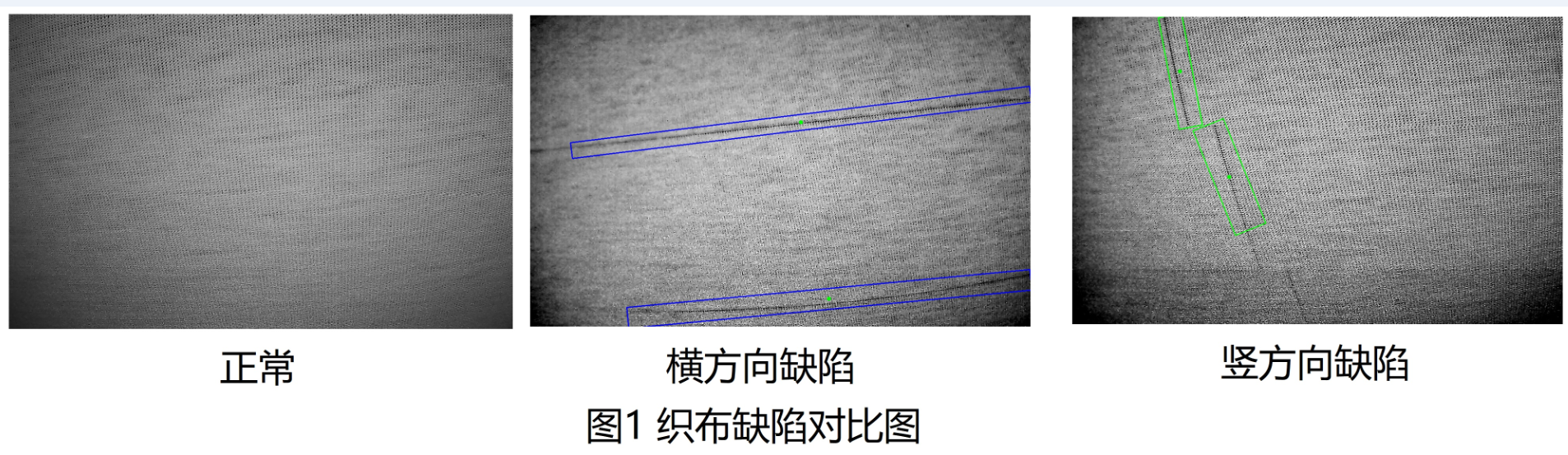
本文针对织布生产过程中,由于断针造成的织布缺陷图像,进行检测,如下图1所示.
1. 图像质量增强
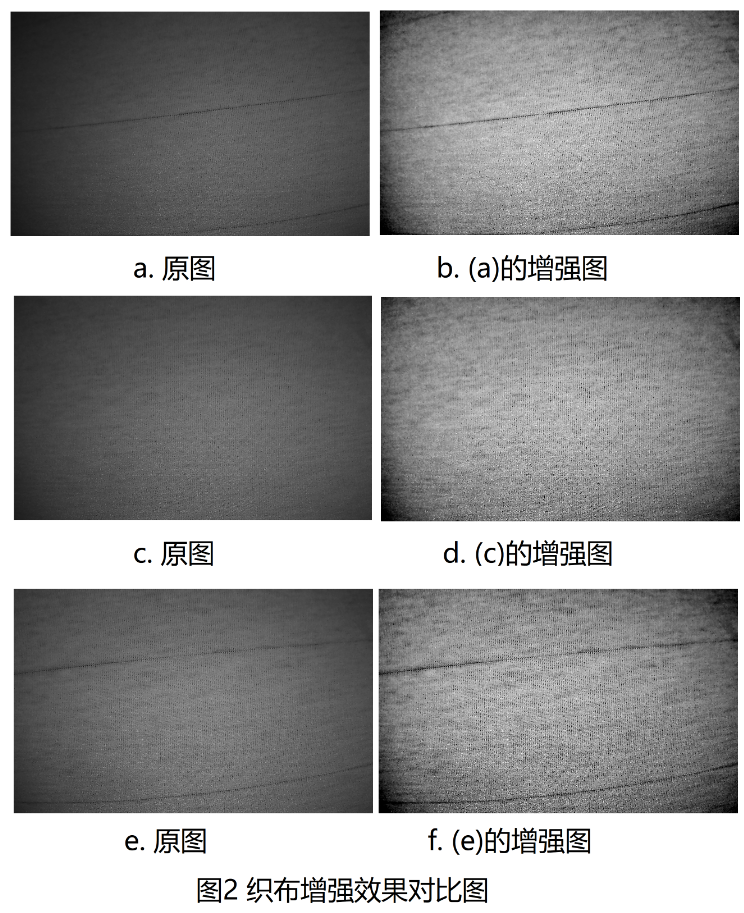
由于织布原图的图像整体偏暗,不利于缺陷部分的检测,考虑改善图像质量,而图像质量增强的算法有很多,本文借鉴Retinex的图像增强算法(SSR, MSR, MSRCR)的实现,效果如图2所示.
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/ajianyingxiaoqinghan/article/details/71435098
2. 低通滤波/边缘检测
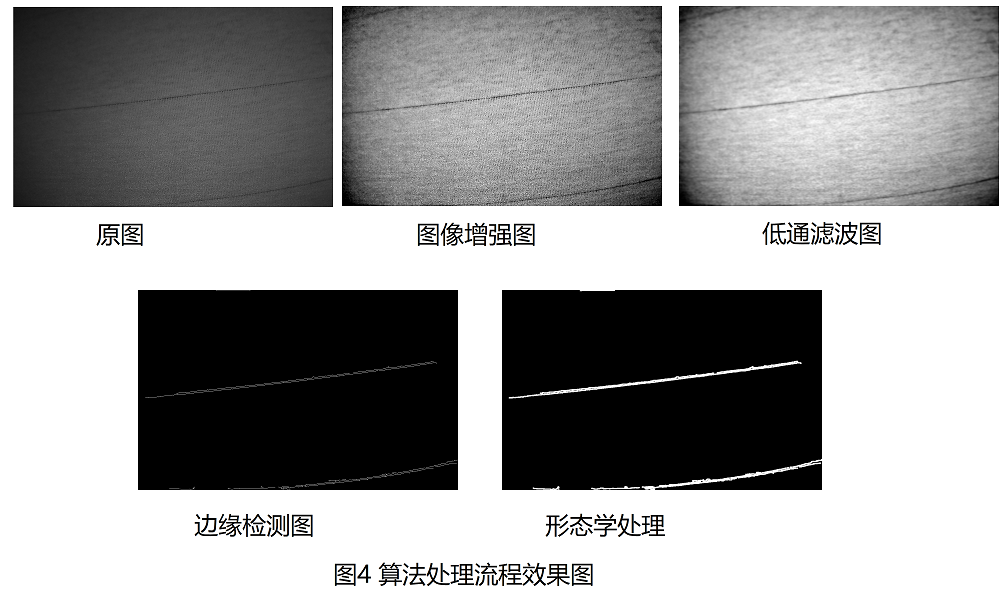
观测图像2中增强后的图像,虽然织布瑕疵部分,相对正常区域有明显的细长暗条纹痕迹,但是如果直接使用边缘检测的方式,来定位瑕疵部分的边缘,很难找到明显的边界条纹(受织布正常纹理部分的影响,如图3的对比效果图所示).
这里用低通滤波器,实现对织布纹理背景的过滤,以提供织布瑕疵缺陷的高频细节部分,利于后续的边缘检测效果.

低通滤波算法,参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40647819/article/details/80600918?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-2.channel_param&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-2.channel_param
边缘检测算法,参考:https://blog.csdn.net/dieju8330/article/details/82814529?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant_t0.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-1.channel_param&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant_t0.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-1.channel_param
3. 形态学处理
对边缘检测后的图像,进行形态学的膨胀处理,就可以增大缺陷区域的轮廓,以便于利用opencv中找轮廓的方式,定位瑕疵部分的位置.
4. 定位瑕疵区域
对形态学处理后的图像,利用opencv中的findContours()函数,通过轮廓的宽高、面积大小等条件设置,来定位织布的瑕疵轮廓区域,具体实现参见代码部分:
5. 实现代码部分
MSRCR.h

#pragma once #ifndef _MSRCR_H_ #define _MSRCR_H_ #include "cv.h" #include "highgui.h" #include "opencv2opencv.hpp" #include <math.h> // 该处使用USE_EXACT_SIGMA,则使用自定义的滤波算法; // 不使用USE_EXACT_SIGMA,则使用OpenCV自带的高斯滤波算法; //#define USE_EXACT_SIGMA using namespace cv; using namespace std; class Msrcr { private: #define pc(image, x, y, c) image->imageData[(image->widthStep * y) + (image->nChannels * x) + c] #define INT_PREC 1024.0 #define INT_PREC_BITS 10 inline double int2double(int x) { return (double)x / INT_PREC; } inline int double2int(double x) { return (int)(x * INT_PREC + 0.5); } inline int int2smallint(int x) { return (x >> INT_PREC_BITS); } inline int int2bigint(int x) { return (x << INT_PREC_BITS); } public: vector<double> CreateKernel(double sigma); vector<int> CreateFastKernel(double sigma); void FilterGaussian(IplImage* img, double sigma); void FilterGaussian(Mat src, Mat &dst, double sigma); void FastFilter(IplImage *img, double sigma); void FastFilter(Mat src, Mat &dst, double sigma); void Retinex(IplImage *img, double sigma, int gain = 128, int offset = 128); void Retinex(Mat src, Mat &dst, double sigma, int gain = 128, int offset = 128); void MultiScaleRetinex(IplImage *img, vector<double> weights, vector<double> sigmas, int gain = 128, int offset = 128); void MultiScaleRetinex(Mat src, Mat &dst, vector<double> weights, vector<double> sigmas, int gain = 128, int offset = 128); void MultiScaleRetinexCR(IplImage *img, vector<double> weights, vector<double> sigmas, int gain = 128, int offset = 128, double restoration_factor = 6, double color_gain = 2); void MultiScaleRetinexCR(Mat src, Mat &dst, vector<double> weights, vector<double> sigmas, int gain = 128, int offset = 128, double restoration_factor = 6, double color_gain = 2); }; #endif
MSRCR.cpp

#include "MSRCR.h" /*=========================================================== * 函数: CreateKernel * 说明:创建一个标准化的一维高斯核; * 参数: * double sigma: 高斯核标准偏差 * 返回值: * double*: 长度为((6*sigma)/2) * 2 + 1的double数组 * 注: * 调用者需要删除该内核; * -------------------------------------------------------- * Summary: * Creates a normalized 1 dimensional gaussian kernel. * * Arguments: * double sigma - the standard deviation of the gaussian kernel. * * Returns: * vector<double> - an vector of values of length ((6*sigma)/2) * 2 + 1. * Note: * Caller is responsable for deleting the kernel. ============================================================= */ vector<double> Msrcr::CreateKernel(double sigma) { int i, x, filter_size; vector<double> filter; double sum; // set sigma's upline // 为sigma设定上限 if (sigma > 300) sigma = 300; // get needed filter size (enforce oddness) // 获取需要的滤波尺寸,且强制为奇数; filter_size = (int)floor(sigma * 6) / 2; filter_size = filter_size * 2 + 1; // Calculate exponential // 计算指数 sum = 0; for (i = 0; i < filter_size; i++) { double tmpValue; x = i - (filter_size / 2); tmpValue = exp(-(x*x) / (2 * sigma*sigma)); filter.push_back(tmpValue); sum += tmpValue; } // Normalize // 归一化计算 for (i = 0, x; i < filter_size; i++) filter[i] /= sum; return filter; } /*=========================================================== * 函数: CreateFastKernel * 说明:创建一个近似浮点的整数类型(左移8bits)的快速高斯核; * 参数: * double sigma: 高斯核标准偏差 * 返回值: * double*: 长度为((6*sigma)/2) * 2 + 1的int数组 * 注: * 调用者需要删除该内核; * -------------------------------------------------------- * Summary: * Creates a faster gaussian kernal using integers that * approximate floating point (leftshifted by 8 bits) * * Arguments: * double sigma - the standard deviation of the gaussian kernel. * * Returns: * vector<int> - an vector of values of length ((6*sigma)/2) * 2 + 1. * * Note: * Caller is responsable for deleting the kernel. ============================================================= */ vector<int> Msrcr::CreateFastKernel(double sigma) { vector<double> fp_kernel; vector<int> kernel; int i, filter_size; // Reject unreasonable demands // 设置上限 if (sigma > 300) sigma = 300; // get needed filter size (enforce oddness) // 获取需要的滤波尺寸,且强制为奇数; filter_size = (int)floor(sigma * 6) / 2; filter_size = filter_size * 2 + 1; // Create Kernel // 创建内核 fp_kernel = CreateKernel(sigma); // Change kernel's data type from double to int // double内核转为int型 for (i = 0; i < filter_size; i++) { int tmpValue; tmpValue = double2int(fp_kernel[i]); kernel.push_back(tmpValue); } return kernel; } /*=========================================================== * 函数:FilterGaussian * 说明:通过内核计算高斯卷积,内核由sigma值得到,且在内核两端值相等; * 参数: * img: 被滤波的IplImage*类型图像 * double sigma: 高斯核标准偏差 * -------------------------------------------------------- * Summary: * Performs a gaussian convolution for a value of sigma that is equal * in both directions. * * Arguments: * IplImage* img - the image to be filtered in place. * double sigma - the standard deviation of the gaussian kernel to use. ============================================================= */ void Msrcr::FilterGaussian(IplImage* img, double sigma) { int i, j, k, source, filter_size; vector<int> kernel; IplImage* temp; int v1, v2, v3; // Reject unreasonable demands // 设置上限 if (sigma > 300) sigma = 300; // get needed filter size (enforce oddness) // 获取需要的滤波尺寸,且强制为奇数; filter_size = (int)floor(sigma * 6) / 2; filter_size = filter_size * 2 + 1; // Create Kernel // 创建内核 kernel = CreateFastKernel(sigma); temp = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), img->depth, img->nChannels); // filter x axis // X轴滤波 for (j = 0; j < temp->height; j++) { for (i = 0; i < temp->width; i++) { // inner loop has been unrolled // 内层循环已经展开 v1 = v2 = v3 = 0; for (k = 0; k < filter_size; k++) { source = i + filter_size / 2 - k; if (source < 0) source *= -1; if (source > img->width - 1) source = 2 * (img->width - 1) - source; v1 += kernel[k] * (unsigned char)pc(img, source, j, 0); if (img->nChannels == 1) continue; v2 += kernel[k] * (unsigned char)pc(img, source, j, 1); v3 += kernel[k] * (unsigned char)pc(img, source, j, 2); } // set value and move on pc(temp, i, j, 0) = (char)int2smallint(v1); if (img->nChannels == 1) continue; pc(temp, i, j, 1) = (char)int2smallint(v2); pc(temp, i, j, 2) = (char)int2smallint(v3); } } // filter y axis // Y轴滤波 for (j = 0; j < img->height; j++) { for (i = 0; i < img->width; i++) { v1 = v2 = v3 = 0; for (k = 0; k < filter_size; k++) { source = j + filter_size / 2 - k; if (source < 0) source *= -1; if (source > temp->height - 1) source = 2 * (temp->height - 1) - source; v1 += kernel[k] * (unsigned char)pc(temp, i, source, 0); if (img->nChannels == 1) continue; v2 += kernel[k] * (unsigned char)pc(temp, i, source, 1); v3 += kernel[k] * (unsigned char)pc(temp, i, source, 2); } // set value and move on pc(img, i, j, 0) = (char)int2smallint(v1); if (img->nChannels == 1) continue; pc(img, i, j, 1) = (char)int2smallint(v2); pc(img, i, j, 2) = (char)int2smallint(v3); } } cvReleaseImage(&temp); } /*=========================================================== * 函数:FilterGaussian * 说明:通过内核计算高斯卷积,内核由sigma值得到,且在内核两端值相等; * 参数: * Mat src: 输入图像 * Mat &dst: 输出图像 * double sigma: 高斯核标准偏差 * -------------------------------------------------------- * Summary: * Performs a gaussian convolution for a value of sigma that is equal * in both directions. * * Arguments: * Mat src - Input Image. * Mat &dst - Output Image. * double sigma - the standard deviation of the gaussian kernel to use. ============================================================= */ void Msrcr::FilterGaussian(Mat src, Mat &dst, double sigma) { IplImage tmp_ipl; tmp_ipl = IplImage(src); FilterGaussian(&tmp_ipl, sigma); dst = cvarrToMat(&tmp_ipl); //dst = Mat(&tmp_ipl); } /*=========================================================== * 函数:FastFilter * 说明:给出任意大小的sigma值,都可以通过使用图像金字塔与可分离滤波器计算高斯卷积; * 参数: * IplImage *img: 被滤波的图像 * double sigma: 高斯核标准偏差 * -------------------------------------------------------- * Summary: * Performs gaussian convolution of any size sigma very fast by using * both image pyramids and seperable filters. Recursion is used. * * Arguments: * img - an IplImage to be filtered in place. * double sigma - the standard deviation of the gaussian kernel to use. ============================================================= */ void Msrcr::FastFilter(IplImage *img, double sigma) { int filter_size; // Reject unreasonable demands // 设置上限 if (sigma > 300) sigma = 300; // get needed filter size (enforce oddness) // 获取需要的滤波尺寸,且强制为奇数; filter_size = (int)floor(sigma * 6) / 2; filter_size = filter_size * 2 + 1; // If 3 sigma is less than a pixel, why bother (ie sigma < 2/3) // 如果3 * sigma小于一个像素,则直接退出 if (filter_size < 3) return; // Filter, or downsample and recurse // 处理方式:(1) 滤波 (2) 高斯光滑处理 (3) 递归处理滤波器大小 if (filter_size < 10) { #ifdef USE_EXACT_SIGMA FilterGaussian(img, sigma); #else cvSmooth(img, img, CV_GAUSSIAN, filter_size, filter_size); #endif } else { if (img->width < 2 || img->height < 2) return; IplImage* sub_img = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width / 2, img->height / 2), img->depth, img->nChannels); cvPyrDown(img, sub_img); FastFilter(sub_img, sigma / 2.0); cvResize(sub_img, img, CV_INTER_LINEAR); cvReleaseImage(&sub_img); } } /*=========================================================== * 函数:FastFilter * 说明:给出任意大小的sigma值,都可以通过使用图像金字塔与可分离滤波器计算高斯卷积; * 参数: * Mat src: 输入图像 * Mat &dst: 输出图像 * double sigma: 高斯核标准偏差 * -------------------------------------------------------- * Summary: * Performs gaussian convolution of any size sigma very fast by using * both image pyramids and seperable filters. Recursion is used. * * Arguments: * Mat src - Input Image. * Mat &dst - Output Image. * double sigma - the standard deviation of the gaussian kernel to use. ============================================================= */ void Msrcr::FastFilter(Mat src, Mat &dst, double sigma) { IplImage tmp_ipl; tmp_ipl = IplImage(src); FastFilter(&tmp_ipl, sigma); dst = cvarrToMat(&tmp_ipl); //dst = Mat(&tmp_ipl); } /*=========================================================== * 函数:Retinex * 说明:单通道SSR方法,基础Retinex复原算法。原图像和被滤波的图像需要被转换到 * 对数域,并做减运算; * 参数: * IplImage *img: 被滤波的图像 * double sigma: 高斯核标准偏差 * int gain: 图像像素值改变范围的增益 * int offset: 图像像素值改变范围的偏移量 * -------------------------------------------------------- * Summary: * Basic retinex restoration. The image and a filtered image are converted * to the log domain and subtracted. * * Arguments: * img - an IplImage to be enhanced in place. * sigma - the standard deviation of the gaussian kernal used to filter. * gain - the factor by which to scale the image back into visable range. * offset - an offset similar to the gain. ============================================================= */ void Msrcr::Retinex(IplImage *img, double sigma, int gain, int offset) { IplImage *A, *fA, *fB, *fC; // Initialize temp images // 初始化缓存图像 fA = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, img->nChannels); fB = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, img->nChannels); fC = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, img->nChannels); // Compute log image // 计算对数图像 cvConvert(img, fA); cvLog(fA, fB); // Compute log of blured image // 计算滤波后模糊图像的对数图像 A = cvCloneImage(img); FastFilter(A, sigma); cvConvert(A, fA); cvLog(fA, fC); // Compute difference // 计算两图像之差 cvSub(fB, fC, fA); // Restore // 恢复图像 cvConvertScale(fA, img, gain, offset); // Release temp images // 释放缓存图像 cvReleaseImage(&A); cvReleaseImage(&fA); cvReleaseImage(&fB); cvReleaseImage(&fC); } /*=========================================================== * 函数:Retinex * 说明:单通道SSR方法,基础Retinex复原算法。原图像和被滤波的图像需要被转换到 * 对数域,并做减运算; * 参数: * Mat src: 输入图像 * Mat &dst: 输出图像 * double sigma: 高斯核标准偏差 * int gain: 图像像素值改变范围的增益 * int offset: 图像像素值改变范围的偏移量 * -------------------------------------------------------- * Summary: * Basic retinex restoration. The image and a filtered image are converted * to the log domain and subtracted. * * Arguments: * Mat src - Input Image. * Mat &dst - Output Image. * sigma - the standard deviation of the gaussian kernal used to filter. * gain - the factor by which to scale the image back into visable range. * offset - an offset similar to the gain. ============================================================= */ void Msrcr::Retinex(Mat src, Mat &dst, double sigma, int gain, int offset) { IplImage tmp_ipl; tmp_ipl = IplImage(src); Retinex(&tmp_ipl, sigma, gain, offset); dst = cvarrToMat(&tmp_ipl); //dst = Mat(&tmp_ipl); } /*=========================================================== * 函数:MultiScaleRetinex * 说明:多通道MSR算法。原图像和一系列被滤波的图像转换到对数域,并与带权重的原图像做减运算。 * 通常情况下,三个权重范围选择低、中、高标准偏差; * * 参数: * IplImage *img: 被滤波的图像 * vector<double> weights: 通道权重 * vector<double> sigmas: 高斯核标准偏差 * int gain: 图像像素值改变范围的增益 * int offset: 图像像素值改变范围的偏移量 * -------------------------------------------------------- * Summary: * Multiscale retinex restoration. The image and a set of filtered images are * converted to the log domain and subtracted from the original with some set * of weights. Typicaly called with three equaly weighted scales of fine, * medium and wide standard deviations. * * Arguments: * IplImage* img - an IplImage to be enhanced in place. * vector<double> weights - Weights of channels * vector<double> sigma - the standard deviation of the gaussian kernal used to filter. * int gain - the factor by which to scale the image back into visable range. * int offset - an offset similar to the gain. ============================================================= */ void Msrcr::MultiScaleRetinex(IplImage *img, vector<double> weights, vector<double> sigmas, int gain, int offset) { int i; double weight; int scales = sigmas.size(); IplImage *A, *fA, *fB, *fC; // Initialize temp images fA = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, img->nChannels); fB = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, img->nChannels); fC = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, img->nChannels); // Compute log image cvConvert(img, fA); cvLog(fA, fB); // Normalize according to given weights for (i = 0, weight = 0; i < scales; i++) weight += weights[i]; if (weight != 1.0) cvScale(fB, fB, weight); // Filter at each scale for (i = 0; i < scales; i++) { A = cvCloneImage(img); double tmp = sigmas[i]; FastFilter(A, tmp); cvConvert(A, fA); cvLog(fA, fC); cvReleaseImage(&A); // Compute weighted difference cvScale(fC, fC, weights[i]); cvSub(fB, fC, fB); } // Restore cvConvertScale(fB, img, gain, offset); // Release temp images cvReleaseImage(&fA); cvReleaseImage(&fB); cvReleaseImage(&fC); } /*=========================================================== * 函数:MultiScaleRetinex * 说明:多通道MSR算法。原图像和一系列被滤波的图像转换到对数域,并与带权重的原图像做减运算。 * 通常情况下,三个权重范围选择低、中、高标准偏差; * * 参数: * Mat src: 输入图像 * Mat &dst: 输出图像 * vector<double> weights: 通道权重 * vector<double> sigmas: 高斯核标准偏差 * int gain: 图像像素值改变范围的增益 * int offset: 图像像素值改变范围的偏移量 * -------------------------------------------------------- * Summary: * Multiscale retinex restoration. The image and a set of filtered images are * converted to the log domain and subtracted from the original with some set * of weights. Typicaly called with three equaly weighted scales of fine, * medium and wide standard deviations. * * Arguments: * Mat src - Input Image. * Mat &dst - Output Image. * vector<double> weights - Weights of channels * vector<double> sigmas - the standard deviation of the gaussian kernal used to filter. * int gain - the factor by which to scale the image back into visable range. * int offset - an offset similar to the gain. ============================================================= */ void Msrcr::MultiScaleRetinex(Mat src, Mat &dst, vector<double> weights, vector<double> sigmas, int gain, int offset) { IplImage tmp_ipl; tmp_ipl = IplImage(src); MultiScaleRetinex(&tmp_ipl, weights, sigmas, gain, offset); dst = cvarrToMat(&tmp_ipl); //dst = Mat(&tmp_ipl); } /*=========================================================== * 函数:MultiScaleRetinexCR * 说明:MSRCR算法,MSR算法加上颜色修复。原图像和一系列被滤波的图像转换到对数域,并与带权重的原图像做减运算。 * 通常情况下,三个权重范围选择低、中、高标准偏差;之后,颜色修复权重应用于每个颜色通道中; * * 参数: * IplImage *img: 被滤波的图像 * double sigma: 高斯核标准偏差 * int gain: 图像像素值改变范围的增益 * int offset: 图像像素值改变范围的偏移量 * double restoration_factor: 控制颜色修复的非线性 * double color_gain: 控制颜色修复增益 * -------------------------------------------------------- * Summary: * Multiscale retinex restoration with color restoration. The image and a set of * filtered images are converted to the log domain and subtracted from the * original with some set of weights. Typicaly called with three equaly weighted * scales of fine, medium and wide standard deviations. A color restoration weight * is then applied to each color channel. * * Arguments: * IplImage *img - an IplImage to be enhanced in place. * double sigma - the standard deviation of the gaussian kernal used to filter. * int gain - the factor by which to scale the image back into visable range. * int offset - an offset similar to the gain. * double restoration_factor - controls the non-linearaty of the color restoration. * double color_gain - controls the color restoration gain. ============================================================= */ void Msrcr::MultiScaleRetinexCR(IplImage *img, vector<double> weights, vector<double> sigmas, int gain, int offset, double restoration_factor, double color_gain) { int i; double weight; int scales = sigmas.size(); IplImage *A, *B, *C, *fA, *fB, *fC, *fsA, *fsB, *fsC, *fsD, *fsE, *fsF; // Initialize temp images // 初始化缓存图像 fA = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, img->nChannels); fB = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, img->nChannels); fC = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, img->nChannels); fsA = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1); fsB = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1); fsC = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1); fsD = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1); fsE = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1); fsF = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1); // Compute log image // 计算对数图像 cvConvert(img, fB); cvLog(fB, fA); // Normalize according to given weights // 依照权重归一化 for (i = 0, weight = 0; i < scales; i++) weight += weights[i]; if (weight != 1.0) cvScale(fA, fA, weight); // Filter at each scale // 各尺度上进行滤波操作 for (i = 0; i < scales; i++) { A = cvCloneImage(img); FastFilter(A, sigmas[i]); cvConvert(A, fB); cvLog(fB, fC); cvReleaseImage(&A); // Compute weighted difference // 计算权重后两图像之差 cvScale(fC, fC, weights[i]); cvSub(fA, fC, fA); } // Color restoration // 颜色修复 if (img->nChannels > 1) { A = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), img->depth, 1); B = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), img->depth, 1); C = cvCreateImage(cvSize(img->width, img->height), img->depth, 1); // Divide image into channels, convert and store sum // 将图像分割为若干通道,类型转换为浮点型,并存储通道数据之和 cvSplit(img, A, B, C, NULL); cvConvert(A, fsA); cvConvert(B, fsB); cvConvert(C, fsC); cvReleaseImage(&A); cvReleaseImage(&B); cvReleaseImage(&C); // Sum components // 求和 cvAdd(fsA, fsB, fsD); cvAdd(fsD, fsC, fsD); // Normalize weights // 带权重矩阵归一化 cvDiv(fsA, fsD, fsA, restoration_factor); cvDiv(fsB, fsD, fsB, restoration_factor); cvDiv(fsC, fsD, fsC, restoration_factor); cvConvertScale(fsA, fsA, 1, 1); cvConvertScale(fsB, fsB, 1, 1); cvConvertScale(fsC, fsC, 1, 1); // Log weights // 带权重矩阵求对数 cvLog(fsA, fsA); cvLog(fsB, fsB); cvLog(fsC, fsC); // Divide retinex image, weight accordingly and recombine // 将Retinex图像切分为三个数组,按照权重和颜色增益重新组合 cvSplit(fA, fsD, fsE, fsF, NULL); cvMul(fsD, fsA, fsD, color_gain); cvMul(fsE, fsB, fsE, color_gain); cvMul(fsF, fsC, fsF, color_gain); cvMerge(fsD, fsE, fsF, NULL, fA); } // Restore // 恢复图像 cvConvertScale(fA, img, gain, offset); // Release temp images // 释放缓存图像 cvReleaseImage(&fA); cvReleaseImage(&fB); cvReleaseImage(&fC); cvReleaseImage(&fsA); cvReleaseImage(&fsB); cvReleaseImage(&fsC); cvReleaseImage(&fsD); cvReleaseImage(&fsE); cvReleaseImage(&fsF); } /*=========================================================== * 函数:MultiScaleRetinexCR * 说明:MSRCR算法,MSR算法加上颜色修复。原图像和一系列被滤波的图像转换到对数域,并与带权重的原图像做减运算。 * 通常情况下,三个权重范围选择低、中、高标准偏差;之后,颜色修复权重应用于每个颜色通道中; * * 参数: * Mat src: 输入图像 * Mat &dst: 输出图像 * double sigma: 高斯核标准偏差 * int gain: 图像像素值改变范围的增益 * int offset: 图像像素值改变范围的偏移量 * double restoration_factor: 控制颜色修复的非线性 * double color_gain: 控制颜色修复增益 * -------------------------------------------------------- * Summary: * Multiscale retinex restoration with color restoration. The image and a set of * filtered images are converted to the log domain and subtracted from the * original with some set of weights. Typicaly called with three equaly weighted * scales of fine, medium and wide standard deviations. A color restoration weight * is then applied to each color channel. * * Arguments: * Mat src - Input Image. * Mat &dst - Output Image. * double sigma - the standard deviation of the gaussian kernal used to filter. * int gain - the factor by which to scale the image back into visable range. * int offset - an offset similar to the gain. * double restoration_factor - controls the non-linearaty of the color restoration. * double color_gain - controls the color restoration gain. ============================================================= */ void Msrcr::MultiScaleRetinexCR(Mat src, Mat &dst, vector<double> weights, vector<double> sigmas, int gain, int offset, double restoration_factor, double color_gain) { IplImage tmp_ipl; tmp_ipl = IplImage(src); MultiScaleRetinexCR(&tmp_ipl, weights, sigmas, gain, offset, restoration_factor, color_gain); dst = cvarrToMat(&tmp_ipl); //dst = Mat(&tmp_ipl); }
Main.cpp

#include "cv.h" #include "highgui.h" #include "opencv2opencv.hpp" #include "MSRCR.h" using namespace cv; using namespace std; //*****************高斯低通滤波器*********************** Mat gaussianlbrf(Mat scr, float sigma) { Mat gaussianBlur(scr.size(), CV_32FC1); //,CV_32FC1 float d0 = 2 * sigma*sigma;//高斯函数参数,越小,频率高斯滤波器越窄,滤除高频成分越多,图像就越平滑 for (int i = 0; i<scr.rows; i++) { for (int j = 0; j<scr.cols; j++) { float d = pow(float(i - scr.rows / 2), 2) + pow(float(j - scr.cols / 2), 2);//分子,计算pow必须为float型 gaussianBlur.at<float>(i, j) = expf(-d / d0);//expf为以e为底求幂(必须为float型) } } //imshow("高斯低通滤波器", gaussianBlur); return gaussianBlur; } //*****************频率域滤波******************* Mat freqfilt(Mat scr, Mat blur) { //***********************DFT******************* Mat plane[] = { scr, Mat::zeros(scr.size() , CV_32FC1) }; //创建通道,存储dft后的实部与虚部(CV_32F,必须为单通道数) Mat complexIm; merge(plane, 2, complexIm);//合并通道 (把两个矩阵合并为一个2通道的Mat类容器) dft(complexIm, complexIm);//进行傅立叶变换,结果保存在自身 //***************中心化******************** split(complexIm, plane);//分离通道(数组分离) int cx = plane[0].cols / 2; int cy = plane[0].rows / 2;//以下的操作是移动图像 (零频移到中心) Mat part1_r(plane[0], Rect(0, 0, cx, cy)); //元素坐标表示为(cx,cy) Mat part2_r(plane[0], Rect(cx, 0, cx, cy)); Mat part3_r(plane[0], Rect(0, cy, cx, cy)); Mat part4_r(plane[0], Rect(cx, cy, cx, cy)); Mat temp; part1_r.copyTo(temp); //左上与右下交换位置(实部) part4_r.copyTo(part1_r); temp.copyTo(part4_r); part2_r.copyTo(temp); //右上与左下交换位置(实部) part3_r.copyTo(part2_r); temp.copyTo(part3_r); Mat part1_i(plane[1], Rect(0, 0, cx, cy)); //元素坐标(cx,cy) Mat part2_i(plane[1], Rect(cx, 0, cx, cy)); Mat part3_i(plane[1], Rect(0, cy, cx, cy)); Mat part4_i(plane[1], Rect(cx, cy, cx, cy)); part1_i.copyTo(temp); //左上与右下交换位置(虚部) part4_i.copyTo(part1_i); temp.copyTo(part4_i); part2_i.copyTo(temp); //右上与左下交换位置(虚部) part3_i.copyTo(part2_i); temp.copyTo(part3_i); //*****************滤波器函数与DFT结果的乘积**************** Mat blur_r, blur_i, BLUR; multiply(plane[0], blur, blur_r); //滤波(实部与滤波器模板对应元素相乘) multiply(plane[1], blur, blur_i);//滤波(虚部与滤波器模板对应元素相乘) Mat plane1[] = { blur_r, blur_i }; merge(plane1, 2, BLUR);//实部与虚部合并 //*********************得到原图频谱图*********************************** magnitude(plane[0], plane[1], plane[0]);//获取幅度图像,0通道为实部通道,1为虚部,因为二维傅立叶变换结果是复数 plane[0] += Scalar::all(1); //傅立叶变o换后的图片不好分析,进行对数处理,结果比较好看 log(plane[0], plane[0]); // float型的灰度空间为[0,1]) normalize(plane[0], plane[0], 1, 0, CV_MINMAX); //归一化便于显示 //imshow("原图像频谱图", plane[0]); //******************IDFT******************************* /* Mat part111(BLUR,Rect(0,0,cx,cy)); //元素坐标(cx,cy) Mat part222(BLUR,Rect(cx,0,cx,cy)); Mat part333(BLUR,Rect(0,cy,cx,cy)); Mat part444(BLUR,Rect(cx,cy,cx,cy)); part111.copyTo(temp); //左上与右下交换位置(虚部) part444.copyTo(part111); temp.copyTo(part444); part222.copyTo(temp); //右上与左下交换位置 part333.copyTo(part222); temp.copyTo(part333); */ idft(BLUR, BLUR); //idft结果也为复数 split(BLUR, plane);//分离通道,主要获取通道 magnitude(plane[0], plane[1], plane[0]); //求幅值(模) normalize(plane[0], plane[0], 1, 0, CV_MINMAX); //归一化便于显示 return plane[0];//返回参数 } void img_processing(Msrcr &msrcr, Mat &img, Mat &outImg, vector<double> sigema, vector<double> weight) { int edge = 10; cv::Rect ROI(edge, edge, img.cols - edge, img.rows - edge); // ************************1. 图像增强 Mat img_msrcr; msrcr.MultiScaleRetinexCR(img, img_msrcr, weight, sigema, 128, 128); // ********************** 2. 低通滤波图 cv::Mat img_gray; cv::cvtColor(img_msrcr, img_gray, cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY); int w = getOptimalDFTSize(img_gray.cols); //获取进行dtf的最优尺寸 int h = getOptimalDFTSize(img_gray.rows); //获取进行dtf的最优尺寸 Mat padded; copyMakeBorder(img_gray, padded, 0, h - img_gray.rows, 0, w - img_gray.cols, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar::all(0)); //边界填充 padded.convertTo(padded, CV_32FC1); //将图像转换为flaot型 Mat gaussianKernel = gaussianlbrf(padded, 50);//高斯低通滤波器 Mat out = freqfilt(padded, gaussianKernel);//频率域滤波 Mat imageF_8UC3; out.convertTo(imageF_8UC3, CV_8UC3, 255); // *********************3. Canny边缘检测 Mat img_gaussian, img_canny; GaussianBlur(imageF_8UC3, img_gaussian, Size(5, 5), 0, 0, BORDER_DEFAULT); //高斯滤波 int edgeThresh = 15; Canny(img_gaussian, img_canny, edgeThresh, edgeThresh*4, 3); //Canny检测 cv::Mat img_canny_cut = cv::Mat(img_canny, ROI); cv::Mat img_canny_roi = img_canny_cut.clone(); // ***********************4. 形态学处理 Mat element, img_dilate; element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(5, 5)); dilate(img_canny_roi, img_dilate, element, Point(-1, -1), 2, BORDER_CONSTANT); Mat img_bin; img_bin = img_dilate.clone(); std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point> > contours; findContours(img_bin, contours, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_NONE); //找轮廓,注意第5个参数为CV_RETR_EXTERNAL,只检索外框 if (contours.size() <= 0 || contours.size() > 999999) { printf("obj_segmentSecond 函数:coutours的大小超出限制..."); return; } int width_less = 0.2*w; double least_area = 1000; std::vector<cv::Rect> boundRect(contours.size()); // 绘制最小外接矩形集合 std::vector<cv::RotatedRect> box(contours.size()); // 定义最小外接矩形集合 Mat img_copy; img_copy = img.clone(); cv::Mat img_copy_cut = cv::Mat(img_copy, ROI); cv::Mat img_copy_roi = img_copy_cut.clone(); for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++) { double area = contourArea(contours[i]); if (area < least_area) continue; box[i] = cv::minAreaRect(cv::Mat(contours[i])); // 计算每个轮廓的最小外接矩形 boundRect[i] = cv::boundingRect(cv::Mat(contours[i])); cv::Point2f rect[4]; box[i].points(rect); // 把最小外接矩形四个端点复制给rect数组 //// 小于分块的边界长度 // 确定竖_方向织布缺陷 if (boundRect[i].width < boundRect[i].height) { int box_X = boundRect[i].x; int box_Y = boundRect[i].y; // 判断缺陷窗口的坐标X是否在边界禁止范围内 if (box_X > img_copy_roi.cols - 50 || box_Y >img_copy_roi.rows - 15) { printf("坐标X在边界禁止范围内... "); continue; } cv::circle(img_copy_roi, cv::Point(box[i].center.x, box[i].center.y), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1, 8); // 绘制最小外接矩形的中心点 /*cv::rectangle(img_copy, cv::Point(boundRect[i].x, boundRect[i].y), cv::Point(boundRect[i].x + boundRect[i].width, boundRect[i].y + boundRect[i].height), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8); */ for (int j = 0; j<4; j++) { cv::line(img_copy_roi, rect[j], rect[(j + 1) % 4], cv::Scalar(255), 2, 8); //绘制最小外接矩形每条边 cv::line(img_copy_roi, rect[j], rect[(j + 1) % 4], cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8); //绘制最小外接矩形每条边 } } else // 确定横_方向织布缺陷 { int box_X = boundRect[i].x; int box_Y = boundRect[i].y; // 判断缺陷窗口的坐标X是否在边界禁止范围内 if (box_X > img_copy_roi.cols - 50 || box_Y >img_copy_roi.rows - 15) { printf("坐标X在边界禁止范围内... "); continue; } if (boundRect[i].width < 0.3*w) continue; cv::circle(img_copy_roi, cv::Point(box[i].center.x, box[i].center.y), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1, 8); // 绘制最小外接矩形的中心点 /*cv::rectangle(img_copy, cv::Point(boundRect[i].x, boundRect[i].y), cv::Point(boundRect[i].x + boundRect[i].width, boundRect[i].y + boundRect[i].height), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8); */ for (int j = 0; j<4; j++) { cv::line(img_copy_roi, rect[j], rect[(j + 1) % 4], cv::Scalar(255), 2, 8); //绘制最小外接矩形每条边 cv::line(img_copy_roi, rect[j], rect[(j + 1) % 4], cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8); //绘制最小外接矩形每条边 } } } outImg = img_copy_roi.clone(); } void read_video() { vector<double> sigema; vector<double> weight; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) weight.push_back(1. / 3); // 由于MSRCR.h中定义了宏USE_EXTRA_SIGMA,所以此处的vector<double> sigema并没有什么意义 sigema.push_back(30); sigema.push_back(150); sigema.push_back(300); Msrcr msrcr; // *****************************1. 测试单张图像***************************************** //Mat img, dst; //img = imread("F:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\织物瑕疵检测\video_photo_fail\570.jpg", 1); //img_processing(msrcr, img, dst, sigema, weight); //imshow("src", img); //imshow("dst", dst); //imwrite("F:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\织物瑕疵检测\frame_fail\570_filter_50.jpg", dst); //waitKey(10000); //return; // *****************************2. 连续测试多帧图像***************************************** string file_path, fileName, grayFile, saveFile_path, saveFileName; file_path = "F:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\织物瑕疵检测\video_photo_fail\"; saveFile_path = "F:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\织物瑕疵检测\frame_detect\"; string str1, str2; Mat srcImage, grayImage, outImg; for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++) { /*if (i < 2000) continue;*/ printf("i =%d ", i); stringstream ss1, ss2; ss1 << i; ss1 >> str1; //cout << str1 << endl; fileName = file_path + str1 + ".jpg"; srcImage = imread(fileName, 1); img_processing(msrcr, srcImage, outImg, sigema, weight); saveFileName = saveFile_path + std::to_string(i) + ".bmp"; imwrite(saveFileName, outImg); imshow("src", srcImage); imshow("dst", outImg); waitKey(1); } } int main() { read_video(); system("pause"); return 0; }
