20182301 2019-2020-1 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验8报告
课程:《程序设计与数据结构》
班级: 1823
姓名: 赵沛凝
学号:20182301
实验教师:王志强
实验日期:2019年11月11日
必修/选修: 必修
1.实验内容
- 参考教材PP16.1,完成链树LinkedBinaryTree的实现(getRight,contains,toString,preorder,postorder),用JUnit或自己编写驱动类对自己实现的LinkedBinaryTree进行测试。
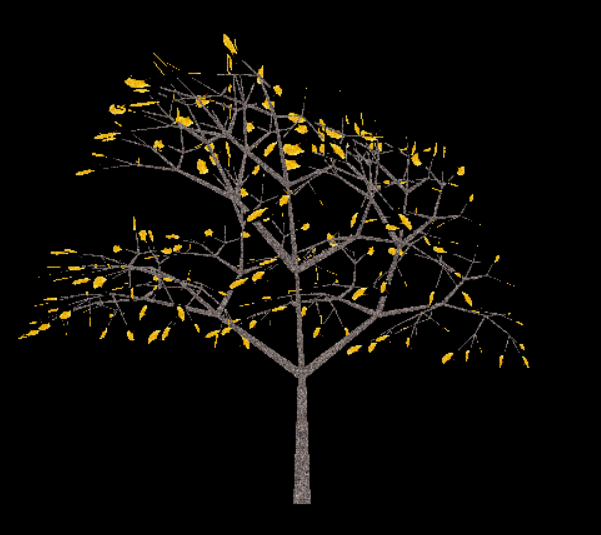
- 基于LinkedBinaryTree,实现基于(中序,先序)序列构造唯一一棵二㕚树的功能,比如给出中序HDIBEMJNAFCKGL和先序ABDHIEJMNCFGKL,构造出附图中的树,用JUnit或自己编写驱动类对自己实现的功能进行测试。
- 自己设计并实现一颗决策树并完成测试。
- 输入中缀表达式,使用树将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,并输出后缀表达式和计算结果
2. 实验过程及结果
第一个:
- 对这几个方法进行补充(getRight,contains,toString,preorder,postorder),代码如下:
- getRight
public LinkedBinaryTree<T> getRight() throws Exception {
if (root == null)
throw new Exception ("Get Right operation "
+ "failed. The tree is empty.");
LinkedBinaryTree<T> result = new LinkedBinaryTree<T>();
result.root = root.getRight();
return result;
}
- contains
public boolean contains (T target) throws Exception {
BTNode<T> node = null;
boolean result = true;
if (root != null)
node = root.find(target);
if(node == null)
result = false;
return result;
}
- preorder
public Iterator<T> preorder() {
ArrayIterator<T> list = new ArrayIterator<>();
if(root!=null)
root.preorder(list);
return list;
}
- toString
public String toString() {
ArrayIterator<T> list = (ArrayIterator<T>) preorder();
String result = "<top of Tree>
";
for(T i : list){
result += i + " ";
}
return result + "<bottom of Tree>";
}
- postorder
public Iterator<T> postorder() {
ArrayIterator<T> list = new ArrayIterator<>();
if(root!=null)
root.postorder(list);
return list;
}
第二个
- 运用先序、中序建立一个脑中的图像并不难,如下:
- 但是在代码上就容易出现问题,在借鉴以及自我理解的基础上,搞了出来:
public static LinkedBinaryTree returnTree(char[] in, char[] pre)
{
LinkedBinaryTree tree;
if(pre.length == 0 || in.length == 0 || pre.length != in.length){ // 终止递归的条件
tree = new LinkedBinaryTree();
}
else {
int x = 0;
while (in[x] != pre[0]) { // 找到根结点
x++;
}
char[] inLeft = new char[x]; // 根结点的左边为左子树,创建新的数组
char[] preLeft = new char[x];
char[] inRight = new char[in.length - x - 1]; // 根结点的右边为右子树,创建新的数组
char[] preRight = new char[pre.length - x - 1];
for (int y = 0; y < in.length; y++) { // 把原数组的数存入新的数组当中
if (y < x) {
inLeft[y] = in[y];
preLeft[y] = pre[y + 1];
} else if (y > x) {
inRight[y - x - 1] = in[y];
preRight[y - x - 1] = pre[y];
}
}
LinkedBinaryTree left = returnTree(inLeft, preLeft); // 左子树递归调用
LinkedBinaryTree right = returnTree(inRight, preRight); // 右子树递归调用
tree = new LinkedBinaryTree(pre[0], left,right);
}
return tree;//HDIBEMJNAFCKGL;ABDHIEJMNCFGKL
}
- 本来我只弄了一个后续遍历的输出,但是看到大家都做出了树,于是又自我学习,详见问题1.
- 最后还是出现了树哦!
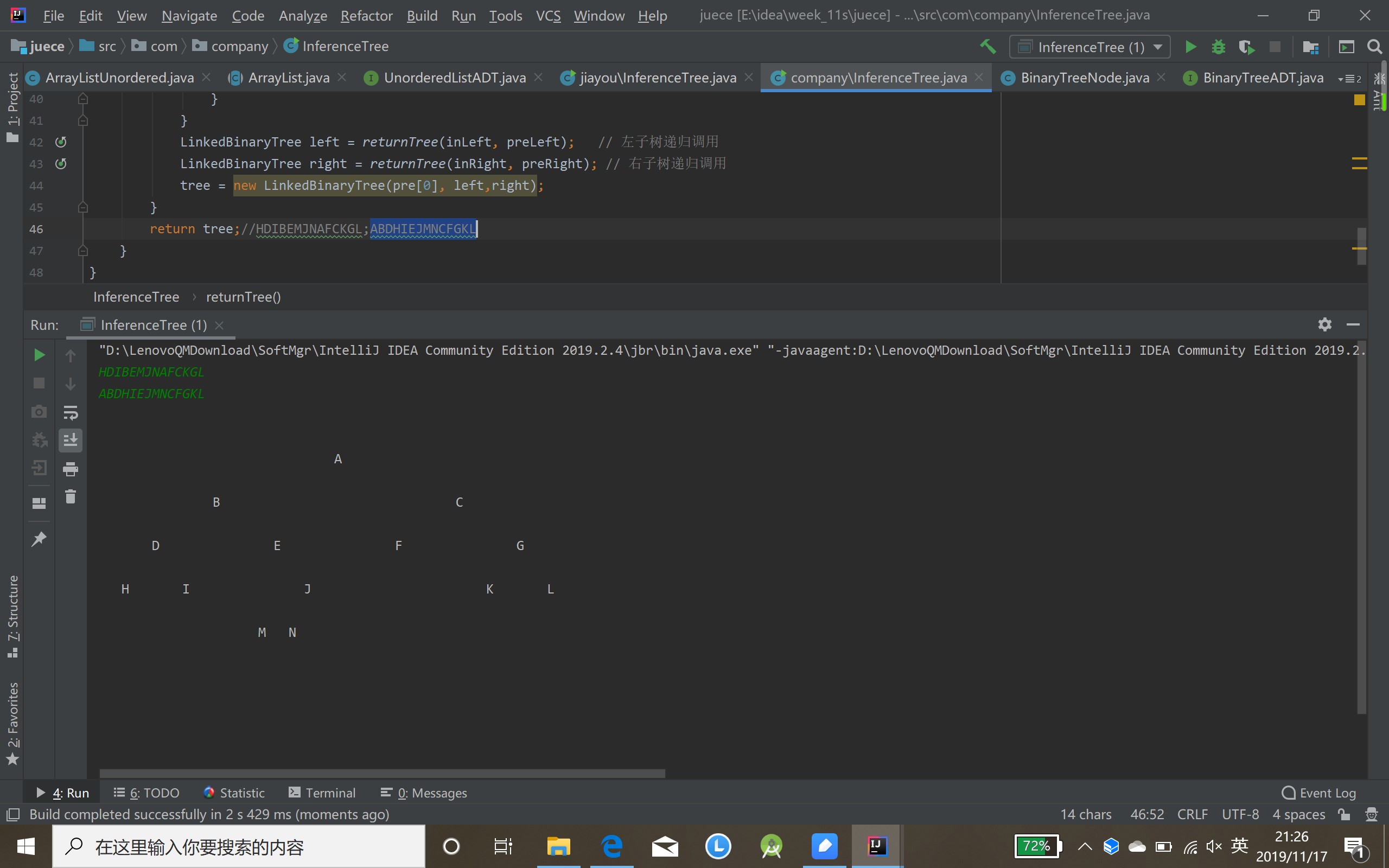
第三个
- 首先要设计决策树的脑图,构建思路,如图所示:
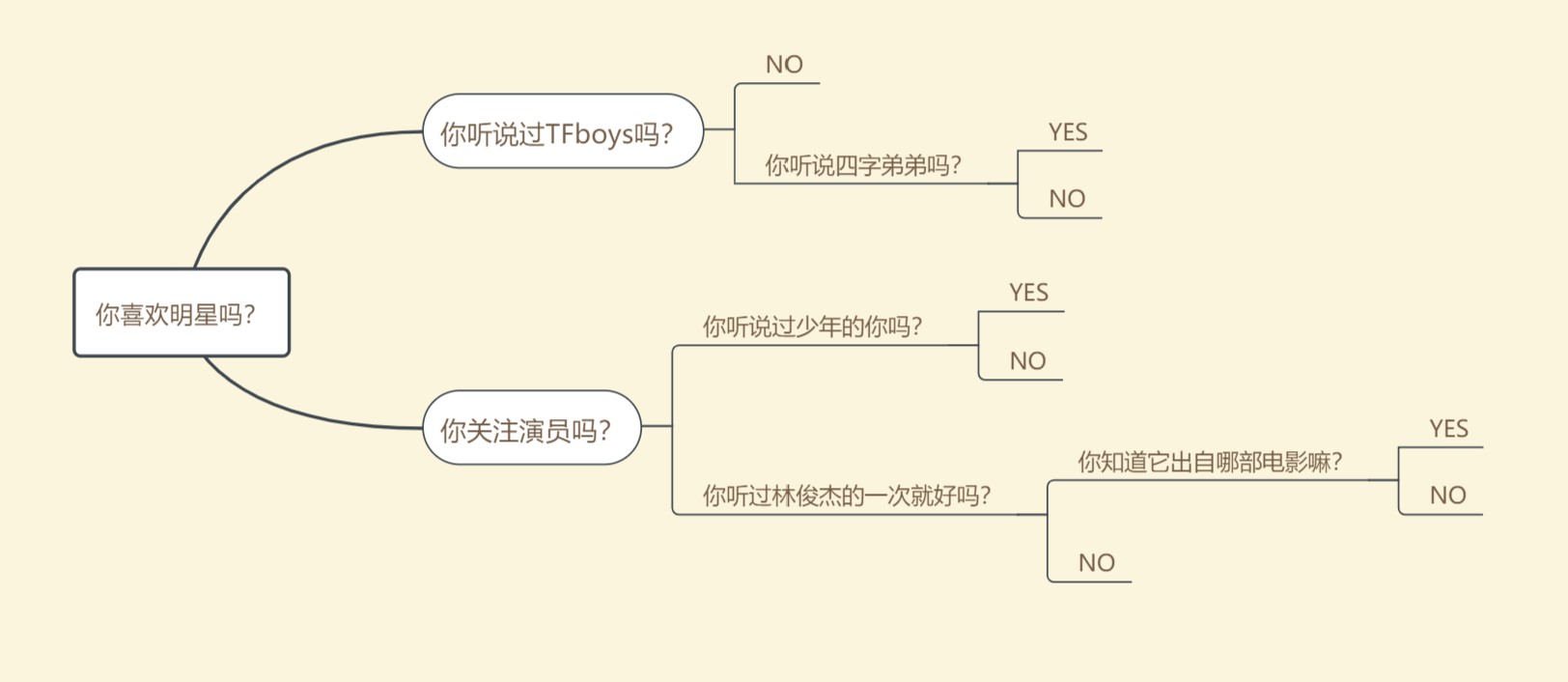
- 从左向右,从上向下进行编号
- 利用如下代码进行构建:
LinkedBinaryTree<String>n2,n3,n4,n5,n6,n7,n8,n9,n10,n11,n12,n13,n14,n15;
n15 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e15);
n14 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e14);
n11 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e11,n14,n15);
n12 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e12);
n13 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e13);
n7 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e7,n12,n13);
n8 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e8);
n9 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e9);
n5 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e5,n8,n9);
n10 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e10);
n6 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e6,n10,n11);
n4 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e4);
n2 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e2,n4,n5);
n3 = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e3,n6,n7);
tree = new LinkedBinaryTree<String>(e1,n2,n3);
- 使用如下方法进行判断
public void diagose() throws Exception {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
LinkedBinaryTree<String>current = tree;
while (current.size() > 1)
{
System.out.println (current.getRootElement());
if (scan.nextLine().equalsIgnoreCase("N"))
current = current.getLeft();
else
current = current.getRight();
}
System.out.println (current.getRootElement());
}
第四个
- 首先我先搞了不使用树的中缀转后缀,代码如下:
public class Postfix {
static Stack<Character> op = new Stack<>();
public static float getv(char op, float f1, float f2){
if(op == '+') return f2 + f1;
else if(op == '-') return f2 - f1;
else if(op == '*') return f2 * f1;
else if(op == '/') return f2 / f1;
else return Float.valueOf(-0);
}
public static float calrp(String rp){
Stack<Float> v = new Stack<>();
char[] arr = rp.toCharArray();
int len = arr.length;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
Character ch = arr[i];
if(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') v.push(Float.valueOf(ch - '0'));
else v.push(getv(ch, v.pop(), v.pop()));
}
return v.pop();
}
public static String getrp(String s){
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
int len = arr.length;
String out ="";
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
char ch = arr[i];
if(ch == ' ') continue;
if(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
out+=ch;
continue;
}
if(ch == '(') op.push(ch);
if(ch == '+' || ch == '-'){
while(!op.empty() && (op.peek() != '('))
out+=op.pop();
op.push(ch);
continue;
}
if(ch == '*' || ch == '/'){
while(!op.empty() && (op.peek() == '*' || op.peek() == '/'))
out+=op.pop();
op.push(ch);
continue;
}
if(ch == ')'){
while(!op.empty() && op.peek() != '(')
out += op.pop();
op.pop();
continue;
}
}
while(!op.empty()) out += op.pop();
return out;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("输入中缀表达式:");
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
String exp=scan.nextLine();
System.out.println("后缀表达式为:");
System.out.println(getrp(exp));
System.out.println("结果为:");
System.out.println(calrp(getrp(exp)));
}
}
- 再有对于使用树进行中缀转后缀,其实它可以定义为表达树,
3. 实验过程中遇到的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:如何真的画出一棵树呢?
- 问题1解决方案:
- 这个代码很复杂,需要仔细理解
public String toString() {
UnorderedListADT<BinaryTreeNode<T>> nodes = new ArrayListUnordered<BinaryTreeNode<T>>();
UnorderedListADT<Integer> levelList = new ArrayListUnordered<Integer>();
BinaryTreeNode<T> current = null;
String result = "";
int printDepth = this.getHeight();
int possibleNodes = (int) Math.pow(2, printDepth + 1);
int countNodes = 0;
nodes.addToRear(root);
Integer currentLevel = 0;
Integer previousLevel = -1;
levelList.addToRear(currentLevel);
while (countNodes < possibleNodes) {
countNodes = countNodes + 1;
try {
current = nodes.removeFirst();
} catch (EmptyCollectionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
currentLevel = levelList.removeFirst();
} catch (EmptyCollectionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (currentLevel > previousLevel) {
result = result + "
";
previousLevel = currentLevel;
for (int j = 0; j < ((Math.pow(2, (printDepth - currentLevel))) - 1); j++)
result = result + " ";
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < (Math.pow(2, (printDepth - currentLevel + 1)) - 1); i++) {
result = result + " ";
}
}
if (current != null) {
result = result + (current.getElement()).toString();
nodes.addToRear(current.getLeft());
levelList.addToRear(currentLevel + 1);
nodes.addToRear(current.getRight());
levelList.addToRear(currentLevel + 1);
} else {
nodes.addToRear(null);
levelList.addToRear(currentLevel + 1);
result = result + " ";
}
}
return result;
}
-
问题2:决策树很容易理解,那么表达树是什么意思呢?详见链接1
-
问题2解决方案:
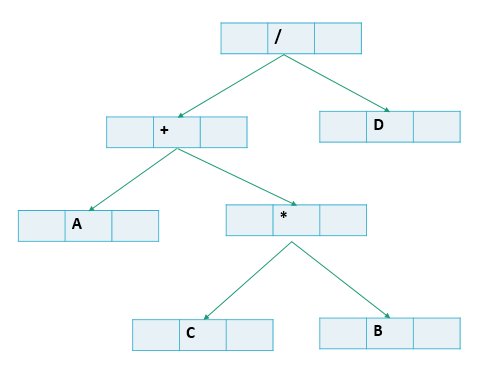
-
前缀表达式(前序遍历):/+A*CBD
-
中缀表达式(中序遍历):A+B*C/D
-
后缀表达式(后序遍历):ACB*+D/
-
代码如下:
public class ExprTree {
//最后访问头结点
public BinaryTreeNode buildExprTree(char postfixExpr[],int size){
LinkedList<BinaryTreeNode> stack=new LinkedList();
BinaryTreeNode node=null;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
if(isOperateNum(postfixExpr[i])){
node=new BinaryTreeNode();
node.setLeft(null);
node.setRight(null);
node.setData(postfixExpr[i]);
stack.push(node);
}else{
BinaryTreeNode leftChild=stack.pop();
BinaryTreeNode rightChild=stack.pop();
node =new BinaryTreeNode();
node.setLeft(leftChild);
node.setRight(rightChild);
node.setData(postfixExpr[i]);
stack.push(node);
}
}
return stack.getLast();
}
//判断是否是操作数
private boolean isOperateNum(char c){
if(c=='/'||c=='+'||c=='*'||c=='-'){
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
其他(感悟、思考等)
在学习树的各种时,可以说是非常难的,但是看到更加优秀的人,创造出更加优秀的树,自己也要不断努力
