/* 给出两个 非空 的链表用来表示两个非负的整数。其中,它们各自的位数是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且它们的每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。 如果,我们将这两个数相加起来,则会返回一个新的链表来表示它们的和。 您可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。 示例: 输入:(2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4) 输出:7 -> 0 -> 8 原因:342 + 465 = 807 解题思路: 1、分别计算出这两个数的位数,同时,指针分别指向末尾。 2、分别将两个链表倒序,遍历单链表得出数相加得num3。 3、将num3建立单链表l3。 */ #include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> #include<malloc.h> struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; }; void print(struct ListNode* L){ ListNode *p=L->next; while(p){ printf("%d ",p->val); p=p->next; } } struct ListNode* createList(int a[],int k){ ListNode *L,*r,*s; L=(ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); L->next=NULL; int i; for(i=0;i<k;i++){ s=(ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); s->val=a[i]; s->next=L->next; L->next=s; } return L; } struct ListNode* createListR(int a[],int k){ ListNode *L,*r,*s; L=(ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); L->next=NULL; r=L; int i; for(i=0;i<k;i++){ s=(ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); s->val=a[i]; r->next=s->next; r=s; } r->next=NULL; return L; } struct ListNode* ListReverse(struct ListNode* L){ ListNode *p=L->next,*s; L->next=NULL; while(p){ s=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); s->val=p->val; s->next=L->next; L->next=s; p=p->next; } return L; } struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2){ int n1=0,n2=0,num1,num2,num3,k=0,n[100]; ListNode *p1,*p2,*l3; p1=l1->next; p2=l2->next; while(p1){ n1++; p1=p1->next; } while(p2){ n2++; p2=p2->next; } int a[n1],b[n2],i,j; ListReverse(l1); ListReverse(l2); p1=l1->next; p2=l2->next; num1=num2=1; while(p1){ n1--; num1+=p1->val*pow(10,n1); p1=p1->next; } while(p2){ n2--; num2=num2+p2->val*pow(10,n2); p2=p2->next; } num3=num1+num2; printf("%d ",num3); while(num3){ n[k]=num3%10; k++; num3=num3/10; } l3=createListR(n,k); return l3; } main() { struct ListNode* l1; struct ListNode* l2; struct ListNode* l3; int a[3]={3,4,2},b[3]={4,6,5}; l1=createList(a,3); l2=createList(b,3); l3=addTwoNumbers(l1,l2); print(l3); }
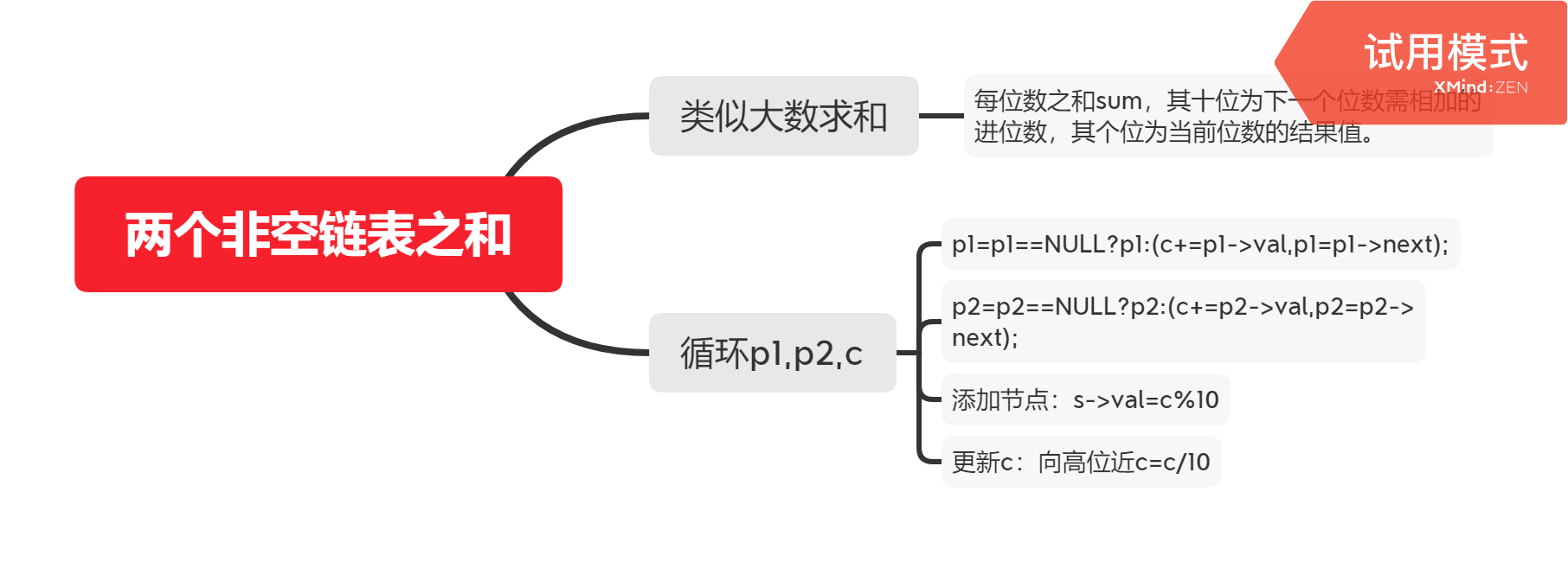
/* 解题思路:类似大数相加 举例:数a=89,数b=12;从低位向高位相加。 第一位: c=9+2=11; s->val=c%10=1; c=c/10=1; 第二位: c=8+1=9; s->val=c%10=9; c=c/10=0; 也就意味着,每位数之和c,其十位为下一个位数和需相加的进位数,其个位为当前位数的结果值。 巧用三目运算符。 */ #include<stdio.h> #include<malloc.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<math.h> #include<string.h> #include <iostream> struct ListNode{ int val; struct ListNode *next; }; void print(struct ListNode* L){ struct ListNode* p=L->next; while(p){ printf("%d ",p->val); p = p->next; } printf(" "); } /*头插法建表*/ struct ListNode* createList(int a[],int k){ struct ListNode *L,*r,*s; L=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); L->next=NULL; int i; for(i=0;i<k;i++){ s=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); s->val=a[i]; s->next=L->next; L->next=s; } return L; } /*尾插法建链表*/ struct ListNode* createListR(int a[],int k){ struct ListNode *L,*r,*s; L=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); L->next=NULL; int i; r=L; for(i=0;i<k;i++){ s=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); s->val=a[i]; r->next=s; r=s; } r->next=NULL; return L; } struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2){ struct ListNode *p1=l1->next,*p2=l2->next,*r,*l3,*s; l3=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); l3->next=NULL; r=l3; int c=0; while(p1||p2||c){ s=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); p1=p1==NULL?p1:(c+=p1->val,p1=p1->next); p2=p2==NULL?p2:(c+=p2->val,p2=p2->next); s->val=c%10; r->next=s; r=s; c=c/10; } r->next=NULL; return l3; } int main() { struct ListNode *l1,*l2,*l3; int a1[]={2,4,3},a2[]={5,6,4}; l1=createListR(a1,3); l2=createListR(a2,3); l3=addTwoNumbers(l1,l2); print(l3); return 0; }