Harry Potter and He-Who-Must-Not-Be-Named engaged in a fight to the death once again. This time they are located at opposite ends of the corridor of length l. Two opponents simultaneously charge a deadly spell in the enemy. We know that the impulse of Harry's magic spell flies at a speed of p meters per second, and the impulse of You-Know-Who's magic spell flies at a speed of q meters per second.
The impulses are moving through the corridor toward each other, and at the time of the collision they turn round and fly back to those who cast them without changing their original speeds. Then, as soon as the impulse gets back to it's caster, the wizard reflects it and sends again towards the enemy, without changing the original speed of the impulse.
Since Harry has perfectly mastered the basics of magic, he knows that after the second collision both impulses will disappear, and a powerful explosion will occur exactly in the place of their collision. However, the young wizard isn't good at math, so he asks you to calculate the distance from his position to the place of the second meeting of the spell impulses, provided that the opponents do not change positions during the whole fight.
The first line of the input contains a single integer l (1 ≤ l ≤ 1 000) — the length of the corridor where the fight takes place.
The second line contains integer p, the third line contains integer q (1 ≤ p, q ≤ 500) — the speeds of magical impulses for Harry Potter and He-Who-Must-Not-Be-Named, respectively.
Print a single real number — the distance from the end of the corridor, where Harry is located, to the place of the second meeting of the spell impulses. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error will not exceed 10 - 4.
Namely: let's assume that your answer equals a, and the answer of the jury is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct if 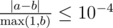 .
.
100
50
50
50
199
60
40
119.4
In the first sample the speeds of the impulses are equal, so both of their meetings occur exactly in the middle of the corridor.
sb模拟题
显然弹几次都是一样的

1 #include<set> 2 #include<map> 3 #include<cmath> 4 #include<ctime> 5 #include<deque> 6 #include<queue> 7 #include<bitset> 8 #include<cstdio> 9 #include<cstdlib> 10 #include<cstring> 11 #include<iostream> 12 #include<algorithm> 13 #define LL long long 14 #define inf 0x7fffffff 15 #define pa pair<int,int> 16 #define pi 3.1415926535897932384626433832795028841971 17 using namespace std; 18 inline LL read() 19 { 20 LL x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar(); 21 while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} 22 while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} 23 return x*f; 24 } 25 double l,a,b,t1; 26 int main() 27 { 28 scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&l,&a,&b); 29 t1=l/(a+b); 30 cout<<l-t1*b<<endl; 31 }
