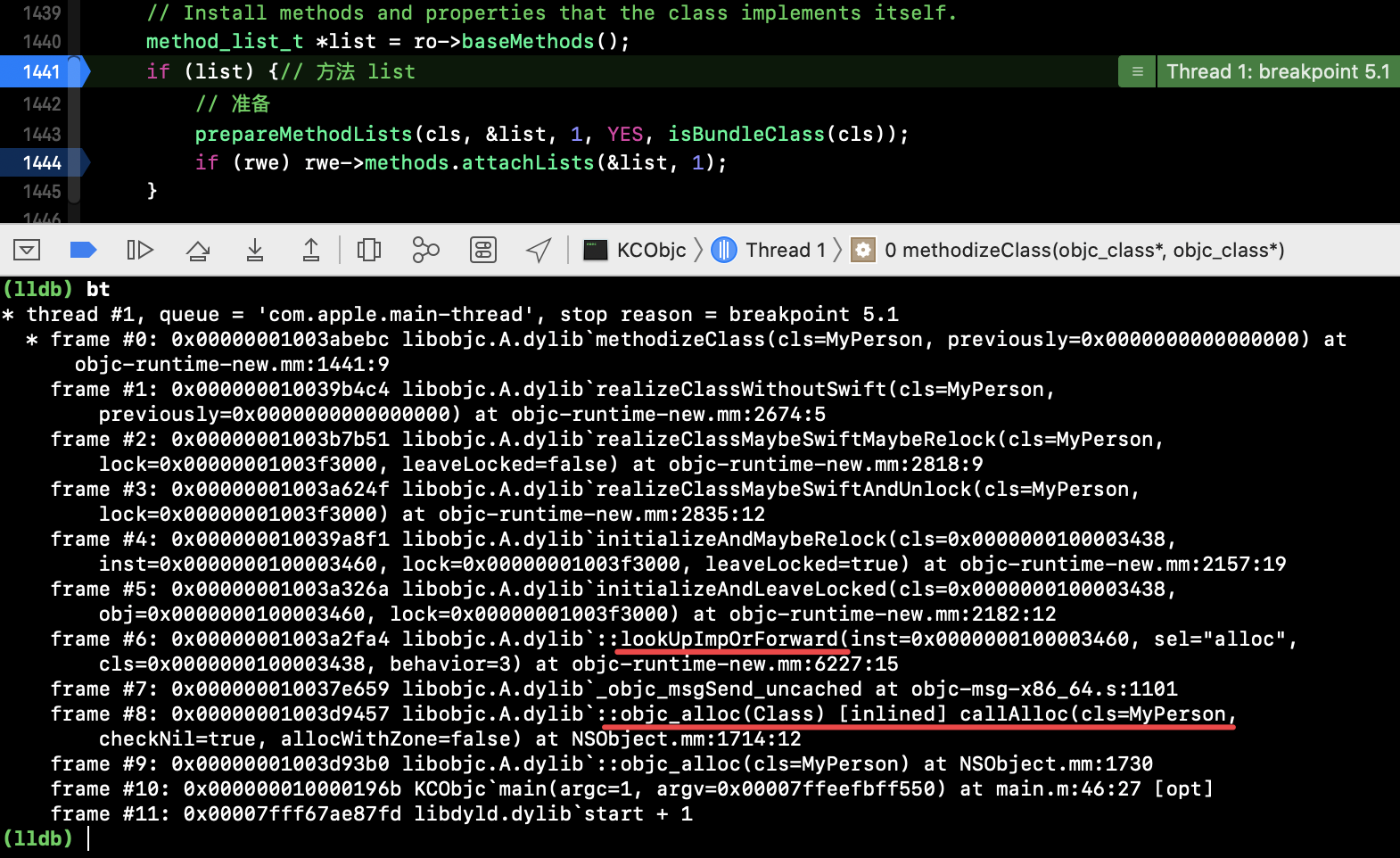
3)本类和分类都懒加载 不实现 load 方法
在第一次方法调用时加载到数据:
执行过程: _read_images() --> readClass(). readClass 中 baseMethodList 的 count 也是13个,数据也是从 data() 里面拿到的:
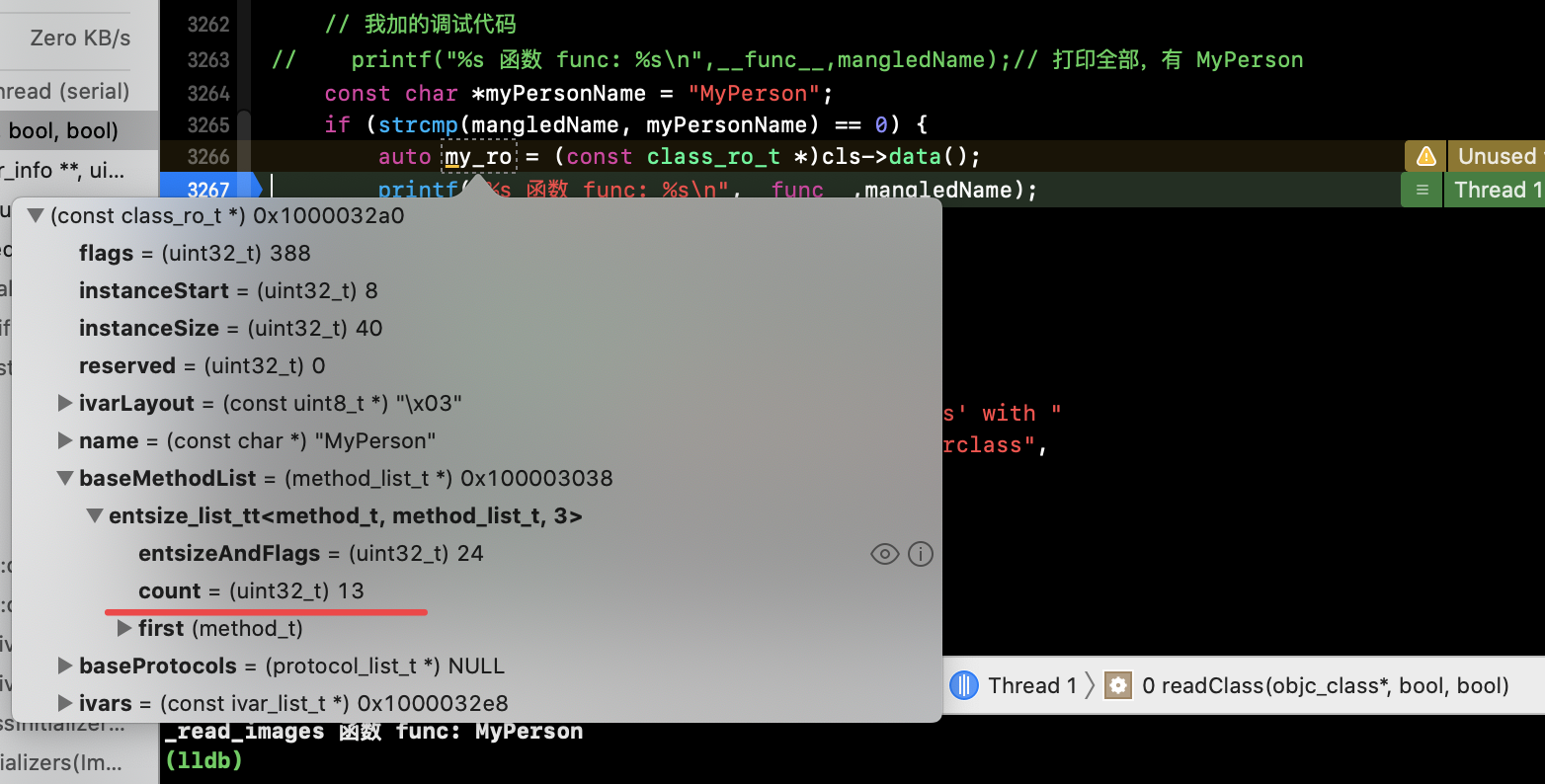
方法排序和 ‘1)’ 中相同。
4)主类不实现 load 分类实现 load
通过堆栈信息查看加载流程:
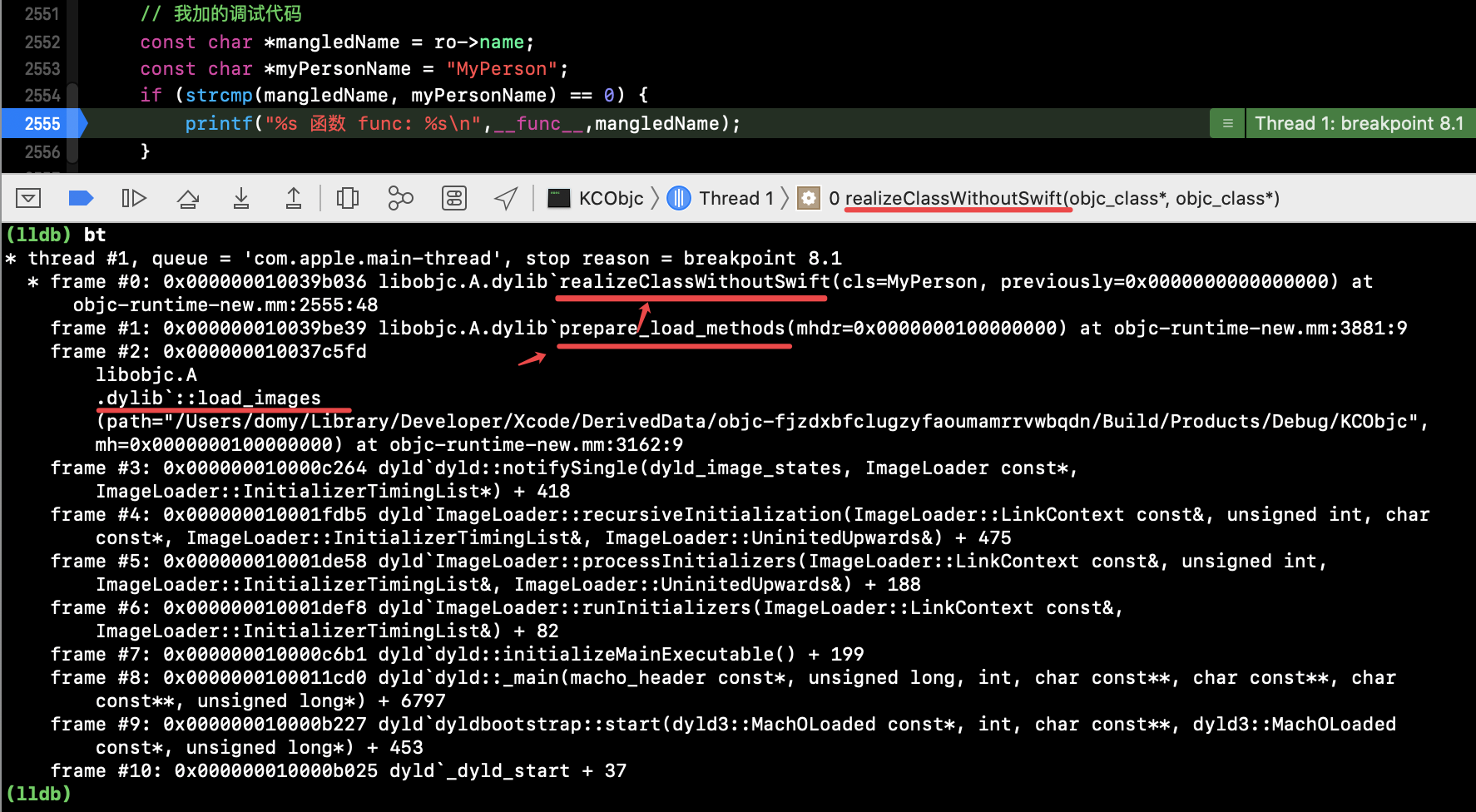
methodList 一直到 执行到 attachToClass() 仍是只有9个方法:

attachToClass() --> 走进了 attachCategories() --> attachLists() .
可得结论:分类实现了load方法会迫使主类进行提前加载数据(但这里本类仍并非是非懒加载,只是被迫使提前加载了而已)。
5)主类和分类 cateMore 非懒加载 - cateTwo 懒加载不实现load方法:
1、运行工程,MyPerson 类第一次进入 attachCategories() -->
cateTwo 的方法加载在 data 中(ro->baseMethods())取出,rwe 为 null 未开辟脏内存.
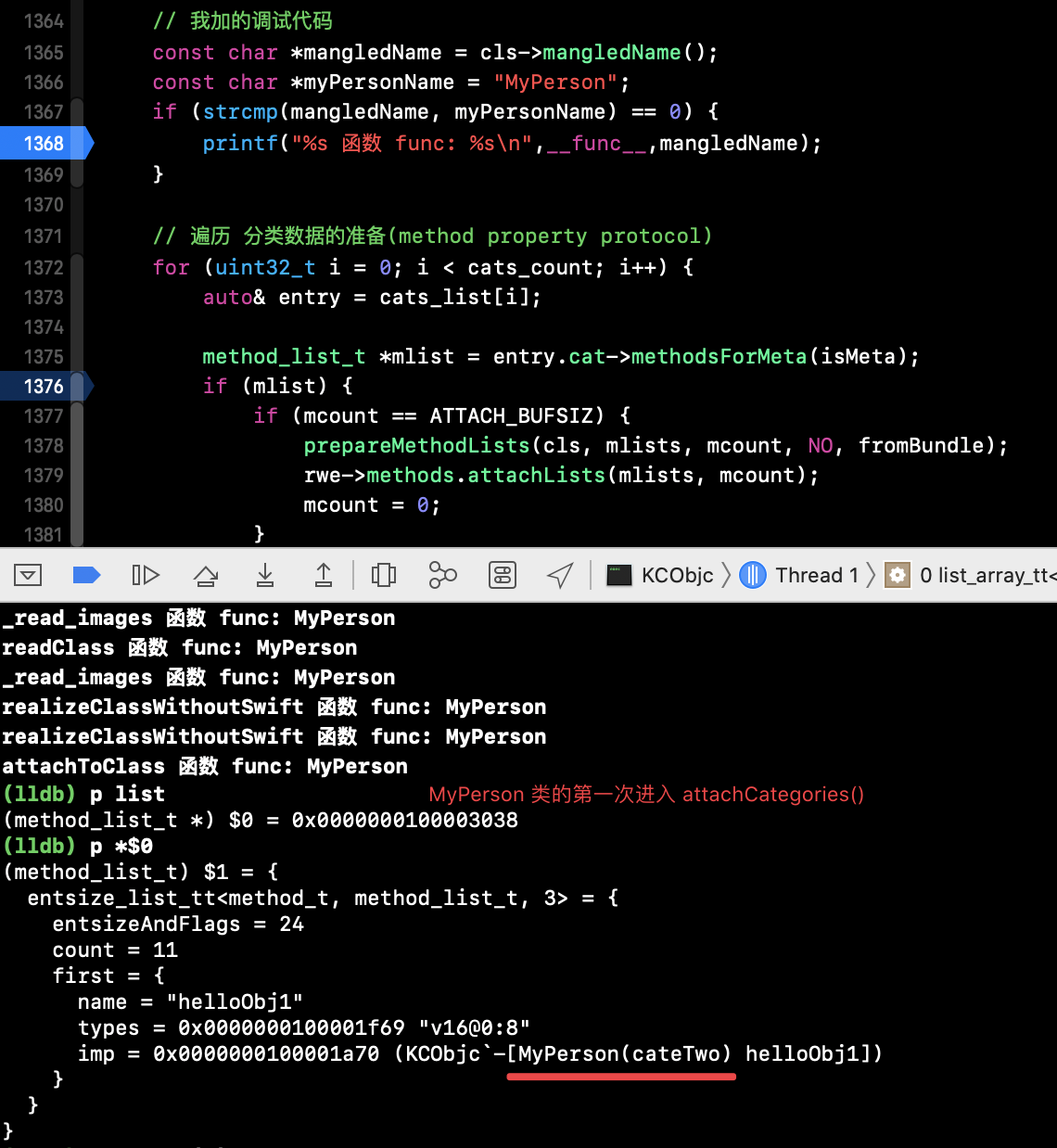
2、继续执行 MyPerson 类第二次进入 load_categories_nolock() --> attachCategories() -->
attachLists(),rew 非 NULL,分类 cateMore 的方法会 attachLists 进来:

所有分类都会走非懒加载!!!对于同一个本类,只要有一个分类是非懒加载,其他所有分类都会非懒加载的。
总结:
- 分类懒加载: 分类的数据信息是从 data 中读取的;
- 有一 or 多个分类非懒加载:主类会提前加载(早于 main 函数),并 attach 到所有非懒加载分类的信息;
- 都为懒加载:在第一次方法调用时从 data() 中取出数据。
问题回顾:通过 OC 底层探索 14 对方法排序源码的分析已知,方法排序:
1、首先根据方法名的地址进行排序 - name 的 address
2、若方法重名则根据 sel 排序:
1. sel 混乱则进行 fixedUp 2. sel 没有混乱则根据 imp 排序。
验证:

文章上面的流程也可得验证。
以上。