一、回顾Vue响应式用法
vue响应式,我们都很熟悉了。当我们修改vue中data对象中的属性时,页面中引用该属性的地方就会发生相应的改变。避免了我们再去操作dom,进行数据绑定。
二、Vue响应式实现分析
对于vue的响应式原理,官网上给了出文字描述 https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/reactivity.html 。
vue内部主要是通过数据劫持和观察者模式实现的
数据劫持:
vue2.x内部使用Object.defineProperty https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Object/defineProperty
vue3.x内部使用的Proxy https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Proxy
观察者模式:https://juejin.cn/post/6995865134132363295
内部成员示意图
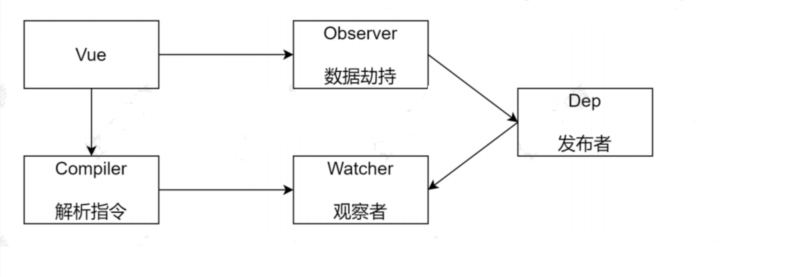
各个成员的功能
Vue:
- 把data中的成员注入到Vue实例中,并把data中的成员转换为getter和setter
Observer:
- 对data对象中的简单类型数据及对象进行监听,当数据发生变化时通知Dep
Compiler:
- 解析每个元素中的指令/差值表达式,并替换成相应的数据
Dep:
- 观察者模式中的通知者,添加观察者,当数据变化时通知观察者
Watcher:
- 每个引用data中的属性的地方都有一个watcher对象,负责更新视图
附:data对象中的属性充当被观察者,引用data对象中属性的地方充当观察者
三、Vue响应式源码实现
Vue对象实现
功能
- 负责接受初始化的参数
- 把data中的属性注入到data实例,转换成getter和setter
- 调用Observer监听data中所有属性的变化
- 调用compiler解析指令、差值表达式.
class Vue{
constructor(options){
// 1、通过属性保存穿进来的属性
this.$options= options||{};
this.$data= options.data||{};
this.$el = typeof options.el ==='string' ? document.querySelector(options.el) : options.el;
// 2、把data参数中的数据转换为getter和setter 挂载到Vue实例上
this._proxyData(this.$data)
// 3、调用observe对象监视data数据的变化
new Observer(this.$data)
// 4、调用compiler对象渲染页面
new Compiler(this)
}
_proxyData(data){
if (data&&Object.keys(data).length>0){
for (const key in data) {
Object.defineProperty(this,key,{
configurable:true,
enumerable:true,
get(){
return data[key]
},
set(value){
if (data[key]===value) {
return;
}
data[key]=value;
}
})
}
}
}
}
Observer对象实现
功能
- 把data选项中的属性进行数据劫持
- data中的某个属性也是对象的话,进行递归转换成响应式对象
- 数据变化发送通知
//数据劫持
class Observer {
constructor(data) {
this.walk(data)
}
walk(data) {
//1、判断data是否是对象
if (!data || typeof data !== 'object') {
return
}
//2、循环调用defineReactive进行数据劫持
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
this.defineReactive(data, key, data[key])
})
}
defineReactive(obj, key, val) {
//创建通知者
const dep = new Dep()
//使用walk把引用对象中的属性变成响应式的
this.walk(val)
const that=this;
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
configurable: true,
enumerable: true,
get() {
//通知者收集观察者
Dep.target && dep.addSub(Dep.target)
return val;
},
set(newVal) {
if (newVal === val) {
return;
}
val = newVal;
that.walk(newVal)
//被观察者发生变化的时候,通知者对象给每个观察者发送通知
dep.notify()
}
})
}
}
Compile对象实现
功能
- 负责编译模板,解析指令、差值表达式
- 负责页面首次渲染
- 当数据发生改变后,负责重新渲染视图
//编译器
class Compiler {
constructor(vm) {
this.el = vm.$el;
this.vm = vm;
this.compile(this.el)
}
//编译模板 判断节点是文本节点还是元素节点
compile(el) {
let childNodes = el.childNodes;
//处理第一层子节点
Array.from(childNodes).forEach(node => {
if (this.isTextNode(node)) {
this.compileText(node)
} else if (this.isElementNode(node)) {
this.compileElement(node)
}
//如果当前节点还有子节点 递归调用编译指令
if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length) {
this.compile(node)
}
})
}
//编译元素节点,处理指令
compileElement(node) {
//遍历所有的指令
Array.from(node.attributes).forEach(attr => {
//判断是不是指令节点
if (this.isDirective(attr.name)) {
const nodeName = attr.name;
const key = attr.nodeValue;
const directive = nodeName.substr(2)
this.updater(directive,node,key)
}
})
}
updater(directive,node,key){
const updaterFn = this[directive+"Updater"]
updaterFn && updaterFn.call(this,node,this.vm[key],key)
}
//v-text
textUpdater(node,value,key){
node.textContent=value
//使用v-text表达式的地方就是一个观察者
new Watcher(this.vm,key,newValue => {
node.textContent = newValue
})
}
//v-model
modelUpdater(node,value,key){
node.value =value
//使用v-model表达式的地方就是一个观察者
new Watcher(this.vm,key,newValue => {
node.value = newValue
})
//实现双向绑定
node.addEventListener('input',()=>{
this.vm[key] = node.value
})
}
//v-html
htmlUpdater(node,value,key){
node.innerHTML = value
//使用v-html表达式的地方就是一个观察者
new Watcher(this.vm,key,newValue => {
node.innerHTML = newValue
})
}
//处理差值表达式
compileText(node) {
//匹配差值表达式的正则
let reg = /{{(.+?)}}/
//用正则匹配node的textContent,如果匹配到了 就替换
if (reg.test(node.textContent)) {
//获取插值表达式的key
let key = RegExp.$1;
let value = node.textContent;
node.textContent = value.replace(reg, this.vm[key])
//使用差值表达式的地方就是一个观察者
new Watcher(this.vm,key,newValue => {
node.textContent = newValue
})
}
}
//是否是指令
isDirective(attrName) {
return attrName.startsWith('v-')
}
//是否是文本节点
isTextNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 3
}
//是否是元素
isElementNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 1
}
}
Dep对象实现
功能
- 收集依赖,添加观察者
- 通知所有观察者
//通知者类
class Dep {
constructor() {
//存储观察者
this.subs = []
}
/**
* 收集观察者
*/
addSub(sub) {
if (sub && sub.update) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
}
/**
* 通知观察者改变状态
*/
notify() {
this.subs.forEach(sub => {
sub.update()
})
}
}
Watcher对象实现
功能
- 当数据变化时,Dep通知所有Watcher实例更新视图
- 自身实例化的时候往Dep对象中添加自己
//观察者类
class Watcher {
constructor (vm,key,cb) {
//Vue实例
this.vm =vm;
// data中的key对象
this.key =key;
// 更新视图的回调函数
this.cb = cb
//把当前观察者实例存放在Dep的target静态属性中
Dep.target =this
//触发Observe的getter方法,把当前实例存放在Dep.subs中
//data中key对应的旧值
this.oldValue = this.vm[this.key]
Dep.target = null
}
//每个观察者都有一个update方法来改变状态
update(){
const newValue = this.vm[this.key]
if ( this.newValue === this.oldValue ) {
return
}
this.cb(newValue)
}
}
测试
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>index</title>
<script src="./js/dep.js"></script>
<script src="./js/watcher.js"></script>
<script src="./js/compiler.js"></script>
<script src="./js/observer.js"></script>
<script src="./js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>差值表达式</h1>
<h3>{{msg}}</h3>
<h3>{{count}}</h3>
<h1>v-text</h1>
<div v-text='msg'></div>
<h1>v-model</h1>
<input type="text" v-model="msg" attr="msg">
<input type="text" v-model="count">
<h1>v-html</h1>
<div v-html="htmlText"></div>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
msg:'信息',
count:'数量',
person:{name:'张三'},
htmlText:"<div style='color:red'>你好</div>"
}
})
</script>
</body>