1、集合set
集合是无序的,不重复的,主要作用:
去重,把一个列表变成集合,就可以自动去重
关系测试,测试两组数据的交集,差集,并集等关系
操作例子如下:
1 list_1 = [1,4,5,7,3,6,7,9] 2 list_1=set(list_1) 3 4 list_2 = set([2,6,0,66,22,8,4]) 5 6 print(list_1,list_2) 7 8 print(list_1,type(list_1)) 9 运行结果如下: 10 D:python35python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py 11 {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22} 12 {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} <class 'set'> 13 14 Process finished with exit code 0
关于集合的功能及操作
1 关于就集合的交集intersection: 2 print(list_1.intersection(list_2)) 3 print(list_1 & list_2) 4 运行结果如下: 5 D:python35python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py 6 {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22} 7 {4, 6} 8 {4, 6} 9 #并集union 10 print(list_1.union(list_2)) 11 print(list_1 | list_2) 12 运行结果如下: 13 D:python35python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py 14 {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22} 15 {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 66, 9, 8, 22} 16 {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 66, 9, 8, 22} 17 18 Process finished with exit code 0 19 #差集difference 20 print(list_1.difference(list_2)) 21 print(list_2.difference(list_1)) 22 print(list_1-list_2) 23 运行结果如下: 24 D:python35python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py 25 {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22} 26 {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 66, 9, 8, 22} 27 {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 66, 9, 8, 22} 28 29 Process finished with exit code 0 30 #子集issubset 31 list_3=set([1,3,7]) 32 print(list_3.issubset(list_1)) 33 print(list_1.issubset(list_2)) 34 #父集issuperset 35 print(list_1.issuperset(list_2)) 36 运行结果如下: 37 D:python35python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py 38 {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22} 39 True 40 False 41 False 42 43 Process finished with exit code 0 44 #对称差集 45 print(list_1.symmetric_difference(list_2)) 46 print(list_1 ^ list_2) 47 运行结果如下: 48 D:python35python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py 49 {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22} 50 {0, 1, 2, 66, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 22} 51 {0, 1, 2, 66, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 22} 52 53 Process finished with exit code 0 54 #判断是否有交集,如果没有返回True 55 list_4 = set([5,6,8]) 56 print(list_4.isdisjoint(list_3)) 57 运行结果如下: 58 D:python35python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/set集合.py 59 {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9} {0, 2, 66, 4, 6, 8, 22} 60 True 61 62 Process finished with exit code 0 63 #增加add 64 list_1.add(999) 65 print(list_1) 66 #更新 67 list_1.update([888,777,555]) 68 print(list_1) 69 #删除 70 list_1.remove(4334) 71 print(list_1) 72 #随机删除 73 list_1.pop() 74 print(list_1) 75 #如果没有存在不会报错,如果是remove的时候会报错 76 list_1.discard() 77 #集合的长度 78 len(list_1) 79 # x in s 判断x是否是s的成员
2、关于文件操作
f = open("file.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") #文件句柄,即文件内存对象
写操作w,这个会将文件清空,即将文件重新写一遍,并且如果没有这个文件会创建
既读又写a----append 只能向文件中追加内容,也是不能读
读写r+
写读w+
追加写a+
1 #循环读这个文件 2 f=open("file.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") 3 for i in f.readlines(): 4 print(i.strip()) 5 f=open("file.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") 6 for index,line in enumerate(f.readlines()): 7 if index==2: 8 print("分割线".center(10,"-")) 9 continue 10 print(line.strip()) 11 但是上面的效率比较低 12 下面这种方式更好 13 f=open("file.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") 14 count =0 15 for line in f: 16 count +=1 17 if count == 3: 18 print("分割线".center(10, "-")) 19 print(line.strip()) 20 21 f.tell()打印当前的位置 22 f.seek()返回某个位置 23 f=open("file.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") 24 print(f.tell()) 25 print(f.readline()) 26 print(f.readline()) 27 print(f.readline()) 28 f.seek(0) 29 print(f.tell()) 30 print(f.readline()) 31 32 对于上面打开文件的时候用的方式,后面都需要加f.close(),有一种方式可以省却这个步骤 33 with open(“file.txt”,‘r’) as f:
3、 Unicode不管是中文和因为都是占两个字符,16位
ASCII 不存在中文,8位
UTF-8可变长字符编码
在utf-8中所有的银根字符用ascii存放,
所有的中文字符都是3个字节
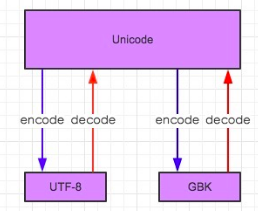
通过上图解释关于不同字符编码之间的转换
GBK转换成UTF-8
需要先通过decode解码转换为Unicode编码格式
再通过encode转换为UTF-8编码格式
4、 函数
函数是指将一组语句的集合通过一个名字封装起来,要想执行这个函数,只需调用其函数名字即可
函数的特性:
减少重复代码
是程序易于扩展
使程序变得容易维护
编程语言中函数定义:函数是逻辑结构化和过程化的一种变成方法
一个函数的定义方法:
1 def test(x): 2 "the function definitions" 3 x+=1 4 return x 5 print(test(2)) 6 运行结果如下: 7 D:python35python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/func.py 8 3 9 10 Process finished with exit code 0 11 其中: 12 def:定义函数的关键字 13 test:函数名 14 ():可以定义参数 15 “”:文档描述 16 return:定义返回值 17 18 一个函数的例子: 19 import time 20 21 def logger_test(): 22 time_format="%Y-%m-%d %X" 23 time_current = time.strftime(time_format) 24 with open("a.txt","a+") as f: 25 f.write('time %s end action ' %time_current) 26 27 def test1(): 28 print("test1 starting action...") 29 logger_test() 30 31 def test2(): 32 print("test2 starting action...") 33 logger_test() 34 35 def test3(): 36 print("test3 starting action...") 37 logger_test() 38 39 test1() 40 test2() 41 test3() 42 运行结果如下: 43 D:python35python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/def函数.py 44 test1 starting action... 45 test2 starting action... 46 test3 starting action... 47 并生成a.txt文件内容如下: 48 time 2016-08-10 10:52:49 end action 49 time 2016-08-10 10:52:49 end action 50 time 2016-08-10 10:52:49 end action 51 从这里也可以看出,通过定义函数,可以让程序更易于扩展
5、 函数和过程
过程定义:就是没有返回值的函数,在一个函数中没有使用return显示定义返回值时,python解释器会隐式的返回None,所以在python中即便是过程也算做函数
6、关于函数的返回值
代码如下: def test01(): pass def test02(): return 0 def test03(): return 3,2,"hello","zf",["zhaofan","name"],{"name":"dean","age":23} t1 = test01() t2=test02() t3=test03() print("from test01 return is %s:" %type(t1),t1) print("from test01 return is %s:" %type(t2),t2) print("from test01 return is %s:" %type(t3),t3) 运行结果如下: D:python35python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/函数2.py from test01 return is <class 'NoneType'>: None from test01 return is <class 'int'>: 0 from test01 return is <class 'tuple'>: (3, 2, 'hello', 'zf', ['zhaofan', 'name'], {'name': 'dean', 'age': 23}) Process finished with exit code 0
从上面可以看出:
返回值=0:返回None
返回值的个数为1返回object
返回值的个数大于1:返回tuple
7、 函数的调用:
调用函数的时候()里可以有参数也可以没有
参数:
形参和实参
形参:形式参数,不是实际存在的,是虚拟变量,在定义函数和函数体的时候使用形参,目的是在函数调用时接收实参
位置参数和关键字参数(标准调用:实参与形参的位置一一对应;关键字参数调用:位置无序固定)
默认参数
参数组
注意:关键参数不能再位置参数前面
关于参数的列子:
#AUTHOR:FAN #接收N个位置参数,转换成元组的形式 def test1(x,*args): print(x) print(args) test1(1,2,3,4,5,6,7) #**kwargs:把N个关键字参数,转换成字典的方式 def test2(**kwargs): print(kwargs) print(kwargs["name"]) print(kwargs["age"]) print(kwargs["sex"]) # # test2(name="zhaofan",age=22,sex="男") test2(**{"name":"zhaofan","age":22,"sex":"男"}) def test3(name,**kwargs): print(name) print(kwargs) test3("alex",age=12,sex="mm") def test4(name,age=18,**kwargs): print(name) print(age) print(kwargs) test4("zhaofan",sex="zz",age=12,hobby="tsl") def test5(name,age=12,*args,**kwargs): print(name) print(age) print(args) print(kwargs) test5("zhaofan",age=34,sex="m",hobby="tsla")
8、变量
局部变量只在函数里生效
字符串、整数等在函数里更改不会影响全局变量
列表和字典,集合,类等可以在函数里进行更改
例子演示:
#AUTHOR:FAN name = "zhaofan" def change_name(name): print("before change:",name) name = "dean" print("after change:",name) change_name(name) print("-----",name) 程序运行结果: D:python35python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/局部变量2.py before change: zhaofan after change: dean ----- zhaofan Process finished with exit code 0
9、 递归
def calc(n): print(n) if int(n/2) >0: return calc(int(n/2)) print("----->",n) calc(10) 运行结果: D:python35python.exe D:/python培训/s14/day3/递归.py 10 5 2 1 -----> 1 Process finished with exit code 0
递归的特性:
必须有一个明确的结束条件
每次进入更深一层时,问题规模要比上次减少
递归效率不高
递归循环只能循环999层