假如有一篇文章file.txt,共有
FirstLine。
TwoLine。
ThreeLine。
三行。
1、输出第n行
sed -n '1p' file.txt

2、替换
sed 's/Line/line/' file.txt

3、只替换Two开头行
sed '/^Two/s/Line/line/' file.txt
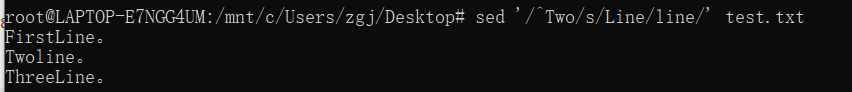
4、从第二行开始替换
sed '2,$ s/Line/line/' file.txt
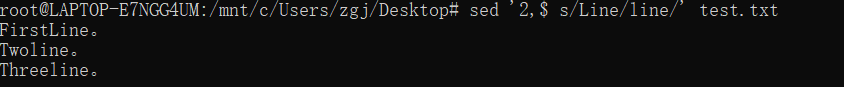
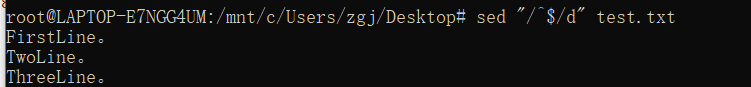
5、删除空行,注意需要格式是Unix LF结尾文件才可以。
sed '/^$/d' file
6、输出两个正则表达式内容
sed -nE '/^foo/,/^bar/p' file.txt
后面的比较复杂,感觉暂时用不上。
Use custom delimiters to make it easy for some strings that contain slashes
sed 's_/bin/bash_/bin/sh_' file.txt
Custom delimiters for regex address combined with the classical delimiter for substitute command (you could also use there a custom delimiter). Useful for paths.
sed '\_/bin/bash_s/grep/egrep/' file.txt
- or using the same delimiter for clarity
sed '\_/bin/bash_s_grep_egrep_' file.txt
Insert a space between lowercase/Uppercase characters using & (which represents the regex match)
sed 's/[a-zA-Z]/& /g' file.txt
Keep the first word of every line (where word is defined by alphanumeric chars + underscores for simplicity sake)
sed -E 's_[a-zA-Z0-9_]+.*_\1_' file.txt
Switch the first two words
sed -E 's_([a-zA-Z0-9_]*) ([a-zA-Z0-9_]*)_\2 \1_' f1
Remove duplicate words separated by a single space (but not triplicate)
sed -E 's_([a-zA-Z0-9_]+) \1_\1_ig' f1
Search and replace for pattern, write just the lines with the replacements in a new file
sed 's_foo_bar_w replaced.txt' file.txt
Multiple replacements
sed -e 's_foo_bar_' -e 's_hello_HELLO_' file.txt
Multiple replacements by using a sed script
#!/usr/bin/sed -f
s/a/A/
s/foo/BAR/
s/hello/HELLO/
- Make executable with
chmod +x myscript.sed, call with./myscript.sed myfile.txt
Multiple commands using the ; operator which in theory concatenates commands (WARNING! It won't work as expected with certain commands such as 'r' or 'w'. Use a sed script instead OR put the command dealing with filenames last). Print line 10 and insert before line 5.
sed '10p;5i\"INSERTED BEFORE LINE 5" file.txt
Remove comments between lines starting with these two keywords. Empty lines will be put there instead
sed -E '/start/,/end/ s/#.*//' file.txt
Delete comments starting with # (no empty lines left behind)
sed -E '/^#/d' f1
Insert an empty line after pattern (after each line containing comment in this case)
sed '/^#/G' file.txt
View lines minus lines between line starting with pattern and end of file
sed '/start/,$ d' file.txt
View lines except lines between line starting with pattern and line ending with pattern
sed -rn '/start/,/end/ !p' file.txt
Print until you encounter pattern then quit
sed '/start/q' file.txt
Insert contents of file after a certain line
sed '5 r newfile.txt' file.txt
Append text after lines containing regex (AFTER FOO)
sed '/foo/a\AFTER FOO' file.txt
Insert text after lines containing regex (BEFORE FOO)
sed '/foo/i\BEFORE FOO' file.txt
Change line containing regex match
sed '/foo/c\FOO IS CHANGED' file.txt
Nested sed ranges with inversion. Between lines 1,100 apply actions where the pattern DOESN'T match.
#!/usr/bin/sed -f
1,100 {
/foo/ !{
s_hello_HELLOOOOWORLD_
s_yes_YES_
}
}
Use nested addresses with change, insert and append to modify: the line before match, the line with match, the line after match.
#!/usr/bin/sed -f
/^#/ {
i\
#BEFFORE ORIGINAL COMMENt
a\
#AFTER ORIGINAL COMMENT
c\
# ORIGINAL COMMENT IS NOW THIS LINE
}
Insert new line before the first comment, after the first comment put in the contents of file and quit immediately afterwards
#!/usr/bin/sed -f
/^#/ {
i\#BEFORE COMMENT
r myotherfile.txt
q
}
Transform text
sed 'y/abc/ABC/' file.txt
Copy all the comments (starting with #) to a new file
sed -E '/^#/w comments.txt' file.txt
Print every second line (substitute ~3 for third line, etc)
sed -n '1~2p' file.txt
Edit file in place but also create a backup
sed -i.bak 's/hello/HELLO/' file.txt
Append two extra lines after regex match
sed -E '/^#/G G' file.txt
Short Sed Tut
Sed commands use an address based on which they operate. The address can be:
- Single lines
sed '10d' file.txt- delete line 10 - Line range
sed '1,10d' file.txt- delete from line 1 to 10 - Line range2
sed '6,$d' file.txt- delete from line 6 to end of file ($ is end of file) - Regex
sed -E '/^#/d' file.txt- delete lines where regex matches - Regex ranges
sed -E '/DEBUG/,/END_DEBUG/d' file.txt- delete lines between regex matches (including lines where regex matches) - Regex and line ranges
sed -E '/DEBUG/,30d' file.txt- delete from line matching DEBUG to line 30 - all lines
sed 'a\AFTER EVERY LINE' file.txt- append this after every line (when no address is present apply to all lines) - Nested - use this with a sed script (see below)
#!/usr/bin/sed -f
1,100 {
/DEBUG/{
/DONE/d
/NOT DONE/a\TO BE DONE URGENTLY
}
}
- between lines 1 and 100:
where matches DEBUG,
delete lines containing /DONE/ and after lines containing /NOT DONE/ append.
You can invert the address by putting a ! in front of the command, not the address.
sed '/PRODUCTION/!d' file.txt- delete all lines not containing regex match. Note the ! in front of d.- Everything inside curly brace (for nested) is a command. You put the ! in front of the curly brace.
#!/usr/bin/sed -f
1,100 {
/DEBUG/ !{
/DONE/d
/NOT DONE/a\TO BE DONE URGENTLY
}
}
- between lines 1,100
on lines NOT containing /DEBUG/
Perform operations
- "Double" nested inversion
#!/usr/bin/sed -f
1,100 {
/DEBUG/ !{
/DONE/!d
}
}
- between lines 1,100
on lines not containing DEBUG
delete lines NOT containing /DONE/
Basic commands:
5d- delete - Delete line 5.5p- print. - print line 5 (you should call sed with-noption when using print to only print the specified lines)5q- quit - after line 5 quit5a\Appended- append - after line 5. Note the backward slash in front of 'a'5c\Changed- change - change line 5 to 'Changed'5i\Before- insert - insert before line 5.5r newfile.txt- read - put the contents of file 'newfile.txt' after line 55w written.txt- write - write line 5 to 'written.txt'5s/foo/bar- substitute - on line 5 search for foo and replace with bar
Advanced & Less used commands
sed -E '/^#/G G' file.txt- append newline to pattern space then append hold space to pattern space - insert two blank lines after every line that matches regex
Regex tricks
&is the matched regex.sed -E '/foo/& & &/' file.txtwill triplicate the foo word\1to\9are the groups id's. You use a group like `sed -E 's/(foo) (bar)/\2 \1' file.txt '. In this very simple example we search for 'foo' followed by space followed by 'bar'. Then we switch these words (instead of 'foo bar' we have 'bar foo')- Flags.
sed 's/foo/bar/gi' file.txt. 'g' will replace all occurrences on the line (instead of just the first as it is by default). 'i' will make the substitute case insensitive.
来源:https://github.com/adrianscheff/useful-sed/edit/master/README.md